2 2 Identify and Apply Basic Cost Behavior Patterns Principles of Accounting, Volume 2: Managerial Accounting
- 1
- 0
- All articles ()
- ! Без рубрики (62)
- 0.015869073920935062 (1)
- 0.038674021625345056 (1)
- 0.06454589940946609 (1)
- 0.07803953922161688 (1)
- 0.08447720963229288 (1)
- 0.08724027720202177 (1)
- 0.09638815068499595 (1)
- 0.09864464062235978 (1)
- 0.10403284341212138 (1)
- 0.12052478983094461 (1)
- 0.12839062591446115 (1)
- 0.12969665332177394 (1)
- 0.13558124162632557 (2)
- 0.1424390675038325 (1)
- 0.1481708440209787 (1)
- 0.1514062810253547 (1)
- 0.15216090002426153 (1)
- 0.19565264941740668 (1)
- 0.24264469978970604 (1)
- 0.2513073562640168 (1)
- 0.2748197173053596 (1)
- 0.30075697073364105 (1)
- 0.30636675912732214 (1)
- 0.3274347673029141 (1)
- 0.3544849106910273 (1)
- 0.363017420510207 (1)
- 0.3901353861396798 (1)
- 0.3914840337504165 (1)
- 0.3962447334682363 (1)
- 0.40348743805808984 (1)
- 0.44096099291640967 (1)
- 0.4493573902918411 (1)
- 0.4595404763683746 (2)
- 0.4689907730961512 (1)
- 0.49984518582056003 (1)
- 0.532814460619006 (1)
- 0.5366864896512812 (1)
- 0.5810755525161744 (1)
- 0.6150359674381758 (1)
- 0.6221958902382839 (1)
- 0.6933883185169163 (1)
- 0.6982825378806452 (1)
- 0.7007736873516788 (1)
- 0.7018830817991892 (1)
- 0.723094895999275 (1)
- 0.7364227578558207 (1)
- 0.7382361634424165 (1)
- 0.7414741488176279 (1)
- 0.7453430812965198 (1)
- 0.7655630714878285 (1)
- 0.7664188684331404 (1)
- 0.7675388179828142 (1)
- 0.7830403779384382 (1)
- 0.79853232509708 (1)
- 0.8626913304408897 (2)
- 0.8721060100275613 (1)
- 0.8967709789162543 (1)
- 0.9045499261478237 (1)
- 0.9259861774828386 (1)
- 0.9498377288041014 (1)
- 0.9690604938393559 (1)
- 0.978907854000516 (1)
- 0.9919333164848703 (1)
- 1 (13)
- 1 Win (1)
- 10 parasta postimyyntiä morsiamen (2)
- 10 parasta postimyyntiä morsiamen (0)
- 11275_ru (1)
- 1Win AZ Casino (4)
- 1win Azerbajany (3)
- 1Win br (1)
- 1win by (1)
- 1Win Casino (4)
- 1WIN Casino Brasil (3)
- 1Win cl (1)
- 1WIN Official In Russia (15)
- 1win Turkiye (2)
- 1win uzbekistan (3)
- 1winRussia (2)
- 1xbet apk (10)
- 1xbet AZ Casino (1)
- 1XBET AZ Giriş (3)
- 1xbet Azerbajan (3)
- 1xbet Azerbaydjan (5)
- 1xbet Brazil (3)
- 1xbet CASINO AZ (6)
- 1xbet egypt (1)
- 1xbet giriş (3)
- 1xbet Kazahstan (7)
- 1xbet Korea (1)
- 1xbet Morocco (4)
- 1xbet Online Casino (1)
- 1xbet qeydiyyat (1)
- 1xbet russia (1)
- 1xbet russian (1)
- 2 (5)
- 22bet IT (1)
- 711 (1)
- 9200_ru (1)
- 9460_ru (1)
- a cash advance (1)
- a cash advance is (1)
- a mail order bride (1)
- a payday advance loan (1)
- a payday loan (1)
- a payday loan company (2)
- a payday loan is (3)
- a payday loan? (1)
- about (2)
- Acheter la mariГ©e par correspondance (4)
- Acheter la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Acheter la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Acheter la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- acheter une mariГ©e par correspondance (5)
- acheter une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- acheter une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- acheter une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- acheter une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- adult (12)
- adult sites (7)
- advance advance cash loan payday (1)
- advance amer cash (2)
- advance amererica cash advance (4)
- advance america and cash advance (3)
- advance america cash (1)
- advance america cash advance (1)
- advance america cash advance payday loan (1)
- advance america cash advance price (2)
- advance america cash advances (1)
- advance america cash cash (3)
- advance america cash check? (2)
- advance america cash loan (1)
- advance america cash loans (1)
- advance america cash payday (1)
- advance america loan payday (2)
- advance america payday loan (1)
- advance america payday loan company (2)
- advance america payday loan near me (1)
- advance america payday loans (2)
- advance american cash (1)
- advance american cash advance (2)
- advance american payday loan (1)
- advance bad cash credit loan loan (1)
- advance bad credit loan payday (0)
- advance cash (0)
- advance cash advance (1)
- advance cash america loan (2)
- advance cash america near me (3)
- advance cash america payday loans (2)
- advance cash american (2)
- advance cash americia (1)
- advance cash cash loan payday (1)
- advance cash company (1)
- advance cash company loan (1)
- advance cash finance company (1)
- advance cash in (1)
- advance cash info (2)
- advance cash loan near me (2)
- advance cash loan payday (1)
- advance cash loans (2)
- advance cash log in (3)
- advance cash near me (4)
- advance cash now (2)
- advance cash payday (1)
- advance cash payday loan (2)
- advance cash payday loans (1)
- advance cash usa (1)
- advance cash usa payday loan (3)
- advance loan payday loan (1)
- advance loans payday (3)
- advance me cash advance (3)
- advance me payday loans (2)
- advance of america cash advance (1)
- advance of america payday loan (3)
- advance payday cash loan (1)
- advance payday loan (1)
- advance payday loan company (3)
- advance payday loan near me (4)
- advance payday loans (2)
- advance payday loans near me (2)
- advance the cash (2)
- advance to payday loans (1)
- advance usa payday loans (1)
- advanced america cash advance (2)
- advanced america cash advance near me (1)
- advanced american cash advance (1)
- advanced american cash advance near (1)
- advanced loan payday (3)
- advanced payday loan (2)
- advanced payday loans (1)
- advice (5)
- african-women free online sites for singles (1)
- Agence de messagerie de commande de mariГ©e (1)
- Agence de vente par correspondance (3)
- Agence de vente par correspondance avec la meilleure rГ©putation (2)
- Agence de vente par correspondance avec la meilleure rГ©putation (0)
- Agences de la mariГ©e par correspondance (6)
- Agences de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Agences de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Agences de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Agences de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Agences de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- agences de mariГ©e par correspondance (2)
- agences de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- agencia de correo de orden de novia (1)
- agencia de novias por correo (1)
- agencia de novias por correo con la mejor reputaciГіn (2)
- agencia de novias por correo con la mejor reputaciГіn (0)
- Agencija za mail za mladenku (1)
- agenzia sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- agenzie sposate per corrispondenza (4)
- AI News (1)
- albanian-brides free online sites for singles (1)
- all blog essay writing service cheap (1)
- america advance cash (2)
- america advance cash advance (1)
- america advance payday loan (2)
- america cash advance in (1)
- america cash advance loans (5)
- america cash advance near me (1)
- america cash payday loan (2)
- america cash payday loans (2)
- america payday loan (1)
- american advance cash (2)
- american advance payday loan (0)
- american advance payday loans (3)
- american bluebird and payday loans (2)
- american cash advance (2)
- american cash advance near me (1)
- american cash advance usa (2)
- american credit payday loans (1)
- american payday cash advance (2)
- american payday loan (1)
- american payday loans (1)
- american payday loans advance america (1)
- american-women+albuquerque-nm site free (1)
- american-women+anchorage-ky free online sites for singles (1)
- american-women+bakersfield-ca site free (1)
- american-women+brownsville-mn site free (1)
- american-women+chattanooga-tn site free (1)
- american-women+cincinnati-ia site free (1)
- american-women+cleveland-ga free online sites for singles (1)
- american-women+durham-ca free online sites for singles (1)
- american-women+el-paso-il site free (1)
- american-women+fort-lauderdale-fl free online sites for singles (1)
- american-women+fremont-oh free online sites for singles (1)
- american-women+gilbert-ia free online sites for singles (1)
- american-women+grand-prairie-tx free online sites for singles (1)
- american-women+henderson-wv free online sites for singles (1)
- american-women+henderson-wv site free (1)
- american-women+huntsville-tx site free (1)
- american-women+irvine-ca free online sites for singles (1)
- american-women+jersey-ga site free (1)
- american-women+lakewood-wa site free (1)
- american-women+las-vegas-nm site free (1)
- american-women+little-rock-sc free online sites for singles (1)
- american-women+los-angeles-ca site free (1)
- american-women+louisville-al site free (1)
- american-women+lubbock-tx free online sites for singles (1)
- american-women+madison-pa free online sites for singles (1)
- american-women+newport-news-va site free (1)
- american-women+ontario-oh free online sites for singles (1)
- american-women+orlando-fl free online sites for singles (0)
- american-women+philadelphia-tn free online sites for singles (1)
- american-women+reno-tx site free (1)
- american-women+rockford-mn site free (1)
- american-women+salem-ma site free (1)
- american-women+san-diego-ca free online sites for singles (1)
- american-women+san-francisco-ca site free (1)
- american-women+san-jose-az site free (1)
- american-women+santa-clarita-ca site free (1)
- american-women+surprise-ne site free (1)
- american-women+tallahassee-fl site free (0)
- american-women+tempe-az site free (1)
- american-women+visalia-ca site free (1)
- amourfeel-review free online sites for singles (1)
- and single site (11)
- Anderson online installment loans (1)
- anexsystem (1)
- anmeldelser av postordrebrudbyrГҐ (1)
- Annapolis Junction online installment loans (1)
- app (6)
- app for (10)
- app free (14)
- app reviews (8)
- apps (10)
- apps for adults (13)
- apps for iphone (11)
- apps free (14)
- apps reddit (11)
- Arcadia online installment loans instant approval (1)
- are cash advance loans (1)
- are payday loans (2)
- are payday loans bad (1)
- are payday loans bad for credit (1)
- are payday loans bad for your credit (2)
- are payday loans useful? (2)
- are-mail-order-brides-illegal free online sites for singles (1)
- argentinian-women+buenos-aires site free (1)
- armenian-women free online sites for singles (1)
- Articles de la mariГ©e par correspondance (3)
- Articles de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Articles de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Artificial intelligence (AI) (1)
- artГculos de novia por correo (4)
- artГculos de novia por correo (0)
- artГculos de novia por correo (0)
- ashley-madison-review free online sites for singles (1)
- asia-beauty-date-review free online sites for singles (1)
- asiame-review site free (1)
- asian brides (1)
- asian mail order bride (1)
- asianbeautydating-review site free (1)
- asianbeautyonline-review site free (1)
- asianladyonline-review site free (1)
- Athens guaranteed installment loans for bad credit direct lenders only (1)
- attractive-single-women free online sites for singles (1)
- au (1)
- Auf der Suche nach Ehe (1)
- Auf der Suche nach einer Mail -Bestellung Braut (5)
- Ault installment loans near me (1)
- Auslandische Brute (3)
- availableloan.net+500-dollar-payday-loan bad credit payday cash loan (0)
- availableloan.net+800-dollar-payday-loan advance cash payday loans (1)
- availableloan.net+balance-transfer-loans cash advance no credit check loan (1)
- availableloan.net+checking-account-with-bad-credit payday loan needed (1)
- availableloan.net+christmas-loans cash advance no credit check loan (1)
- availableloan.net+covid-19-personal-loans cash loan payday advance (1)
- availableloan.net+dental-loans-for-implants payday loan needed (1)
- availableloan.net+direct-express-emergency-cash advance cash payday loans (1)
- availableloan.net+i-need-money-now cash advance no credit check loan (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-ak+eagle get cash advance payday loans (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-ar+appleton how to do a payday loan (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-ar+victoria get cash advance payday loans (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-ca+ontario how to do a cash advance (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-ca+san-diego get cash advance payday loans (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-de+houston cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-ia+augusta nearby payday loans (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-ia+charlotte nearby payday loans (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-ia+portland nearby payday loans (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-il+golden-gate payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-il+hudson payday loans very bad credit (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-il+phoenix how to do a cash advance (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-il+riverside payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-in+hammond get cash advance payday loans (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-in+long-beach payday loans very bad credit (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-ky+edmonton bad credit loans no payday (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-ky+new-castle bad credit loans no payday (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-la+atlanta bad credit loans no payday (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-la+central payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-md+long-beach cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-mn+appleton how to do a payday loan (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-mn+kingston get cash advance payday loans (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-mo+philadelphia no credit check loan payday (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-mo+windsor nearby payday loans (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-ms+austin payday loans very bad credit (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-mt+columbus how to do a cash advance (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-nc+bolton how to do a cash advance (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-nc+nashville how to do a cash advance (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-ne+blue-springs how to do a cash advance (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-nv+kingston how much interest on a cash advance (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-nv+las-vegas nearby payday loans (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-ny+cleveland how to do a payday loan (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-oh+fresno how to do a cash advance (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-or+ontario how to do a payday loan (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-pa+eagle payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-sc+windsor get cash advance at bank (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-tn+charlotte payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-tn+kingston payday loans no credit check places (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-tx+los-angeles bad credit loans no payday (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-ut+central bad credit loans no payday (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-wi+abbotsford my payday loan (1)
- availableloan.net+loans-for-400-credit-score payday loans banks (1)
- availableloan.net+loans-for-immigrants advance cash payday loans (1)
- availableloan.net+loans-for-pensioners what are good payday loan company (1)
- availableloan.net+loans-for-veterans bad credit payday cash loan (1)
- availableloan.net+medical-school-loans short payday loans no credit check (1)
- availableloan.net+no-origination-fee-personal-loan advance cash payday loans (1)
- availableloan.net+no-teletrack-installment-loans payday cash advance loans near me (1)
- availableloan.net+online-installment-loans-instant-approval cash advance no credit check loan (1)
- availableloan.net+payday-advance-app payday cash advance loans near me (1)
- availableloan.net+payday-loans-ar+austin payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- availableloan.net+payday-loans-ar+blue-mountain cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- availableloan.net+payday-loans-ar+nashville payday loans no credit check places (1)
- availableloan.net+payday-loans-az+miami how to do a payday loan (1)
- availableloan.net+payday-loans-ca+oasis how to do a cash advance (1)
- availableloan.net+payday-loans-ca+san-diego no credit check loan payday (1)
- availableloan.net+payday-loans-co+delta payday loans no credit check places (1)
- availableloan.net+payday-loans-de+magnolia payday loans very bad credit (1)
- availableloan.net+payday-loans-ga+jacksonville how to do a payday loan (1)
- availableloan.net+payday-loans-ia+riverside how much interest on a cash advance (1)
- availableloan.net+payday-loans-il+kingston how much interest on a cash advance (1)
- availableloan.net+payday-loans-in+atlanta get cash advance at bank (1)
- availableloan.net+payday-loans-in+columbus how much interest on a cash advance (0)
- availableloan.net+payday-loans-in+indianapolis how to do a payday loan (1)
- availableloan.net+payday-loans-with-prepaid-debit-card where to get payday loans near me (1)
- availableloan.net+personal-loans-mo+denver get cash advance payday loans (1)
- availableloan.net+personal-loans-mo+oakland bad credit loans no payday (1)
- availableloan.net+personal-loans-mo+philadelphia cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- availableloan.net+personal-loans-ms+columbus bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- availableloan.net+personal-loans-ne+emerald nearby payday loans (1)
- availableloan.net+personal-loans-ne+oakland no credit check loan payday (1)
- availableloan.net+personal-loans-nm+columbus bad credit loans no payday (1)
- availableloan.net+personal-loans-nm+san-jose bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- availableloan.net+personal-loans-ny+riverside cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- availableloan.net+personal-loans-oh+hamilton bad credit loans no payday (1)
- availableloan.net+personal-loans-ok+clearview how much interest on a cash advance (1)
- availableloan.net+personal-loans-tn+central payday loans very bad credit (1)
- availableloan.net+personal-loans-tx+lubbock payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- availableloan.net+personal-loans-tx+memphis how to do a payday loan (1)
- availableloan.net+personal-loans-tx+miami my payday loan (1)
- availableloan.net+personal-loans-tx+portland cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- availableloan.net+personal-loans-ut+central bad credit loans no payday (1)
- availableloan.net+personal-loans-va+new-castle no credit check loan payday (1)
- availableloan.net+personal-loans-wa+kingston bad credit loans no payday (1)
- availableloan.net+personal-loans-wi+columbus payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- availableloan.net+personal-loans-wi+dallas bad credit loans no payday (1)
- availableloan.net+personal-loans-wi+dallas bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- availableloan.net+personal-loans-wi+eagle how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- availableloan.net+personal-loans-wy+riverside how to do a cash advance (1)
- availableloan.net+quick-cash-loans short payday loans no credit check (1)
- availableloan.net+refinance-personal-loan payday loans banks (1)
- availableloan.net+same-day-payday-loans bad credit payday cash loan (1)
- availableloan.net+same-day-payday-loans short payday loans no credit check (1)
- availableloan.net+same-day-personal-loans advance cash payday loans (1)
- availableloan.net+signature-installment-loans advance cash payday loans (1)
- availableloan.net+signature-loans advance cash bank (1)
- availableloan.net+small-payday-loans cash loan payday advance (1)
- average cost of a mail order bride (1)
- average cost of mail order bride (1)
- average mail order bride prices (1)
- average price for mail order bride (2)
- average price of a mail order bride (1)
- average price of mail order bride (1)
- Avis des mariГ©es par correspondance (1)
- azerbaijan-women site free (1)
- azerbaijan-women+aran site free (1)
- Azerbajany Mostbet (3)
- är postorder brud värt det (1)
- b1bet apostas (3)
- bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (4)
- bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (0)
- bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (0)
- bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (0)
- bad bad credit payday loans (1)
- bad credi payday loans (2)
- bad crediit payday loans (2)
- bad credit and payday loans (2)
- bad credit cannot get payday loan (1)
- bad credit cash advance (4)
- bad credit cash advance loan (1)
- bad credit cash advance loans (3)
- bad credit credit loans not payday (1)
- bad credit guarenteed payday loan (1)
- bad credit loan payday (2)
- bad credit loans no payday (1)
- bad credit loans no payday loans (4)
- bad credit loans not payday (1)
- bad credit loans not payday advance (2)
- bad credit loans not payday loans (2)
- bad credit loans payday (1)
- bad credit loans payday advance (2)
- bad credit loans payday loans (2)
- bad credit loans that are not payday loans (2)
- bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- bad credit not payday loans (1)
- bad credit payday advance loan (2)
- bad credit payday advance loans (2)
- bad credit payday cash advance (1)
- bad credit payday loan (1)
- bad credit payday loan no bank check (4)
- bad credit payday loan no credit check (1)
- bad credit payday loan no credit check near me (2)
- bad credit payday loan no credit check us (1)
- bad credit payday loans (1)
- bad credit payday loans no credit check (4)
- badcreditloanapproving online installment loans (1)
- badoo-review site free (1)
- Ballwin guaranteed installment loans for bad credit direct lenders only (1)
- Bana bir posta sipariЕџi gelini bul (2)
- Bana bir posta sipariЕџi gelini bul (0)
- bank america payday loan (4)
- bank cash advance loans (2)
- bank payday loan (2)
- bank with cash advance (2)
- Bankobet (1)
- banks cash advance (2)
- banks for cash advance (1)
- banks payday loans (1)
- banks that do cash advance (2)
- banks that do payday loans (1)
- banks with payday loans (2)
- Basaribet (1)
- bästa land att hitta postorder brud (1)
- bästa landet att hitta en postorderbrud (1)
- bästa länder för en postorderbrud (2)
- bästa länder för en postorderbrud (0)
- bästa plats för postorderbrud (1)
- bästa postorder brud byrå reddit (1)
- bästa postorder brud platser (1)
- bästa postorder brudens webbplatser 2022 (1)
- bästa stället att få postorder brud (1)
- bästa webbplats postorder brud (3)
- bästa webbplats postorder brud (0)
- bästa webbplats postorder brud (0)
- beautiful women (1)
- beautiful-single-women site free (1)
- Bedford online installment loans instant approval (1)
- bedst bedГёmte postordre brudesider (2)
- bedst bedГёmte postordre brudesider (0)
- bedste land til postordre brud reddit (3)
- bedste land til postordrebrud (2)
- bedste lande til at fГҐ en postordrebrud (1)
- bedste legitime postordre brudewebsteder (1)
- bedste mail ordre brude sider anmeldelser (2)
- bedste mail ordre brude sider anmeldelser (0)
- bedste mail ordre brude websteder (2)
- bedste mail ordre brude websteder (0)
- bedste mail ordre brudewebsted (2)
- bedste omdГёmme mail ordre brud (1)
- bedste postordre brud agentur (3)
- bedste postordre brud agentur reddit (1)
- bedste postordre brud nogensinde (2)
- bedste postordre brud steder (1)
- bedste postordre brude service (1)
- bedste postordre brude websteder 2022 (3)
- bedste postordre brudefirma (2)
- bedste postordre brudeland (2)
- bedste postordre brudeside (2)
- bedste postordre brudesider (2)
- bedste postordrebrud (1)
- bedste rigtige postordre brudeside (2)
- bedste rigtige postordre brudeside (0)
- bedste rigtige postordre brudesider (1)
- bedste site mail ordre brud (1)
- bedste sted at fГҐ en postordrebrud (3)
- bedste sted at fГҐ en postordrebrud (0)
- bedste sted at fГҐ en postordrebrud (0)
- bedste steder for postordrebrud (1)
- belgian-women site free (1)
- benaughty-review site for people (1)
- Berthoud online installment loans (1)
- best apps (9)
- best asian dating sites (1)
- BEST bewertete Versandauftragsbrautseiten (1)
- best countries for a mail order bride (1)
- best countries to get a mail order bride (1)
- best country for mail order bride (1)
- best country for mail order bride reddit (1)
- best country to find a mail order bride (0)
- best country to find mail order bride (1)
- best dating reviews (1)
- best dating sites for over 40 (1)
- best dating websites (1)
- best essay cheap (1)
- best essay writing service reviews (1)
- best latin dating websites (1)
- best mail order bride agency (1)
- best mail order bride agency reddit (1)
- best mail order bride companies (2)
- best mail order bride company (3)
- best mail order bride countries (2)
- best mail order bride ever (0)
- best mail order bride places (2)
- best mail order bride site (1)
- best mail order bride site reddit (1)
- best mail order bride sites (1)
- best mail order bride sites reviews (2)
- best mail order bride websites (1)
- best mail order bride websites 2022 (2)
- best place to get a mail order bride (2)
- best place to get mail order bride (5)
- best places for mail order bride (2)
- best places to find mail order bride (1)
- best places to get mail order bride (2)
- best rangerte postordrebrudesider (5)
- best real mail order bride site (3)
- best real mail order bride sites (3)
- best site (8)
- best sites (21)
- best sites for singles (12)
- best website to find a mail order bride (3)
- best-pickup-lines free online sites for singles (1)
- Beste echte Mail -Bestellung Brautseite (5)
- Beste echte Mail -Bestellung Brautseiten (3)
- beste ekte postordre brudeside (1)
- beste land for en postordrebrud (2)
- beste land for postordre brud reddit (2)
- beste land for postordrebrud (3)
- beste land for ГҐ fГҐ en postordrebrud (1)
- beste landet ГҐ finne en postordrebrud (2)
- beste landet ГҐ finne en postordrebrud (0)
- beste landet ГҐ finne postordrebrud (3)
- beste landet ГҐ finne postordrebrud (0)
- beste landet ГҐ finne postordrebrud (0)
- beste legit postordre brud nettsteder (3)
- Beste legitime Mail -Bestellung Brautwebsites (1)
- Beste Lender fГјr eine Postanweisung Braut (2)
- Beste Lender fГјr eine Postanweisung Braut (0)
- Beste Lender, um eine Versandbestellbraut zu erhalten (1)
- Beste Mail -Bestellung Braut (2)
- Beste Mail -Bestellung Braut (0)
- Beste Mail -Bestellung Braut -Websites Bewertungen (3)
- Beste Mail -Bestellung Braut aller Zeiten (1)
- Beste Mail -Bestellung Braut Site Reddit (1)
- Beste Mail -Bestellung Braut Websites 2022 (1)
- Beste Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- Beste Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur Reddit (3)
- Beste Mail -Bestellung Brautpletze (2)
- Beste Mail -Bestellung Brautseite (2)
- Beste Mail -Bestellung Brautseiten (1)
- Beste Mail -Bestellung Brautunternehmen (1)
- Beste Mail -Bestellung Brautwebsite (1)
- Beste Mail -Bestellung Brautwebsites (6)
- beste nettsted for ГҐ finne en postordrebrud (2)
- beste nettsted for ГҐ finne en postordrebrud (0)
- beste nettsted post ordre brud (6)
- beste omdГёmme postordre brud (1)
- Beste Orte, um Versandbestellbraut zu erhalten (2)
- Beste Orte, um Versandbestellbraut zu finden (4)
- beste postordre brud nettsted (1)
- beste postordre brud nettsteder (4)
- beste postordre brud nettsteder 2022 (2)
- beste postordre brud nettstedet reddit (4)
- beste postordre brudbyrГҐ (2)
- beste postordre brudbyrГҐ (0)
- beste postordre brudebyrГҐ reddit (2)
- beste postordre brudebyrГҐ reddit (0)
- beste postordre brudeside (2)
- beste postordre brudfirma (2)
- beste postordre brudland (2)
- beste postordre brudplasser (3)
- beste postordre brudselskaper (1)
- beste postordre brudtjeneste (1)
- Beste Site -Mail -Bestellung Braut (2)
- beste steder for postordrebrud (2)
- beste steder ГҐ finne postordrebrud (2)
- beste steder ГҐ finne postordrebrud (0)
- beste steder ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- beste stedet for postordrebrud (1)
- beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (3)
- beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (0)
- beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (0)
- Beste Versandbestellung Braut Land (2)
- Beste Versandbestellung Braut Land (0)
- Beste Versandbestellung Brautlender (4)
- Bester Mail -Bestellung Brautservice (2)
- Bester Ort, um Versandbestellbraut zu erhalten (2)
- Bestes Land fГјr Versandbestellbraut Reddit (1)
- Bestes Land, um eine Versandbestellbraut zu finden (2)
- Bestes Land, um Versandbestellbraut zu finden (4)
- Bethesda installment loans near me (1)
- Betmotion brazil (1)
- bharat-matrimony-review free online sites for singles (1)
- bh_aug (2)
- bh_sep (1)
- BH_TOP (2)
- Bir Gelin Posta SipariЕџi (2)
- Bir Gelin Posta SipariЕџi (0)
- Bir gelin sipariЕџ edebilir misin (1)
- Bir Posta SipariЕџi Gelin (1)
- Bir posta siparişi gelini bulmak için en iyi web sitesi (1)
- Bir posta siparişi gelini bulmak için en iyi ülke (1)
- Bir posta sipariЕџi gelini bulun (1)
- Bir posta siparişi gelini için en iyi ülkeler (2)
- Bir posta siparişi gelini için en iyi ülkeler (0)
- Bir posta siparişi gelini için ortalama fiyat (3)
- Bir posta siparişi gelini için ortalama fiyat (0)
- Bir posta siparişi gelini için ortalama fiyat (0)
- bir posta sipariЕџi gelini nasД±l evlenir (2)
- bir posta sipariЕџi gelini nasД±l evlenir (0)
- Bir posta sipariЕџi gelini nasД±l Г§alД±ЕџД±r (3)
- Bir posta sipariЕџi gelini nasД±l Г§alД±ЕџД±r (0)
- Bir posta sipariЕџi gelini nasД±l Г§alД±ЕџД±r (0)
- Bir posta sipariЕџi gelini nerede bulabilirim (5)
- Bir posta sipariЕџi gelini nerede bulabilirim (0)
- Bir posta sipariЕџi gelini nerede bulabilirim (0)
- Bir posta sipariЕџi gelini nerede bulabilirim (0)
- Bir posta sipariЕџi gelini nerede bulabilirim (0)
- Bir posta sipariЕџi geliniyle Г§Д±kmalД± mД±yД±m (3)
- Bir posta sipariЕџi geliniyle Г§Д±kmalД± mД±yД±m (0)
- Bir posta sipariЕџi geliniyle Г§Д±kmalД± mД±yД±m (0)
- Bir posta sipariЕџinin ortalama fiyatД± (1)
- bizzo casino (1)
- bla gjennom postordrebruden (4)
- blog (145)
- bläddra i postorder bruden (1)
- bolivian-women+la-paz site free (1)
- bon site Web de mariГ©e par correspondance (7)
- bon site Web de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- bon site Web de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- bon site Web de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- bon site Web de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- bon site Web de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- bon site Web de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- book of ra (1)
- Bookkeeping (5)
- bosnian-women site free (1)
- bra postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- bra postorder brudens webbplats (2)
- Brandon guaranteed installment loans for bad credit (1)
- Braut Mail -Bestellung (1)
- Brautbestellversandagentur (1)
- bravodate-review free online sites for singles (1)
- brazilian-women+americana site free (1)
- brazilian-women+campina-grande site free (1)
- brazilian-women+formosa site free (1)
- brazilian-women+fortaleza site free (1)
- brazilian-women+natal free online sites for singles (1)
- brazilian-women+porto-alegre free online sites for singles (1)
- brazilian-women+porto-seguro free online sites for singles (1)
- brazilian-women+recife free online sites for singles (1)
- brazilian-women+santos site free (1)
- bride mail order (1)
- bride order mail (1)
- bride order mail agency (3)
- Bride World Order Mail Brides (2)
- brides (1)
- bridesconfidential.com costa-rican-bruder postordre brudinformasjon (1)
- bridesconfidential.com da+amerikanske-brude-til-aegteskab de bedste steder at finde postordrebrud (1)
- bridesconfidential.com da+indiske-brude de bedste steder at finde postordrebrud (1)
- bridesconfidential.com da+mexicanske-brude de bedste steder at finde postordrebrud (1)
- bridesconfidential.com da+mongolske-brude de bedste steder at finde postordrebrud (1)
- bridesconfidential.com da+norske-brude hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- bridesconfidential.com da+portugisiske-brude Г¦gte mail ordre brude websteder (1)
- bridesconfidential.com da+postordrebrude Г¦gte mail ordre brude websteder (1)
- bridesconfidential.com da+varme-mexicanske-kvinder de bedste steder at finde postordrebrud (1)
- bridesconfidential.com de+chinesische-hochzeitstraditionen Mail-Order-Braut (1)
- bridesconfidential.com de+heise-und-sexy-kolumbianische-frauen Wie funktioniert die Mail -Bestellung Braut? (1)
- bridesconfidential.com de+japanische-braute Top -bewertete Versandauftragsbrautseiten (1)
- bridesconfidential.com de+kambodschanische-braute Wie funktioniert die Mail -Bestellung Braut? (1)
- bridesconfidential.com de+okcupid-test Bester Mail -Bestellung Brautservice (1)
- bridesconfidential.com es+mujeres-rusas-calientes-y-sexys que es como la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- bridesconfidential.com es+novias-eslavas que es como la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- bridesconfidential.com es+novias-mexicanas agencias de novias por correo (1)
- bridesconfidential.com es+novias-rumanas que es como la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- bridesconfidential.com es+novias-tailandesas mejor orden de correo novia (1)
- bridesconfidential.com fi+albanialaiset-morsiamet oikeita postimyynti morsiamen tarinoita (1)
- bridesconfidential.com fi+kiinalaiset-morsiamet oikeita postimyynti morsiamen tarinoita (1)
- bridesconfidential.com fi+kuumat-ukrainalaiset-naiset legit postimyynti morsiamen sivustot reddit (1)
- bridesconfidential.com fi+kuumimmat-naiset-maailmassa postimyynti morsiamen tarinoita reddit (1)
- bridesconfidential.com fr+east-meet-east-avis sites de mariГ©e par correspondance les mieux notГ©s (0)
- bridesconfidential.com fr+les-femmes-les-plus-chaudes-du-monde sites de mariГ©e par correspondance les mieux notГ©s (1)
- bridesconfidential.com fr+mariees-irlandaises sites de mariГ©e par correspondance reddit (1)
- bridesconfidential.com hotteste-koreanske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ en postordrebrud (1)
- bridesconfidential.com it+donne-brasiliane-calde dove posso ottenere una sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- bridesconfidential.com it+donne-ucraine-calde il posto migliore per ottenere una sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- bridesconfidential.com it+le-donne-piu-calde-del-mondo dove posso ottenere una sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- bridesconfidential.com it+sposa-per-corrispondenza il posto migliore per ottenere una sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- bridesconfidential.com it+spose-colombiane dove posso ottenere una sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- bridesconfidential.com it+spose-costa-rican trova una sposa (1)
- bridesconfidential.com it+spose-honduregne trova una sposa (1)
- bridesconfidential.com main_es mejor orden de correo novia (1)
- bridesconfidential.com main_it sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- bridesconfidential.com main_no postordre brud pГҐ ordentlig? (1)
- bridesconfidential.com norske-bruder postordre brudinformasjon (1)
- bridesconfidential.com pt+noivas-argentinas correio em ordem noiva (1)
- bridesconfidential.com pt+noivas-indonesias melhor ordem de correio agГЄncia noiva reddit (1)
- bridesconfidential.com pt+noivas-turcas top dez site de noiva por ordem de correio (1)
- bridesconfidential.com sv+albaniska-brudar postorder brud definiera (1)
- bridesconfidential.com sv+heta-och-sexiga-ryska-kvinnor legitimte postorder brudtjänst (1)
- bridesconfidential.com sv+heta-och-sexiga-ryska-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brudens webbplatser (1)
- bridesconfidential.com sv+hetaste-koreanska-kvinnor postorder brud definition (1)
- bridesconfidential.com sv+indiska-brudar postorder brud definition (1)
- bridesconfidential.com sv+israeliska-brudar topp 10 postorder brudens webbplatser (0)
- bridesconfidential.com sv+rumanska-brudar topp 10 postorder brudens webbplatser (1)
- bridesconfidential.com svenske-bruder postordre brud pГҐ ordentlig? (1)
- bridesconfidential.com tr+avrupa-gelinleri Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Reddit NasД±l HazД±rlanД±r (1)
- bridesconfidential.com tr+brezilyali-gelinler En Д°yi Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmeti (1)
- bridesconfidential.com ungarske-bruder postordre brud pГҐ ordentlig? (1)
- brightwomen.net amolatina-recension postorder brudkataloger (1)
- brightwomen.net ar-postordrebrud-lagliga postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- brightwomen.net argentinska-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- brightwomen.net armensk-kvinna postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- brightwomen.net bangladesh-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- brightwomen.net belarus-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- brightwomen.net da+anastasia-date-anmeldelser hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net da+aserbajdsjanske-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- brightwomen.net da+belarus-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- brightwomen.net da+cambodian-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net da+dominikansk-kvinde hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net da+eharmony-anmeldelser bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- brightwomen.net da+hollandske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net da+italienske-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- brightwomen.net da+kazakhstan-kvinde hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net da+kinesiske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net da+kroatiske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net da+malaysiske-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- brightwomen.net da+maltesiske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net da+moldoviske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net da+pakistanske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net da+paraguayanske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net da+peruanske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net da+polsk-kvinde bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- brightwomen.net da+sri-lankan-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- brightwomen.net da+ukrainske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net da+varme-afrikanske-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- brightwomen.net da+varme-israelske-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- brightwomen.net da+varme-latinske-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- brightwomen.net da+varme-russiske-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- brightwomen.net da+varme-thailandske-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- brightwomen.net de+agyptische-frauen Mail-Order-Braut (1)
- brightwomen.net de+anastasia-date-test Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (0)
- brightwomen.net de+armenische-frau Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- brightwomen.net de+belgische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- brightwomen.net de+birmanische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- brightwomen.net de+britische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- brightwomen.net de+cupid-com-test Mail-Order-Braut (1)
- brightwomen.net de+deutsche-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- brightwomen.net de+die-kosten-von-katalogheirat Mail-Order-Braut (1)
- brightwomen.net de+eharmony-test Mail-Order-Braut (1)
- brightwomen.net de+filipino-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- brightwomen.net de+franzosische-frau Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- brightwomen.net de+georgische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- brightwomen.net de+haitianische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- brightwomen.net de+heise-asiatische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (0)
- brightwomen.net de+heise-filipino-frauen Mail-Order-Braut (1)
- brightwomen.net de+heise-indische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- brightwomen.net de+heise-thai-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- brightwomen.net de+israelische-frauen Mail-Order-Braut (1)
- brightwomen.net de+italienische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- brightwomen.net de+jamaikanische-frauen Mail-Order-Braut (1)
- brightwomen.net de+kubanische-frauen Mail-Order-Braut (1)
- brightwomen.net de+mongolische-frauen Mail-Order-Braut (1)
- brightwomen.net de+norwegische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- brightwomen.net de+osterreichische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- brightwomen.net de+polnische-frau Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- brightwomen.net de+russische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (0)
- brightwomen.net de+spanische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- brightwomen.net de+tschechische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- brightwomen.net de+uzbek-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- brightwomen.net de+will-katalogheirat-nur-mich-fur-mein-geld Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- brightwomen.net eharmony-recension postorder brudkataloger (1)
- brightwomen.net es+amolatina-opinion revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+mujer-japonesa que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+mujer-jordana que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+mujer-salvadorena que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+mujeres-afganas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+mujeres-argentinas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+mujeres-asiaticas-calientes que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+mujeres-azerbaiyanas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+mujeres-belgas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+mujeres-brasilenas-calientes revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+mujeres-colombianas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+mujeres-finlandesas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+mujeres-holandesas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+mujeres-iranies que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+mujeres-israelies-calientes revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+mujeres-lebanesas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+mujeres-lituanas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+mujeres-moldavas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+mujeres-panamenas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+mujeres-portuguesas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+mujeres-rumanas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+mujeres-rusas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+mujeres-vietnamitas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+mujeres-vietnamitas-calientes revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+novia-por-correo-solo-me-quieres-por-mi-dinero revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+son-legales-novia-por-correo que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net fi+armenialainen-nainen tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- brightwomen.net fi+egyptilaiset-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- brightwomen.net fi+filippiininaiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- brightwomen.net fi+iranilaiset-naiset wikipedia postimyynti morsian (1)
- brightwomen.net fi+kreikkalaiset-naiset wikipedia postimyynti morsian (1)
- brightwomen.net fi+kuumat-meksikolaiset-naiset wikipedia postimyynti morsian (1)
- brightwomen.net fi+lyhyt-historia-postimyynnissa-morsian tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- brightwomen.net fi+macedonian-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- brightwomen.net fi+montenegro-naiset wikipedia postimyynti morsian (1)
- brightwomen.net fi+perulaiset-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- brightwomen.net fi+ruotsalainen-nainen wikipedia postimyynti morsian (1)
- brightwomen.net fi+serbialaiset-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- brightwomen.net fi+tanskalaiset-naiset wikipedia postimyynti morsian (1)
- brightwomen.net fi+tsekin-naiset wikipedia postimyynti morsian (1)
- brightwomen.net fi+turkkilaisen-naiset wikipedia postimyynti morsian (1)
- brightwomen.net fi+venalaiset-naiset wikipedia postimyynti morsian (1)
- brightwomen.net fi+venezuelalaiset-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- brightwomen.net filippinska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- brightwomen.net fr+arabian-saoudienne Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- brightwomen.net fr+femme-japonaise Mail dans l'ordre de la mariГ©e (1)
- brightwomen.net fr+femme-kazakhstan Mail dans l'ordre de la mariГ©e (1)
- brightwomen.net fr+femmes-afghanes Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- brightwomen.net fr+femmes-autrichiennes Mail dans l'ordre de la mariГ©e (1)
- brightwomen.net fr+femmes-bresiliennes-chaudes Mail dans l'ordre de la mariГ©e (1)
- brightwomen.net fr+femmes-bulgares Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- brightwomen.net fr+femmes-croates Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- brightwomen.net fr+femmes-cubaines Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- brightwomen.net fr+femmes-equatoriennes Mail dans l'ordre de la mariГ©e (1)
- brightwomen.net fr+femmes-irlandaises Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- brightwomen.net fr+femmes-irlandaises-chaudes Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- brightwomen.net fr+femmes-japonaises-chaudes Mail dans l'ordre de la mariГ©e (1)
- brightwomen.net fr+femmes-malaisiennes Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- brightwomen.net fr+femmes-norvegiennes Mail dans l'ordre de la mariГ©e (1)
- brightwomen.net fr+femmes-panamiennes Mail dans l'ordre de la mariГ©e (1)
- brightwomen.net fr+femmes-portoricaines Mail dans l'ordre de la mariГ©e (1)
- brightwomen.net fr+femmes-portugaises Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- brightwomen.net fr+femmes-tcheques Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- brightwomen.net fr+femmes-thai Mail dans l'ordre de la mariГ©e (1)
- brightwomen.net fr+femmes-thai-chaudes Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- brightwomen.net fr+le-cout-de-mariee-par-correspondance Mail dans l'ordre de la mariГ©e (1)
- brightwomen.net fransk-kvinna postorder brudens webbplats (0)
- brightwomen.net guatemalanska-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- brightwomen.net heta-filippinska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- brightwomen.net heta-irlandska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- brightwomen.net heta-japanska-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- brightwomen.net heta-ukrainska-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- brightwomen.net hur-fungerar-postordrebrud postorder brudkataloger (1)
- brightwomen.net indiska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- brightwomen.net it+anastasia-date-recensione ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- brightwomen.net it+belarus-donne etГ media della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- brightwomen.net it+come-funziona-sposa-per-corrispondenza ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- brightwomen.net it+donna-armena vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- brightwomen.net it+donna-giordana vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- brightwomen.net it+donna-polacca vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- brightwomen.net it+donna-svedese etГ media della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- brightwomen.net it+donne-afgane vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- brightwomen.net it+donne-africane-calde etГ media della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- brightwomen.net it+donne-belghe etГ media della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- brightwomen.net it+donne-boliviane vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- brightwomen.net it+donne-brasiliane ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- brightwomen.net it+donne-brasiliane-calde etГ media della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- brightwomen.net it+donne-del-bangladesh vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- brightwomen.net it+donne-ecuadoriane vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- brightwomen.net it+donne-filippine vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- brightwomen.net it+donne-giamaicane vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- brightwomen.net it+donne-indonesiane vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- brightwomen.net it+donne-messicane-calde vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- brightwomen.net it+donne-portoghesi ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- brightwomen.net it+donne-russe-calde ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- brightwomen.net it+donne-serbe vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- brightwomen.net it+donne-spagnole vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- brightwomen.net it+donne-ucraine ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- brightwomen.net it+donne-ucraine-calde ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- brightwomen.net it+donne-vietnamite-calde ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- brightwomen.net kazakhstan-kvinna postorder brudkataloger (1)
- brightwomen.net kinesiska-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- brightwomen.net latvianska-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- brightwomen.net luxemburgska-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- brightwomen.net main_it ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- brightwomen.net main_pt Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- brightwomen.net main_tr Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek (1)
- brightwomen.net malaysiska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- brightwomen.net no+bulgarske-kvinner online postordre brud (1)
- brightwomen.net no+dominikansk-kvinne online postordre brud (1)
- brightwomen.net no+greske-kvinner online postordre brud (1)
- brightwomen.net no+guyanese-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net no+indiske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net no+indonesiske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net no+italienske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net no+latviske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net no+meksikanske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net no+paraguayanske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net no+russiske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net no+saudiarabisk-kvinne beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net no+syriske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net no+varme-filippinske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net no+varme-latinske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net osterrikiska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- brightwomen.net pt+cupid-com-recensao Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (0)
- brightwomen.net pt+mulher-do-cazaquistao Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- brightwomen.net pt+mulher-jordaniana Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- brightwomen.net pt+mulher-salvadorana Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- brightwomen.net pt+mulheres-africanas-gostosas Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- brightwomen.net pt+mulheres-checas Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- brightwomen.net pt+mulheres-chileanas Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- brightwomen.net pt+mulheres-croatas Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- brightwomen.net pt+mulheres-do-quirguistao Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- brightwomen.net pt+mulheres-guatemaltecas Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- brightwomen.net pt+mulheres-holandesas Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- brightwomen.net pt+mulheres-indianas Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- brightwomen.net pt+mulheres-iranianas Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- brightwomen.net pt+mulheres-israelenses Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- brightwomen.net pt+mulheres-israelenses-gostosas Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- brightwomen.net pt+mulheres-italianas-quentes Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- brightwomen.net pt+mulheres-mongois Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- brightwomen.net pt+mulheres-norueguesas Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- brightwomen.net pt+mulheres-peruanas Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- brightwomen.net pt+mulheres-russas-gostosas Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- brightwomen.net pt+mulheres-sirias Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- brightwomen.net pt+mulheres-uzbek Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- brightwomen.net pt+sri-lankan-women Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- brightwomen.net pt+tailandesas Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- brightwomen.net puerto-rico-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- brightwomen.net russian-cupid-recension postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- brightwomen.net schweiziska-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- brightwomen.net skotska-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- brightwomen.net tr+amolatina-inceleme Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek (1)
- brightwomen.net tr+anastasia-date-inceleme bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- brightwomen.net tr+belcikali-kadinlar Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek (1)
- brightwomen.net tr+danimarkali-kadinlar Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek (1)
- brightwomen.net tr+ermeni-kadin bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- brightwomen.net tr+estonyali-kadinlar bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- brightwomen.net tr+hintli-kadinlar bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- brightwomen.net tr+hirvat-kadinlar bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- brightwomen.net tr+malt-kadin bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- brightwomen.net tr+pakistanli-kadinlar bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- brightwomen.net tr+posta-siparisi-gelinler-maliyeti bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- brightwomen.net tr+sicak-israil-kadinlari bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- brightwomen.net tr+singapur-kadinlari bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- brightwomen.net tr+sri-lankan-kadinlar bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- brightwomen.net tr+suudi-arabistanli-kadin bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- brightwomen.net tr+turk-kadinlari bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- brightwomen.net tr+turkmen-kadinlar bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- brightwomen.net tr+ukraynali-kadinlar bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- brightwomen.net vietnamesiska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- browse mail order bride (1)
- brud mail ordre (1)
- brud ordre mail (3)
- brud ordre mail agentur (1)
- brud postorder (1)
- brudbeställning mail (1)
- brudbeställning mail (1)
- brudbeställning postbyrå (1)
- brude-tjenester til top mail-ordre (1)
- brudebestillings mail (1)
- brudebestillings postbyrГҐ (3)
- brudebestillings postbyrГҐ (0)
- brudebestillings postbyrГҐ (0)
- brudens världs postorder brudar (4)
- brudens världs postorder brudar (0)
- brudens världs postorder brudar (0)
- brudeparets ordre bruder (2)
- brudepostordre (1)
- brudesider med Гёverste postordre (2)
- brudesider med Гёverste postordre (0)
- Brush installment loans online (1)
- bt_aug (3)
- buen correo orden sitio web de la novia (2)
- buenos sitios de novias por correo (2)
- buon sito web per la sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- buona idea per la sposa per corrispondenza? (1)
- buona posta elettronica siti sposa (1)
- buscando matrimonio (4)
- buscando una novia por correo (2)
- buy a mail order bride (2)
- buy an essay online cheap (2)
- buy essay cheap (1)
- buy mail order bride (1)
- buy online essay cheap (1)
- buying a mail order bride (1)
- bästa land att hitta postorder brud (2)
- bästa land att hitta postorder brud (0)
- bästa landet att hitta en postorderbrud (2)
- bästa landet att hitta en postorderbrud (0)
- bästa länder för en postorderbrud (1)
- bästa plats för postorderbrud (1)
- bästa postorder brud byrå reddit (1)
- bästa postorder brud webbplats reddit (2)
- bästa postorder brud webbplats reddit (0)
- bästa postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- bästa postorder brud webbplatser recensioner (3)
- bästa postorder brud webbplatser recensioner (0)
- bästa postorder brud webbplatser recensioner (0)
- bästa postorder brudbyrå (1)
- bästa postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- bästa postorder brudens webbplatser 2022 (2)
- bästa postorder brudens webbplatser 2022 (0)
- bästa postorder brudens webbplatser reddit (4)
- bästa postorder brudens webbplatser reddit (0)
- bästa postorder brudens webbplatser reddit (0)
- bästa postorder brudens webbplatser reddit (0)
- bästa postorder brudföretag (2)
- bästa postorder brudföretag (0)
- bästa postorder brudland (2)
- bästa postorder brudland (0)
- bästa postorder brudländer (1)
- bästa postorderbrud någonsin (2)
- bästa postorderbrud någonsin (0)
- bästa rankade postorder brud webbplatser (3)
- bästa rankade postorder brud webbplatser (0)
- bästa rankade postorder brud webbplatser (0)
- bästa riktiga postorder brud webbplatser (3)
- bästa riktiga postorder brud webbplatser (0)
- bästa riktiga postorder brud webbplatser (0)
- bästa rykte postorder brud (1)
- bästa ställen att få postorder brud (2)
- bästa ställen att få postorder brud (0)
- bästa ställen att hitta postorderbrud (2)
- bästa ställen att hitta postorderbrud (0)
- bästa stället att få postorder brud (2)
- bästa stället att få postorder brud (0)
- bästa webbplats för att hitta en postorderbrud (2)
- bästa webbplats för att hitta en postorderbrud (0)
- bästa webbplats postorder brud (1)
- California guaranteed installment loans for bad credit (1)
- californiapaydayloanonline installment loans bad credit (1)
- cambodian-women free online sites for singles (1)
- cambodian-women+phnom-penh free online sites for singles (1)
- can anyone get a payday loan (1)
- can i get a cash advance (1)
- can i get a mail order bride if i am already married? (1)
- can i get a payday loan from a bank (5)
- can i get a payday loan with bad crdit (2)
- can i get a payday loan with very bad credit (2)
- can i get cash advance (2)
- can i get cash advance with no credit (0)
- can i have payday loans and get cash advance (3)
- can payday loan (2)
- can payday loans go on your credit (2)
- can payday loans improve your credit (1)
- can someone write my essay for me (1)
- can you get a cash advance (1)
- can you get a cash advance from bank (1)
- can you get a cash advance with no money? (1)
- can you get a payday loan from your bank (2)
- can you get a payday loan with no credit (3)
- can you get bad credit payday loan (1)
- can you get payday loan with no credit (1)
- can you get payday loans with bad credit (1)
- can you mail order a bride (1)
- Canfield bad credit installment loans (1)
- Canon City installment loans near me (1)
- cash advance (1)
- cash advance advance (3)
- cash advance advance america (1)
- cash advance america (1)
- cash advance america advance (2)
- cash advance america cash advance (2)
- cash advance america near me (2)
- cash advance america payday (2)
- cash advance america payday loan (2)
- cash advance america payday loans (2)
- cash advance america usa (3)
- cash advance america usa loan (1)
- cash advance american (1)
- cash advance and payday loans (2)
- cash advance at banks (1)
- cash advance bad credit (1)
- cash advance bad credit loans (3)
- cash advance bank (1)
- cash advance banking (1)
- cash advance banks (1)
- cash advance cash (3)
- cash advance cash advance (1)
- cash advance cash america (2)
- cash advance company (4)
- cash advance credit (1)
- cash advance d?finition (2)
- cash advance def (2)
- cash advance defintion (1)
- cash advance for bad credit (1)
- cash advance for bad credit no (1)
- cash advance for horrible credit (2)
- cash advance from your bank (1)
- cash advance how to (1)
- cash advance how to get it? (3)
- cash advance in america (2)
- cash advance in usa (1)
- cash advance is cash usa (1)
- cash advance is what (1)
- cash advance is? (2)
- cash advance items (5)
- cash advance lenders no check systems no credit check (2)
- cash advance lenders no credit check (1)
- cash advance loan (0)
- cash advance loan for bad credit (2)
- cash advance loan in usa (1)
- cash advance loan near me (3)
- cash advance loan no credit check (2)
- cash advance loan no interest (1)
- cash advance loan payday advance (1)
- cash advance loan usa (1)
- cash advance loand (2)
- cash advance loans bad credit (3)
- cash advance loans for bad credit (1)
- cash advance loans how do they work (3)
- cash advance loans no credit (1)
- cash advance loans no credit check direct lender (2)
- cash advance loans no credit check near me (1)
- cash advance loans now (1)
- cash advance loans usa (2)
- cash advance loans with no credit check (2)
- cash advance near (1)
- cash advance near me (1)
- cash advance near me bad credit (2)
- cash advance near me no credit check (1)
- cash advance near me now (1)
- cash advance nearby (3)
- cash advance nearme (1)
- cash advance neat me (1)
- cash advance new (2)
- cash advance newr me (4)
- cash advance no (1)
- cash advance no credit (3)
- cash advance no credit check (1)
- cash advance no credit check loan (3)
- cash advance no credit check near me (2)
- cash advance no credit check no bank account (1)
- cash advance no interest (1)
- cash advance now (2)
- cash advance now bad credit (3)
- cash advance now loan (1)
- cash advance now loans (3)
- cash advance now no credit check (1)
- cash advance of america (2)
- cash advance on a loan (2)
- cash advance payday advance (1)
- cash advance payday loan near me (2)
- cash advance payday loans near me (1)
- cash advance usa (2)
- cash advance usa loan (1)
- cash advance usa loan company (1)
- cash advance usa near me (2)
- cash advance usa price (1)
- cash advance what is (1)
- cash advance what is needed (1)
- cash advance with bad credit (1)
- cash advance with no (1)
- cash advance? (2)
- cash advances and payday loans (0)
- cash advances payday loans (1)
- cash america advance (4)
- cash america advance loans (1)
- cash america advance near me (1)
- cash america advance payday loans (1)
- cash america cash advance (1)
- cash america loans cash advance loans (1)
- cash america payday loan near me (1)
- cash america payday loans (3)
- cash an advance loan (1)
- cash and advance (2)
- cash and go payday loans (1)
- cash cash payday loan (2)
- cash company advance (3)
- cash credit payday loans (2)
- cash for you payday loans (0)
- cash go payday loan (3)
- cash in advance (0)
- cash in advance loans no credit check (5)
- cash in advance payday loan (2)
- cash in advance payday loans (1)
- cash loan advance (1)
- cash loan advance bad credit (2)
- cash loan now payday (3)
- cash loan payday (1)
- cash loan payday loan (1)
- cash loans advance (1)
- cash loans advance america (1)
- cash loans and payday advances (4)
- cash loans payday advance (1)
- cash loans payday loans (2)
- cash of advance (1)
- cash on advance (1)
- cash on go payday loans (3)
- cash payday advance loan (1)
- cash payday advance loans (2)
- cash payday loan (2)
- cash payday loan near me (1)
- cash payday loan now (1)
- cash payday loans (3)
- cash payday loans bad credit (2)
- cash to advance (2)
- cash to go payday loans (3)
- cash to payday loan (3)
- cash to payday loans near me (1)
- cash to you payday loans (1)
- cash usa payday loan (1)
- cashadvanceamerica.net+1-hour-direct-deposit-loans-in-minutes payday loan needed (1)
- cashadvanceamerica.net+250-dollar-payday-loan payday loans banks (1)
- cashadvanceamerica.net+300-dollar-payday-loan cash advance no credit check loan (1)
- cashadvanceamerica.net+5000-dollar-payday-loan advance cash payday loans (1)
- cashadvanceamerica.net+check-cashing-near-me payday loans banks (1)
- cashadvanceamerica.net+christmas-loans payday cash advance loans near me (1)
- cashadvanceamerica.net+fixed-rate-loans payday loans banks (1)
- cashadvanceamerica.net+payday-loans-for-self-employed payday loans banks (1)
- cashadvanceamerica.net+payday-loans-with-no-bank-account advance cash payday loans (1)
- cashadvanceamerica.net+personal-loans bad credit payday cash loan (1)
- cashadvanceamerica.net+school-loans-for-bad-credit how to get a cash advance loan (1)
- cashadvanceamerica.net+short-term payday loans banks (1)
- cashadvanceamerica.net+signature-installment-loans payday loans banks (1)
- cashadvanceamerica.net+students-loans-for-bad-credit cash loan payday advance (1)
- cashadvanceamerica.net+web-cash-loans bad credit payday cash loan (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+1500-dollar-payday-loan payday loan needed (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+3000-dollar-payday-loan bad credit payday cash loan (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+400-dollar-payday-loan payday loan needed (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+business-loans bad credit payday cash loan (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+emergency-loans-no-credit-check how to get a cash advance loan (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+flex-loans short payday loans no credit check (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+get-a-personal-loan-with-no-credit-history cash loan payday advance (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-al+carolina how much interest on a cash advance (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-ar+cincinnati how to do a cash advance (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-ar+portland get cash advance at bank (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-ca+richmond no credit check loan payday (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-ga+dallas how much interest on a cash advance (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-ia+portland nearby payday loans (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-il+augusta bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-in+richmond how to do a cash advance (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-ky+london payday loans no credit check places (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-la+spokane how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-mi+portland bad credit loans no payday (0)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-mn+long-beach how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-mo+birmingham payday loans very bad credit (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-ms+philadelphia payday loans very bad credit (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-nc+bolton payday loans very bad credit (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-nc+windsor bad credit loans no payday (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-nd+columbus how to do a cash advance (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-ne+columbus how to do a payday loan (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-nm+sacramento my payday loan (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-oh+cincinnati bad credit loans no payday (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-oh+hudson how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-oh+london no credit check loan payday (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-ok+clearview payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-or+ontario get cash advance at bank (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-pa+houston how to do a payday loan (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-pa+hudson bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-pa+oakwood how much interest on a cash advance (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-pa+riverside payday loans very bad credit (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-sc+central how to do a cash advance (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-tn+cleveland bad credit loans no payday (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-tx+cleveland how to do a cash advance (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-tx+oakwood payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-tx+san-antonio payday loans very bad credit (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-tx+tyler payday loans no credit check places (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-ut+cleveland payday loans very bad credit (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-va+victoria how to do a payday loan (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-wi+dallas bad credit loans no payday (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-wi+hammond how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-wi+ontario payday loans no credit check places (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-wv+carolina get cash advance payday loans (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-wv+prince payday loans no credit check places (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-wy+hudson how to do a payday loan (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+loans-by-phone cash loan payday advance (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+loans-for-bad-credit payday loan needed (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+no-origination-fee-personal-loan what are good payday loan company (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+payday-loans-al+blue-springs how to do a cash advance (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+payday-loans-ar+jacksonville how to do a payday loan (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+payday-loans-ca+bakersfield payday loans very bad credit (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+payday-loans-co+new-castle payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+payday-loans-de+magnolia payday loans no credit check places (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+payday-loans-fl+memphis get cash advance at bank (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+payday-loans-for-self-employed cash advance no credit check loan (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+payday-loans-for-self-employed short payday loans no credit check (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+payday-loans-ia+delta payday loans very bad credit (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+payday-loans-il+hammond how much interest on a cash advance (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+payday-loans-il+richmond payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-for-good-credit what are good payday loan company (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-mn+victoria how to do a payday loan (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-mo+bakersfield payday loans very bad credit (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-mo+birmingham cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-mo+memphis how to do a cash advance (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-ms+blue-mountain how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-ms+bolton payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-ms+columbus how to do a cash advance (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-ms+victoria bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-nc+hudson how to do a cash advance (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-nc+jacksonville how to do a payday loan (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-ne+emerald bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-nm+albuquerque payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-nv+las-vegas cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-oh+magnolia bad credit loans no payday (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-ok+tulsa nearby payday loans (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-or+phoenix how to do a cash advance (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-pa+delta payday loans very bad credit (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-pa+kingston nearby payday loans (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-ri+kingston my payday loan (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-tn+cleveland bad credit loans no payday (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-tn+nashville get cash advance payday loans (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-tx+combine bad credit loans no payday (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-tx+portland how much interest on a cash advance (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-tx+reno how much interest on a cash advance (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-ut+salt-lake-city get cash advance payday loans (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-wi+montreal get cash advance at bank (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-wv+carolina bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+signature-loans cash loan payday advance (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+small-loans cash advance no credit check loan (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+student-loan-rates advance cash payday loans (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+sunday-payday-loans cash advance no credit check loan (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com_MAIN payday loan in usa (1)
- casino (27)
- casino en ligne fr (2)
- casino onlina ca (1)
- casino online ar (1)
- casinò online it (1)
- casinomhub_aug (1)
- Casinos (2)
- Casinozer gg Online (1)
- Castalia guaranteed installment loans for bad credit no credit check (1)
- Castle Rock guaranteed installment loans for bad credit (1)
- cataloghi di sposi per corrispondenza (2)
- catalogo sposa per corrispondenza (4)
- Catalogue de la mariГ©e par correspondance (8)
- Catalogue de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Catalogue de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Catalogue de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Catalogue de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Catalogue de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Catalogue de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Catalogue de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Catalogues de la commande par correspondance (4)
- Catalogues de la commande par correspondance (0)
- category+freiburg+freiburg+ladyboy escort near me (1)
- category+kanton-bern+biel-bienne+koreanisch escort near me (1)
- category+niederosterreich+stockerau+trans escort girls (1)
- category+nordrhein-westfalen+duren+frauen escort girl (1)
- category+oberosterreich+steyr+ladyboy escort girls (1)
- category+oberosterreich+steyr+trans escorts (1)
- category+rheinland-pfalz+koblenz+modell escort girls (1)
- category+vorarlberg+bregenz+trans escort buchen (1)
- category+wallis+video-mit-sex best escort girl here (1)
- catГЎlogo de novias por correo (4)
- catГЎlogo de novias por correo (0)
- catГЎlogo de novias por correo (0)
- catГЎlogo de novias por correo (0)
- cebuanas-review free online sites for singles (1)
- ch (1)
- chat-avenue-review free online sites for singles (1)
- Chatham installment loans near me (1)
- che cos'ГЁ il servizio di sposa per corrispondenza (3)
- che cos'ГЁ il servizio di sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- che cos'ГЁ il servizio di sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- che sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- cheap custom essay papers (1)
- cheap custom essay service (1)
- cheap essay (1)
- cheap essay buy (2)
- cheap essay for sale (1)
- cheap essay papers (1)
- cheap essay writing (1)
- cheap essay writing service fast (2)
- cheap essay writing service review (1)
- cheap essay writing service us (1)
- cheap write my essay (0)
- cheapest write my essay (2)
- cheapest write my essay service (2)
- chechen-women free online sites for singles (1)
- Chesapeake guaranteed installment loans for bad credit (1)
- Cheshire personal installment loans (1)
- Child development (6)
- chinese dating sites (1)
- chinese-women+altay free online sites for singles (1)
- chinese-women+chengdu free online sites for singles (1)
- chinese-women+guilin free online sites for singles (1)
- chinese-women+houma free online sites for singles (1)
- chinese-women+nanjing free online sites for singles (1)
- chinese-women+shangri-la free online sites for singles (1)
- chinese-women+taishan free online sites for singles (1)
- chinese-women+xuzhou free online sites for singles (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+1500-dollar-payday-loan how much of a payday loan can i get (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+2500-dollar-payday-loan short payday loans no credit check (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+500-dollar-payday-loan short payday loans no credit check (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+balance-transfer-loans payday loans banks (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+balance-transfer-loans short payday loans no credit check (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+emergency-loans payday cash advance loans near me (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+holiday-loans advance cash payday loans (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+im-in-desperate-need-of-a-loan-with-bad-credit payday cash advance loans near me (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-al+carolina payday loans very bad credit (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-al+riverside nearby payday loans (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-ar+cincinnati get cash advance payday loans (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-ar+kingston payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-az+tucson payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-ca+fresno payday loans very bad credit (0)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-ca+modesto my payday loan (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-ca+san-jose my payday loan (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-de+houston payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-de+new-castle nearby payday loans (0)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-ga+augusta payday loans very bad credit (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-ga+jacksonville nearby payday loans (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-id+eagle get cash advance at bank (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-il+atlanta my payday loan (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-il+columbus payday loans no credit check places (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-il+nashville how to do a payday loan (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-il+riverside how to do a cash advance (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-il+san-jose bad credit loans no payday (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-in+new-castle how to do a cash advance (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-ks+columbus payday loans very bad credit (0)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-ks+kansas-city bad credit loans no payday (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-ky+richmond bad credit loans no payday (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-la+atlanta how to do a payday loan (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-la+spokane how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-me+portland get cash advance payday loans (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-mi+portland nearby payday loans (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-mo+atlanta how to do a cash advance (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-mo+richmond get cash advance at bank (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-mo+richmond payday loans no credit check places (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-nc+bolton payday loans very bad credit (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-nc+hamilton how much interest on a cash advance (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-nc+hudson bad credit loans no payday (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-nc+windsor nearby payday loans (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-nj+windsor no credit check loan payday (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-oh+ontario get cash advance at bank (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-ok+castle bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-ok+clearview no credit check loan payday (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-or+phoenix nearby payday loans (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-pa+houston how to do a cash advance (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-sc+windsor bad credit loans no payday (0)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-tn+philadelphia my payday loan (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-tx+early bad credit loans no payday (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-tx+miami payday loans very bad credit (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-tx+richmond how to do a payday loan (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-wv+carolina cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+list-of-online-payday-lenders short payday loans no credit check (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+loans-for-surgery payday loans banks (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+loans-with-instant-bank-verification advance cash bank (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+medical-loans short payday loans no credit check (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+payday-loans-al+hamilton how to do a cash advance (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+payday-loans-ca+los-angeles payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+payday-loans-co+denver bad credit loans no payday (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+payday-loans-co+portland how to do a cash advance (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+payday-loans-ga+columbus no credit check loan payday (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+payday-loans-ia+jacksonville no credit check loan payday (0)
- clickcashadvance.com+payday-loans-il+augusta payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+payday-loans-il+cleveland nearby payday loans (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+payday-loans-il+hamilton nearby payday loans (0)
- clickcashadvance.com+payday-loans-il+ottawa nearby payday loans (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+payday-loans-il+richmond how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+payday-loans-that-accept-netspend-accounts short payday loans no credit check (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+payday-loans-with-prepaid-debit-card cash loan payday advance (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-mo+birmingham get cash advance at bank (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-mo+birmingham how to do a payday loan (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-mo+kingston how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-mo+montreal bad credit loans no payday (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-mo+oakwood how to do a payday loan (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-ms+austin payday loans very bad credit (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-ms+victoria how to do a payday loan (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-mt+hamilton how to do a cash advance (0)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-nc+hudson no credit check loan payday (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-nc+windsor bad credit loans no payday (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-nc+windsor no credit check loan payday (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-ne+eagle how to do a payday loan (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-nm+las-vegas payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-nv+oasis bad credit loans no payday (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-oh+bolton how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-oh+delta get cash advance at bank (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-oh+fresno how much interest on a cash advance (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-oh+hamilton payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-oh+ontario payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-ok+clearview payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-or+jacksonville payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-tn+central bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-tx+hamilton how much interest on a cash advance (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-tx+jacksonville my payday loan (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-tx+richmond get cash advance payday loans (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-ut+central payday loans very bad credit (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-va+alberta payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-vt+jacksonville bad credit loans no payday (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-wa+seattle my payday loan (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-wa+spokane nearby payday loans (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-wi+cleveland my payday loan (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-wi+eagle payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+pre-approved-installment-loans payday loans banks (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+pre-approved-personal-loan what are good payday loan company (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+same-day-personal-loans cash advance no credit check loan (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+single-payment-loans payday loan needed (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+sunday-payday-loans cash loan payday advance (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+tribal-loans-teletrack cash loan payday advance (1)
- Clinton guaranteed installment loans for bad credit direct lenders only (1)
- Codere Italy (4)
- Cognitive training/mental fitness (1)
- colombialady-review free online sites for singles (1)
- colombian women for marriage (1)
- colombian-women free online sites for singles (1)
- colombian-women+la-paz free online sites for singles (1)
- colombian-women+lourdes free online sites for singles (1)
- colombian-women+murillo free online sites for singles (1)
- Colorado online installment loans instant approval (1)
- come acquistare una sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- come fare una sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- come funziona la sposa per corrispondenza (8)
- come funziona la sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- come funziona una sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- come funzionano i siti di sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- come ordinare la sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- come ordinare una sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- come ordinare una sposa russa per corrispondenza (3)
- come ordinare una sposa russa per posta (1)
- come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (4)
- come spedire la sposa (1)
- come spedire una sposa (3)
- come sposare una sposa per corrispondenza (3)
- come uscire con una sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- Commandage mariГ©e Craigslist (1)
- Commande de courrier Г©lectronique (9)
- Commande de courrier Г©lectronique (0)
- Commande de courrier Г©lectronique (0)
- Commande de courrier Г©lectronique (0)
- Commande de courrier Г©lectronique (0)
- Commande de courrier Г©lectronique (0)
- Commande de courrier Г©lectronique (0)
- Commande de courrier Г©lectronique (0)
- Commande de courrier Г©lectronique (0)
- Commande par correspondance Definitiom (2)
- Commande par courrier lГ©gitime? (2)
- Commande par courrier lГ©gitime? (0)
- commander par courrier une mariГ©e (2)
- commander par courrier une mariГ©e (0)
- Commandez de la courrier mariГ©e rГ©elles histoires (2)
- Commandez de la courrier mariГ©e rГ©elles histoires (0)
- Commandez la mariГ©e rГ©el du site rГ©el (3)
- Commandez la mariГ©e rГ©el du site rГ©el (0)
- Commandez la mariГ©e rГ©el du site rГ©el (0)
- Commandez par la poste pour de vrai? (2)
- commanditГ© (6)
- commanditГ© (0)
- commanditГ© (0)
- commanditГ© (0)
- commanditГ© (0)
- commanditГ© (0)
- commanditГ© (0)
- Comment commander de la mariГ©e (2)
- Comment commander de la mariГ©e (0)
- Comment commander la commande par courrier mariГ©e (3)
- Comment commander la commande par courrier mariГ©e (0)
- Comment commander la commande par courrier mariГ©e (0)
- Comment commander par la poste une mariГ©e (4)
- Comment commander par la poste une mariГ©e (0)
- Comment commander par la poste une mariГ©e (0)
- Comment commander par la poste une mariГ©e (0)
- Comment commander une mariГ©e par correspondance (6)
- Comment commander une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Comment commander une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Comment commander une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Comment commander une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Comment commander une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Comment commander une mariГ©e par correspondance russe (6)
- Comment commander une mariГ©e par correspondance russe (0)
- Comment commander une mariГ©e par correspondance russe (0)
- Comment commander une mariГ©e par correspondance russe (0)
- Comment commander une mariГ©e par correspondance russe (0)
- Comment commander une mariГ©e par correspondance russe (0)
- Comment commander une mariГ©e russe mail (6)
- Comment commander une mariГ©e russe mail (0)
- Comment commander une mariГ©e russe mail (0)
- Comment commander une mariГ©e russe mail (0)
- Comment commander une mariГ©e russe mail (0)
- Comment commander une mariГ©e russe mail (0)
- Comment faire de la vente par la poste (3)
- Comment faire de la vente par la poste (0)
- Comment fonctionne la mariГ©e par courrier (3)
- Comment fonctionne la mariГ©e par courrier (0)
- Comment fonctionne la mariГ©e par courrier (0)
- Comment fonctionne une mariГ©e par correspondance (3)
- Comment fonctionne une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Comment fonctionne une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Comment fonctionnent la mariГ©e par courrier (4)
- Comment fonctionnent la mariГ©e par courrier (0)
- Comment fonctionnent la mariГ©e par courrier (0)
- Comment fonctionnent la mariГ©e par courrier (0)
- Comment fonctionnent les sites de mariГ©e par courrier (2)
- Comment fonctionnent les sites de mariГ©e par courrier (0)
- Comment prГ©parer une mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- Comment prГ©parer une mariГ©e par correspondance Reddit (2)
- Comment prГ©parer une mariГ©e par correspondance Reddit (0)
- Comment sortir avec une mariГ©e par correspondance (2)
- Comment sortir avec une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Comment Г©pouser une mariГ©e par correspondance (2)
- Comment Г©pouser une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Commout Mail Entre Russian Bride (1)
- compagnie di sposa legittime per corrispondenza (5)
- company cash advance (2)
- company loan new payday (1)
- company loan payday (1)
- company payday loans (1)
- compaГ±Гas de novias legГtimas de pedidos por correo (1)
- compra la sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- compra una sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- comprar correo orden novia (5)
- comprar una novia por correo (5)
- comprar una novia por correo (0)
- comprare una sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- correo de la novia orden (4)
- correo de pedidos de la novia (3)
- correo en orden cuestan novia (1)
- correo en orden novia (6)
- correo legГtimo ordenar sitios de novias reddit (4)
- correo legГtimo ordenar sitios de novias reddit (0)
- correo legГtimo ordenar sitios de novias reddit (0)
- correo lГ©sbico ordenar novia reddit (1)
- correo orden cupГіn de novia (5)
- correo orden cupГіn de novia (0)
- correo orden cupГіn de novia (0)
- correo orden cupГіn de novia (0)
- correo orden cupГіn de novia (0)
- correo orden de citas de novias (1)
- correo orden de cuentos de novias reddit (1)
- correo orden de los paГses de la novia (2)
- correo orden de los paГses de la novia (0)
- correo orden de preguntas frecuentes de la novia (1)
- correo orden de reseГ±as de sitios web de novias (5)
- correo orden de reseГ±as de sitios web de novias (0)
- correo orden de reseГ±as de sitios web de novias (0)
- correo orden de reseГ±as de sitios web de novias (0)
- correo orden de reseГ±as de sitios web de novias (0)
- correo orden de reseГ±as del sitio web de la novia (3)
- correo orden de reseГ±as del sitio web de la novia (0)
- correo orden de reseГ±as del sitio web de la novia (0)
- correo orden de trabajo de novia? (2)
- correo orden informaciГіn de la novia (4)
- correo orden informaciГіn de la novia (0)
- correo orden informaciГіn de la novia (0)
- correo orden informaciГіn de la novia (0)
- correo orden novia buena idea? (2)
- correo orden novia craigslist (3)
- correo orden novia definitiom (2)
- correo orden novia legГtima (3)
- correo orden novia legГtima (0)
- correo orden novia legГtima (0)
- correo orden novia legГtima? (1)
- correo orden novia real (1)
- correo orden novia reveiw (2)
- correo orden novia reveiw (0)
- correo orden novia sitio real (4)
- correo orden novia wiki (2)
- correo orden novia wikipedia (1)
- correo orden sitios de novias reddit (2)
- correo orden sitios web de novias reddit (1)
- correo para ordenar novia (3)
- correo superior bride order web (4)
- correo-pedido-novia (5)
- cos'ГЁ la sposa per corrispondenza (7)
- cos'ГЁ la sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- cos'ГЁ la sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- cos'ГЁ la sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- cos'ГЁ la sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- cos'ГЁ la sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- cos'ГЁ la sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- cos'ГЁ la sposa per corrispondenza? (1)
- cos'ГЁ una sposa per corrispondenza (7)
- cos'ГЁ una sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- cos'ГЁ una sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- cos'ГЁ una sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- cos'ГЁ una sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- cos'ГЁ una sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- cos'ГЁ una sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- cos'ГЁ una sposa per corrispondenza? (2)
- cos'ГЁ una sposa per corrispondenza? (0)
- costa-rican-brides free online sites for singles (1)
- costo medio della sposa per corrispondenza (3)
- costo medio di una sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- costo promedio de la novia del pedido por correo (3)
- costo promedio de una novia por correo (2)
- cougar-life-review site for people (1)
- Counter Strike 2 (1)
- countries-with-the-most-beautiful-women free online sites for singles (1)
- Coupon de mariГ©e par correspondance (2)
- Coupon de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- coupon sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- courrier des commandes de la mariГ©e (2)
- courrier des commandes de la mariГ©e (0)
- Courrier pour commander la mariГ©e (3)
- Courrier pour commander la mariГ©e (0)
- Courrier pour commander la mariГ©e (0)
- courrier Г©lectronique (2)
- courrier Г©lectronique (0)
- CoГ»t moyen d'une mariГ©e par correspondance (3)
- CoГ»t moyen d'une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- CoГ»t moyen d'une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- CoГ»t moyen de la mariГ©e par correspondance (5)
- CoГ»t moyen de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- CoГ»t moyen de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- CoГ»t moyen de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- CoГ»t moyen de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Creative teaching approaches (1)
- credit loan payday (3)
- credit payday loan (2)
- credit payday loans (1)
- Crofton guaranteed installment loans for bad credit (1)
- cummalot.com+category+anal only fans accounts (1)
- cummalot.com+category+bondage only fans (1)
- cummalot.com+category+cougar onlyfans accounts (1)
- cummalot.com+category+creampie only fans (1)
- cummalot.com+category+crossdresser only fans models (1)
- cummalot.com+category+cumshot onlyfans (1)
- cummalot.com+category+explicit only fans models (1)
- cummalot.com+category+german onlyfans (1)
- cummalot.com+category+hardcore best onlyfans (1)
- cummalot.com+category+hottest onlyfans (1)
- cummalot.com+category+midget only fans (1)
- cummalot.com+category+pornstar best onlyfans accounts (1)
- cummalot.com+category+small-tits onlyfans accounts (2)
- cummalot.com+category+streaming best only fans (1)
- cummalot.com+category+streaming onlyfans (1)
- cummalot.com+category+striptease onlyfans models (1)
- cummalot.com+category+taboo best only fans (1)
- cummalot.com+category+trans best only fans (1)
- cummalot.com+category+twitter onlyfans accounts (1)
- cummalot.com+category+xxx best only fans account (1)
- cupid-com-review site free (1)
- custom cheap essay (1)
- custom essay writing service cheap (1)
- czech-women site free (1)
- cГіmo casarse con una novia por correo (2)
- cГіmo casarse con una novia por correo (0)
- cГіmo comprar una novia por correo (1)
- cГіmo enviar por correo a la novia (4)
- cГіmo enviar por correo a la novia (0)
- cГіmo enviar por correo a la novia (0)
- cГіmo enviar por correo a la novia (0)
- cГіmo enviar por correo a una novia (4)
- cГіmo enviar por correo a una novia (0)
- cГіmo enviar por correo a una novia (0)
- cГіmo hacer pedidos por correo novia (4)
- cГіmo hacer pedidos por correo novia (0)
- cГіmo hacer pedidos por correo novia (0)
- cГіmo hacer un pedido por correo novia (1)
- cГіmo ordenar correo orden novia (1)
- cГіmo pedir una novia rusa por correo (3)
- cГіmo pedir una novia rusa por correo (0)
- cГіmo pedir una novia rusa por correo (0)
- cГіmo pedir una novia rusa por correo (0)
- cГіmo preparar un correo orden novia reddit (2)
- cГіmo preparar un correo orden novia reddit (0)
- cГіmo preparar una novia por correo (1)
- cГіmo salir con una novia por correo (2)
- cГіmo salir con una novia por correo (0)
- danish-women+aarhus free online sites for singles (1)
- danish-women+aarhus site free (1)
- Datation de la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- dateinasia-review site free (1)
- daterussiangirl-review site free (0)
- dateukrainiangirl-review site free (1)
- Dating Game Rules (1)
- dating sites guide (1)
- dating sites review (1)
- dating tips (1)
- dating women online (1)
- dating-in-your-30s free online sites for singles (1)
- de bedste steder at finde postordrebrud (1)
- de+adultfriendfinder-test Versandbestellbraut wert? (0)
- de+amerikanische-braeute Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+amourfactory-test Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+argentinisch-braeute Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+asiame-test Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+asianladyonline-test Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+asiatische-braeute Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+australische-braeute Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+bbwcupid-test Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+beste-laender-zu-finden-eine-treue-frau Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+blackpeoplemeet-test Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+britische-dating-sites-und-apps Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+catholicmatch-test Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+charmdate-test Versandbestellbraut wert? (0)
- de+charmromance-test Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+colombian-cupid-test Versandbestellung Frau (0)
- de+cupidates-test Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+dateniceukrainian-test Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+daterussiangirl-test Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+der-beste-ort-um-alleinstehende-frauen Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+deutsch-frauen Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+deutsche-dating-seiten-und-apps Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+die-schoensten-frauen-der-welt Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+dil-mil-test Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+dominikanische-dating-sites-und-apps Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+filipinocupid-test Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+findeuropeanbeauty-test Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+findmate-test Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+fitness-singles-test Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+guam-frauen Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+heated-affairs-test Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+heiss-griechische-frauen Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+heiss-polnisch-frauen Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+heisse-aethiopische-frauen Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+heisse-albanische-frauen Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+heisse-argentinische-frauen Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+heisse-frauen-aus-sri-lanka Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+heisse-indische-frauen Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+heisse-irakische-frauen Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+heisse-jordanische-frauen Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+heisse-kambodschanische-frauen Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+heisse-kanadische-frauen Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+heisse-kubanische-frauen Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+heisse-medellin-frauen Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+heisse-mongolische-frauen Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+heisse-niederlaendische-frauen Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+heisse-portugiesische-frauen Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+heisse-puerto-ricanische-frauen Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+heisse-slawische-frauen Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+heisse-slowenische-frauen Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+heisse-uruguay-frauen Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+heisse-usbekische-frauen Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+heisse-venezolanische-frauen Versandbestellung Frau (0)
- de+indiamatch-test Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+indianer-braeute Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+internationalcupid-test Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+israeli-frauen Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+italienische-braeute Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+jamaikanische-braeute Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+jdate-test Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+jeevansathi-test Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+jemanden-aus-einem-anderen-land-heiraten Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+junge-alleinstehende-frauen Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+kambodschanische-frauen Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+kismia-test Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+kolumbianische-braeute Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+koreanische-frauen Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+kroaten-frauen Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+liebe-mit-altersunterschied-moeglich Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+marokkanische-frauen Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+meetme-test Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+meetville-test Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+mexikanische-braeute Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+moldawien-frauen Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+mollige-alleinstehende-frauen Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+mongolen-frauen Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+norwegische-braeute Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+offene-beziehung Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+omegle-test Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+orchidromance-test Versandbestellung Frau (0)
- de+osteuropaeerinnen-frauen Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+peruanische-braeute Versandbestellbraut wert? (0)
- de+philippinische-braeute Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+portugiesisch-frauen Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+puerto-ricanische-frauen BEST bewertete Versandauftragsbrautseiten (1)
- de+pure-test Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+reife-alleinstehende-frauen Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+russische-dating-sites-und-apps Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+russische-vs-ukrainische-frauen-sind-es-irgendwelche-unterschiede Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+schwedische-braeute Versandbestellung Frau (0)
- de+schwedische-dating-sites-und-apps BEST bewertete Versandauftragsbrautseiten (1)
- de+schweizerinnen BEST bewertete Versandauftragsbrautseiten (1)
- de+secret-benefits-test BEST bewertete Versandauftragsbrautseiten (1)
- de+seeking-arrangement-test Versandbestellung Frau (0)
- de+serbisch-frauen BEST bewertete Versandauftragsbrautseiten (1)
- de+skandinavische-braeute Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+slawische-braeute BEST bewertete Versandauftragsbrautseiten (1)
- de+slowakische-braeute Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+somali-frauen BEST bewertete Versandauftragsbrautseiten (1)
- de+sri-lankan-braeute Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+suedafrikanische-frauen Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+tadschikistan-frauen Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+tinder-test BEST bewertete Versandauftragsbrautseiten (1)
- de+tuerkisch-braeute BEST bewertete Versandauftragsbrautseiten (1)
- de+turkmenistan-frauen BEST bewertete Versandauftragsbrautseiten (1)
- de+usbekistan-frauen Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+venezolanische-braeute Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+victoriabrides-test Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+was-ist-eine-mail-order-braut Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+whatsyourprice-test Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+wichtige-tipps-zum-dating-in-ihren-30ern Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+wie-finde-ich-eine-frau Versandbestellbraut wert? (0)
- de+wie-lange-bis-datiert-vor-ehe Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+wie-man-eine-versandhandelsbraut-wird Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- deberГa comprar una orden de correo novia (1)
- deberГa salir con una novia por correo (1)
- Definicija narudЕѕbe poЕЎte (1)
- definiciГіn de servicios de novias por correo (3)
- definiciГіn de servicios de novias por correo (0)
- definiciГіn de servicios de novias por correo (0)
- definisjon av postordre brud tjenester (5)
- definizione dei servizi per la sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- definizione sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- definição de serviços de noiva para pedidos por correio (1)
- Des Peres bad credit installment loans (1)
- deutschland username (1)
- deutschland+baden-wurttemberg+freiburg sign up (1)
- deutschland+baden-wurttemberg+freiburg support (1)
- deutschland+baden-wurttemberg+ludwigsburg username (1)
- deutschland+baden-wurttemberg+mannheim nutte buchen (1)
- deutschland+baden-wurttemberg+stuttgart tips (1)
- deutschland+baden-wurttemberg+villingen-schwenningen escort girl (1)
- deutschland+baden-wurttemberg+villingen-schwenningen tips (1)
- deutschland+bayern escort (1)
- deutschland+bayern+augsburg username (1)
- deutschland+bayern+erlangen visitors (1)
- deutschland+bayern+furth nutten finden (1)
- deutschland+bayern+furth sign up (1)
- deutschland+brandenburg+cottbus visitors (2)
- deutschland+hamburg-staat+hamburg sign in (1)
- deutschland+hessen+darmstadt sign up (1)
- deutschland+hessen+frankfurt escort girl (1)
- deutschland+niedersachsen+essen sign in (1)
- deutschland+niedersachsen+essen support (1)
- deutschland+niedersachsen+gottingen username (1)
- deutschland+niedersachsen+hannover sign up (1)
- deutschland+niedersachsen+hannover support (1)
- deutschland+niedersachsen+hannover tips (1)
- deutschland+niedersachsen+hildesheim escort girl link (1)
- deutschland+niedersachsen+munster tips (1)
- deutschland+niedersachsen+oldenburg nutten finden (1)
- deutschland+nordrhein-westfalen+aachen nutten finden (1)
- deutschland+nordrhein-westfalen+bonn visitors (1)
- deutschland+nordrhein-westfalen+dortmund escort near me (1)
- deutschland+nordrhein-westfalen+dortmund visitors (1)
- deutschland+nordrhein-westfalen+duisburg escort girl (1)
- deutschland+nordrhein-westfalen+duren username (1)
- deutschland+nordrhein-westfalen+hagen escort (1)
- deutschland+nordrhein-westfalen+hagen tips (1)
- deutschland+nordrhein-westfalen+halle escort girls (1)
- deutschland+nordrhein-westfalen+halle sign up (1)
- deutschland+nordrhein-westfalen+marl escort girl (1)
- deutschland+nordrhein-westfalen+marl nutten buchen (1)
- deutschland+nordrhein-westfalen+neuss sign in (1)
- deutschland+nordrhein-westfalen+neuss visitors (1)
- deutschland+nordrhein-westfalen+oberhausen escort (1)
- deutschland+nordrhein-westfalen+ratingen tips (1)
- deutschland+nordrhein-westfalen+remscheid escort (1)
- deutschland+rheinland-pfalz+ludwigshafen username (1)
- deutschland+rheinland-pfalz+trier username (1)
- deutschland+sachsen+chemnitz visitors (1)
- deutschland+sachsen+zwickau tips (1)
- deutschland+sachsen-anhalt escort girls (1)
- deutschland+sachsen-anhalt+dessau-rosslau sign up (1)
- deutschland+sachsen-anhalt+magdeburg escort girl link (1)
- deutschland+sachsen-anhalt+magdeburg nutten finden (1)
- deutschland+schleswig-holstein+kiel escorts (1)
- deutschland+thuringen support (1)
- devrais-je acheter une mariГ©e par correspondance (2)
- devrais-je acheter une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- devrais-je sortir avec une mariГ©e par correspondance (2)
- devrais-je sortir avec une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Die Mail -Bestellungsbrautstelle (1)
- Die Versandbestellbraut (1)
- diez mejores sitios para novias por correo (2)
- diez mejores sitios web de novias por correo (1)
- dj tools reviews (1)
- do payday loans go on credit (3)
- do payday loans go on your credit (1)
- dominican-dating-sites-and-apps free online sites for singles (1)
- donde compro una orden de correo novia (3)
- dove acquistare una sposa per corrispondenza (3)
- dove posso ottenere una sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- dove posso trovare una sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- dove trovare una sposa per corrispondenza (4)
- dove trovo una sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- Dream Honeymoon Destinations (1)
- Durchschnittliche Kosten einer Versandbestellbraut (1)
- Durchschnittliche Kosten fГјr Versandbestellbraut (3)
- Durchschnittliche Kosten fГјr Versandbestellbraut (0)
- Durchschnittliche Kosten fГјr Versandbestellbraut (0)
- Durchschnittliche Versandauftragspreise (1)
- Durchschnittsalter der Postanweisung Braut (2)
- Durchschnittspreis fГјr eine Versandbestellbraut (6)
- Durchschnittspreis fГјr eine Versandbestellbraut (0)
- Durchschnittspreis fГјr eine Versandbestellbraut (0)
- Durchschnittspreis fГјr eine Versandbestellbraut (0)
- Durchschnittspreis fГјr eine Versandbestellbraut (0)
- Durchschnittspreis fГјr eine Versandbestellbraut (0)
- Durchschnittspreis fГјr Versandbestellbraut (2)
- Durchschnittspreis fГјr Versandbestellbraut (0)
- dutch-women+arnhem site free (1)
- dutch-women+maastricht site free (1)
- DГ©couvrez la mariГ©e par correspondance (3)
- DГ©couvrez la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- DГ©couvrez la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- DГ©finition de la mariГ©e par correspondance (3)
- DГ©finition de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- DГ©finition de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- DГ©finition des services de vente par correspondance (1)
- dГіnde comprar una novia por correo (2)
- dГіnde comprar una novia por correo (0)
- dГіnde encontrar una novia por correo (5)
- dГіnde encontrar una novia por correo (0)
- dГіnde encontrar una novia por correo (0)
- dГіnde encontrar una novia por correo (0)
- dГіnde encontrar una novia por correo (0)
- e-mail ordine sposa (2)
- e-post ordre brud (3)
- e-post ordre brud nettsted anmeldelser (4)
- E-posta SipariЕџi Gelin (1)
- e-postorder brud (1)
- e-postordre brud nettsteder anmeldelser (3)
- easiest payday loans no credit check (1)
- easternhoneys-review free online sites for singles (1)
- Echte Versandauftragsbrautgeschichten (1)
- Echte Versandbestellbraut -Sites (3)
- Echte Versandungsbraut (2)
- Echter Mail -Bestellung Brautservice (1)
- ecuadorian-women+cuenca free online sites for singles (1)
- edad promedio de la novia del pedido por correo (3)
- Eine legitime Versandbrautbraut (3)
- Eine Versandauftragsbraut (3)
- Eine Versandauftragsbraut (0)
- ekte postordre brud nettsted (4)
- ekte postordre brud nettsteder (2)
- ekte postordre brudhistorier (4)
- ekte postordre brudtjeneste (6)
- ekte postordrebrud (6)
- el sitio de la novia por correo (4)
- el sitio de la novia por correo (0)
- elenco dei migliori siti di sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+500-dollar-payday-loan how to get a cash advance loan (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+business-loans what are good payday loan company (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+edd-card-cash-advance what are good payday loan company (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans bad credit payday cash loan (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-ak+houston how to do a payday loan (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-ar+victoria how much interest on a cash advance (0)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-fl+hudson how to do a payday loan (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-ga+kingston bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-ia+early how to do a cash advance (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-ia+early how to do a payday loan (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-ia+riverside cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-il+lawrence how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-il+oakland bad credit loans no payday (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-il+phoenix how to do a cash advance (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-in+columbus payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-in+hammond get cash advance payday loans (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-in+hammond how much interest on a cash advance (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-in+nashville nearby payday loans (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-ks+kansas-city payday loans no credit check places (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-ky+richmond how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-ky+sacramento payday loans very bad credit (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-la+baton-rouge bad credit loans no payday (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-la+hammond get cash advance payday loans (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-md+long-beach bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-mi+birmingham how much can you get on a payday loan (0)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-mi+memphis bad credit loans no payday (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-mn+alberta no credit check loan payday (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-mo+augusta payday loans very bad credit (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-mo+bakersfield get cash advance payday loans (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-mo+jacksonville how to do a cash advance (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-mo+oakwood bad credit loans no payday (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-ms+cleveland payday loans very bad credit (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-ms+hamilton how much interest on a cash advance (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-ms+hamilton how to do a cash advance (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-nc+charlotte payday loans very bad credit (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-nc+jacksonville how to do a cash advance (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-nc+nashville payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-nd+hamilton bad credit loans no payday (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-nj+kingston cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-oh+birmingham payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-oh+bolton nearby payday loans (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-oh+nashville nearby payday loans (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-ok+avant get cash advance payday loans (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-ok+miami payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-or+ontario how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-or+portland payday loans no credit check places (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-pa+austin how to do a payday loan (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-tx+hamilton payday loans very bad credit (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-tx+houston how to do a cash advance (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-tx+miami how to do a payday loan (0)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-ut+kingston bad credit loans no payday (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-va+new-castle payday loans very bad credit (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-wi+ontario nearby payday loans (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+legitimate-online-loans cash advance no credit check loan (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+loans-for-veterans what are good payday loan company (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+payday-loans-ak+central no credit check loan payday (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+payday-loans-al+jacksonville how to do a payday loan (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+payday-loans-ar+blue-mountain payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+payday-loans-ca+windsor no credit check loan payday (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+payday-loans-co+denver payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+payday-loans-ia+jacksonville bad credit loans no payday (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+payday-loans-id+eagle payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+payday-loans-il+cleveland payday loans very bad credit (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+payday-loans-il+magnolia get cash advance payday loans (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+payday-loans-il+ottawa payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+payday-loans-in+atlanta payday loans very bad credit (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+payday-loans-in+columbus bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+payday-loans-in+denver how to do a cash advance (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+payday-loans-that-accept-netspend-accounts cash advance no credit check loan (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+payday-loans-with-no-checking-account payday loans banks (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+payday-loans-with-savings-account payday loans banks (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+personal-loan-rates cash advance no credit check loan (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+personal-loans-ms+houston how to do a cash advance (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+personal-loans-nc+nashville how to do a payday loan (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+personal-loans-nj+kingston bad credit loans no payday (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+personal-loans-nj+magnolia get cash advance payday loans (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+personal-loans-nj+new-brunswick bad credit loans no payday (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+personal-loans-nm+kingston nearby payday loans (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+personal-loans-oh+cleveland payday loans very bad credit (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+personal-loans-oh+riverside bad credit loans no payday (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+personal-loans-oh+riverside my payday loan (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+personal-loans-or+ontario how to do a payday loan (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+personal-loans-pa+hudson bad credit loans no payday (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+personal-loans-pa+oakwood how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+personal-loans-tx+austin payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+personal-loans-tx+miami bad credit loans no payday (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+personal-loans-tx+portland payday loans very bad credit (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+personal-loans-ut+cleveland how much interest on a cash advance (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+personal-loans-ut+delta cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+personal-loans-va+new-castle get cash advance payday loans (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+personal-loans-wi+ontario how to do a payday loan (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+school-loans-for-bad-credit cash advance no credit check loan (1)
- elitesingles (1)
- En iyi 10 posta sipariЕџi gelin sitesi (1)
- En iyi 10 posta sipariЕџi gelini (3)
- En iyi 10 posta sipariЕџi gelini (0)
- En iyi 10 posta sipariЕџi gelini (0)
- En iyi 10 posta sipariЕџi gelini web siteleri (2)
- En iyi 10 posta sipariЕџi gelini web siteleri (0)
- En iyi 5 posta sipariЕџi gelin sitesi (2)
- En iyi 5 posta sipariЕџi gelin sitesi (0)
- En iyi posta sipariЕџi gelin hizmeti nedir (1)
- En iyi posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri nelerdir (4)
- En iyi posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri nelerdir (0)
- En iyi posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri nelerdir (0)
- En iyi posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri nelerdir (0)
- En iyi posta sipariЕџi gelin yerleri (2)
- En iyi posta sipariЕџi gelin yerleri (0)
- En iyi posta sipariЕџi gelin Гјlke (2)
- En iyi posta sipariЕџi gelin Гјlke (0)
- En iyi posta sipariЕџi gelin Гјlkesi nedir (3)
- En iyi posta sipariЕџi gelin Гјlkesi nedir (0)
- En iyi posta sipariЕџi gelin Гјlkesi nedir (0)
- En iyi posta sipariЕџi gelini sitesi (2)
- En iyi posta sipariЕџi gelini sitesi (0)
- En iyi posta sipariЕџi gelini sitesi nedir (1)
- En iyi posta sipariЕџi gelini web siteleri (2)
- En iyi posta sipariЕџi gelini web siteleri (0)
- En iyi posta sipariЕџi gelini web siteleri reddit (2)
- En iyi posta sipariЕџi gelini web siteleri reddit (0)
- En iyi posta sipariЕџi gelini web sitesi (3)
- En iyi posta sipariЕџi gelini web sitesi (0)
- En iyi posta sipariЕџi gelini web sitesi (0)
- En iyi site posta sipariЕџi gelin (1)
- en legitim postordrebrud (4)
- en legitim postordrebrud (0)
- en postorderbrud (4)
- en postordrebrud (3)
- En sД±cak posta sipariЕџi gelini (1)
- En İyi Gerçek Posta Siparişi Gelin Siteleri (4)
- En İyi Gerçek Posta Siparişi Gelin Siteleri (0)
- En İyi Gerçek Posta Siparişi Gelin Siteleri (0)
- En Д°yi Nominal Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Siteleri (3)
- En Д°yi Nominal Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Siteleri (0)
- En Д°yi Posta SipariЕџi Gelin (1)
- En Д°yi Posta SipariЕџi Gelin AjansД± (2)
- En Д°yi Posta SipariЕџi Gelin AjansД± (0)
- En Д°yi Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmeti (1)
- En Д°yi Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Siteleri Listesi (3)
- En Д°yi Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Siteleri Listesi (0)
- En Д°yi Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Siteleri Listesi (0)
- En Д°yi Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Siteleri Д°ncelemeleri (3)
- En Д°yi Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Siteleri Д°ncelemeleri (0)
- En Д°yi Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Siteleri Д°ncelemeleri (0)
- En Д°yi Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Sitesi Reddit (1)
- En Д°yi Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Гњlkeleri (1)
- En Д°yi Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Ећirketi (2)
- En Д°yi Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Ећirketi (0)
- En Д°yi Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Ећirketleri (1)
- En Д°yi Yasal Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Web Siteleri (1)
- en+austria+burgenland escort girls (1)
- en+austria+burgenland+eisenstadt escorts near me (1)
- en+austria+burgenland+eisenstadt tips (1)
- en+austria+carinthia+klagenfurt escorts near me (1)
- en+austria+carinthia+villach escort girl (1)
- en+austria+lower-austria+amstetten escort (1)
- en+austria+lower-austria+amstetten visitors (1)
- en+austria+lower-austria+bad-voslau escort near me (1)
- en+austria+lower-austria+korneuburg escort near me (1)
- en+austria+lower-austria+krems-an-der-donau tips (1)
- en+austria+lower-austria+traiskirchen best escort platform (1)
- en+austria+lower-austria+tulln escorts (1)
- en+austria+lower-austria+wiener-neustadt escort girl (1)
- en+austria+salzburg-state username (1)
- en+austria+salzburg-state+wals support (1)
- en+austria+tyrol+lienz username (1)
- en+austria+upper-austria+bad-ischl escort girl here (1)
- en+austria+upper-austria+braunau-am-inn escort girl link (1)
- en+austria+upper-austria+gmunden escort (1)
- en+austria+upper-austria+leonding escort (1)
- en+austria+upper-austria+linz visitors (1)
- en+austria+upper-austria+ried-im-innkreis username (1)
- en+austria+upper-austria+steyr escort service (1)
- en+austria+vienna-state escorts (1)
- en+austria+vienna-state+vienna username (1)
- en+austria+vorarlberg tips (1)
- en+austria+vorarlberg+bregenz find escort girls (1)
- en+austria+vorarlberg+dornbirn escort service (1)
- en+category+berlin-state+berlin+granny find escort (1)
- en+category+grisons+davos+trans find escort (1)
- en+category+styria+graz+japanese escort girls (1)
- en+category+vienna-state+vienna+muscular escort service (2)
- en+category+vienna-state+vienna+muscular escort service (0)
- en+germany+baden-wurttemberg+heidelberg escort girl link (1)
- en+germany+baden-wurttemberg+heilbronn visitors (1)
- en+germany+baden-wurttemberg+mannheim visitors (1)
- en+germany+baden-wurttemberg+reutlingen escort girl (1)
- en+germany+baden-wurttemberg+stuttgart escort (1)
- en+germany+baden-wurttemberg+tubingen username (1)
- en+germany+baden-wurttemberg+ulm escort (1)
- en+germany+bavaria escort girl (1)
- en+germany+bavaria+erlangen visitors (1)
- en+germany+bavaria+ingolstadt tips (1)
- en+germany+bavaria+wurzburg escort here link (1)
- en+germany+berlin-state tips (1)
- en+germany+brandenburg-state+potsdam support (1)
- en+germany+brandenburg-state+potsdam tips (1)
- en+germany+bremen-state tips (1)
- en+germany+bremen-state+bremen escort (1)
- en+germany+bremen-state+bremen escorts near me (1)
- en+germany+hesse escort girls (1)
- en+germany+hesse+hanau escort (1)
- en+germany+hesse+hanau escort girls (1)
- en+germany+lower-saxony+brunswick find escort (1)
- en+germany+lower-saxony+osnabruck escorts near me (1)
- en+germany+lower-saxony+wolfsburg support (1)
- en+germany+north-rhine-westphalia+bonn tips (1)
- en+germany+north-rhine-westphalia+hagen tips (1)
- en+germany+north-rhine-westphalia+minden visitors (1)
- en+germany+north-rhine-westphalia+witten username (1)
- en+germany+rhineland-palatinate+trier best escort platform (1)
- en+germany+saarland+saarbrucken escorts (1)
- en+germany+saxony+zwickau support (1)
- en+germany+saxony+zwickau username (1)
- en+germany+saxony-anhalt escort girl link (1)
- en+germany+saxony-anhalt+dessau-rosslau support (1)
- en+germany+thuringia+erfurt escort (1)
- en+s+models+ch visitors (1)
- en+s+models+de-bw+karlsruhe sign up (1)
- en+s+models+nl-nb+eindhoven username (1)
- en+switzerland best escort plattform (1)
- en+switzerland+aargau escort (1)
- en+switzerland+aargau+oftringen best escort platform (1)
- en+switzerland+aargau+oftringen find escort (1)
- en+switzerland+aargau+oftringen visitors (1)
- en+switzerland+aargau+spreitenbach tips (1)
- en+switzerland+aargau+wettingen escort (1)
- en+switzerland+aargau+zofingen username (1)
- en+switzerland+appenzell-ausserrhoden+herisau escorts near me (1)
- en+switzerland+basel-city username (1)
- en+switzerland+basel-landschaft best escort plattform (1)
- en+switzerland+basel-landschaft escort service (1)
- en+switzerland+basel-landschaft find escort (1)
- en+switzerland+basel-landschaft+binningen username (1)
- en+switzerland+basel-landschaft+liestal escort (1)
- en+switzerland+basel-landschaft+munchenstein escort (1)
- en+switzerland+basel-landschaft+oberwil find escort girls (1)
- en+switzerland+canton-of-bern+bern tips (1)
- en+switzerland+canton-of-bern+biel-bienne best escort platform (1)
- en+switzerland+canton-of-bern+langenthal support (1)
- en+switzerland+canton-of-bern+ostermundigen tips (1)
- en+switzerland+canton-of-bern+thun tips (1)
- en+switzerland+canton-of-schwyz support (1)
- en+switzerland+canton-of-schwyz+einsiedeln support (1)
- en+switzerland+canton-of-schwyz+einsiedeln visitors (1)
- en+switzerland+canton-of-schwyz+schwyz escorts near me (1)
- en+switzerland+canton-of-schwyz+schwyz tips (1)
- en+switzerland+canton-of-solothurn find escort (1)
- en+switzerland+canton-of-zug+zug escort near me (1)
- en+switzerland+geneva-state+geneva tips (1)
- en+switzerland+glarus-state+glarus find escort girls (1)
- en+switzerland+grisons escort near me (1)
- en+switzerland+grisons+davos tips (1)
- en+switzerland+jura escort girl (1)
- en+switzerland+lucerne-state+lucerne tips (1)
- en+switzerland+neuchatel visitors (1)
- en+switzerland+schaffhausen-state escort girls (1)
- en+switzerland+schaffhausen-state+schaffhausen visitors (1)
- en+switzerland+st-gallen-state+buchs escort girl (1)
- en+switzerland+st-gallen-state+st-gallen support (1)
- en+switzerland+thurgau escort near me (1)
- en+switzerland+thurgau+amriswil visitors (1)
- en+switzerland+thurgau+arbon visitors (1)
- en+switzerland+thurgau+kreuzlingen escort service (1)
- en+switzerland+thurgau+weinfelden find escort (1)
- en+switzerland+ticino escort girl here (1)
- en+switzerland+ticino+locarno escort girl here (1)
- en+switzerland+ticino+locarno visitors (1)
- en+switzerland+ticino+lugano support (1)
- en+switzerland+valais+martigny escort (1)
- en+switzerland+valais+sierre visitors (1)
- en+switzerland+valais+sion tips (1)
- en+switzerland+zurich-canton+adliswil escort (1)
- en+switzerland+zurich-canton+adliswil escort service (1)
- en+switzerland+zurich-canton+bulach escort sites (1)
- en+switzerland+zurich-canton+dietikon username (1)
- en+switzerland+zurich-canton+kloten escorts near me (1)
- en+switzerland+zurich-canton+pfaffikon escort (1)
- en+switzerland+zurich-canton+pfaffikon tips (1)
- en+switzerland+zurich-canton+regensdorf escort girl link (1)
- en+switzerland+zurich-canton+regensdorf find escort girls (1)
- en+switzerland+zurich-canton+thalwil escort girl (1)
- en+switzerland+zurich-canton+thalwil escort girl here (1)
- en+switzerland+zurich-canton+wadenswil escort girls (1)
- en+switzerland+zurich-canton+wallisellen escort girl link (1)
- en+switzerland+zurich-canton+winterthur find escort (1)
- encontrar correo orden novia (3)
- encontrar una novia (2)
- encontrar una novia por correo (4)
- encuГ©ntrame una novia por correo (3)
- encuГ©ntrame una novia por correo (0)
- encuГ©ntrame una novia por correo (0)
- er postordre brud ekte (3)
- er postordre brud sikker (2)
- er postordre brud trygt (1)
- er postordre brud verdt det (4)
- er postordre brud Г¦gte (3)
- er postordre brud Г¦gte (0)
- er postordre brud Г¦gte (0)
- er postordrebrud en rigtig ting (1)
- ES (4)
- es correo orden novia real (2)
- es correo orden novia segura (2)
- es la novia del pedido por correo algo real (2)
- es+amor-con-edad-diferencia-posible sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+asiafriendfinder-opinion mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+belga-mujeres sitios de novias por correo de leggit (0)
- es+belice-mujeres mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+bharat-matrimony-opinion mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+caliente-letonia-mujeres mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+caliente-moldovan-mujeres mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+caliente-nepal-mujeres mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+caliente-nigeriana-mujeres mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+caliente-sudafrica-mujeres sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+caliente-tayikistan-mujeres sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+cebuanas-opinion mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+charmdate-opinion mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+citas-en-tus-30 mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+conocer-mujeres-locales sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+corea-vs-china-vs-japonesa-mujeres sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+cougar-life-opinion sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+cuanto-tiempo-hasta-la-fecha-antes-del-matrimonio mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+dateinasia-opinion sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+dating-profile-tips-for-guys mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+dream-singles-opinion mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+eastmeeteast-opinion sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+espanol-citas-sitios-y-aplicaciones sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+espanol-mujeres sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+estonia-mujeres mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+europeandate-opinion mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+findukrainianbeauty-opinion sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+fitness-singles-opinion sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+historias-de-novias-por-correo mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+interracial-dating-central-opinion sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+japancupid-opinion mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+jollyromance-opinion mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+jpeoplemeet-opinion mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+kissrussianbeauty-opinion sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+las-mujeres-de-europa-del-este sitios de novias por correo de leggit (0)
- es+las-mujeres-rusas-contra-las-ucranianas-hay-alguna-diferencia mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+latin-woman-date-opinion mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+latinamericancupid-opinion mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (0)
- es+marroqui-mujeres sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+meetslavicgirls-opinion mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+mingle2-opinion sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+mujeres-austriacas-calientes sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+mujeres-britanicas-calientes mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+mujeres-calientes-caribenas mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+mujeres-calientes-de-bombay sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+mujeres-calientes-de-laos sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+mujeres-calientes-de-turkmenistan mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+mujeres-calientes-escandinavas mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+mujeres-calientes-israelies sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+mujeres-calientes-uzbekistan mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+mujeres-de-la-isla-caliente sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+mujeres-dominicanas-calientes sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+mujeres-ecuatorianas-calientes mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+mujeres-egipcias sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+mujeres-eslovacas-calientes sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+mujeres-espanolas-calientes sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+mujeres-finlandesas-calientes mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+mujeres-guatemaltecas-calientes mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+mujeres-hondurenas-calientes mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+mujeres-iraquies sitios de novias por correo de leggit (0)
- es+mujeres-jordanas mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+mujeres-latinas-calientes mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+mujeres-letonas mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+mujeres-libanesas-calientes sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+mujeres-nicaragueenses sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+mujeres-panamenas-calientes mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+mujeres-peruanas sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+mujeres-polacas-calientes mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+mujeres-portuguesas-calientes sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+mujeres-rusas sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+mujeres-salvadorenas-calientes mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+mujeres-siberianas sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+mujeres-solteras-altas sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+mujeres-solteras-con-ninos sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+mujeres-solteras-sin-hijos sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+mujeres-solteras-viejas mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+mujeres-sudanesas mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+mujeres-surcoreanas-calientes sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+mujeres-tailandesas-calientes sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+mujeres-turcas mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+novia-extranjera-a-visa-a-los-ee-uu sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+novias-albanesas mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+novias-brasilenas mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+novias-canadienses sitios de novias por correo de leggit (0)
- es+novias-checas mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+novias-costarricenses sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+novias-cubanas mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+novias-escandinavas sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+novias-haitianas mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+novias-hungaras sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+novias-jamaicanas mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+novias-japonesas mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+novias-mexicanas mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+novias-noruegas sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+novias-ucranianas mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+pequenas-mujeres-solteras sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+que-es-una-novia-por-correo sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+rubias-famosas-mujeres mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+singapur-mujeres sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+sitios-y-aplicaciones-de-citas-britanicos mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+sitios-y-aplicaciones-de-citas-colombianos sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+sitios-y-aplicaciones-de-citas-en-chino mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+sitios-y-aplicaciones-de-citas-indias sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+sitios-y-aplicaciones-de-citas-tailandeses sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+sitios-y-aplicaciones-de-citas-turcos mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+sueco-mujeres sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+theluckydate-opinion sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+turkmenistan-mujeres mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (0)
- es+uruguay-mujeres mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+uzbekistan-mujeres sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+valentime-opinion mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+victoriabrides-opinion sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+vietnamita-mujeres mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es-steroid (7)
- esposa de pedidos por correo (2)
- esposas de pedidos por correo (1)
- esposas por ordem de correio (1)
- essay help cheap (1)
- essay papers cheap (1)
- essay write for me (2)
- essay writing for cheap (1)
- essay writing service cheap help (1)
- etsi minulle postimyynti morsian (2)
- etsi postimyynti morsian (3)
- etsitkö postimyynti morsiamaa (2)
- etsitkö postimyynti morsiamaa (0)
- etГ media della sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- etГ media della sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- europeandate-review site free (1)
- Evlilik ArД±yor (2)
- Evlilik ArД±yor (0)
- Faits de mariГ©e par correspondance (4)
- Faits de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Faits de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Faits de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Fall In Love With Someone You Don't Share A Common Language (1)
- fansfan.com+category+anal sign up (1)
- fansfan.com+category+asian search (1)
- fansfan.com+category+best search (1)
- fansfan.com+category+big-tits sign up (1)
- fansfan.com+category+blowjob username (1)
- fansfan.com+category+brunette search (1)
- fansfan.com+category+cougar support (1)
- fansfan.com+category+deepthroat search (1)
- fansfan.com+category+femdom tips (1)
- fansfan.com+category+fitness sign up (1)
- fansfan.com+category+foot-fetish sign in (1)
- fansfan.com+category+free sign up (1)
- fansfan.com+category+free support (1)
- fansfan.com+category+german sign in (1)
- fansfan.com+category+hairy sign up (1)
- fansfan.com+category+indian sign in (1)
- fansfan.com+category+interracial support (1)
- fansfan.com+category+male sign up (1)
- fansfan.com+category+masturbation tips (1)
- fansfan.com+category+mom-and-daughter sign in (1)
- fansfan.com+category+petite sign in (1)
- fansfan.com+category+pornstar visitors (1)
- fansfan.com+category+public support (1)
- fansfan.com+category+roleplay sign in (1)
- fansfan.com+category+small-tits sign up (1)
- fansfan.com+category+small-tits username (1)
- fansfan.com+category+snapchat visitors (1)
- fansfan.com+category+squirt search (1)
- fansfan.com+category+taboo support (1)
- fansfan.com+category+voyeur support (1)
- fansfan.com+category+youtube tips (1)
- FAQ de la commande par correspondance (1)
- fast payday loan company (3)
- fast payday loans company (1)
- femme de commande par correspondance (3)
- Festus online installment loans instant approval (1)
- fi+afrikkalaiset-naiset legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+amourfactory-arvostelu legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+armenialaiset-morsiamet parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+asianmelodies-arvostelu legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+australian-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+badoo-arvostelu legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+bangladesh-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+bolivialais-morsiamet parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+charmdate-arvostelu parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+chilelaiset-morsiamet parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+chinalovecupid-arvostelu parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+colombialady-arvostelu legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+dil-mil-arvostelu legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+eronneet-naimattomat-naiset legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+filipinocupid-arvostelu legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+filippiinilaiset-morsiamet legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+findasianbeauty-arvostelu legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+findmate-arvostelu legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+fitness-singles-arvostelu parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+godatenow-arvostelu parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+haitilaiset-morsiamet legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+hollantilaiset-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+honduran-morsiamet legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+hyesingles-arvostelu parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+indiamatch-arvostelu legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+intialaiset-treffisivustot-ja-sovellukset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+jemenin-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+jump4love-arvostelu legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+kanadalaiset-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+kanadan-morsiamet legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+karibian-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+kazakstan-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+kirgisia-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+kissrussianbeauty-arvostelu legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+kuinka-loytaa-vaimo-vuonna parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+kuuma-belize-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+kuuma-chilelais-naiset legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+kuuma-ecuador-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+kuuma-espanja-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+kuuma-hollantilaiset-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+kuuma-intialainen-naiset legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+kuuma-islanti-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+kuuma-jordanian-naiset legit postimyynti morsian (0)
- fi+kuuma-karibia-naiset legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+kuuma-kazakstan-naiset legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+kuuma-kuubalainen-naiset legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+kuuma-meksikolainen-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+kuuma-nicaraguan-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+kuuma-puerto-rican-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+kuuma-siperian-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+kuuma-slovakian-naiset legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+kuuma-sudanilaiset-naiset legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+kuuma-tadzikistan-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+kuuma-tanska-naiset legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+kuumat-balttilaiset-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+kuumat-eurooppalaiset-naiset legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+kuumat-laosin-naiset legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+kuumat-tsetseeni-naiset legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+la-date-arvostelu parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+latinfeels-arvostelu legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+libanonilaiset-morsiamet parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+liettualaiset-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+lovefort-arvostelu parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+maailman-kuumimmat-naiset legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+meetville-arvostelu legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+mongolian-naiset legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+nicaragualaiset-naiset legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+norja-morsiamet legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+nuoret-naimattomat-naiset legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+paras-tapa-tavata-naisia-verkossa parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+perun-morsiamet legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+pohjoismaiset-naiset legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+postimyyntimorsiamet-ovatko-he-laillisia legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+puertoricolais-treffisivustot-ja-sovellukset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+puolalaiset-treffisivustot-ja-sovellukset legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+ranska-treffisivustot-ja-sovellukset legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+romania-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+saksan-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+serbian-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (0)
- fi+shaadi-arvostelu legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+skandinaaviset-morsiamet parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+slovakian-morsiamet legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+slovakian-naiset legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+suomi-naiset legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+sveitsilaiset-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+syyrialaiset-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+tadzikistan-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+tawkify-arvostelu legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+treffit-30-luvulla legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+tsetseeni-naiset legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+turkkilaiset-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+turkkilaiset-treffisivustot-ja-sovellukset legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+ukrainalaiset-morsiamet parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+unkarilaiset-morsiamet parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+uruguay-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+venaejaen-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+venalaiset-vs-ukrainalaiset-naiset-ovat-siella-mitaan-eroja parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+victoriyaclub-arvostelu legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+yksinaiset-naiset-joilla-on-lapsia parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- filipino women for marriage (1)
- filipino-brides free online sites for singles (1)
- filipino-dating-sites-and-apps free online sites for singles (1)
- filipino-women free online sites for singles (1)
- filipino-women+banga site free (1)
- filipino-women+bulacan free online sites for singles (1)
- filipino-women+cadiz site free (1)
- filipino-women+cebu-city site free (1)
- filipino-women+dumaguete free online sites for singles (1)
- filipino-women+pagadian site free (1)
- filipino-women+san-juan free online sites for singles (1)
- filipino-women+san-juan site free (1)
- filipino-women+victorias site free (1)
- filipino-women+zamboanga site free (1)
- filipinocupid-review free online sites for singles (0)
- find a bride (3)
- find a bride (0)
- find a bride online (1)
- find a mail order bride (2)
- find en brud (1)
- find en postordrebrud (2)
- find en postordrebrud (0)
- find japanese wife online (1)
- find mig en postordrebrud (1)
- find nearest payday loan company (1)
- find payday loans no credit check (1)
- finde en postordrebrud (2)
- finde en postordrebrud (0)
- Finden Sie eine Braut (3)
- Finden Sie mir eine Versandbestellbraut (3)
- finding a mail order bride (1)
- finn en brud (3)
- finn en postordrebrud (3)
- finn meg en postordrebrud (1)
- finn postordrebrud (3)
- finne en postordrebrud (3)
- finnish-women site free (1)
- FinTech (5)
- first time payday loan no credit check (1)
- flirtwomen.net cupidates-review app free (1)
- flirtwomen.net da+varme-og-sexede-colombianske-kvinder de bedste steder at finde postordrebrud (1)
- flirtwomen.net de+datelatinbeauty-test Bester Mail -Bestellung Brautservice (1)
- flirtwomen.net de+heise-und-sexy-belarus-frauen Wie funktioniert die Mail -Bestellung Braut? (1)
- flirtwomen.net de+heise-und-sexy-irische-frauen Mail auf Bestellung Braut (1)
- flirtwomen.net de+heise-und-sexy-japanische-frauen Bester Mail -Bestellung Brautservice (1)
- flirtwomen.net de+heise-und-sexy-kolumbianische-frauen Top -bewertete Versandauftragsbrautseiten (1)
- flirtwomen.net de+heise-und-sexy-peruanische-frauen Top -bewertete Versandauftragsbrautseiten (1)
- flirtwomen.net de+heise-und-sexy-puertoricanische-frauen Wie funktioniert die Mail -Bestellung Braut? (1)
- flirtwomen.net es+latinwomanlove-opinion orden de correo novia vale la pena (1)
- flirtwomen.net es+mujeres-portuguesas-calientes-y-sexys orden de correo novia vale la pena (1)
- flirtwomen.net fi+kuumat-ja-seksikkaat-lansimaiset-aasialaiset-naiset postimyynti morsian (1)
- flirtwomen.net fi+kuumia-ja-seksikkaita-portugalilaisia-naisia postimyynti morsian (1)
- flirtwomen.net fr+femmes-suedoises-chaudes-et-sexy sites de mariГ©e par correspondance reddit (1)
- flirtwomen.net hot-and-sexy-argentinian-women app free (0)
- flirtwomen.net hot-and-sexy-icelandic-women websites (1)
- flirtwomen.net hot-and-sexy-romanian-women app free (1)
- flirtwomen.net hot-and-sexy-spanish-women sites for singles (1)
- flirtwomen.net it+datelatinbeauty-recensione trova una sposa (1)
- flirtwomen.net it+donne-norvegesi-calde-e-sexy trova una sposa (1)
- flirtwomen.net no+dateukrainiangirl-anmeldelse hva er en postordrebrud (1)
- flirtwomen.net no+varme-og-sexy-brasilianske-kvinner postordre brudinformasjon (1)
- flirtwomen.net no+varme-og-sexy-venezuela-kvinner postordre brudinformasjon (1)
- flirtwomen.net pt+meetnicerussian-recensao melhores paГses da noiva por correspondГЄncia (1)
- flirtwomen.net pt+mulheres-argentinas-quentes-e-sensuais melhores paГses da noiva por correspondГЄncia (1)
- flirtwomen.net pt+mulheres-cubanas-gostosas-e-sexy correio em ordem noiva (1)
- flirtwomen.net sv+charmcupid-recension topp 10 postorder brudens webbplatser (1)
- flirtwomen.net sv+heta-och-sexiga-latina-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brudens webbplatser (0)
- flirtwomen.net sv+heta-och-sexiga-turkiska-kvinnor postorder brud definition (1)
- flirtwomen.net sv+heta-och-sexiga-venezuela-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brudens webbplatser (1)
- flirtwomen.net tr+charmromance-inceleme Posta siparişi gelini bulmak için en iyi yerler (1)
- Florence installment loans near me (1)
- for adults (10)
- for free (16)
- foreign brides (2)
- fr+asiacharm-avis Commandez la mariГ©e rГ©el du site rГ©el (1)
- fr+belize-femmes Commandez la mariГ©e rГ©el du site rГ©el (1)
- fr+chat-avenue-avis Commandez la mariГ©e rГ©el du site rГ©el (1)
- fr+croates-femmes Commandez la mariГ©e rГ©el du site rГ©el (1)
- fr+daterussiangirl-avis Commandez la mariГ©e rГ©el du site rГ©el (1)
- fr+dateukrainiangirl-avis Commandez la mariГ©e rГ©el du site rГ©el (1)
- fr+dil-mil-avis Commandez la mariГ©e rГ©el du site rГ©el (1)
- fr+eharmony-avis Commandez la mariГ©e rГ©el du site rГ©el (1)
- fr+epouses-canadiennes Commandez la mariГ©e rГ©el du site rГ©el (1)
- fr+epouses-ethiopiennes Commandez la mariГ©e rГ©el du site rГ©el (1)
- fr+epouses-indonesiennes Commandez la mariГ©e rГ©el du site rГ©el (1)
- fr+fdating-avis Commandez la mariГ©e rГ©el du site rГ©el (1)
- free (29)
- free adult (7)
- free and single site (16)
- free apps (11)
- free online (10)
- free online sites for singles (13)
- free sex (12)
- free singles site (17)
- free site (9)
- free sites (9)
- free sites for (8)
- free websites (10)
- Gaithersburg installment loans near me (1)
- gdje kupiti mladenku za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (1)
- gdje mogu kupiti mladenku za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (1)
- gdje pronaći mladenku za narudžbu pošte (1)
- Gelin DГјnya Posta SipariЕџi Gelinleri (2)
- Gelin DГјnya Posta SipariЕџi Gelinleri (0)
- Gelin Posta SipariЕџi (1)
- Gelin SipariЕџ PostasД± (1)
- Gelin siparişi vermek için posta (3)
- Gelin siparişi vermek için posta (0)
- Gelin siparişi vermek için posta (0)
- gennemse postordrebrud (1)
- gennemsnitlige omkostninger ved postordrebrud (2)
- gennemsnitlige postordre brudepriser (1)
- gennemsnitspris for en postordrebrud (1)
- gennemsnitspris for postordrebrud (2)
- genomsnittlig kostnad för postorderbruden (1)
- genomsnittlig kostnad för en postorderbrud (1)
- genomsnittlig kostnad för postorderbruden (1)
- genomsnittliga postorder brudpriser (4)
- genomsnittspris för en postorderbrud (5)
- genomsnittspris för en postorderbrud (0)
- genomsnittspris för en postorderbrud (0)
- genomsnittspris för en postorderbrud (0)
- genomsnittspris för en postorderbrud (0)
- genomsnittspris för postorderbrud (2)
- genomsnittspris för postorderbrud (0)
- georgiapaydayloans installment loans bad credit (1)
- Gerçek için posta siparişi gelin? (3)
- Gerçek için posta siparişi gelin? (0)
- Gerçek için posta siparişi gelin? (0)
- Gerçek Posta Siparişi Gelin (5)
- Gerçek Posta Siparişi Gelin (0)
- Gerçek Posta Siparişi Gelin (0)
- Gerçek Posta Siparişi Gelin (0)
- Gerçek Posta Siparişi Gelin (0)
- Gerçek Posta Siparişi Gelin Hikayeleri (2)
- Gerçek Posta Siparişi Gelin Hikayeleri (0)
- Gerçek Posta Siparişi Gelin Hizmeti (1)
- Gerçek posta siparişi gelin siteleri (1)
- Gerçek Posta Siparişi Gelin Web Siteleri (3)
- Gerçek Posta Siparişi Gelin Web Siteleri (0)
- Gerçek Posta Siparişi Gelin Web Siteleri (0)
- Gerçek Posta Siparişi Gelin Web Sitesi (4)
- Gerçek Posta Siparişi Gelin Web Sitesi (0)
- Gerçek Posta Siparişi Gelin Web Sitesi (0)
- Gerçek Posta Siparişi Gelin Web Sitesi (0)
- Gerçek posta siparişi gelini sitesi (1)
- Gerçek İçin Posta Siparişi Gelin (4)
- Gerçek İçin Posta Siparişi Gelin (0)
- Gerçek İçin Posta Siparişi Gelin (0)
- get a cash advance (1)
- get a cash advance now (1)
- get a cash advance with bad credit (4)
- get a payday loan (3)
- get a payday loan near me (0)
- get a payday loan no credit check (0)
- get a payday loan no interest (2)
- get a payday loan now (1)
- get a payday loan now bad credit (1)
- get a payday loan with bad credit (1)
- get a payday loan with no credit (2)
- get a payday loans with other payday loans (3)
- get advance cash now (1)
- get cash advance (2)
- get cash advance at bank (1)
- get cash advance loans (1)
- get cash advance no credit check (1)
- get cash advance now (2)
- get cash advance payday loans (2)
- get cash in advance (2)
- get cash now on a payday loan (2)
- get cash now payday loan (3)
- get cash payday loan (1)
- get cash payday loan loan (2)
- get loan payday (1)
- get my payday loan (2)
- get oui of payday loans (2)
- get payday loan (1)
- get payday loan near me (1)
- get payday loan no credit check (1)
- get payday loan no interest (3)
- get payday loan now (2)
- getbride.org da+5-attraktive-og-beromte-blonde-kvinder-du-burde-kende bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- getbride.org da+amerikanske-kvinder-vs-europaeiske-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- getbride.org da+australske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org da+bedste-land-for-postordrebrude hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org da+britiske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (0)
- getbride.org da+canadiske-kvinder-vs-amerikanske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org da+cubanske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org da+hotteste-ukrainske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org da+indonesiske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org da+jamaicanske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org da+latin-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org da+portugisiske-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- getbride.org da+russian-cupid-anmeldelser bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- getbride.org da+russiske-kvinder-vs-amerikanske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org da+taiwanske-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- getbride.org da+tyrkiske-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- getbride.org da+tysk-datingside hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org da+varme-caribiske-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- getbride.org da+varme-chilenske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org da+varme-mexicanske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org de+amerikanische-frauen-gegen-europaische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- getbride.org de+arabische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- getbride.org de+australische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- getbride.org de+belgien-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- getbride.org de+chilaische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- getbride.org de+danische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- getbride.org de+daterussiangirl-test Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- getbride.org de+heise-britische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- getbride.org de+heise-dominikanische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- getbride.org de+heise-guatemalanische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- getbride.org de+heise-indonesische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- getbride.org de+heise-kambodschanische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- getbride.org de+heise-panamaische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- getbride.org de+heise-serbische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- getbride.org de+italienische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- getbride.org de+karibische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- getbride.org de+koreanische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- getbride.org de+latinfeels-test Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- getbride.org de+niederlandische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- getbride.org de+portugiesische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- getbride.org de+sexy-und-heise-russische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- getbride.org de+singapur-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- getbride.org de+slowakische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- getbride.org de+slowenische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- getbride.org de+spanische-dating-site Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- getbride.org de+taiwanesische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- getbride.org de+ukraine-dating-site Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- getbride.org es+el-salvador-mujeres que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+filipinas-sexy-y-caliente-mujeres que es la novia del pedido por correo (0)
- getbride.org es+mujer-francesa que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+mujeres-argentinas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+mujeres-asiaticas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+mujeres-camboyanas-calientes que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+mujeres-caribenas-calientes revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+mujeres-checas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+mujeres-chileanas-calientes que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+mujeres-de-pulido-caliente revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (0)
- getbride.org es+mujeres-egipcias que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+mujeres-eslovacas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+mujeres-finlandesas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+mujeres-francesas-calientes que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+mujeres-hungaras-calientes que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+mujeres-japonesas-vs-mujeres-americanas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+mujeres-kirguistan que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+mujeres-mexicanas-calientes revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+mujeres-peruanas-calientes que es la novia del pedido por correo (0)
- getbride.org es+mujeres-portuguesas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+mujeres-puertorriquenas-mas-calientes que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+mujeres-tajikistan revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+mujeres-turcas-calientes que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+mujeres-venezolanas-calientes revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+novias-rumanas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+paraguay-mujeres revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+russian-cupid-opinion revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (0)
- getbride.org es+sitio-de-citas-alemanas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+sitio-de-citas-espanol que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+uruguay-mujeres que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- getbride.org filippiininaiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- getbride.org hollantilaiset-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- getbride.org islantilaiset-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- getbride.org it+asiandating-recensione vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- getbride.org it+donne-argentine vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- getbride.org it+donne-austriache ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- getbride.org it+donne-brasiliane ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- getbride.org it+donne-britanniche vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- getbride.org it+donne-bulgari ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- getbride.org it+donne-calde-di-taiwan ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- getbride.org it+donne-cambogiane-calde vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- getbride.org it+donne-caraibiche-calde vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- getbride.org it+donne-cilene ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- getbride.org it+donne-costa-rican vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- getbride.org it+donne-cubane vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- getbride.org it+donne-del-tajikistan ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- getbride.org it+donne-delleuropa-orientale ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- getbride.org it+donne-dominicane vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- getbride.org it+donne-etiopi vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- getbride.org it+donne-filippine ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- getbride.org it+donne-guatemalan-calde ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- getbride.org it+donne-messicane vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- getbride.org it+donne-olandesi ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- getbride.org it+donne-panamensi ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- getbride.org it+donne-russe vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- getbride.org it+donne-sloveni ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- getbride.org it+donne-svedesi ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- getbride.org it+donne-tailandesi vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- getbride.org it+donne-taiwanesi vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- getbride.org it+donne-uzbekistan vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- getbride.org it+donne-venezuelane ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- getbride.org it+donne-venezuelane-calde ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- getbride.org it+donne-vietnamite ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- getbride.org it+siti-di-incontri-dominicani vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- getbride.org it+sono-sposa-per-corrispondenza-illegali ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- getbride.org kazakstanin-naiset wikipedia postimyynti morsian (1)
- getbride.org kuubalaiset-naiset wikipedia postimyynti morsian (1)
- getbride.org kuumat-argentiinalaiset-naiset wikipedia postimyynti morsian (1)
- getbride.org kuumat-haitilaiset-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- getbride.org kuumat-indonesialaiset-naiset wikipedia postimyynti morsian (1)
- getbride.org kuumat-meksikolaiset-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- getbride.org kuumat-taiwan-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- getbride.org kuumia-ecuadorin-naisia wikipedia postimyynti morsian (1)
- getbride.org kuumimmat-brasilialaiset-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- getbride.org kuumimmat-korealaiset-naiset wikipedia postimyynti morsian (1)
- getbride.org latinalaiset-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- getbride.org latinfeels-arvostelu tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- getbride.org main_fi tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- getbride.org miten-saat-postimyynnissa-morsian tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- getbride.org moldovan-naiset wikipedia postimyynti morsian (1)
- getbride.org no+australske-kvinner online postordre brud (1)
- getbride.org no+dominikanske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org no+er-postordrebrud-ulovlig online postordre brud (1)
- getbride.org no+estonske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org no+etiopiske-kvinner online postordre brud (1)
- getbride.org no+europeiske-kvinner online postordre brud (1)
- getbride.org no+greske-kvinner online postordre brud (1)
- getbride.org no+italienske-kvinner online postordre brud (1)
- getbride.org no+kanadiske-bruder beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org no+kinesiske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (0)
- getbride.org no+kirgisiske-kvinner online postordre brud (0)
- getbride.org no+koreanske-kvinner online postordre brud (1)
- getbride.org no+makedonske-kvinner online postordre brud (1)
- getbride.org no+meksikanske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org no+mongolske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org no+nederlandske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org no+osteuropeiske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org no+pakistanske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org no+russiske-kvinner online postordre brud (1)
- getbride.org no+sexy-og-hete-russiske-kvinner online postordre brud (1)
- getbride.org no+singapore-kvinner online postordre brud (1)
- getbride.org no+slaviske-bruder online postordre brud (1)
- getbride.org no+sri-lanka-kvinner online postordre brud (1)
- getbride.org no+taiwanske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org no+tyrkiske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org no+ukrainske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (0)
- getbride.org no+varme-britiske-kvinner online postordre brud (1)
- getbride.org no+varme-guatemalanske-kvinner online postordre brud (1)
- getbride.org no+varme-japanske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org no+varme-nederlandske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org no+varme-serbiske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org no+varme-tsjekkiske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org no+varme-vietnamesiske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org no+venezuelanske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org postimyynnissa-morsian-tilastot tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- getbride.org pt+estatisticas-noiva-por-correspondencia Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- getbride.org pt+mulheres-austriacas Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- getbride.org pt+mulheres-bosnianas Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- getbride.org pt+mulheres-britanicas-gostosas Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- getbride.org pt+mulheres-caribenhas-quentes Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- getbride.org pt+mulheres-chileanas-gostosas Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- getbride.org pt+mulheres-colombianas Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- getbride.org pt+mulheres-croatas Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- getbride.org pt+mulheres-de-belgica Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- getbride.org pt+mulheres-do-cazaquistao Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- getbride.org pt+mulheres-eslovenas Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- getbride.org pt+mulheres-estonianas Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- getbride.org pt+mulheres-etiopes Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- getbride.org pt+mulheres-haitianas-gostosas Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- getbride.org pt+mulheres-holandesas Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- getbride.org pt+mulheres-macedonias Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- getbride.org pt+mulheres-panamenhas-quentes Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- getbride.org pt+mulheres-peruanas-quentes Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- getbride.org pt+mulheres-porto-riquenhas Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- getbride.org pt+mulheres-romenas-gostosas Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- getbride.org pt+mulheres-russas Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- getbride.org pt+mulheres-russas-vs-americanas Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- getbride.org pt+russian-cupid-recensao Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- getbride.org pt+site-de-namoro-na-ucrania Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- getbride.org slaavilaiset-morsiamet tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- getbride.org suomalaiset-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- getbride.org sv+5-attraktiva-och-beromda-blonda-kvinnor-du-borde-kanna-till postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- getbride.org sv+amerikanska-kvinnor-mot-europeiska-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- getbride.org sv+ar-postordrebrud-olagliga postorder brudkataloger (1)
- getbride.org sv+cherryblossoms-recension postorder brudkataloger (1)
- getbride.org sv+egyptiska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- getbride.org sv+estniska-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- getbride.org sv+franska-kvinnor-mot-amerikanska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- getbride.org sv+heta-argentinska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (0)
- getbride.org sv+heta-asiatiska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- getbride.org sv+heta-guatemalanska-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- getbride.org sv+heta-haitianska-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- getbride.org sv+heta-hollandska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- getbride.org sv+heta-rumanska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- getbride.org sv+heta-tjeckiska-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- getbride.org sv+heta-ungerska-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- getbride.org sv+hetaste-indiska-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- getbride.org sv+hetaste-italienska-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- getbride.org sv+hetaste-kvinnor-i-puerto-rico postorder brudkataloger (1)
- getbride.org sv+islandska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- getbride.org sv+kambodjanska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- getbride.org sv+kanadiska-brudar postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- getbride.org sv+koreanska-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- getbride.org sv+makedonska-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (0)
- getbride.org sv+mexikanska-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- getbride.org sv+moldoviska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- getbride.org sv+pakistanska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (0)
- getbride.org sv+polska-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- getbride.org sv+portugisiska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- getbride.org sv+russian-cupid-recension postorder brudkataloger (0)
- getbride.org sv+schweiziska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- getbride.org sv+sexiga-och-heta-filippinska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- getbride.org sv+spanska-datingsida postorder brudkataloger (1)
- getbride.org sv+sri-lanka-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- getbride.org sv+thai-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- getbride.org sv+ukraina-datingsida postorder brudkataloger (1)
- getbride.org sv+ukrainedate-recension postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- getbride.org sv+vietnamesiska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- getbride.org taiwanilaiset-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- getbride.org tr+amerikali-kadinlar-vs-avrupa-kadinlari bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- getbride.org tr+arap-kadinlari Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek (1)
- getbride.org tr+avusturyali-kadinlar Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek (1)
- getbride.org tr+cek-kadinlari bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- getbride.org tr+dogu-avrupa-kadinlari-vs-amerikan-kadinlari Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek (0)
- getbride.org tr+el-salvador-kadinlari bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- getbride.org tr+guatemalan-kadinlar Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek (1)
- getbride.org tr+gurcu-kadinlar Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek (1)
- getbride.org tr+ingiliz-kadinlar bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- getbride.org tr+japon-kadin-vs-amerikan-kadin bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- getbride.org tr+japon-kadinlar bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- getbride.org tr+koreli-kadinlar Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek (1)
- getbride.org tr+kuba-kadinlari Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek (1)
- getbride.org tr+malezya-kadinlari bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- getbride.org tr+meksikali-kadinlar Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek (1)
- getbride.org tr+mogol-kadinlar bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- getbride.org tr+pakistanli-kadinlar bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- getbride.org tr+rus-kadinlari-vs-amerikali-kadinlar Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek (1)
- getbride.org tr+sicak-asyali-kadinlar Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek (1)
- getbride.org tr+sicak-bulgar-kadinlar bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- getbride.org tr+sicak-cek-kadinlar Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek (1)
- getbride.org tr+sicak-cila-kadinlar Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek (1)
- getbride.org tr+sicak-ingiliz-kadinlar bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- getbride.org tr+sicak-japon-kadinlar Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek (1)
- getbride.org tr+sicak-kolombiyali-kadinlar Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek (1)
- getbride.org tr+sicak-sili-kadinlari bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- getbride.org tr+sicak-turk-kadinlari bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- getbride.org tr+sirp-kadinlar bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- getbride.org tr+tajikistan-kadinlari bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- getbride.org tr+venezuela-kadinlari Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek (0)
- getbride.org vietnamilaiset-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- getting a cash advance (2)
- getting a cash advance at a bank (1)
- getting a loan from cash advance america (1)
- getting a payday loan with bad credit (1)
- getting cash advance (1)
- Getting Married In College (1)
- getting payday loan (1)
- girls for marriage (1)
- gjennomsnittlig kostnad for en postordrebrud (1)
- gjennomsnittlig kostnad for postordrebruden (1)
- gjennomsnittsalder for postordrebruden (1)
- gjennomsnittspris for en postordrebrud (1)
- gjennomsnittspris for postordrebrud (3)
- gjennomsnittspris pГҐ en postordrebrud (2)
- gjennomsnittspris pГҐ en postordrebrud (0)
- god postordre brudesider (1)
- gode postordre brud nettsteder (2)
- good mail order bride website (4)
- Goose Creek online installment loans (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net charm-date que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net chicas-chinas-calientes-y-sexys revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net chicas-coreanas-calientes-y-sexys que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net chicas-eslavas-calientes-y-sexys revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net chicas-filipinas-calientes-y-sexys que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net chicas-negras-calientes-y-sexys que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net chicas-ucranianas-calientes-y-sexys que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net chicas-vietnamitas-calientes-y-sexys que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net como-conocer-mujeres-en-linea que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net da+amerikanske-kvinder-vs-europaeiske-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net da+amour-factory bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net da+asia-me hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net da+asian-melodies bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net da+asiatiske-brude bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net da+date-ukrainsk-pige hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net da+find-asian-beauty hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net da+graeske-brude bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net da+hvordan-man-kober bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net da+jolly-romance bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net da+latin-kvinde-kaerlighed hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net da+sverige-brude bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net da+varme-og-sexede-kinesiske-piger bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net da+varme-og-sexede-russiske-piger bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net da+venezuelanske-brude bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net date-asian-woman que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net de+altere-braute Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (0)
- gorgeousbrides.net de+arabische-braute Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net de+asia-me Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net de+asiatische-braute Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net de+asiatische-frauen-treffen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net de+beste-lander-fur-dating Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (0)
- gorgeousbrides.net de+colombialady Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (0)
- gorgeousbrides.net de+costa-rica-braute Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net de+einfrau Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net de+franzosische-braute Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net de+frauen-die-altere-manner-suchen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net de+heise-und-sexy-ukrainische-madchen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net de+heise-und-sexy-venezolanische-madchen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net de+lateinamerikanische-frau-liebe Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net de+latin-beauty-date Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net de+russische-braute Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net de+slawische-braute Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net de+treffen-sie-ukrainische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net de+ukrainebride4you Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net de+was-ist-katalogheirat Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net de+werden-sie-ein-katalogheirat Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net de+wie-man-eine-frau-findet Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net fi+asian-melodies tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net fi+avioliiton-treffisivustot tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (0)
- gorgeousbrides.net fi+date-russian-girl tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (0)
- gorgeousbrides.net fi+irlantilaiset-morsiamet tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net fi+itakuusa tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net fi+italialaiset-morsiamet tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net fi+kuinka-ostaa tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net fi+kuumia-ja-seksikkaita-japanilaisia-tyttoja tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net fi+la-date tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net fi+mika-on-postimyynnissa-morsian tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net fi+oikeudelliset-kysymykset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net fi+puerto-rican-morsiamet tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net fi+romanialaiset-morsiamet tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net fi+tapaa-latinalaisia-naisia tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (0)
- gorgeousbrides.net fi+tavata-kiinalaisia-naisia tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net fi+yhden-naisen tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net it+amour-feel ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- gorgeousbrides.net it+asia-me vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net it+asian-beauty-online vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net it+asian-melodies ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- gorgeousbrides.net it+come-trovare vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net it+love-fort ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net it+ragazze-calde-e-sexy-del-mondo vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net it+ragazze-svedesi-calde-e-sexy ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net it+ragazze-ucraine-calde-e-sexy vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net it+ragazze-venezuelane-calde-e-sexy vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net it+spose-ceche vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net it+spose-cubane vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net it+spose-europee ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- gorgeousbrides.net it+spose-giapponesi vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net it+spose-honduregne ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- gorgeousbrides.net it+spose-venezuelane vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net it+ukrainebride4you vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net la-date que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net latin-beauty-date que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net latin-feels revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net lover-whirl revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net main_no beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net no+amour-factory beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net no+honduran-bruder beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net no+irske-bruder beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net novia-extranjera revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net novia-por-correo-meme revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net novias-albanesas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net novias-arabes que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net novias-australianas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net novias-brasilenas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net novias-chinas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net novias-filipinas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net novias-hondurenas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net novias-suecas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net novias-tailandesas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net paises-que-aman-a-los-hombres-estadounidenses revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net pt+conhecer-mulheres-asiaticas Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net pt+date-asian-woman Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net pt+date-russian-girl Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net pt+garotas-alemas-gostosas-e-sexy Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net pt+garotas-colombianas-gostosas-e-sexy Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net pt+garotas-espanholas-gostosas-e-sexy Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net pt+garotas-filipinas-gostosas-e-sexy Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net pt+garotas-italianas-gostosas-e-sexy Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net pt+garotas-romanas-gostosas-e-sexy Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net pt+garotas-suecas-gostosas-e-sexy Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net pt+la-date Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net pt+latam-date Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net pt+mulher-asiatica-fofa Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net pt+noivas-francesas Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- gorgeousbrides.net pt+noivas-hungaras Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net pt+noivas-japonesas Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net pt+noivas-vietnamitas Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net pt+questoes-legais Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net pt+sofiadate Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net sv+amerikanska-brudar postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net sv+amerikanska-kvinnor-mot-europeiska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net sv+asia-me postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net sv+asiatiska-brudar postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net sv+colombianska-brudar postorder brudkataloger (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net sv+costa-rican-brudar postorder brudkataloger (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net sv+date-asian-woman postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net sv+datum-ukrainsk-tjej postorder brudkataloger (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net sv+heta-och-sexiga-franska-flickor postorder brudkataloger (0)
- gorgeousbrides.net sv+heta-och-sexiga-koreanska-flickor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net sv+heta-och-sexiga-mexikanska-flickor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net sv+heta-och-sexiga-polska-flickor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net sv+heta-och-sexiga-thai-flickor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net sv+irlandska-brudar postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net sv+latin-brudar postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net sv+latvianska-brudar postorder brudkataloger (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net sv+mexikanska-brudar postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net sv+postordrebrud-bedragerier postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net sv+serbiska-brudar postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net sv+theluckydate postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net sv+traffa-asiatiska-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net sv+traffa-latinska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net sv+ukrainebride4you postorder brudkataloger (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net ukrainebride4you revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- Green City personal installment loans (1)
- guide to payday loans (2)
- Gute Mail -Bestellung Brautseiten (4)
- Gute Mail -Bestellung Brautwebsite (1)
- högst rankade postorder brudar webbplatser (1)
- högst rankade postorder brudtjänst (1)
- health (2)
- heartbrides.com alemanha-perfis-de-mulheres top dez site de noiva por ordem de correio (1)
- heartbrides.com da+filippinske-kvindelige-profiler Г¦gte mail ordre brude websteder (1)
- heartbrides.com da+honduranske-brude Г¦gte mail ordre brude websteder (1)
- heartbrides.com da+hvordan-fungerer-postordrebrude Г¦gte mail ordre brude websteder (1)
- heartbrides.com da+lande-der-elsker-amerikanske-maend hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- heartbrides.com de+lander-die-amerikanische-manner-lieben Bester Mail -Bestellung Brautservice (1)
- heartbrides.com de+tschechische-braute Wie funktioniert die Mail -Bestellung Braut? (1)
- heartbrides.com es+novias-africanas agencias de novias por correo (1)
- heartbrides.com es+novias-colombianas que es como la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- heartbrides.com es+novias-coreanas que es como la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- heartbrides.com es+perfiles-de-mujeres-ucranianas que es una novia de pedidos por correo (1)
- heartbrides.com fi+dominikaani-vs-puerto-rikaani todellinen postimyynti morsiamen sivusto (1)
- heartbrides.com fi+perun-morsiamet postimyynti morsian todellinen (1)
- heartbrides.com fr+cout-des-mariees-bresiliennes histoires de la mariГ©e par correspondance rГ©elle (1)
- heartbrides.com it+costo-delle-spose-filippine trova una sposa (1)
- heartbrides.com it+latin-feels-recensione puoi spedire una sposa (1)
- heartbrides.com it+profili-delle-donne-della-thailandia il posto migliore per ottenere una sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- heartbrides.com it+spose-portoricane dove posso ottenere una sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- heartbrides.com it+spose-turche dove posso ottenere una sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- heartbrides.com no+date-russian-girl-anmeldelse hva er en postordrebrud (1)
- heartbrides.com no+dominican-vs-puerto-rican postordre brudinformasjon (1)
- heartbrides.com no+slavisk hva er en postordrebrud (1)
- heartbrides.com no+ukrainebrides4you-anmeldelse hva er en postordrebrud (1)
- heartbrides.com noivas-bosnianas procurando casamento (1)
- heartbrides.com noivas-japonesas melhores paГses da noiva por correspondГЄncia (1)
- heartbrides.com noivas-japonesas uma noiva por correspondГЄncia (1)
- heartbrides.com noivas-paquistanesas melhores paГses da noiva por correspondГЄncia (1)
- heartbrides.com perfis-de-mulheres-bulgaras correio em ordem noiva (1)
- heartbrides.com perfis-de-mulheres-polonesas melhores paГses da noiva por correspondГЄncia (1)
- heartbrides.com site-de-namoro correio em ordem noiva (1)
- heartbrides.com sv+latin postorder brud definition (1)
- heartbrides.com sv+tyskland-kvinnor-profiler topp 10 postorder brudens webbplatser (1)
- heartbrides.com tr+alman-gelinleri Posta siparişi gelini bulmak için en iyi yerler (1)
- heartbrides.com tr+asyali-kadin-profilleri Posta SipariЕџi Gelin EndГјstrisi (1)
- heartbrides.com tr+cuteasianwoman-inceleme Posta siparişi gelini bulmak için en iyi yerler (1)
- heartbrides.com tr+filipina-gelinleri En Д°yi Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmeti (1)
- heartbrides.com tr+latin-women-date-inceleme En Д°yi Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmeti (1)
- heartbrides.com tr+tayland-gelinleri-maliyeti En Д°yi Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmeti (1)
- heartbrides.com tr+yabanci-bir-gelin-nasil-bulunur Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Web Siteleri Д°ncelemeleri (1)
- heated-affairs-review only reviews (1)
- heiГџeste Mail -Bestellung Braut (3)
- heiГџeste Mail -Bestellung Braut (0)
- heiГџeste Mail -Bestellung Braut (0)
- help me to write my essay (2)
- help me write my college essay (1)
- help me write my critical essay (1)
- help me write my essay online (2)
- help to write my essay (1)
- help write my essay today (1)
- hetaste postorderbruden (2)
- hi-ly.com (1)
- Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (2)
- Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- histoires de la mariГ©e par correspondance rГ©elle (5)
- histoires de la mariГ©e par correspondance rГ©elle (0)
- histoires de la mariГ©e par correspondance rГ©elle (0)
- histoires de la mariГ©e par correspondance rГ©elle (0)
- histoires de la mariГ©e par correspondance rГ©elle (0)
- histoires de la mariГ©e par la courrier Г©lectronique (5)
- histoires de la mariГ©e par la courrier Г©lectronique (0)
- histoires de la mariГ©e par la courrier Г©lectronique (0)
- histoires de la mariГ©e par la courrier Г©lectronique (0)
- histoires de la mariГ©e par la courrier Г©lectronique (0)
- Histoires de mariГ©e par correspondance reddit (2)
- Histoires de mariГ©e par correspondance reddit (0)
- Histoires de vente par correspondance (3)
- historia correo orden novia (3)
- historia om postorderbruden (1)
- historia real de la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- historiapostitilaus morsian (1)
- historias de novias de pedidos por correo (1)
- historias de novias de pedidos por correo real (1)
- historie postordre brud (2)
- historien til postordrebruden (1)
- Historique de la mariГ©e par correspondance (6)
- Historique de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Historique de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Historique de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Historique de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Historique de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- History -Mail -Bestellung Braut (1)
- history mail order bride (4)
- hitta en postorderbrud (4)
- hitta mig en postorderbrud (2)
- hitta postorder brud (2)
- honduran-women site free (1)
- hongkongcupid-review site free (1)
- horny (9)
- hot (2)
- hot mail order bride (2)
- hot mail ordre brud (3)
- hot-american-women free online sites for singles (1)
- hot-argentina-women free online sites for singles (1)
- hot-armenian-women free online sites for singles (1)
- hot-asian-women free online sites for singles (1)
- hot-bali-women free online sites for singles (0)
- hot-baltic-women site free (1)
- hot-bangladesh-women free online sites for singles (1)
- hot-brazilian-women site free (1)
- hot-costa-rican-women site free (1)
- hot-cuban-women free online sites for singles (1)
- hot-eastern-european-women site free (1)
- hot-egyptian-women site free (1)
- hot-ghanaian-women free online sites for singles (1)
- hot-guyana-women site free (1)
- hot-guyanese-women site free (1)
- hot-haitian-women site free (1)
- hot-indonesian-women site free (0)
- hot-iranian-women free online sites for singles (1)
- hot-jamaican-women free online sites for singles (1)
- hot-kazakhstan-women free online sites for singles (1)
- hot-kyrgyzstan-women site free (1)
- hot-latvia-women free online sites for singles (1)
- hot-nepal-women free online sites for singles (1)
- hot-peruvian-women site free (1)
- hot-scottish-women site free (1)
- hot-serbian-women site free (1)
- hot-siberian-women free online sites for singles (1)
- hot-somali-women free online sites for singles (1)
- hot-spanish-women free online sites for singles (1)
- hot-sudanese-women free online sites for singles (1)
- hot-venezuelan-women free online sites for singles (1)
- hot-vietnamese-women site free (1)
- hottest mail order bride (2)
- hottest mail order bride (0)
- hotteste postordrebrud (4)
- hotteste postordrebrud (0)
- hottestwomen.net da+danske-kvinder de bedste steder at finde postordrebrud (1)
- hottestwomen.net da+mongolske-kvinder Г¦gte mail ordre brude websteder (1)
- hottestwomen.net de+schwedische-frauen Top -bewertete Versandauftragsbrautseiten (1)
- hottestwomen.net de+wer-sollte-zuerst-nach-dem-ersten-datum-schreiben Beste Mail bestellen Braut Websites Reddit (1)
- hottestwomen.net es+mujer-britanica agencia de novias por correo (1)
- hottestwomen.net es+mujeres-chinas que es como la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- hottestwomen.net es+mujeres-filipinas agencias de novias por correo (1)
- hottestwomen.net es+mujeres-noruegas que es como la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- hottestwomen.net fi+dominikaaninen-nainen postimyynti morsian (1)
- hottestwomen.net fi+irlantilaiset-naiset postimyynti morsian (1)
- hottestwomen.net fi+slovenialaiset-naiset oikeita postimyynti morsiamen tarinoita (1)
- hottestwomen.net fr+les-femmes-laotiennes sites de mariГ©e par correspondance reddit (1)
- hottestwomen.net fr+les-femmes-tcheques sites de mariГ©e par correspondance reddit (1)
- hottestwomen.net it+donna-britannica trova una sposa (1)
- hottestwomen.net it+donna-portoricana migliori recensioni per i siti della sposa (1)
- hottestwomen.net no+argentinsk-kvinne postordre brudinformasjon (1)
- hottestwomen.net no+japanske-kvinner postordre brudinformasjon (1)
- hottestwomen.net no+malaysiske-kvinner postordre brudinformasjon (1)
- hottestwomen.net no+slovakiske-kvinner hva er en postordrebrud (1)
- hottestwomen.net pt+com-recensao noiva por correspondГЄncia (1)
- hottestwomen.net pt+mulher-cubana correio em ordem noiva (1)
- hottestwomen.net pt+mulheres-chinesas melhores paГses da noiva por correspondГЄncia (0)
- hottestwomen.net pt+mulheres-servias correio em ordem noiva (1)
- hottestwomen.net sirp-kadinlar En Д°yi Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmeti (1)
- hottestwomen.net sv+kroatiska-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brudens webbplatser (1)
- hottestwomen.net sv+latvianska-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplatser reddit (1)
- hottestwomen.net sv+litauiska-kvinnor postorder brud definition (1)
- hottestwomen.net sv+miss-travel-recension postorder brud definition (1)
- hottestwomen.net sv+salvadoranska-kvinnor postorder brud definition (1)
- How Can I Date A Girl From A Different Country (1)
- how can i get a payday loan (3)
- how can i get a payday loan? (2)
- how can you get a payday loan (1)
- how cash advance (1)
- how do a payday loan work (1)
- how do cash advance work (1)
- how do i do a cash advance (3)
- how do i do cash advance (2)
- how do i get a cash advance from a bank (1)
- how do i get a cash advance with (2)
- how do i get a cash advance? (1)
- how do i get a payday loan (1)
- how do i get a payday loan with bad credit (2)
- how do i get a payday loans (2)
- how do mail order bride sites work (0)
- how do payday loans (2)
- how do payday loans work (1)
- how do payday loans works (1)
- how do you do cash advance (2)
- how do you do cash advance? (1)
- how do you get a cash advance (3)
- how do you get a payday loan (1)
- how do you use a cash advance (3)
- how does a cash advance work (1)
- how does a cash advance works (1)
- how does a mail order bride work (1)
- how does a payday cash advance work (0)
- how does a payday loan interest work (4)
- how does advance cash work (2)
- how does cash advance america work (3)
- how does cash advance interest work (1)
- how does cash advance on (1)
- how does cash advance work (4)
- how does cash in advance work (3)
- how does cash in advance works (1)
- how does getting a cash advance work (1)
- how does mail order bride work (2)
- how does mail order bride works (2)
- how does payday cash advance work (1)
- how does payday loan work (2)
- how does payday loans work (3)
- how does the cash advance work (2)
- how is payday loans work (1)
- how much are payday loans (1)
- how much can i get for a payday loan (1)
- how much can i get from a payday loan (4)
- how much can i get from cash advance (1)
- how much can i get in a payday loan (1)
- how much can i get on a payday loan (1)
- how much can you get a payday loan for (1)
- how much can you get from a payday loan (2)
- how much can you get from payday loans (1)
- how much can you get on a cash advance (1)
- how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- how much can you get on a payday loan? (2)
- how much cash advance (1)
- how much cash advance can i get (0)
- how much cash can you get from a cash advance (1)
- how much could i get on a payday loan (1)
- how much do you get for payday loan (2)
- how much for a cash advance (2)
- how much for cash advance (1)
- how much interest cash advance (2)
- how much interest do payday loans charge? (2)
- how much interest do you pay on a cash advance (2)
- how much interest do you pay on a payday loan (1)
- how much interest for a payday loan (2)
- how much interest for cash advance (2)
- how much interest is on a payday loan (1)
- how much interest on a cash advance (1)
- how much interest on a payday loan (2)
- how much interest on cash advance (1)
- how much interest on payday loans (1)
- how much interest payday loan (1)
- how much is a cash advance (1)
- how much is a cash advance from advance america (2)
- how much is a payday loan for (2)
- how much is interest on a cash advance (2)
- how much is interest on cash advance (3)
- how much is my cash advance interest (1)
- how much is payday loan interest (1)
- how much is the interest on payday loans (2)
- how much of a cash advance can i get (2)
- how much of a payday loan can i get (1)
- how much to pay for payday loans (4)
- how mush interest on a payday loan (3)
- how payday loan work (4)
- how payday loans work in usa (3)
- how soon do i have to pay payday loans (1)
- how soon do you have to pay payday loan (2)
- how to cash advance (1)
- how to cash advance at other bank (2)
- how to cash advance from a bank (2)
- how to cash advance on credit (3)
- how to do a cash advance (4)
- how to do a mail order bride (1)
- how to do cash advance at bank (3)
- how to do mail order bride (1)
- how to do payday loan (3)
- how to do payday loans (1)
- how to get a cash advance from a bank (1)
- how to get a cash advance from a bank credit (2)
- how to get a cash advance from payday (2)
- how to get a cash advance loan (1)
- how to get a cash advance with bad credit (2)
- how to get a loan from cash advance (4)
- how to get a payday advance loan (2)
- how to get a payday loan (1)
- how to get a payday loan bad credit (2)
- how to get a payday loan with bad credit (2)
- how to get a payday loan with bad credit? (1)
- how to get a payday loan with no credit check (1)
- how to get cash advance from (1)
- how to get cash advance from bank (1)
- how to get cash advance loan (1)
- how to get cash advance out of your credit (3)
- how to get cash advance with bad credit (1)
- how to get cash from credit wtihout cash advance (3)
- how to get cash in advance (1)
- how to get payday loan with bad credit (2)
- how to get you payday loan (1)
- how to marry a mail order bride (3)
- how to order a mail order bride (1)
- how to order a russian mail order bride (3)
- how to order mail order bride (3)
- how to payday loan (1)
- how to payday loans (2)
- how to payday loans work (2)
- how to prepare a mail order bride (1)
- how to prepare a mail order bride reddit (3)
- how to use a cash advance (1)
- how to use cash advance (1)
- how to use credit cash advance (1)
- how to use payday loans (2)
- how-long-to-date-before-marriage free online sites for singles (1)
- hr+2redbeans-recenzija Prava narudЕѕba za mladenku (1)
- hr+afroromance-recenzija Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+asia-beauty-date-recenzija Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+azijske-nevjeste Prava narudЕѕba za mladenku (1)
- hr+belize-zene Prava narudЕѕba za mladenku (1)
- hr+brazilske-zene Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+cougar-life-recenzija Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+dateinasia-recenzija Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+daterussiangirl-recenzija Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+egipcanke-zene Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+europeandate-recenzija Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+findukrainianbeauty-recenzija Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+honduraske-zene Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+islandske-zene Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+jamajcanke-nevjeste Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+japancupid-recenzija Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+jpeoplemeet-recenzija Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+juznoafricke-zene Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+kineski-zene Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+koreancupid-recenzija Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+makedonija-zene Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+meetme-recenzija Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+meksicke-zene Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+najzgodnije-zene-na-svijetu Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+omegle-recenzija Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+pakistanske-zene Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+plavusa-poznate-zene Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+ruske-stranice-i-aplikacije-za-upoznavanje Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+ruski-zene Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+russianbeautydate-recenzija Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+vruce-armenske-zene Prava narudЕѕba za mladenku (1)
- hr+vruce-bangladeske-zene Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+vruce-bosanske-zene Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+vruce-britanske-zene Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+vruce-indonezijske-zene Prava narudЕѕba za mladenku (0)
- hr+vruce-irske-zene Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+vruce-istocnoeuropske-zene Prava narudЕѕba za mladenku (1)
- hr+vruce-izraelske-zene Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+vruce-makedonke-zene Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+vruce-portorikanske-zene Prava narudЕѕba za mladenku (1)
- hr+vruce-rumunjske-zene Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+vruce-slavenske-zene Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+vruce-sudanske-zene Prava narudЕѕba za mladenku (1)
- huippuposti tilaus morsian (4)
- huippusähköpostitilaus morsiamen sivustot. (2)
- huippusähköpostitilaus morsiamen sivustot. (0)
- huipputarjous morsiamen maat (1)
- huipputarjous morsiamen palvelut (1)
- huipputarjous morsiamen sivustot (2)
- huipputarjous morsian istuu (3)
- hungarian-women free online sites for singles (1)
- Hungary escort girl here (1)
- hur beställer post brudarbete (1)
- hur beställer post brudarbete (6)
- hur beställer post brudarbete (0)
- hur beställer post brudarbete (0)
- hur beställer post brudarbete (0)
- hur beställer post brudarbete (0)
- hur beställer post brudarbete (0)
- hur fungerar en postorderbrud (2)
- hur fungerar postorderbrudplatser (1)
- hur man beställer en postorderbrud (2)
- hur man beställer en postorderbrud (0)
- hur man beställer en postorderbrud (4)
- hur man beställer en postorderbrud (0)
- hur man beställer en postorderbrud (0)
- hur man beställer en postorderbrud (0)
- hur man beställer en rysk brud (2)
- hur man beställer en rysk brud (0)
- hur man beställer en rysk postorderbrud (1)
- hur man beställer postorder brud (2)
- hur man beställer postorder brud (0)
- hur man förbereder en postorderbrud (1)
- hur man går med en postorderbrud (1)
- hur man gГҐr med en postorderbrud (1)
- hur man skickar beställning brud (4)
- hur man skickar beställning brud (0)
- hur man skickar beställning brud (0)
- hur man skickar beställning brud (0)
- hur man skickar en beställning av en brud (3)
- hur man skickar en beställning av en brud (0)
- hur man skickar en beställning av en brud (0)
- hva en postordrebrud (4)
- hva er de beste postordrebrudstedene (4)
- hva er den beste postordrebrudstedet (1)
- hva er den beste postordrebrudtjenesten (2)
- Hva er en postordre brud (1)
- hva er en postordrebrud (2)
- hva er en postordrebrud? (2)
- hva er postordre brud tjenester (2)
- hva er postordrebrud (7)
- hva er postordrebrud? (1)
- hva er postordrebruden? (2)
- hvad er de bedste postordre brudesider (3)
- hvad er den bedste postordre brude service (3)
- hvad er den bedste postordre brude service (0)
- hvad er en postordrebrud (5)
- hvad er en postordrebrud? (1)
- hvad er postordre brude tjenester (1)
- hvad er postordrebruden? (1)
- hvor du finner en postordrebrud (2)
- hvor du kan kjГёpe en postordrebrud (2)
- hvor du kan kjГёpe en postordrebrud (0)
- hvor finder jeg en postordrebrud (1)
- hvor finner jeg en postordrebrud (3)
- hvor kan jeg finde en postordrebrud (2)
- hvor kan jeg finne en postordrebrud (1)
- hvor kan jeg fГҐ en postordrebrud (2)
- hvor kan jeg fГҐ en postordrebrud (0)
- hvor kjГёper jeg en postordrebrud (1)
- hvor kГёber jeg en postordrebrud (2)
- hvor kГёber jeg en postordrebrud (0)
- hvordan bestille en russisk brud (1)
- hvordan bestille en russisk postordrebrud (4)
- hvordan date en postordrebrud (2)
- hvordan du bestiller en postordrebrud (2)
- hvordan du bestiller postordrebrud (3)
- hvordan du forbereder en postordre brud reddit (3)
- hvordan du forbereder en postordrebrud (3)
- hvordan du gifter deg med en postordrebrud (1)
- hvordan du gjГёr en postordrebrud (2)
- hvordan du gjГёr en postordrebrud (0)
- hvordan du gjГёr postordrebrud (5)
- hvordan du gjГёr postordrebrud (0)
- hvordan du gjГёr postordrebrud (0)
- hvordan du gjГёr postordrebrud (0)
- hvordan du gjГёr postordrebrud (0)
- hvordan du kan sende en brud pГҐ mail (1)
- hvordan du sender ordrebrud (2)
- hvordan fungerer en postordrebrud (2)
- hvordan fungerer postordre brud (2)
- hvordan fungerer postordrebruden (5)
- hvordan fungerer postordrebrudesider (1)
- hvordan fungerer postordrebrudswebsteder (3)
- hvordan fungerer postordrebrudswebsteder (0)
- hvordan kjГёpe en postordrebrud (1)
- hvordan man bestiller en russisk postbrud (1)
- hvordan man bestiller en russisk postordrebrud (3)
- hvordan man bestiller postordrebrud (1)
- hvordan man forbereder en postordre brud reddit (1)
- hvordan man forbereder en postordrebrud (2)
- hvordan man gГҐr ud med en postordrebrud (1)
- hvordan man kГёber en postordrebrud (1)
- hvordan man laver en postordrebrud (1)
- hvordan man sender en ordre (1)
- hyesingles-review free online sites for singles (1)
- hyviä postimyynti morsiamen sivustoja (1)
- i 10 migliori siti di sposa per corrispondenza (4)
- i 10 migliori siti di sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- i 10 migliori siti web di sposa per corrispondenza (3)
- i 5 migliori siti di sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- i migliori paesi della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- i migliori paesi per ottenere una sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- i migliori posti per la sposa per corrispondenza (3)
- i migliori siti web per la sposa per corrispondenza (3)
- i need a cash advance (2)
- i need a cash advance now (3)
- i need a loan not a payday loan (1)
- i need a payday loan (1)
- i need a payday loan bad credit (2)
- i need a payday loan but have bad credit (1)
- i need a payday loan but i have bad credit (1)
- i need a payday loan for bad credit (2)
- i need a payday loan no credit check (2)
- i need a payday loan now (1)
- i need a payday loan now with bad credit (2)
- i need a payday loan with no credit check (0)
- i need a payday loan? (1)
- i need a payday loans (1)
- i need cash advance now (5)
- i need payday loan (1)
- i need payday loans (1)
- i posti migliori per ricevere la sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- i posti migliori per trovare la sposa per corrispondenza (5)
- i siti della sposa con le migliori offerte (1)
- i want a mail order bride (1)
- Idaho guaranteed installment loans for bad credit (1)
- if a payday loan (2)
- if cash advance (4)
- il posto migliore per ottenere una sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- in cerca di matrimonio (3)
- in cerca di matrimonio (0)
- in cerca di una sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- India Mostbet (8)
- indian-dating-sites-and-apps free online sites for singles (1)
- indian-women+agartala free online sites for singles (1)
- indian-women+chandigarh free online sites for singles (1)
- indian-women+delhi free online sites for singles (1)
- indian-women+indore free online sites for singles (1)
- indian-women+jalandhar free online sites for singles (1)
- indian-women+kanpur free online sites for singles (1)
- indian-women+madurai free online sites for singles (0)
- indian-women+shimla free online sites for singles (1)
- indian-women+silchar free online sites for singles (1)
- indian-women+thiruvananthapuram free online sites for singles (0)
- indiancupid-review free online sites for singles (1)
- indonesian-women+surabaya free online sites for singles (1)
- indonesiancupid-review free online sites for singles (1)
- Industrie des mariГ©es par correspondance (4)
- Industrie des mariГ©es par correspondance (0)
- Industrie des mariГ©es par correspondance (0)
- Industrie des mariГ©es par correspondance (0)
- informaciГіn de la novia del pedido por correo (5)
- informaciГіn de la novia del pedido por correo (0)
- informaciГіn de la novia del pedido por correo (0)
- informaciГіn de la novia del pedido por correo (0)
- Informations sur les mariГ©es par correspondance (6)
- Informations sur les mariГ©es par correspondance (0)
- Informations sur les mariГ©es par correspondance (0)
- Informations sur les mariГ©es par correspondance (0)
- Informations sur les mariГ©es par correspondance (0)
- Informations sur les mariГ©es par correspondance (0)
- instabang-review site for people (1)
- installmentloansindian guaranteed installment loans for bad credit no credit check (1)
- installmentloansindian personal installment loans (1)
- installmentloansvirginia (2) guaranteed installment loans for bad credit no credit check (1)
- installmentloansvirginia (2) installment loans (1)
- installmentloansvirginia (2) installment loans no credit check (1)
- instant cash advance no credit check (1)
- instant payday loan direct lender no credit check (1)
- instant payday loan lenders no credit check (1)
- instant payday loan no credit check (2)
- instant payday loan no credit check direct lender (3)
- instant payday loans company (1)
- instant payday loans no brokers no credit check (1)
- instant payday loans no credit check (1)
- instant payday loans no credit check direct lenders (2)
- internasjonal postordrebrud (2)
- international mail order bride (1)
- international postordrebrud (2)
- international postordrebrud (0)
- Internationale Mail -Bestellung Braut (2)
- internationalwomen.net asiandate-recensione etГ media della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- internationalwomen.net charmdate-recensione etГ media della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+asiatiske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+belarus-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+bogota-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+bosniske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+brasilianske-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+cali-colombiske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+cambodian-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+ecuadorianske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+guyanesiske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+haitisk-kvinde hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+hot-latina-piger bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+indonesiske-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+internationale-datingsider bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+iranske-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+irske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+kazakhstan-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+kinesiske-piger hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+kroatiske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+lebanesiske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+mexicanske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+mode-lokale-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (0)
- internationalwomen.net da+nicaraguanske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+norske-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+osteuropaeiske-kvinder-der-daterer bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+russian-brides-anmeldelser bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+sloviske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+sverige-datingsider hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+sydafrikanske-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+tjekkiske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+varme-japanske-piger hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+varme-kinesiske-piger bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+varme-russiske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+agyptische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+asiatische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+asiatische-frauen-dating-sites Mail-Order-Braut (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+brasilianische-frauen Mail-Order-Braut (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+bulgarische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+cali-kolumbianische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+chatrooms-finden-ihren-besten-online-chatroom Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+heise-arabische-frauen Mail-Order-Braut (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+heise-indische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+heise-und-sexy-kolumbianische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+heiseste-frauen-der-welt Mail-Order-Braut (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+hong-kong-madchen Mail-Order-Braut (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+indische-dating-sites Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+internationale-dating-sites Mail-Order-Braut (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+italienische-madchen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+japanische-dating-sites Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+kubanische-madchen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+medellin-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+mexikanische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+moldawienfrauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+mongolische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+nigerianische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+nordische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+polnische-madchen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+russische-frauen-aus-websites Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+salvadorianische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+sao-paulo-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+schottische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+spanische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+tschechische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+turkische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+ukraine-date-test Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- internationalwomen.net donne-bionde-calde etГ media della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- internationalwomen.net donne-bogota vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- internationalwomen.net donne-bulgari etГ media della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- internationalwomen.net donne-cambogiane etГ media della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- internationalwomen.net donne-ceche etГ media della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- internationalwomen.net donne-coreane vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- internationalwomen.net donne-della-cartagena vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- internationalwomen.net donne-indiane vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- internationalwomen.net donne-nordiche vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- internationalwomen.net donne-portoghesi vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- internationalwomen.net donne-ucraine-calde vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+asiandate-opinion revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+chicas-cubanas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+chicas-de-filipina-caliente revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+chicas-hong-kong revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+chicas-suecas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+mujer-haitiana revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+mujeres-africanas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+mujeres-asiaticas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+mujeres-austriacas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+mujeres-colombianas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+mujeres-colombianas-calientes-y-sexys que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+mujeres-europeas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+mujeres-filipinas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+mujeres-ghana que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+mujeres-holandesas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+mujeres-indias revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+mujeres-irlandesas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+mujeres-lituanas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+mujeres-mongol que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+mujeres-negras-calientes revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+mujeres-nigerianas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+mujeres-noruegas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+mujeres-sudafricanas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+mujeres-suizas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+sitios-de-citas-colombianas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+sitios-de-citas-de-mujeres-rusas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net fi+aasialaisten-naisten-treffisivustot tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- internationalwomen.net fi+argentiinalaiset-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- internationalwomen.net fi+bolivian-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- internationalwomen.net fi+espanjalaiset-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- internationalwomen.net fi+etiopialaiset-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- internationalwomen.net fi+japanilaiset-treffisivustot tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- internationalwomen.net fi+kiinalaiset-treffisivustot tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- internationalwomen.net fi+kuumat-thaimaalaiset-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- internationalwomen.net fi+kuumia-japanilaisia-tyttoja tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- internationalwomen.net fi+latinalaiset-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (0)
- internationalwomen.net fi+latinalaisten-naisten-treffisivustot tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- internationalwomen.net fi+marokon-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- internationalwomen.net fi+paras-maa-loytaa-vaimo tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- internationalwomen.net fi+parhaat-rotujenvaliset-treffisivustot tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- internationalwomen.net fi+portugalilaiset-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- internationalwomen.net fi+ruotsin-treffisivustot tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- internationalwomen.net fi+suomalaiset-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- internationalwomen.net fr+femmes-asiatiques-chaudes Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- internationalwomen.net fr+femmes-autrichiennes Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- internationalwomen.net fr+femmes-ecossaises Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- internationalwomen.net fr+femmes-irlandaises-chaudes Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- internationalwomen.net fr+femmes-marocaines Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- internationalwomen.net fr+femmes-slovaques Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- internationalwomen.net fr+femmes-tcheques Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- internationalwomen.net fr+filles-chinoises Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- internationalwomen.net fr+filles-phillipina-chaudes Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- internationalwomen.net fr+filles-tijuana Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- internationalwomen.net fr+sites-de-rencontres-de-femmes-russes Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- internationalwomen.net latin-american-cupid-recensione vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- internationalwomen.net migliori-siti-di-incontri-interrazziali vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- internationalwomen.net no+albaniske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net no+bogota-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net no+irske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net no+kinesiske-jenter beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net no+mongolske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net no+pakistanske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net no+sexy-og-varme-brunette-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net no+sloveniske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net no+ukrainske-datingsider beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net no+uruguay-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net no+varme-meksikanske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net siti-di-incontri-giapponesi vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- internationalwomen.net sv+azerbaijan-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- internationalwomen.net sv+basta-landet-att-hitta-en-fru postorder brudkataloger (1)
- internationalwomen.net sv+belize-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- internationalwomen.net sv+bosniska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- internationalwomen.net sv+charmdate-recension postorder brudkataloger (1)
- internationalwomen.net sv+danska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- internationalwomen.net sv+heta-arabiska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (0)
- internationalwomen.net sv+heta-irlandska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- internationalwomen.net sv+heta-och-sexiga-colombianska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- internationalwomen.net sv+sexiga-och-heta-brunettkvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- internationalwomen.net sv+tyska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- internationalwomen.net sv+uruguay-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- internationalwomen.net tr+afrikali-kadinlar bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- internationalwomen.net tr+avustralya-kadinlari bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- internationalwomen.net tr+bogota-kadinlar bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- internationalwomen.net tr+danimarkali-kadinlar bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- internationalwomen.net tr+fince-kadinlar bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- internationalwomen.net tr+hint-tanisma-siteleri bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- internationell postorderbrud (1)
- internet payday loans no credit check (2)
- interracial dating (1)
- Interracial Mail -Bestellung Braut (1)
- interracial postorder brud (1)
- interracial postordre brud (1)
- Iraan installment loans near me (1)
- is a cash advance a loan (1)
- is a cash advance bad (3)
- is a cash advance bad for your credit (2)
- is a payday loan secured? (1)
- is cash advance (2)
- is cash advance a loan (1)
- is cash advance bad (2)
- is cash advance bad for your credit (2)
- is mail order bride a real thing (2)
- is mail order bride safe (1)
- is mail order bride worth it (2)
- is payday loan (2)
- Ist die Versandbraut real (1)
- Ist Versandbestellbraut eine echte Sache (1)
- Ist Versandbestellbraut es wert? (1)
- Ist Versandbestellbraut sicher (1)
- Istinita priДЌa o mladenki (2)
- Istinita priДЌa o mladenki (0)
- IT Education (1)
- IT Vacancies (1)
- IT Вакансії (1)
- IT Образование (3)
- it+2redbeans-recensione come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+adultfriendfinder-recensione come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+asiacharm-recensione come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+bali-donne come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+belga-donne come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+blackpeoplemeet-recensione come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+calde-donne-norvegesi come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+calde-donne-svedesi come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+canadese-donne come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+coreano-donne come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+costa-rican-donne come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+dateasianwoman-recensione come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+dateeuropeangirl-recensione come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+donne-africane-calde come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+donne-alte-singole come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+donne-armene-calde come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+donne-calde-mumbai come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+donne-calde-tagikistan come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+donne-coreane-contro-cinesi-contro-giapponesi come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+donne-indiane come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+donne-iraniane come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (0)
- it+donne-malesi-calde come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+donne-marocchine-calde come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+donne-mongole-calde come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+donne-pachistane-calde come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+donne-single-mature come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+donne-single-senza-figli come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+donne-venezuelane-calde come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+feeld-recensione come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+filippino-donne come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+filippino-spose come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+german-spose come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (0)
- it+interracial-dating-central-recensione come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+islandese-spose ordine postale legittimo sposa russa (1)
- it+italo-donne come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+jeevansathi-recensione ordine postale legittimo sposa russa (1)
- it+jswipe-recensione top 10 sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- it+jump4love-recensione come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+kazakistan-donne ordine postale legittimo sposa russa (1)
- it+laos-donne ordine postale legittimo sposa russa (0)
- it+leta-media-del-matrimonio top 10 sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- it+malaysian-spose top 10 sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- it+malese-donne come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+match-recensione top 10 sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- it+matchtruly-recensione come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+meetme-recensione ordine postale legittimo sposa russa (1)
- it+meetnicerussian-recensione ordine postale legittimo sposa russa (0)
- it+messicano-spose come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+mingle2-recensione top 10 sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- it+mongolo-donne top 10 sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- it+mumbai-donne top 10 sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- it+muslima-recensione top 10 sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- it+paesi-che-amano-gli-uomini-americani come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+paesi-con-le-donne-piu-belle top 10 sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- it+polacco-siti-e-app-di-incontri come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+positive-singles-recensione ordine postale legittimo sposa russa (1)
- it+pure-recensione top 10 sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- it+relazione-aperta top 10 sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- it+rosebrides-recensione top 10 sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- it+rumeno-siti-di-incontri-e-app come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+secret-benefits-recensione come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+shaadi-recensione come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+silversingles-recensione top 10 sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- it+singapore-donne come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+siti-di-incontri-indiani-e-app ordine postale legittimo sposa russa (1)
- it+siti-e-app-di-incontri-messicani come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+siti-e-app-di-incontri-portoricani come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+siti-e-app-di-incontri-tailandesi come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+spagnolo-siti-e-app-di-incontri come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+sposare-qualcuno-da-un-altro-paese ordine postale legittimo sposa russa (1)
- it+spose-cinesi come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+tagikistan-donne come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+ucraino-donne ordine postale legittimo sposa russa (1)
- it+ungherese-spose come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+uzbekistan-donne come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+vietnamita-donne ordine postale legittimo sposa russa (1)
- it-steroid (8)
- Jag vill ha en postorderbrud (2)
- japanese women for marriage (1)
- Je li mladenka narudЕѕba prava prava stvar (1)
- Je veux une mariГ©e par correspondance (3)
- Je veux une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Je veux une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- jeg vil ha en postordrebrud (2)
- Jeg vil have en postordrebrud (1)
- JetX Casino (1)
- Kahoka guaranteed installment loans for bad credit direct lenders only (1)
- kaikkien aikojen paras postimyynti (3)
- Kako napraviti mladenku za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (2)
- Kako napraviti mladenku za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (0)
- Kako radi mladenka za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (1)
- Kako radi mladenke za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (1)
- Kako radi na narudЕѕbi Mail (1)
- Kakva narudЕѕba poЕЎte (1)
- kan du skicka en brud (2)
- Kann ich eine Versandungsbraut bekommen, wenn ich bereits verheiratet bin? (1)
- Kasyno Online PL (1)
- Kauf einer Mail -Bestellung Braut (3)
- Kaufen Sie eine Mail -Bestellung Braut (2)
- köp en postorderbrud (1)
- Kenbridge online installment loans (1)
- kenosha+erotic-massage username (1)
- keskimääräiset postimyynti morsiamen hinnat (2)
- keskimääräiset postimyynti morsiamen hinnat (0)
- king johnnie (2)
- kjГёp en postordrebrud (1)
- kjГёp postordrebrud (2)
- kjГёp postordrebrud (0)
- Koja je najbolja sluЕѕba za mladenku za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (1)
- Koja je najbolja web stranica za mladenku (2)
- koja je narudЕѕba poЕЎte (1)
- kuinka mennä naimisiin postimyynti morsiamen kanssa (1)
- kuinka postimyynti morsiamen (2)
- kuinka tehdä postimyynti morsiamen (4)
- kuinka tehdä postimyynti morsiamen (0)
- kuinka tehdä postimyynti morsiamen (0)
- kuinka tehdä postimyynti morsiamen (0)
- kuinka tilata morsiamen postitse (3)
- kuinka tilata postia venäläinen morsian (5)
- kuinka tilata postia venäläinen morsian (0)
- kuinka tilata postia venäläinen morsian (0)
- kuinka tilata postia venäläinen morsian (0)
- kuinka tilata postia venäläinen morsian (0)
- kuinka tilata postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- kuinka valmistaa postimyynti morsiamen (3)
- kuinka valmistaa postimyynti morsian reddit (4)
- Kupnja mladenke za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (2)
- Kupnja mladenke za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (0)
- kymmenen eniten postimyynti morsiamen sivusto (5)
- kymmenen eniten postimyynti morsiamen verkkosivustot (1)
- kymmenen parasta postimyynti morsiamen sivustoa (2)
- Können Sie eine Braut bestellen? (4)
- Können Sie eine Braut bestellen? (0)
- Können Sie eine Braut bestellen? (0)
- Können Sie eine Braut bestellen? (0)
- köp postorder brud (3)
- köp postorder brud (0)
- köp postorder brud (0)
- köper en postorderbrud (1)
- kГёb postordrebrud (1)
- La commande par correspondance en vaut-elle la peine (3)
- La commande par correspondance en vaut-elle la peine (0)
- La courrier Г©lectronique en vaut la peine? (3)
- La courrier Г©lectronique en vaut la peine? (0)
- La courrier Г©lectronique en vaut la peine? (0)
- La Jara installment loans near me (1)
- la mariГ©e par correspondance (2)
- la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- La mariГ©e par correspondance en vaut la peine (3)
- La mariГ©e par correspondance en vaut la peine (0)
- La mariГ©e par correspondance en vaut la peine (0)
- La mariГ©e par correspondance est-elle une chose rГ©elle (2)
- La mariГ©e par correspondance est-elle une chose rГ©elle (0)
- la migliore sposa per corrispondenza di sempre (1)
- la novia de la orden de correo superior se sienta (1)
- la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- la sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- la sposa per corrispondenza ne vale la pena? (2)
- laillinen postimyynti morsiamen verkkosivusto (3)
- laillinen postimyynti morsian (4)
- lailliset postimyynti morsiamen palvelut (3)
- lailliset postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (2)
- lailliset postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (0)
- lailliset postimyynti morsiamen verkkosivustot (4)
- lailliset postimyyntiyritykset (1)
- latin brides (1)
- latin mail order bride (1)
- latin mail order brides (1)
- Laurel installment loans near me (1)
- Le site de la mariГ©e par correspondance (4)
- Le site de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Le site de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Le site de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- legale Versandhandel Seiten für Bräute (7)
- Legale Versandhandel Seiten für Bräute (0)
- legale Versandhandel Seiten für Bräute (0)
- Legale Versandhandel Seiten für Bräute (0)
- legale Versandhandel Seiten für Bräute (0)
- Legale Versandhandel Seiten für Bräute (0)
- Legale Versandhandel Seiten für Bräute (0)
- leggi led per corrispondenza i siti della sposa (2)
- Leggit Mail bestellen Brautseiten (1)
- leggit mail order bride sites (3)
- leggit post beställning brud webbplatser (1)
- leggit postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (2)
- leggit postordre brud nettsteder (3)
- Legit Mail narudЕѕba mladenka (1)
- Legit Mail narudЕѕbe mladenke (1)
- legit mail order bride (1)
- legit mail order bride service (1)
- legit mail order bride sites (1)
- legit mail order bride sites reddit (5)
- legit mail ordre brud (1)
- legit mail ordre brude service (1)
- legit mail ordre brude site (2)
- legit mail ordre brude site (0)
- legit mail ordre russisk brud (1)
- legit no credit check payday loans (2)
- legit payday loan no credit check (3)
- legit postimyynti morsian (5)
- legit postorder brud (5)
- legit postorder brud webbplatser (3)
- legit postorder brud webbplatser (0)
- legit postorder brud webbplatser reddit (5)
- legit postorder brud webbplatser reddit (0)
- legit postorder ryska bruden (6)
- legit postordre brud (2)
- legit postordre brud nettsted (2)
- legit postordre brud nettsteder (5)
- legit postordre brudtjeneste (3)
- legitim mail ordre brude service (1)
- legitim postorder brud (1)
- legitim postorder brud webbplats (1)
- legitim postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- legitim postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- legitim postorder brudföretag (1)
- legitim postorder brudtjänst (1)
- legitim postordre brudeside (3)
- legitim postordre brudewebsted (3)
- legitim postordre brudsted (2)
- legitimale Mail -Bestellung Braut (5)
- legitimate mail order bride companies (1)
- legitimate mail order bride services (1)
- legitimate mail order bride site (2)
- legitimate mail order bride sites (1)
- legitimate mail order bride websites (1)
- legitimate payday loans no credit check (1)
- legitime Mail -Bestellung Braut Site (3)
- legitime Mail -Bestellung Brautdienste (1)
- legitime Mail bestellen Brautunternehmen (1)
- Legitime Mail bestellen Brautwebsite (1)
- legitime Mail bestellen Brautwebsites (1)
- legitime postordre brude tjenester (3)
- legitime postordre brudesider (1)
- legitime postordre brudevirksomheder (1)
- legitime postordre brudtjenester (1)
- legitime postordrebrud nettsteder (1)
- legitime postordrebrudesider (3)
- legitime postordrebrudselskaper (3)
- legitime Versandbestellbraut (2)
- legitime Versandbestellbrautstandorte (3)
- legitimer Versandauftragsbrautservice (3)
- legitimert postordre brudtjeneste (2)
- legitimna web stranica za mladenku (2)
- legitimt postordrebrud nettsted (1)
- Legitimte -Mail -Bestellung Brautservice (1)
- legitimte mail narudЕѕbe mladenke (1)
- legitimte mail order bride service (2)
- legitimte postimyynti morsiamen palvelu (6)
- legititna poЕЎta naredba ruska mladenka (1)
- legittimare il servizio di sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- LeoVegas Finland (6)
- LeoVegas Sweden (4)
- Les meilleurs pays pour obtenir une mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- Les meilleurs sites de mariГ©es par correspondance. (6)
- Les meilleurs sites de mariГ©es par correspondance. (0)
- Les meilleurs sites de mariГ©es par correspondance. (0)
- Les meilleurs sites de mariГ©es par correspondance. (0)
- Les meilleurs sites de mariГ©es par correspondance. (0)
- Les meilleurs sites de mariГ©es par correspondance. (0)
- Les sites de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitimes (10)
- Les sites de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitimes (0)
- Les sites de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitimes (0)
- Les sites de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitimes (0)
- Les sites de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitimes (0)
- Les sites de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitimes (0)
- Les sites de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitimes (0)
- Les sites de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitimes (0)
- Les sites de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitimes (0)
- Les sites de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitimes (0)
- lesbian mail order bride (1)
- Lesbienne Mail Commande Bride Reddit (2)
- lesbische Versandbestellung Braut (3)
- lesbisk postorder brud (4)
- lesbisk postorder brud reddit (2)
- lesbisk postordre bruden reddit (3)
- lesbisk postordrebrud (3)
- lesbo postimyynti morsian reddit (1)
- letar efter en postorderbrud (1)
- letar efter Г¤ktenskap (1)
- Lewistown online installment loans instant approval (1)
- Lezbijska narudЕѕba za mladenku Reddit (3)
- Lezbijska narudЕѕba za mladenku Reddit (0)
- Lezbijska narudЕѕba za mladenku Reddit (0)
- Lezbiyen Posta SipariЕџi Gelin (5)
- Lezbiyen Posta SipariЕџi Gelin (0)
- Lezbiyen Posta SipariЕџi Gelin (0)
- Lezbiyen Posta SipariЕџi Gelin (0)
- Lezbiyen Posta SipariЕџi Gelin (0)
- liechtenstein escort girl (1)
- list of best mail order bride sites (1)
- lista över bästa postorderbrudsajter (1)
- lista de los mejores sitios para novias por correo (3)
- lista över bästa postorderbrudsajter (1)
- Liste der besten Mail -Bestell -Braut -Sites (3)
- Liste der besten Mail -Bestell -Braut -Sites (0)
- Liste des meilleurs sites de mariГ©es par correspondance (1)
- Live Credit Score For Montana Sixth Is V Pirin Blagoevgrad - 827 (4)
- loan cash advance (2)
- loan cash advance near me (1)
- loan for bad credit not a payday loan (1)
- loan for cash advance (4)
- loan for payday (2)
- loan instead of payday loan (1)
- loan me payday loan (1)
- loan payday advance (2)
- loan payday bad credit (3)
- loan payday loan (1)
- loan payday loans near me (1)
- loan payday no credit check (2)
- loan to pay payday loan (5)
- loans and cash advance (2)
- loans bad credit payday (2)
- loans but not payday loans (1)
- loans cash advance (2)
- loans for bad credit no payday loans (3)
- loans for bad credit not payday (3)
- loans for bad credit not payday loans (1)
- loans for bad credit payday (2)
- loans for bad credit payday loans (2)
- loans for payday (3)
- loans instead of payday (1)
- loans near me payday (2)
- loans no payday loans (0)
- loans not payday (2)
- loans not payday for bad credit (1)
- loans not payday loans (1)
- loans now but not payday (3)
- loans payday (2)
- loans payday bad credit (1)
- loans payday cash advance (3)
- loans payday loan (2)
- loans payday loans (1)
- loans to payday (1)
- loans with bad credit not payday loans (2)
- loans with no credit check no payday loeans (3)
- local (10)
- local payday loans no credit check (1)
- login (11)
- long term payday loans no credit check (3)
- looking for a cash advance (1)
- looking for a mail order bride (2)
- looking for a payday loan (1)
- looking for a payday loan with bad credit (1)
- looking for marriage (1)
- looking for payday loan (1)
- los 10 mejores sitios para novias por correo (3)
- los 10 principales sitios web de novias por correo (2)
- los 5 mejores sitios para novias por correo (2)
- los mejores paГses para obtener un pedido por correo novia (5)
- los mejores paГses para obtener un pedido por correo novia (0)
- los mejores paГses para obtener un pedido por correo novia (0)
- los mejores paГses para obtener un pedido por correo novia (0)
- Lotoclub (1)
- lovingwomen.org asiatische-chatrooms Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- lovingwomen.org athiopische-dating-sites Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (0)
- lovingwomen.org beste-lander-um-zu-heiraten Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- lovingwomen.org bestes-afrikanisches-land-um-eine-frau-zu-finden Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- lovingwomen.org brasilianische-braut Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- lovingwomen.org chinesische-dating-sites Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+aeldre-kvinder-der-soger-yngre-maend hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+bedste-europaeiske-land-til-at-finde-en-kone bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+bedste-land-til-dating hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+brasilianske-datingsider hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+cambodian-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+chatrum-med-singler bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+chilenske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+cubanske-datingsider bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+dating-com-anmeldelser hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+dating-kultur-i-japan bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+europaeiske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (0)
- lovingwomen.org da+europaeiske-postordrebrude-websteder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+filipina-brud bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+franske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+gifte-sig-med-en-japansk-kvinde hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+graeske-datingsider hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+graeske-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+hotteste-og-mest-sexede-kvinder-i-verden bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+hvordan-man-finder-en-kone bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+italienske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+japanske-chatrum hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+koreansk-brud bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+latin-dating-sider bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+latin-postordrebrude-sider hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+mexicanske-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+rumaenske-datingsider bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+thai-datingsider hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+thailandske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+tjekkiske-datingsider bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+udenlandske-kvinder-pa-udkig-efter-amerikanske-maend bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+uruguay-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org dating-com-test Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- lovingwomen.org dating-sites-fur-die-ehe Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- lovingwomen.org dating-sites-fur-ernsthafte-beziehungen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- lovingwomen.org die-heisesten-und-sexiesten-frauen-der-welt Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- lovingwomen.org e-mail-bestellung-heiratsstatistik Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- lovingwomen.org ecuadorianische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (0)
- lovingwomen.org el-salvador-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- lovingwomen.org es+casarse-con-una-mujer-dominicana revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- lovingwomen.org es+cultura-de-citas-en-mexico revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- lovingwomen.org es+donde-conocer-mujeres-solteras revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- lovingwomen.org es+mejor-pais-para-salir revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- lovingwomen.org es+mejores-paises-para-casarse revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (0)
- lovingwomen.org es+mujeres-buscando-matrimonio revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- lovingwomen.org es+mujeres-checas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- lovingwomen.org es+mujeres-cubanas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- lovingwomen.org es+mujeres-eslavas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- lovingwomen.org es+mujeres-latinas-calientes-y-sexys revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- lovingwomen.org es+mujeres-rumanas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- lovingwomen.org es+mujeres-turcas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- lovingwomen.org es+mujeres-vietnamitas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- lovingwomen.org es+salas-de-chat-mexicanas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- lovingwomen.org es+salas-de-chat-ucranianas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- lovingwomen.org es+sitios-de-citas-armenias revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- lovingwomen.org es+sitios-de-citas-caribenas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- lovingwomen.org es+sitios-de-citas-checas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- lovingwomen.org es+sitios-de-citas-coreanas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- lovingwomen.org es+sitios-de-citas-de-larga-distancia revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- lovingwomen.org es+sitios-de-citas-de-pakistan que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- lovingwomen.org es+sitios-de-citas-espanolas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- lovingwomen.org es+sitios-de-citas-griegas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- lovingwomen.org es+sitios-de-citas-portuguesas que es la novia del pedido por correo (0)
- lovingwomen.org es+sitios-de-citas-venezolanas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- lovingwomen.org es+sitios-de-citas-vietnamitas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- lovingwomen.org europaische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- lovingwomen.org fi+turkkilaiset-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- lovingwomen.org fi+ukrainalainen-morsian wikipedia postimyynti morsian (1)
- lovingwomen.org fi+uruguay-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- lovingwomen.org fi+vietnamilainen-morsian wikipedia postimyynti morsian (1)
- lovingwomen.org filipino-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (0)
- lovingwomen.org fr+bumble-avis Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- lovingwomen.org franzosische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- lovingwomen.org frauen-polieren Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- lovingwomen.org guatemalanische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- lovingwomen.org heise-und-sexy-deutsche-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- lovingwomen.org heise-und-sexy-kolumbianische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- lovingwomen.org heise-und-sexy-koreanische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- lovingwomen.org heise-und-sexy-latina-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- lovingwomen.org heise-und-sexy-spanische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- lovingwomen.org heise-und-sexy-ukrainische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- lovingwomen.org internationale-chatrooms Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+come-trovare-una-moglie ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+cultura-degli-appuntamenti-in-cina ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+cultura-degli-appuntamenti-in-dominicano vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+cultura-degli-appuntamenti-nella-corea-del-sud ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+donne-asiatiche ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+donne-brasiliane ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+donne-cilene ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+donne-colombiane-calde-e-sexy ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+donne-costa-rican vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+donne-europee vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+donne-rumene ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+donne-slave vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- lovingwomen.org it+donne-spagnole-calde-e-sexy ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+donne-vietnamite vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+il-miglior-paese-per-un-uomo-americano-per-trovare-una-moglie ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+siti-asiatici-sposa-per-corrispondenza ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+siti-di-incontri-argentini vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+siti-di-incontri-brasiliani vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+siti-di-incontri-caraibici ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+siti-di-incontri-coreani ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+siti-di-incontri-dominicani vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+sposa-messicana vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+sposa-per-corrispondenza-prezzo vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+sposa-rumena vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+sposa-russa vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- lovingwomen.org it+sposare-qualcuno-di-un-altro-paese vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+sposare-una-donna-messicana vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- lovingwomen.org italienische-dating-sites Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- lovingwomen.org italienische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- lovingwomen.org jamaikanische-dating-sites Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- lovingwomen.org japanische-braut Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (0)
- lovingwomen.org katalogheirat-standorte Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- lovingwomen.org kolumbianische-braut Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- lovingwomen.org kolumbianische-dating-sites Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- lovingwomen.org koreanische-braut Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (0)
- lovingwomen.org koreanische-dating-sites Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- lovingwomen.org main_it vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- lovingwomen.org main_pt Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- lovingwomen.org main_sv postorder brudkataloger (1)
- lovingwomen.org mexikanische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+armeniske-datingsider online postordre brud (0)
- lovingwomen.org no+asiatiske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+beste-land-a-gifte-seg-i online postordre brud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+brasilianske-datingsider online postordre brud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+colombian-brud online postordre brud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+colombian-datingsider beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+dating-com-anmeldelse online postordre brud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+datingkultur-i-brasil online postordre brud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+datingkultur-i-sor-korea online postordre brud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+datingsider-for-ekteskap online postordre brud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+europeiske-kvinner online postordre brud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+franske-datingsider online postordre brud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+franske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+gifte-deg-med-en-brasiliansk-kvinne beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+jamaicanske-datingsider beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+japansk-brud online postordre brud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+karibiske-datingsider online postordre brud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+kinesisk-brud online postordre brud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+koreanske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+kosta-rican-datingsider beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+kubanske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+portugisiske-datingsider beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+postordrebrud-priser beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+puertorikanske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+russisk-brud beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+slovakiske-kvinner online postordre brud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+thai-brud beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+tsjekkiske-datingsider online postordre brud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+ukrainske-datingsider online postordre brud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+varme-og-sexy-filippinske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+varme-og-sexy-koreanske-kvinner online postordre brud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+venezuelansk-brud online postordre brud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+venezuelanske-kvinner online postordre brud (1)
- lovingwomen.org panamaische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- lovingwomen.org pt+casar-com-uma-mulher-colombiana Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- lovingwomen.org pt+cultura-de-namoro-em-dominicano Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- lovingwomen.org pt+cultura-de-namoro-no-mexico Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- lovingwomen.org pt+melhor-pais-com-as-mulheres-mais-bonitas Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- lovingwomen.org pt+mulheres-alemas-gostosas-e-sexy Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- lovingwomen.org pt+mulheres-colombianas Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- lovingwomen.org pt+mulheres-equatorianas Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- lovingwomen.org pt+mulheres-eslavas Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- lovingwomen.org pt+mulheres-eslovacas Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- lovingwomen.org pt+mulheres-gregas Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- lovingwomen.org pt+mulheres-italianas-gostosas-e-sexy Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- lovingwomen.org pt+mulheres-mexicanas-gostosas-e-sexy Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- lovingwomen.org pt+mulheres-ucranianas-quentes-e-sensuais Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- lovingwomen.org pt+mulheres-vietnamitas Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- lovingwomen.org pt+noiva-vietnamita Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- lovingwomen.org pt+onde-conhecer-mulheres-solteiras Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- lovingwomen.org pt+sites-asiaticos-noiva-por-correspondencia Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- lovingwomen.org pt+sites-de-namoro-armenios Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- lovingwomen.org pt+sites-de-namoro-brasileiros Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- lovingwomen.org pt+sites-de-namoro-de-longa-distancia Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- lovingwomen.org pt+sites-de-namoro-eslavo Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- lovingwomen.org pt+sites-de-namoro-indianos Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- lovingwomen.org pt+sites-de-namoro-italianos Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- lovingwomen.org pt+sites-de-namoro-latino Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- lovingwomen.org pt+sites-de-namoro-no-caribe Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- lovingwomen.org rumanische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (0)
- lovingwomen.org russische-dating-sites Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- lovingwomen.org slowenische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- lovingwomen.org sv+asiandate-recension postorder brudkataloger (1)
- lovingwomen.org sv+basta-afrikanska-land-att-hitta-en-fru postorder brudkataloger (1)
- lovingwomen.org sv+basta-europeiska-land-att-hitta-en-fru postorder brudkataloger (1)
- lovingwomen.org sv+basta-land-for-dejting postorder brudkataloger (1)
- lovingwomen.org sv+basta-lander-med-de-mest-lojala-fruarna postorder brudkataloger (1)
- lovingwomen.org sv+basta-landet-att-hitta-en-fru postorder brudkataloger (1)
- lovingwomen.org sv+belarus-dating-webbplatser postorder brudkataloger (1)
- lovingwomen.org sv+datingkultur-i-mexiko postorder brudkataloger (1)
- lovingwomen.org sv+datingsajter-for-allvarliga-relationer postorder brudkataloger (1)
- lovingwomen.org sv+el-salvador-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- lovingwomen.org sv+europeiska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- lovingwomen.org sv+indiska-datingsajter postorder brudkataloger (1)
- lovingwomen.org sv+japanska-chattrum postorder brudkataloger (1)
- lovingwomen.org sv+japanska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (0)
- lovingwomen.org sv+kubanska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- lovingwomen.org sv+latin-postordrebrud-webbplatser postorder brudkataloger (1)
- lovingwomen.org sv+postorder-aktenskapstatistik postorder brudkataloger (1)
- lovingwomen.org sv+puerto-rico-datingsidor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- lovingwomen.org sv+ryska-datingsajter postorder brudkataloger (1)
- lovingwomen.org sv+slaviska-postordrebrud-webbplatser postorder brudkataloger (1)
- lovingwomen.org sv+spanska-datingsajter postorder brudkataloger (1)
- lovingwomen.org sv+yngre-kvinnor-som-soker-aldre-man postorder brudkataloger (1)
- lovingwomen.org tr+amerikali-bir-adam-icin-bir-es-bulmak-icin-en-iyi-ulke Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek (1)
- lovingwomen.org tr+asya-sohbet-odalari bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- lovingwomen.org tr+avrupa-posta-siparisi-gelinler-siteleri bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- lovingwomen.org tr+bekarlarla-sohbet-odalari bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- lovingwomen.org tr+bumble-inceleme bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- lovingwomen.org tr+cinde-flort-kulturu Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek (1)
- lovingwomen.org tr+hong-kong-tanisma-siteleri bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- lovingwomen.org tr+isvec-arkadaslik-siteleri bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- lovingwomen.org tr+italyan-tanisma-siteleri Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek (1)
- lovingwomen.org tr+japon-tanisma-siteleri bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- lovingwomen.org tr+japonyada-flort-kulturu bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- lovingwomen.org tr+kolombiyali-kadinlar bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- lovingwomen.org tr+kosta-rika-kadinlar Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek (1)
- lovingwomen.org tr+posta-siparisi-gelinler-nasil-calisir bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- lovingwomen.org tr+romen-kadinlar bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- lovingwomen.org tr+romen-tanisma-siteleri bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- lovingwomen.org tr+sicak-ve-seksi-japon-kadinlar bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- lovingwomen.org tr+taylandli-kadinlar bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- lovingwomen.org tr+vietnamli-gelin bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- lovingwomen.org ukrainische-chatrooms Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- lovingwomen.org vietnamesische-braut Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- low interest payday loans no credit check (3)
- luettelo parhaista postimyynti morsiamen sivustoista (3)
- lunaprofitmax.org (1)
- löytää morsian (2)
- löytää morsian (0)
- löytää postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- macedonia-women+cair free online sites for singles (1)
- macedonia-women+skopje free online sites for singles (1)
- Macon bad credit installment loans (1)
- Macon online installment loans (1)
- Mail -Bestellung Braut (5)
- Mail -Bestellung Braut -Websites ?ГјberprГјfen (2)
- Mail -Bestellung Braut -Websites ?ГјberprГјfen (0)
- Mail -Bestellung Braut Datierung (1)
- Mail -Bestellung Braut definieren (1)
- Mail -Bestellung Braut echt (2)
- Mail -Bestellung Braut es wert ist (2)
- Mail -Bestellung Braut legitim (3)
- Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur mit dem besten Ruf (2)
- Mail -Bestellung Brautagenturen (2)
- Mail -Bestellung Brautbewertung (1)
- Mail -Bestellung Brautdating Site (3)
- Mail -Bestellung Brautdefinition (1)
- Mail -Bestellung Brautdienste (2)
- Mail -Bestellung Brautdienste Definition (1)
- Mail -Bestellung Brautindustrie (3)
- Mail -Bestellung Brautkatalog (4)
- Mail -Bestellung Brautkataloge (1)
- Mail -Bestellung Brautservice (6)
- Mail -Bestellung Bride Agency Reviews (2)
- Mail an die Braut bestellen (3)
- Mail an die Braut bestellen (0)
- Mail auf Bestellung Braut (1)
- Mail bestellen Braut Arbeit? (1)
- Mail bestellen Braut Craigslist (3)
- Mail bestellen Braut echte Geschichten (1)
- Mail bestellen Braut FAQ (2)
- Mail bestellen Braut gute Idee? (1)
- Mail bestellen Braut legitim (1)
- Mail bestellen Braut Reales Standort (2)
- Mail bestellen Braut Reveiw (3)
- Mail bestellen Braut Websites Reddit (1)
- Mail bestellen Braut Wiki (6)
- Mail bestellen Braut Wikipedia (1)
- Mail bestellen Brautartikel (1)
- Mail bestellen Brautbewertungen (3)
- Mail bestellen Brautdating -Sites (3)
- Mail bestellen Brautgeschichten (1)
- Mail bestellen Brautgesetze (2)
- Mail bestellen Brautinformationen (1)
- Mail bestellen Brautstandorte legitim (2)
- Mail bestellen Brautwebes Reddit (2)
- Mail bestellen Brautwebsite (5)
- Mail bestellen Brautwebsites (1)
- Mail bestellen eine Braut (1)
- Mail bestellen Frauen (1)
- mail bestil en brud (3)
- Mail Bride Order (2)
- mail brud ordre (1)
- mail brudbeställning (1)
- Mail dans l'ordre de la mariГ©e (7)
- Mail dans l'ordre de la mariГ©e (0)
- Mail dans l'ordre de la mariГ©e (0)
- Mail dans l'ordre de la mariГ©e (0)
- Mail dans l'ordre de la mariГ©e (0)
- Mail dans l'ordre de la mariГ©e (0)
- Mail dans l'ordre de la mariГ©e (0)
- Mail dans l'ordre du coГ»t de la mariГ©e (4)
- Mail dans l'ordre du coГ»t de la mariГ©e (0)
- Mail dans l'ordre du coГ»t de la mariГ©e (0)
- Mail dans l'ordre du coГ»t de la mariГ©e (0)
- Mail dans la dГ©finition de la mariГ©e (3)
- Mail dans la dГ©finition de la mariГ©e (0)
- Mail dans la dГ©finition de la mariГ©e (0)
- mail for ГҐ bestille brud (4)
- mail for ГҐ bestille brud (0)
- mail for ГҐ bestille brud (0)
- mail for ГҐ bestille brud (0)
- mail för att beställa brud (2)
- mail för att beställa brud (0)
- mail i ordning brud kostar (2)
- mail i ordning bruddefinition (2)
- mail i ordre brud (3)
- mail i ordre brudefinition (1)
- mail i rekkefГёlge brud (5)
- mail i rekkefГёlge brud (0)
- mail i rekkefГёlge brud (0)
- mail i rekkefГёlge brud (0)
- mail i rekkefГёlge brud (0)
- Mail in der Bestellung Brautdefinition (2)
- mail in order bride (1)
- mail in ordine definizione sposa (5)
- Mail Mail (2)
- Mail narudЕѕba Katalog mladenke (2)
- Mail narudЕѕba Katalog mladenke (0)
- Mail narudЕѕba mladenka definira (1)
- Mail narudЕѕba mladenka vrijedi (1)
- Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (2)
- Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (0)
- Mail narudЕѕbe mladenke agencije (1)
- Mail narudЕѕbe mladenke web stranice Reddit (4)
- Mail narudЕѕbe mladenke web stranice Reddit (0)
- Mail narudЕѕbe mladenke web stranice Reddit (0)
- Mail narudЕѕbe mladenke web stranice Reddit (0)
- Mail narudЕѕbe za mladenke (1)
- Mail narudЕѕbe za mladenke legitimne (4)
- Mail narudЕѕbe za mladenke legitimne (0)
- Mail narudЕѕbe za mladenke legitimne (0)
- Mail narudЕѕbe za mladenke legitimne (0)
- Mail narudЕѕbena agencija s najboljom reputacijom (1)
- Mail on Order Bride (4)
- mail order bride (3)
- mail order bride agency (1)
- mail order bride agency with the best reputation (2)
- mail order bride articles (1)
- mail order bride catalog (2)
- mail order bride catalogs (1)
- mail order bride catalogue (2)
- mail order bride catalogue (0)
- mail order bride countries (1)
- mail order bride coupon (2)
- mail order bride craigslist (1)
- mail order bride dating (2)
- mail order bride dating site (1)
- mail order bride dating sites (1)
- mail order bride define (2)
- mail order bride definitiom (0)
- mail order bride facts (1)
- mail order bride faq (0)
- mail order bride for real (3)
- mail order bride good idea? (1)
- mail order bride industry (3)
- mail order bride info (0)
- mail order bride legit sites (2)
- mail order bride legit? (1)
- mail order bride pricing (1)
- mail order bride real (1)
- mail order bride real stories (2)
- mail order bride review (2)
- mail order bride review (0)
- mail order bride reviews (2)
- mail order bride service (2)
- mail order bride services definition (1)
- mail order bride sites legitimate (2)
- mail order bride sites reddit (3)
- mail order bride sites review (2)
- mail order bride stories (3)
- mail order bride story (2)
- mail order bride website reviews (1)
- mail order bride websites (2)
- mail order bride websites reddit (1)
- mail order bride websites reviews (1)
- mail order bride wiki (4)
- mail order bride work? (2)
- mail order bride worth it? (2)
- mail order brides (1)
- mail order girlfriend (1)
- mail order sposa informazioni (1)
- mail order wife (3)
- mail order wives (3)
- mail order wives (0)
- mail ordina le informazioni sulla sposa (2)
- mail ordina una sposa (3)
- mail ordre brude anmeldelser (1)
- mail ordre brude definition (2)
- mail ordre brude info (1)
- mail ordre brude websted anmeldelser (1)
- mail ordre brude websteder anmeldelser (1)
- mail ordre brudesider gennemgang (2)
- mail pГҐ bestilling brud (1)
- mail på beställning brud (2)
- mail på beställning brud (0)
- mail til ordre brud (1)
- mail to order bride (1)
- mail-order bride (1)
- Mail-Order-Braut (7)
- Mail-order-bride (3)
- mail-order-brides-statistics free online sites for singles (1)
- Mail. Bride Legit (3)
- maila i ordning brud (2)
- Mailbrautbestellung (6)
- main de username (1)
- main_pt-pt bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- malaysian-women+johor-bahru free online sites for singles (1)
- Mandeville installment loans near me (1)
- mariГ©e par correspondance (16)
- mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance chaude (5)
- mariГ©e par correspondance chaude (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance chaude (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance chaude (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance chaude (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance dГ©finir (3)
- mariГ©e par correspondance dГ©finir (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance dГ©finir (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance en ligne (3)
- mariГ©e par correspondance en ligne (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance en ligne (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance internationale (4)
- mariГ©e par correspondance internationale (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance internationale (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance internationale (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance interraciale (2)
- mariГ©e par correspondance interraciale (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance la plus chaude (2)
- mariГ©e par correspondance la plus chaude (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance lesbienne (2)
- mariГ©e par correspondance lesbienne (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (11)
- mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance pour de vrai (2)
- mariГ©e par correspondance pour de vrai (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance reveiw (3)
- mariГ©e par correspondance reveiw (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance reveiw (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance rГ©elle (8)
- mariГ©e par correspondance rГ©elle (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance rГ©elle (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance rГ©elle (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance rГ©elle (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance rГ©elle (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance rГ©elle (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance rГ©elle (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance wikipedia (4)
- mariГ©e par correspondance wikipedia (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance wikipedia (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance wikipedia (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance Г vendre (2)
- mariГ©e par correspondance Г vendre (0)
- mariГ©e par courrier wikipedia (2)
- mariГ©e par courrier wikipedia (0)
- mariГ©e par la poste d'historique (1)
- Marriage Certificate Requirements (1)
- Marshall online installment loans (1)
- Masalbet (1)
- Mechanicsville online installment loans instant approval (1)
- medelålder för postorderbruden (1)
- meet asian women (1)
- meet women online (1)
- meetme-review free online sites for singles (1)
- meetslavicgirls-review free online sites for singles (1)
- Meilleur endroit pour la mariГ©e par correspondance (2)
- Meilleur endroit pour la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleur endroit pour obtenir la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- Meilleur endroit pour obtenir une mariГ©e par correspondance (2)
- Meilleur endroit pour obtenir une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleur pays de mariГ©e par correspondance (3)
- Meilleur pays de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleur pays de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleur pays pour la mariГ©e par correspondance (2)
- Meilleur pays pour la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleur pays pour la mariГ©e par correspondance Reddit (3)
- Meilleur pays pour la mariГ©e par correspondance Reddit (0)
- Meilleur pays pour la mariГ©e par correspondance Reddit (0)
- Meilleur pays pour trouver la mariГ©e par correspondance (3)
- Meilleur pays pour trouver la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleur pays pour trouver la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleur pays pour trouver une mariГ©e par correspondance (6)
- Meilleur pays pour trouver une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleur pays pour trouver une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleur pays pour trouver une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleur pays pour trouver une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleur pays pour trouver une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleur service de mariГ©e par correspondance (3)
- Meilleur service de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleur service de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (2)
- Meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance reddit (1)
- Meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance rГ©el (1)
- Meilleur site Web de mariГ©e par correspondance (2)
- Meilleur site Web de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleur site Web pour trouver une mariГ©e par correspondance (3)
- Meilleur site Web pour trouver une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleur site Web pour trouver une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleure agence de mariГ©e par correspondance (4)
- Meilleure agence de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleure agence de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleure agence de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleure agence de mariГ©e par correspondance reddit (1)
- Meilleure entreprise de mariГ©e par correspondance (3)
- Meilleure entreprise de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleure entreprise de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleure mariГ©e de la vente par correspondance du site (1)
- Meilleure mariГ©e par correspondance (4)
- Meilleure mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleure mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleure mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleure mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleure mariГ©e par correspondance de tous les temps (4)
- Meilleure mariГ©e par correspondance de tous les temps (0)
- Meilleure mariГ©e par correspondance de tous les temps (0)
- Meilleure mariГ©e par correspondance de tous les temps (0)
- Meilleure mariГ©e par correspondance de tous les temps (0)
- Meilleure Г©pouse de vente par correspondance de rГ©putation (2)
- Meilleure Г©pouse de vente par correspondance de rГ©putation (0)
- Meilleures sociГ©tГ©s de mariГ©es par correspondance (1)
- Meilleurs avis sur les sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- Meilleurs endroits pour la mariГ©e par correspondance (4)
- Meilleurs endroits pour la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleurs endroits pour la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleurs endroits pour la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleurs endroits pour obtenir la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- Meilleurs endroits pour trouver la mariГ©e par correspondance (2)
- Meilleurs endroits pour trouver la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleurs lieux de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- Meilleurs pays de la mariГ©e par correspondance (2)
- Meilleurs pays de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- meilleurs pays pour une mariГ©e par correspondance (6)
- meilleurs pays pour une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- meilleurs pays pour une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- meilleurs pays pour une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- meilleurs pays pour une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- meilleurs pays pour une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleurs sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (2)
- Meilleurs sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleurs sites de mariГ©s par correspondance rГ©el (3)
- Meilleurs sites de mariГ©s par correspondance rГ©el (0)
- Meilleurs sites de mariГ©s par correspondance rГ©el (0)
- Meilleurs sites Web de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (1)
- Meilleurs sites Web de mariГ©es par correspondance reddit (1)
- mejor agencia de pedidos por correo (1)
- mejor correo orden novia agencia reddit (2)
- mejor correo orden sitios web de novias reddit (2)
- mejor correo pedido novia paГs (3)
- mejor correo pedido novia paГs (0)
- mejor correo pedido novia paГs (0)
- mejor lugar para la novia por correo (1)
- mejor lugar para recibir pedidos por correo novia (2)
- mejor lugar para recibir un pedido por correo novia (1)
- mejor novia de pedidos por correo (1)
- mejor orden de correo de la novia (1)
- mejor orden de correo novia (1)
- mejor paГs para encontrar la novia del pedido por correo (5)
- mejor paГs para encontrar la novia del pedido por correo (0)
- mejor paГs para encontrar la novia del pedido por correo (0)
- mejor paГs para encontrar la novia del pedido por correo (0)
- mejor paГs para encontrar una novia por correo (2)
- mejor paГs para encontrar una novia por correo (0)
- mejor paГs para la novia del pedido por correo (3)
- mejor paГs para la novia del pedido por correo (0)
- mejor paГs para la novia del pedido por correo (0)
- mejor paГs para pedidos por correo novia reddit (4)
- mejor paГs para pedidos por correo novia reddit (0)
- mejor paГs para pedidos por correo novia reddit (0)
- mejor paГs para pedidos por correo novia reddit (0)
- mejor reputaciГіn correo orden novia (2)
- mejor reputaciГіn correo orden novia (0)
- mejor sitio de novias de pedidos por correo real (1)
- mejor sitio de novias por correo (3)
- mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (2)
- mejor sitio web para encontrar una novia por correo (0)
- mejores empresas de novias por correo (2)
- mejores lugares para encontrar la novia por correo (2)
- mejores lugares para la novia por correo (2)
- mejores lugares para novias por correo (4)
- mejores lugares para recibir pedidos por correo novia (2)
- mejores paГses de novias por correo (1)
- mejores paГses para una novia por correo (3)
- mejores paГses para una novia por correo (0)
- mejores pedidos por correo de reseГ±as de sitios de novias (3)
- mejores pedidos por correo de reseГ±as de sitios de novias (0)
- mejores pedidos por correo de reseГ±as de sitios de novias (0)
- mejores sitios de novias de pedidos por correo real (4)
- mejores sitios de novias de pedidos por correo real (0)
- mejores sitios para novias por correo (2)
- mejores sitios para novias por correo (0)
- mejores sitios web de novias por correo (2)
- mejores sitios web de novias por correo 2022 (2)
- mejores sitios web de novias por correo legГtimo (3)
- mejores sitios web de novias por correo legГtimo (0)
- mejores sitios web de novias por correo legГtimo (0)
- melhor ordem de correio do site noiva (1)
- Melville online installment loans (1)
- Mental Math benefits (2)
- Mercedes installment loans near me (1)
- Mercedes installment loans online (1)
- MeД‘unarodna narudЕѕba poЕЎte (1)
- MeЕџru bir posta sipariЕџi gelini (2)
- MeЕџru bir posta sipariЕџi gelini (0)
- MeЕџru posta sipariЕџi gelin hizmeti (1)
- MeЕџru posta sipariЕџi gelin hizmetleri (1)
- MeЕџru posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (2)
- MeЕџru posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (0)
- MeЕџru posta sipariЕџi gelin web siteleri (3)
- MeЕџru posta sipariЕџi gelin web siteleri (0)
- MeЕџru posta sipariЕџi gelin web siteleri (0)
- MeЕџru posta sipariЕџi gelini (1)
- MeЕџru posta sipariЕџi gelini sitesi (3)
- MeЕџru posta sipariЕџi gelini sitesi (0)
- MeЕџru posta sipariЕџi gelini sitesi (0)
- Miami guaranteed installment loans for bad credit no credit check (1)
- miglior ordine di posta sposa sito reddit (1)
- miglior ordine postale agenzia sposa reddit (1)
- miglior ordine postale sposa paese (1)
- miglior paese per la sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- miglior paese per trovare la sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- miglior paese per trovare una sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- miglior servizio di sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- miglior sito per corrispondenza sposa (3)
- miglior sito per sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- miglior sito per sposa per corrispondenza reale (3)
- miglior sito web per la sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- miglior sito web per trovare una sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- migliore agenzia sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- migliore compagnia di sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- migliore reputazione per corrispondenza sposa (4)
- migliore sposa per corrispondenza (3)
- migliori compagnie di sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- migliori paesi sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- migliori recensioni per i siti della sposa (2)
- migliori siti di sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- migliori siti web di sposa ordinazione per corrispondenza (1)
- migliori siti web per la sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- migliori vendita per corrispondenza siti web sposa 2022 (1)
- mikä on paras postimyynti morsiamen maa (3)
- mikä on paras postimyynti morsiamen maa (0)
- mikä on paras postimyynti morsiamen maa (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsiamen palvelut (5)
- mikä on postimyynti morsiamen palvelut (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsiamen palvelut (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsiamen palvelut (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsiamen palvelut (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsiamena (1)
- mikä on postimyynti morsian (13)
- mikä on postimyynti morsian (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsian (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsian (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsian (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsian (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsian (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsian (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsian (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsian (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsian (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsian (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsian (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsian? (10)
- mikä on postimyynti morsian? (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsian? (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsian? (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsian? (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsian? (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsian? (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsian? (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsian? (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsian? (0)
- mikä postimyynti morsian (3)
- mikä postimyynti morsian (0)
- mikä postimyynti morsian (0)
- MINDES MINDES Web lokacije. (1)
- Missouri guaranteed installment loans for bad credit direct lenders only (1)
- mistä löydän postimyynti morsiamen (2)
- mistä löydän postimyynti morsiamen (0)
- mistä löytää postimyynti morsiamen (2)
- mistä löytää postimyynti morsiamen (0)
- mistä ostaa postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- mistä ostan postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- mistä saan postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- miten postimyynti morsiamen sivustot toimivat (2)
- miten postimyynti morsian toimii (3)
- Mjesto za mladenku s gornjom poЕЎtom (2)
- Mjesto za mladenku s gornjom poЕЎtom (0)
- mladenka (1)
- mladenka lezbijske poЕЎte (1)
- mladenka s najviЕЎe poЕЎte (1)
- mladenke za mladenke mladenke (2)
- mogli per corrispondenza (1)
- moldova-women+chisinau free online sites for singles (1)
- mongolian-women free online sites for singles (1)
- Monte Vista online installment loans (1)
- Montross guaranteed installment loans for bad credit (1)
- morsiamen maailman postimyynti morsiamet (2)
- morsiamen postimyynti (3)
- morsiamen tilausposti (5)
- mostbet apk (17)
- mostbet az 90 (18)
- Mostbet AZ Casino (4)
- Mostbet Azerbaijan (5)
- Mostbet Bonus Program Code Amnyxlm For National Football League Week 7: $200 Broncos-saints Bonus Amnewyork - 195 (4)
- Mostbet Casino (3)
- Mostbet Casino AZ (1)
- Mostbet Casino Azerbaycan (5)
- Mostbet Casino Review Marketing Promotions, Slots & More" - 812 (4)
- mostbet giriş (12)
- mostbet hungary (1)
- Mostbet in Russia (3)
- Mostbet India (6)
- mostbet italy (1)
- Mostbet kazinosu (3)
- mostbet kirish (1)
- Mostbet kumarhanesi (3)
- Mostbet Online Casino (1)
- mostbet ozbekistonda (2)
- Mostbet Referral Bonus, Get Some Sort Of Free Bonus 2024" - 399 (0)
- mostbet royxatga olish (1)
- mostbet tr (2)
- mostbet uz (7)
- Mostbet UZ Casino (2)
- Mostbet UZ Kirish (5)
- mostbet-ru-serg (13)
- Mount Gilead guaranteed installment loans for bad credit no credit check (1)
- MoЕѕete li naruДЌiti mladenku (1)
- my cash advance payday loans (1)
- my cash now payday loan (2)
- my cash now payday loans (1)
- my cash payday loan (1)
- my payday loan (1)
- my payday loan com (1)
- my payday loans (1)
- Najbolja mjesta za dobivanje mladenke za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (2)
- Najbolja mjesta za dobivanje mladenke za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (0)
- Najbolja mjesta za pronalaЕѕenje mladenke za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (2)
- Najbolja mjesta za pronalaЕѕenje mladenke za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (0)
- Najbolja narudЕѕba poЕЎte (1)
- Najbolja narudЕѕba za mladenke (3)
- Najbolja narudЕѕba za mladenke (0)
- Najbolja narudЕѕba za mladenke (0)
- Najbolja narudЕѕba za mladenku (5)
- Najbolja narudЕѕba za mladenku (0)
- Najbolja narudЕѕba za mladenku (0)
- Najbolja narudЕѕba za mladenku (0)
- Najbolja narudЕѕba za mladenku (0)
- Najbolja narudЕѕba za mladenku Reddit (3)
- Najbolja narudЕѕba za mladenku Reddit (0)
- Najbolja narudЕѕba za mladenku Reddit (0)
- Najbolja web stranica za pronalaЕѕenje mladenke za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (1)
- Najbolja zemlja za mladenku za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (2)
- Najbolja zemlja za mladenku za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (0)
- Najbolja zemlja za pronalaЕѕenje mladenke za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (1)
- Najbolje mjesto za mladenku za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (2)
- Najbolje mjesto za mladenku za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (0)
- Najbolje narudЕѕbe mladenke (2)
- Najbolje narudЕѕbe mladenke (0)
- Najbolje narudЕѕbe za mladenke (3)
- Najbolje narudЕѕbe za mladenke (0)
- Najbolje narudЕѕbe za mladenke (0)
- Najbolje narudЕѕbe za mladenke 2022 (1)
- Najbolje narudЕѕbe za mladenke recenzije (1)
- Najbolje ocijenjene web stranice za mladenke (1)
- Najbolje ocijenjene web stranice za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (3)
- Najbolje ocijenjene web stranice za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (0)
- Najbolje ocijenjene web stranice za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (0)
- Najbolje web stranice za mladenke prave poЕЎte (1)
- Najbolje zemlje za mladenku za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (4)
- Najbolje zemlje za mladenku za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (0)
- najbolje zemlje za mladenku za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (0)
- Najbolje zemlje za mladenku za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (0)
- Najtoplija narudЕѕba poЕЎte (1)
- NajviЕЎe narudЕѕbe zaruДЌnice sjedi (1)
- NarudЕѕba poЕЎte (1)
- NarudЕѕba poЕЎte Dobra ideja? (1)
- NarudЕѕba poЕЎte Legit? (1)
- narudЕѕba poЕЎte mladenka craigslist (3)
- narudЕѕba poЕЎte mladenka craigslist (0)
- narudЕѕba poЕЎte mladenka wiki (2)
- narudЕѕba poЕЎte mladenka wiki (0)
- narudЕѕba poЕЎte mladenka wikipedia (1)
- narudЕѕbe maila za mladenke reddit (1)
- NarudЕѕbe za mladenke (2)
- NarudЕѕbe za mladenke (0)
- NaruДЌite mail mladenku (3)
- NaruДЌite mail mladenku (0)
- NaruДЌite mail mladenku (0)
- NaruДЌivanje poЕЎte FAQ FAQ (2)
- NaruДЌivanje poЕЎte FAQ FAQ (0)
- NaruДЌivanje poЕЎte Legalne stranice mladenke (2)
- NaruДЌivanje poЕЎte Legalne stranice mladenke (0)
- NaruДЌivanje poЕЎte mladenka Real web mjesto (3)
- NaruДЌivanje poЕЎte mladenka Real web mjesto (0)
- NaruДЌivanje poЕЎte mladenka Real web mjesto (0)
- NaruДЌivanje poЕЎte stvarne priДЌe (2)
- NaruДЌivanje poЕЎte stvarne priДЌe (0)
- NaruДЌivanje za mladenku kupon (2)
- NaruДЌivanje za mladenku kupon (0)
- nationaltitleloan guaranteed installment loans for bad credit no credit check (1)
- nationaltitleloan online installment loans (1)
- navegar por correo orden novia (1)
- Ne posta sipariЕџi gelin (3)
- Ne posta sipariЕџi gelin (0)
- near me cash advance (3)
- nearby cash advance (3)
- nearby payday loan (2)
- nearby payday loans (1)
- nearest payday loan near me (1)
- nearest payday loan to me (2)
- nearest payday loans (2)
- nearest payday loans from here (1)
- need a cash advance (1)
- need a cash advance now (3)
- need a loan but not a payday loan (3)
- need a loan not a payday loan (1)
- need a payday loan (1)
- need a payday loan bad credit (2)
- need a payday loan no credit check (1)
- need a payday loan now (2)
- need a payday loan now bad credit (0)
- need a payday loan with no credit check (2)
- need a payday loans (1)
- need cash advance (3)
- need cash no payday loans (2)
- need cash now payday loan (1)
- need payday loan (1)
- need payday loan now (1)
- need payday loan now bad credit (2)
- need payday loans (2)
- need someone to write my essay (0)
- need to be a member cash advance (2)
- need to get a payday loan (2)
- Nevjesta narudЕѕba poЕЎte (1)
- Nevjesta za internetsku poЕЎta (1)
- Nevjesta za narudžbu vruće pošte (1)
- new cash advance (1)
- new payday loan (2)
- new payday loans bad credit (2)
- new payday loans no credit check (1)
- new year payday loan (1)
- News (3)
- next payday loan for bad credit no credit check (1)
- nl+argentinie escort girl here (1)
- nl+australie escort dating platform (1)
- nl+italie escort women (1)
- nl+polen escort girl link (1)
- no credit check advance payday loans (1)
- no credit check bad credit payday loans (3)
- no credit check cash advance lenders (3)
- no credit check cash advance loans (2)
- no credit check cash advance near me (2)
- no credit check cash advance places near me (1)
- no credit check direct deposit payday loans (1)
- no credit check direct lender payday loan (1)
- no credit check direct lender payday loans (1)
- no credit check instant cash advance (1)
- no credit check instant payday loans (2)
- no credit check loan payday (2)
- no credit check no payday loans (2)
- no credit check non payday loan (1)
- no credit check non payday loans (2)
- no credit check payday loan (1)
- no credit check payday loan direct lenders (1)
- no credit check payday loan direct lenders only (1)
- no credit check payday loan lender (1)
- no credit check payday loan lenders (3)
- no credit check payday loan near me (1)
- no credit check payday loans direct lender (2)
- no credit check payday loans lenders only (2)
- no credit check payday loans near me (1)
- no credit check payday loans on line (1)
- no credit check payday low intrest loan (3)
- no+afroromance-anmeldelse topp postordre brud sitter (1)
- no+apent-forhold topp postordre brud sitter (1)
- no+asianfeels-anmeldelse topp postordre brud sitter (1)
- no+australske-bruder topp postordre brud sitter (1)
- no+beste-land-a-finne-en-lojal-kone topp postordre brud sitter (1)
- no+bosniske-kvinner topp postordre brud sitter (1)
- North Dakota guaranteed installment loans for bad credit (1)
- novia de pedidos por correo (4)
- novias extranjeras (1)
- Oak Ridge guaranteed installment loans for bad credit (1)
- Oakland online installment loans (0)
- Ohio online installment loans instant approval (1)
- oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- oikeat postimyynti morsiamen verkkosivustot (1)
- oikeita postimyynti morsiamen tarinoita (2)
- Oklahoma guaranteed installment loans for bad credit direct lenders only (1)
- on postimyynti morsian todellinen (2)
- on postimyynti morsian todellinen asia (1)
- onde eu compro uma noiva por correspondГЄncia (1)
- onedayloan no credit check installment loans (1)
- online (28)
- Online -Mail -Bestellung Braut (3)
- Online Casino (1)
- online casino au (1)
- online dating (1)
- Online Dating First Date Kiss (1)
- online mail order bride (1)
- online mail ordre brud (1)
- online postorder brud (1)
- online postordre brud (1)
- online-postitilaus morsian (1)
- only (15)
- only consumer reports (15)
- only reviews (8)
- or payday loan (1)
- orden de correo de la industria de la novia (2)
- orden de correo de la novia (6)
- orden de correo de las agencias de la novia (3)
- orden de correo de las agencias de la novia (0)
- orden de correo definiciГіn de novia (1)
- orden de correo electrГіnico novia (2)
- orden de correo electrГіnico novia (0)
- orden de correo en lГnea novia (2)
- orden de correo en lГnea novia (0)
- orden de correo historia de la novia (2)
- orden de correo interracial novia (2)
- orden de correo legГtimo novia (4)
- orden de correo legГtimo novia (0)
- orden de correo legГtimo novia (0)
- orden de correo legГtimo novia (0)
- orden de correo lГ©sbico novia (5)
- orden de correo lГ©sbico novia (0)
- orden de correo lГ©sbico novia (0)
- orden de correo lГ©sbico novia (0)
- orden de correo lГ©sbico novia (0)
- orden de correo novia (3)
- orden de correo novia de verdad (2)
- orden de correo novia de verdad? (2)
- orden de correo novia definir (2)
- orden de correo novia vale la pena (3)
- orden de correo novia vale la pena? (3)
- orden de correo real novia (2)
- orden de correo una novia (1)
- ordenar por correo hechos de novia (3)
- ordenar por correo historias de novias (1)
- order an essay cheap (1)
- order essay online cheap (1)
- ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- ordine postale legittimo sposa russa (3)
- ordine postale sposa definire (1)
- ordine postale sposa definizione (3)
- ordine postale sposa legittima (2)
- ordine postale sposa legittima? (1)
- ordini postali recensioni sposa (2)
- ordini postali recensioni sposa (0)
- Ortalama posta sipariЕџi gelin fiyatlarД± (1)
- ostaa postimyynti morsiamen (4)
- ostamalla postimyynti morsiamen (6)
- osterreich+niederosterreich+amstetten escort girls (1)
- osterreich+niederosterreich+amstetten visitors (1)
- osterreich+niederosterreich+baden-bei-wien escort girl link (1)
- osterreich+niederosterreich+brunn-am-gebirge escort buchen (1)
- osterreich+niederosterreich+stockerau escort (1)
- osterreich+niederosterreich+traiskirchen username (2)
- osterreich+niederosterreich+traiskirchen username (0)
- osterreich+niederosterreich+tulln best escort platform (1)
- osterreich+niederosterreich+tulln escort girl (1)
- osterreich+niederosterreich+tulln sign up (1)
- osterreich+niederosterreich+wiener-neustadt nutte buchen (1)
- osterreich+oberosterreich escort girl (1)
- osterreich+oberosterreich+ansfelden escort buchen (1)
- osterreich+oberosterreich+ansfelden sign in (1)
- osterreich+oberosterreich+gmunden best escort platform (1)
- osterreich+oberosterreich+gmunden sign in (1)
- osterreich+oberosterreich+traun escorts (1)
- osterreich+oberosterreich+traun sign in (1)
- osterreich+oberosterreich+vocklabruck escort girl (1)
- osterreich+oberosterreich+wels escort service (1)
- osterreich+salzburg-staat+salzburg support (1)
- osterreich+steiermark+bruck-an-der-mur tips (1)
- osterreich+tirol+hall-in-tirol escort girl (1)
- osterreich+tirol+hall-in-tirol visitors (1)
- osterreich+tirol+kufstein escort near me (1)
- osterreich+vorarlberg nutten finden (1)
- osterreich+vorarlberg+bregenz escort girl here (1)
- osterreich+vorarlberg+bregenz escort girls (1)
- osterreich+vorarlberg+bregenz support (1)
- osterreich+vorarlberg+bregenz tips (1)
- osterreich+wiener-staat best escort platform (1)
- ourtime-review free online sites for singles (1)
- oГ№ acheter une mariГ©e par correspondance (4)
- oГ№ acheter une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- oГ№ acheter une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- oГ№ acheter une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- OГ№ puis-je acheter une mariГ©e par correspondance (6)
- OГ№ puis-je acheter une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- OГ№ puis-je acheter une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- OГ№ puis-je acheter une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- OГ№ puis-je acheter une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- OГ№ puis-je acheter une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- oГ№ puis-je obtenir une mariГ©e par correspondance (6)
- oГ№ puis-je obtenir une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- oГ№ puis-je obtenir une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- oГ№ puis-je obtenir une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- oГ№ puis-je obtenir une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- oГ№ puis-je obtenir une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- oГ№ puis-je trouver une mariГ©e par correspondance (3)
- oГ№ puis-je trouver une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- oГ№ puis-je trouver une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- oГ№ trouver une mariГ©e par correspondance (4)
- oГ№ trouver une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- oГ№ trouver une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- oГ№ trouver une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- pagbet brazil (1)
- panamanian-women free online sites for singles (1)
- paraguay-women+santa-maria site free (1)
- paraguay-women+trinidad free online sites for singles (1)
- paras maa löytää postimyynti morsiamen (9)
- paras maa löytää postimyynti morsiamen (0)
- paras maa löytää postimyynti morsiamen (0)
- paras maa löytää postimyynti morsiamen (0)
- paras maa löytää postimyynti morsiamen (0)
- paras maa löytää postimyynti morsiamen (0)
- paras maa löytää postimyynti morsiamen (0)
- paras maa löytää postimyynti morsiamen (0)
- paras maa löytää postimyynti morsiamen (0)
- paras maa postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- paras maa postimyynti morsiamen reddit (2)
- paras maa postimyynti morsiamen reddit (0)
- paras paikka postimyynti morsiamenelle (2)
- paras paikka saada postimyynti morsiamen (3)
- paras postimyynti morsiamen maa (3)
- paras postimyynti morsiamen palvelu (2)
- paras postimyynti morsiamen sivusto (1)
- paras postimyynti morsiamen verkkosivusto (4)
- paras postimyynti morsiamenvirasto (2)
- paras postimyynti morsiamenvirasto reddit (1)
- paras postimyynti morsiamenyritys (1)
- paras postimyynti morsian (2)
- paras sivustopostitilaus morsian (3)
- paras sivustopostitilaus morsian (0)
- paras todellinen postimyynti morsiamen sivusto (2)
- parhaat legit postimyynti morsiamen verkkosivustot (3)
- parhaat maat postimyynti morsiamen kanssa (2)
- parhaat maat saada postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- parhaat paikat löytää postimyynti morsiamen (3)
- parhaat paikat löytää postimyynti morsiamen (0)
- parhaat paikat löytää postimyynti morsiamen (0)
- parhaat paikat postimyynti morsiamen (2)
- parhaat paikat saada postimyynti morsiamen (5)
- parhaat postimyynti morsiamen paikat (1)
- parhaat postimyynti morsiamen sivustojen arvostelut (2)
- parhaat postimyynti morsiamen verkkosivustot 2022 (3)
- parhaat postimyynti morsiamen verkkosivustot reddit (6)
- parhaat postimyynti morsiamenyritykset (4)
- parhaiten arvioidut postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (6)
- parhaiten arvioitu postimyynti morsiamen palvelu (2)
- Parnu Jk Vaprus Vs Tartu Jk Tammeka Result 2-2 Meistriliiga On 18 September 2024" - 106 (2)
- pay advance and cash advance (3)
- pay cash advance (3)
- pay cash advance loans (2)
- pay cash in advance (2)
- pay for a essay (1)
- pay for an essay (1)
- pay for an essay online (1)
- pay for essay writers (1)
- pay for someone to do my essay (1)
- pay for someone to write an essay (2)
- pay for someone to write essay (1)
- pay for someone to write my essay (1)
- pay payday loan (1)
- pay payday loans (2)
- pay someone to write essay for you (1)
- pay someone to write my essay for me (1)
- pay you to write my essay (1)
- payday advance cash (1)
- payday advance cash america (3)
- payday advance cash loans (3)
- payday advance loan (2)
- payday advance loan near me (1)
- payday advance loans bad (1)
- payday advance loans bad credit (1)
- payday advance loans for bad credit (1)
- payday advance loans near me (2)
- payday advance loans no credit check (2)
- payday advance loans with no credit check (2)
- payday advances loan (0)
- payday advances or payday loans (1)
- payday and cash advance loans (1)
- payday bad credit loan (2)
- payday bad credit loans (3)
- payday bank loans (1)
- payday cash advance bad credit (2)
- payday cash advance for bad credit (1)
- payday cash advance loan (2)
- payday cash advance loan bad credit (2)
- payday cash advance loans com (1)
- payday cash advance loans near me (3)
- payday cash advance near me (3)
- payday cash advance no credit check (1)
- payday cash loan (3)
- payday cash loan advance (1)
- payday cash loans (1)
- payday cash loans bad credit (1)
- payday cash loans with bad credit (1)
- payday in advance loans (1)
- payday instant loans no credit check (1)
- payday istallment loans (2)
- payday loan (1)
- payday loan advance (1)
- payday loan advance near me (3)
- payday loan advances (1)
- payday loan agency no credit check (2)
- payday loan america (1)
- payday loan american (4)
- payday loan at a bank (1)
- payday loan bad credit (1)
- payday loan bad credit loan (2)
- payday loan bad credit no credit check (2)
- payday loan bad credit no credit check direct lender (1)
- payday loan bad credit no credit check near me (2)
- payday loan bad for credit (1)
- payday loan bank (2)
- payday loan banks (3)
- payday loan cash (2)
- payday loan cash advance (4)
- payday loan cash advance near me (3)
- payday loan cash america (1)
- payday loan cash in minutess (1)
- payday loan companies no credit check (1)
- payday loan companies with no credit check (2)
- payday loan company (2)
- payday loan company near me (2)
- payday loan compay in usa (2)
- payday loan creator (2)
- payday loan def (1)
- payday loan direct lender no credit check (1)
- payday loan direct lender only no credit check (0)
- payday loan direct lenders no credit check (2)
- payday loan for (1)
- payday loan for bad credit (2)
- payday loan for bad credit and no credit check (1)
- payday loan for bad credit near me (2)
- payday loan for no credit (2)
- payday loan for terrible credit (3)
- payday loan for very bad credit (1)
- payday loan in (2)
- payday loan in usa (2)
- payday loan interest (1)
- payday loan interest rates? (2)
- payday loan leanders (2)
- payday loan lender no credit check (1)
- payday loan lender only no credit check (2)
- payday loan lenders no credit check (3)
- payday loan lenders no credit check list (2)
- payday loan lenders with no credit check (1)
- payday loan loans (1)
- payday loan near (1)
- payday loan near me bad credit (2)
- payday loan near me no interest (1)
- payday loan nearby (2)
- payday loan nearest me (2)
- payday loan needed (1)
- payday loan new (2)
- payday loan no (3)
- payday loan no broker no credit check (1)
- payday loan no credit (2)
- payday loan no credit check (1)
- payday loan no credit check bad credit (2)
- payday loan no credit check direct lender (1)
- payday loan no credit check direct lenders (3)
- payday loan no credit check instant (1)
- payday loan no credit check instant payout (1)
- payday loan no credit check lender (2)
- payday loan no credit check no bank account (1)
- payday loan no credit check no bank statement (2)
- payday loan no credit check no checking account (0)
- payday loan no credit check or bank account (1)
- payday loan no direct deposit no credit check (3)
- payday loan no hard credit check (2)
- payday loan no interest (1)
- payday loan now (1)
- payday loan now no credit check (1)
- payday loan now with bad credit (2)
- payday loan of america (1)
- payday loan or cash advance (1)
- payday loan organization no credit check (3)
- payday loan payday loans (1)
- payday loan places near me no credit check (2)
- payday loan places no credit check (1)
- payday loan usa (1)
- payday loan what do i need (3)
- payday loan what is payday loan (1)
- payday loan with (1)
- payday loan with bad credit (3)
- payday loan with bad credit and no credit check (2)
- payday loan with bad credit near me (2)
- payday loan with no credit (2)
- payday loan with no credit check (3)
- payday loan with no interest (2)
- payday loan with very bad credit (1)
- payday loan work (2)
- payday loan works (2)
- payday loan? (1)
- payday loans (1)
- payday loans advance (3)
- payday loans advances (5)
- payday loans america (5)
- payday loans and cash (2)
- payday loans and cash advances (2)
- payday loans and credit (1)
- payday loans and how they work (2)
- payday loans are bad (3)
- payday loans as (1)
- payday loans bad cradit? (1)
- payday loans bad credit (1)
- payday loans bad credit advance america (1)
- payday loans bad credit loans and cash advance loans (1)
- payday loans bad credit no credit check (2)
- payday loans bad credit payday loans (1)
- payday loans bad creditt (4)
- payday loans bad for credit (1)
- payday loans bank (3)
- payday loans banks (1)
- payday loans cash (3)
- payday loans cash advance (4)
- payday loans cash advance america (2)
- payday loans cash advance for bad credit (1)
- payday loans cash advance no credit check (2)
- payday loans cash loans (1)
- payday loans cash now (2)
- payday loans com (1)
- payday loans company (1)
- payday loans credit (2)
- payday loans def (1)
- payday loans direct lender bad credit no credit check (1)
- payday loans direct lenders no credit check (5)
- payday loans direct lenders only no credit check (2)
- payday loans direct lenders with no credit check (5)
- payday loans facts (2)
- payday loans finder (2)
- payday loans for (1)
- payday loans for anyone (5)
- payday loans for awful credit (2)
- payday loans for bad credit direct lender no credit check (2)
- payday loans for bad credit loans (1)
- payday loans for bad credit near me (1)
- payday loans for bad credit no credit check (2)
- payday loans for extremely bad credit (1)
- payday loans for fair credit (3)
- payday loans for horrible credit (2)
- payday loans for no credit check (1)
- payday loans for nocredit (1)
- payday loans for usa (1)
- payday loans for very bad credit (2)
- payday loans forbad credit (2)
- payday loans how much interest (0)
- payday loans how they work (1)
- payday loans how to (2)
- payday loans in usa (2)
- payday loans lenders near me no credit check (1)
- payday loans lenders no credit check (0)
- payday loans lenders not brokers no credit check (1)
- payday loans low interest no credit check (1)
- payday loans near me (1)
- payday loans near me bad credit (5)
- payday loans near me for bad credit (3)
- payday loans near me no credit (1)
- payday loans near me no credit check (2)
- payday loans near me no credit check direct payday loans (1)
- payday loans near me no credit check near me (1)
- payday loans near me no credit check no bank account (1)
- payday loans near me with bad credit (2)
- payday loans near me with no credit check (2)
- payday loans nearby (1)
- payday loans neat me (2)
- payday loans need credit (1)
- payday loans new (1)
- payday loans no (3)
- payday loans no bad credit (1)
- payday loans no bank account no credit check (2)
- payday loans no bank account no credit check near me (2)
- payday loans no credit (1)
- payday loans no credit check (1)
- payday loans no credit check direct deposit (4)
- payday loans no credit check direct lender (2)
- payday loans no credit check direct lenders (2)
- payday loans no credit check direct lenders only (3)
- payday loans no credit check instant decision (2)
- payday loans no credit check instant payout (2)
- payday loans no credit check lender (1)
- payday loans no credit check lenders (2)
- payday loans no credit check lenders only (1)
- payday loans no credit check low interest (3)
- payday loans no credit check near me (1)
- payday loans no credit check no checking account (3)
- payday loans no credit check no direct deposit (2)
- payday loans no credit check no lenders (1)
- payday loans no credit check or bank account (5)
- payday loans no credit check places (1)
- payday loans no credit check usa (3)
- payday loans no debit card credit check (2)
- payday loans now (1)
- payday loans now bad credit (1)
- payday loans of america (2)
- payday loans on (1)
- payday loans on bad credit (3)
- payday loans on benefits no credit check (3)
- payday loans only (1)
- payday loans only in cash (2)
- payday loans or bad credit loans (1)
- payday loans or cash advance (1)
- payday loans or cash advances (4)
- payday loans places near me no credit check (2)
- payday loans that work (3)
- payday loans tomorrow (1)
- payday loans usa (2)
- payday loans use passport (1)
- payday loans very bad credit (2)
- payday loans what are (3)
- payday loans what are they (2)
- payday loans what do i need (2)
- payday loans what do you need (3)
- payday loans what is (1)
- payday loans with (3)
- payday loans with bad credit (1)
- payday loans with bad credit near me (2)
- payday loans with bad credit no credit check (1)
- payday loans with no credit (5)
- payday loans with no credit check (3)
- payday loans with no credit check or bank account (1)
- payday loans with no credit check or checking account (3)
- payday loans with no job verification or credit check (3)
- payday loans: (2)
- payday loans? (2)
- payday loans\ (1)
- payday no credit check loan (1)
- payday now cash advance (3)
- payday now loans (2)
- payday usa loan (1)
- payday usa loans (1)
- paydayloanadvance online installment loans no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+abbeville cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+akron nearby payday loans (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+alexander-city cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+allgood nearby payday loans (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+arab cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+argo bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+ariton my payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+ashland how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+babbie how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+baileyton get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+ballplay bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+banks get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+belle-fontaine cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+berlin bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+billingsley my payday loan (0)
- paydayloanalabama.com+birmingham cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+blountsville my payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+blue-ridge how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+bon-secour cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+brantleyville payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+brent how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+brewton payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+bristow-cove no credit check loan payday (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+brook-highland cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+brookside my payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+camp-hill cash advance loans with no credit check (0)
- paydayloanalabama.com+cardiff cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+carolina cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+center-point bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+centre get a cash advance (0)
- paydayloanalabama.com+chunchula cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+citronelle nearby payday loans (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+cleveland payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+clio nearby payday loans (0)
- paydayloanalabama.com+coats-bend cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+coffee-springs cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+coffeeville bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+colony cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+columbiana payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+concord get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+cordova cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+cottondale get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+cottonwood my payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+cowarts my payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+crossville cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+cusseta bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+dadeville cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+daleville payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+delta payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+elkmont payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+elmore cash advance loans with no credit check (0)
- paydayloanalabama.com+eunola how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+evergreen get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+excel payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+fairfield get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+fayette bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+five-points my payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+florala get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+fort-payne get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+frisco-city no credit check loan payday (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+fultondale cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+gainesville payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+geraldine cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+gilbertown get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+goldville my payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+goshen cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+grove-hill cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+gu-win cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+guin payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+gulfcrest get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+guntersville get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+hamilton get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+hatton how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+hazel-green cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+helena bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+highland-lakes my payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+hokes-bluff bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+hollins get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+homewood cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+hytop how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+ivalee no credit check loan payday (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+kellyton get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+kimberly my payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+lincoln bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+littleville bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+lowndesboro nearby payday loans (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+luverne get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+madrid get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+malcolm payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+maplesville payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+marbury payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+maytown how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+mccalla payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+mcintosh my payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+memphis bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+midland-city cash to go and advance america (2)
- paydayloanalabama.com+mignon cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+millbrook cash to go and advance america (2)
- paydayloanalabama.com+millport get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+mobile cash to go and advance america (2)
- paydayloanalabama.com+monroeville no credit check loan payday (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+mooresville get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+morrison-crossroads get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+mountain-brook get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+mulga nearby payday loans (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+munford cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+nances-creek my payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+natural-bridge my payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+new-union payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+newton my payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+newville bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+nixburg payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+north-courtland get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+oak-grove get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+ohatchee cash to go and advance america (2)
- paydayloanalabama.com+oneonta get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+orrville cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+paint-rock get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+pea-ridge get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+pelham cash to go and advance america (2)
- paydayloanalabama.com+pell-city get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+pinckard cash to go and advance america (2)
- paydayloanalabama.com+pine-apple cash to go and advance america (2)
- paydayloanalabama.com+pine-level cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+pine-ridge payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+pinson my payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+point-clear bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+pollard my payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+prichard bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+rainsville payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+ray cash to go and advance america (2)
- paydayloanalabama.com+rosa cash to go and advance america (2)
- paydayloanalabama.com+sand-rock payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+sanford cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+saraland bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+selma payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+shoal-creek get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+shorter payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+sipsey get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+slocomb how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+smoke-rise how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+somerville no credit check loan payday (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+south-vinemont get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+spanish-fort my payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+springville cash to go and advance america (2)
- paydayloanalabama.com+st-florian get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+st-stephens my payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+stapleton payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+sterrett how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+sumiton nearby payday loans (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+sylvania get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+talladega get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+thomaston get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+thomasville cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+tillmans-corner payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+union-springs payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+valley bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+vandiver my payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+vestavia-hills cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+vina my payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+vincent get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+west-point cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+woodstock my payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+yellow-bluff how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+air-force-academy no credit check loan payday (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+alamosa-east get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+amherst bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+arvada bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+avon get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+battlement-mesa get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+berkley get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+black-forest cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+blende get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+bonanza-mountain-estates nearby payday loans (0)
- paydayloancolorado.net+boone my payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+branson bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+brick-center cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+brush cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+burlington payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+calhan get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+capulin cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+carbondale bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+castle-pines-village get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+cattle-creek how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+cedaredge how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+center how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+cherry-creek get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+collbran payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+colona cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+colorado-city get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+cope payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+copper-mountain get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+de-beque get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+deer-trail cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+divide bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+dove-creek get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+eads payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+eaton cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+echo-hills get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+el-jebel cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+eldora payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+empire get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+estes-park nearby payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+evans my payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+evergreen no credit check loan payday (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+fairmount payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+flagler cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+fleming cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+floyd-hill get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+fort-carson payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+fort-garland my payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+fort-lupton no credit check loan payday (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+four-square-mile how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+fowler bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+gardner cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+genesee get cash advance at bank (0)
- paydayloancolorado.net+genoa my payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+georgetown cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+gleneagle cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+granby cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+grand-junction nearby payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+greeley my payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+gunbarrel cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+hartman cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+haswell how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+heeney get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+hidden-lake payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+highlands-ranch nearby payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+hillrose no credit check loan payday (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+hoehne cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+holly-hills no credit check loan payday (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+hooper cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+indian-hills bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+jackson-lake payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+johnstown get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+ken-caryl no credit check loan payday (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+kittredge bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+la-junta-gardens get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+laird nearby payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+lake-city how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+lamar cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+las-animas payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+limon get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+lincoln-park nearby payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+littleton cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+lochbuie get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+loghill-village payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+loma nearby payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+lone-tree get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+longmont cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+mancos bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+manzanola no credit check loan payday (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+matheson my payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+mead my payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+meeker my payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+moffat get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+montrose get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+mount-crested-butte no credit check loan payday (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+mountain-view cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+mountain-village cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+new-castle get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+niwot get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+norwood no credit check loan payday (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+nucla cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+nunn get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+oak-creek get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+olathe get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+ophir cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+orchard-city cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+orchard-mesa cash advance loans with no credit check (0)
- paydayloancolorado.net+padroni get cash advance at bank (0)
- paydayloancolorado.net+pagosa-springs how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+palisade bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+paonia cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+parachute cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+peoria bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+pitkin my payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+placerville get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+poncha-springs bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+ramah nearby payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+rangely payday loan instant funding no credit check (0)
- paydayloancolorado.net+redlands cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+rock-creek-park get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+roxborough-park my payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+saguache cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+san-luis my payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+security-widefield get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+sedalia cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+seven-hills nearby payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+severance no credit check loan payday (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+sheridan get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+sheridan-lake nearby payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+silt bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+silver-plume how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+silverton no credit check loan payday (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+simla payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+snyder payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+st-ann-highlands get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+stepping-stone bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+sterling-ranch cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+strasburg bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+stratton bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+superior payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+tabernash my payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+tall-timber cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+towaoc get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+trail-side cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+upper-bear-creek how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+vilas my payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+walden get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+walsh cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+westminster my payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+windsor payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+woodland-park my payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+woodmoor get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloanmaryland guaranteed installment loans for bad credit no credit check (1)
- paydayloanmaryland.com guaranteed installment loans for bad credit (1)
- paydayloanmaryland.com guaranteed installment loans for bad credit no credit check (1)
- paydayloanmaryland.com installment loans no credit check (1)
- paydayloanmissouri.com installment loans bad credit (1)
- paydayloanmissouri.com personal installment loans (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+baltic no credit check loan payday (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+bantam cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+bigelow-corners my payday loan (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+botsford cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+branchville get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+branford-center cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+bridgeport payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+bridgewater cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+bristol get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+broad-brook payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+candlewood-isle get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+candlewood-knolls cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+candlewood-lake-club payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+cannondale payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+chester-center cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+collinsville nearby payday loans (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+cos-cob bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+coventry-lake no credit check loan payday (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+crystal-lake bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+danbury nearby payday loans (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+darien-downtown cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+dodgingtown cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+falls-village payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+gaylordsville get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+glastonbury-center my payday loan (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+heritage-village get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+indian-field get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+inglenook bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+kensington get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+lakeside-woods my payday loan (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+mansfield-center cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+new-britain get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+new-canaan payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+new-haven my payday loan (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+noank get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+noroton payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+northwest-harwinton how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+norwalk payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+norwich cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+old-saybrook-center get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+oxoboxo-river get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+pemberwick payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+plantsville my payday loan (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+plattsville payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+quasset-lake cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+quinnipiac-university cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+riverton cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+sacred-heart-university payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+saugatuck cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+south-coventry cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+southport get cash advance at bank (0)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+storrs cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+suffield-depot bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+tashua get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+torrington get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+trumbull-center no credit check loan payday (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+wallingford-center payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+wauregan get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloansindiana online installment loans (1)
- paydayloansnc personal installment loans (1)
- paydayloansnc.com installment loans bad credit (1)
- paydayloansohio bad credit installment loans (1)
- paydayloansohio tribal installment loans direct lenders no credit check (1)
- paydayloanssouthcarolina installment loans near me (1)
- paydayloanssouthdakota no credit check installment loans (1)
- paydayloanssouthdakota online installment loans no credit check (1)
- paydayloanstennessee no credit check installment loans (1)
- paydayloantexas bad credit installment loans (1)
- paydayloantexas installment loans no credit check (1)
- paydayloantexas installment loans online (1)
- paydayloantexas personal installment loans (1)
- paydayloanwisconsin online installment loans no credit check (0)
- Pays des mariГ©es par correspondance (8)
- Pays des mariГ©es par correspondance (0)
- Pays des mariГ©es par correspondance (0)
- Pays des mariГ©es par correspondance (0)
- Pays des mariГ©es par correspondance (0)
- Pays des mariГ©es par correspondance (0)
- Pays des mariГ©es par correspondance (0)
- Pays des mariГ©es par correspondance (0)
- pb_aug (3)
- PB_TOP (1)
- Pdc World Darts Championship Odds, Picks: Betting Breakdown Intended For Day 1 - 473 (2)
- pedidos por correo de catГЎlogos de novias (1)
- pedidos por correo de reseГ±as de agencias de novias (1)
- pedidos por correo de reseГ±as de novias (2)
- pedidos por correo de reseГ±as de novias (0)
- pedidos por correo sitios de novias legГtimos (3)
- pedidos por correo sitios de novias legГtimos (0)
- per corrispondenza (4)
- per corrispondenza i siti della sposa reddit (1)
- per corrispondenza la sposa ne vale la pena (2)
- per corrispondenza paesi sposa (1)
- per corrispondenza sposa reale (1)
- per corrispondenza sposa siti web reddit (2)
- per corrispondenza sposa siti web reddit (0)
- per corrispondenza sposa storia (1)
- per corrispondenza sposa storie reddit (2)
- per corrispondenza sposa wikipedia (2)
- per corrispondenza storie di sposi (3)
- personalloancolorado no credit check installment loans (1)
- peruvian-women+laredo site free (1)
- peruvian-women+miramar free online sites for singles (1)
- peruvian-women+vice free online sites for singles (1)
- peruvian-women+vice site free (1)
- Petersburg online installment loans (1)
- petite-single-women free online sites for singles (1)
- Pin UP AZ Casino (1)
- Pin UP AZ Online (1)
- Pin Up Brazil (1)
- pin up casino (5)
- Pin UP Casino AZ (4)
- Pin UP Online AZ (1)
- pinco (1)
- PinUp apk (30)
- pitäisikö minun ostaa postimyynti morsiamen (3)
- pitäisikö minun ostaa postimyynti morsiamen (0)
- pitäisikö minun ostaa postimyynti morsiamen (0)
- pitäisikö minun päivätä postimyynti morsiamen (2)
- pitäisikö minun päivätä postimyynti morsiamen (0)
- Pixbet Cassino (1)
- Pl-steroid (2)
- plinko (1)
- Podaci o narudЕѕbi poЕЎte (3)
- Podaci o narudЕѕbi poЕЎte (0)
- Podaci o narudЕѕbi poЕЎte (0)
- poland escort girl link (1)
- polish dating sites (1)
- polish-brides free online sites for singles (1)
- polish-women+lodz site free (1)
- polish-women+poznan site free (1)
- portuguese-women+anta free online sites for singles (1)
- portuguese-women+beja free online sites for singles (1)
- portuguese-women+beja site free (0)
- portuguese-women+fatima free online sites for singles (1)
- portuguese-women+monsanto free online sites for singles (1)
- posso ottenere una sposa per corrispondenza se sono giГ sposato? (1)
- post brud ordre (3)
- Post in der Bestellung Braut (3)
- Post in der Bestellung Brautkosten (3)
- post-order-brud (4)
- posta dell'ordine della sposa (2)
- Posta Gelin SipariЕџi (1)
- posta in ordine costo sposa (1)
- posta in ordine sposa (2)
- posta per ordinare la sposa (4)
- Posta sipariЕџ gelini nedir? (3)
- Posta sipariЕџ gelini nedir? (0)
- Posta sipariЕџ gelini nedir? (0)
- posta sipariЕџi (5)
- posta sipariЕџi (0)
- posta sipariЕџi (0)
- posta sipariЕџi (0)
- posta sipariЕџi (0)
- posta sipariЕџi eЕџleri (1)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin (2)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin AjanslarД± (3)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin AjanslarД± (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin AjanslarД± (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin AjansД± (1)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin AjansД± Д°ncelemeleri (1)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin ArkadaЕџ Siteleri (2)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin ArkadaЕџ Siteleri (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Bilgileri (3)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Bilgileri (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Bilgileri (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Bilgisi (1)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Bulma (1)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelin buna deДџer (3)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelin buna deДџer (0)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelin buna deДџer (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Craigslist (2)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Craigslist (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin EndГјstrisi (3)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin EndГјstrisi (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin EndГјstrisi (0)
- Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek (1)
- Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek Hikayeler (2)
- Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek Hikayeler (0)
- Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek Site (2)
- Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek Site (0)
- Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçekleri (1)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hikayeleri (4)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hikayeleri (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hikayeleri (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hikayeleri (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hikayesi (3)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hikayesi (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hikayesi (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmeti (2)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmeti (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmetleri Nedir (2)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmetleri Nedir (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmetleri TanД±mД± (3)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmetleri TanД±mД± (0)
- posta sipariЕџi gelin iyi fikir? (1)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin KataloglarД± (2)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin KataloglarД± (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin KataloДџu (4)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin KataloДџu (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin KataloДџu (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin KataloДџu (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Kuponu (1)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Makaleleri (3)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Makaleleri (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Makaleleri (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin NasД±l HazД±rlanД±r (3)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin NasД±l HazД±rlanД±r (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin NasД±l HazД±rlanД±r (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin NasД±l SatД±n AlД±nД±r (3)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin NasД±l SatД±n AlД±nД±r (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin NasД±l SatД±n AlД±nД±r (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin NasД±l YapД±lД±r (4)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin NasД±l YapД±lД±r (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin NasД±l YapД±lД±r (0)
- posta sipariЕџi gelin nasД±l Г§alД±ЕџД±r (2)
- posta sipariЕџi gelin nasД±l Г§alД±ЕџД±r (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin NasД±l Г‡alД±ЕџД±r (1)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Nedir (6)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Nedir (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Nedir (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Nedir (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Nedir (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Nedir (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Reddit NasД±l HazД±rlanД±r (1)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Siteleri (3)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Siteleri (0)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri meЕџru (2)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri meЕџru (0)
- posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri nasД±l Г§alД±ЕџД±r (2)
- posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri nasД±l Г§alД±ЕџД±r (0)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri reddit (1)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Siteleri Д°ncelemesi (1)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin SSS (2)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin SSS (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin TanД±mД± (3)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin TanД±mД± (0)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelin tanД±Еџma sitesi (1)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Tarihi (1)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Web Siteleri (2)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Web Siteleri (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Web Siteleri Д°ncelemeleri (2)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Web Siteleri Д°ncelemeleri (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Web Sitesi (3)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Web Sitesi (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Web Sitesi (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Web Sitesi YorumlarД± (2)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Web Sitesi YorumlarД± (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Wiki (1)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Wikipedia (2)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Wikipedia (0)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelin yasal mД±? (1)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Yasal Siteleri (2)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Yasal Siteleri (0)
- posta sipariЕџi gelin Гјlkeleri (2)
- posta sipariЕџi gelin Гјlkeleri (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Д°ncelemesi (1)
- posta sipariЕџi geline deДџer mi (1)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini (2)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini (0)
- Posta siparişi gelini almak için en iyi yer (1)
- Posta siparişi gelini almak için en iyi ülkeler (2)
- Posta siparişi gelini almak için en iyi ülkeler (0)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini almalД± mД±yД±m (3)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini almalД± mД±yД±m (0)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini almalД± mД±yД±m (0)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini arД±yor (3)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini arД±yor (0)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini arД±yor (0)
- Posta siparişi gelini bulmak için en iyi yerler (2)
- Posta siparişi gelini bulmak için en iyi yerler (0)
- posta siparişi gelini bulmak için en iyi ülke (1)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini bulun (2)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini bulun (0)
- Posta siparişi gelini flört (2)
- Posta siparişi gelini flört (0)
- posta siparişi gelini gerçek bir şey mi (1)
- posta siparişi gelini gerçek mi (2)
- posta siparişi gelini gerçek mi (0)
- posta sipariЕџi gelini gГјvenli mi (1)
- posta siparişi gelini için en iyi yer (1)
- posta siparişi gelini için en iyi yerler (1)
- posta siparişi gelini için en iyi ülke (1)
- posta siparişi gelini için ortalama fiyat (3)
- posta siparişi gelini için ortalama fiyat (0)
- posta siparişi gelini için ortalama fiyat (0)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini nasД±l sipariЕџ edilir (6)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini nasД±l sipariЕџ edilir (0)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini nasД±l sipariЕџ edilir (0)
- posta sipariЕџi gelini nasД±l sipariЕџ edilir (0)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini nasД±l sipariЕџ edilir (0)
- posta sipariЕџi gelini nasД±l yapД±lД±r (2)
- posta sipariЕџi gelini nasД±l yapД±lД±r (0)
- posta sipariЕџi gelini nasД±l Г§alД±ЕџД±r (1)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini nedir (5)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini nedir (0)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini nedir (0)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini nedir (0)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini nedir (0)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini nedir? (3)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini nedir? (0)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini nedir? (0)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini nereden alabilirim (3)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini nereden alabilirim (0)
- Posta siparişi gelini reddit için en iyi ülke (2)
- Posta siparişi gelini reddit için en iyi ülke (0)
- posta sipariЕџi gelini reveiw (2)
- posta sipariЕџi gelini reveiw (0)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini satД±n almak (2)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini satД±n almak (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelini SatД±n AlД±n (3)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelini SatД±n AlД±n (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelini SatД±n AlД±n (0)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini tanД±mlayД±n (1)
- posta sipariЕџi gelini web siteleri reddit (3)
- posta sipariЕџi gelini web siteleri reddit (0)
- posta sipariЕџi gelinin ortalama fiyatД± (1)
- posta sipariЕџi gelinin ortalama maliyeti (1)
- Posta Siparişi Gelinine Göz atın (3)
- Posta Siparişi Gelinine Göz atın (0)
- Posta sipariЕџi karД±sД± (3)
- Posta sipariЕџi karД±sД± (0)
- posta sipariЕџi nereden alД±nД±r (1)
- posta su ordinazione sposa (5)
- posti migliori per la sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- posti morsiamen määritelmän mukaan (2)
- posti morsiamen määritelmän mukaan (0)
- postimyynti (6)
- postimyynti morsiamen (2)
- postimyynti morsiamen agences (2)
- postimyynti morsiamen artikkeleita (1)
- postimyynti morsiamen arvoinen? (4)
- postimyynti morsiamen arvostelu (5)
- postimyynti morsiamen arvostelut (3)
- postimyynti morsiamen craigslist (1)
- postimyynti morsiamen faq (4)
- postimyynti morsiamen historia (1)
- postimyynti morsiamen hyvä idea? (1)
- postimyynti morsiamen keski-ikä (1)
- postimyynti morsiamen keskimääräinen hinta (8)
- postimyynti morsiamen keskimääräinen hinta (0)
- postimyynti morsiamen keskimääräinen hinta (0)
- postimyynti morsiamen keskimääräinen hinta (0)
- postimyynti morsiamen keskimääräinen hinta (0)
- postimyynti morsiamen keskimääräinen hinta (0)
- postimyynti morsiamen keskimääräinen hinta (0)
- postimyynti morsiamen keskimääräinen hinta (0)
- postimyynti morsiamen keskimääräiset kustannukset (2)
- postimyynti morsiamen keskimääräiset kustannukset (0)
- postimyynti morsiamen legit (3)
- postimyynti morsiamen legit? (1)
- postimyynti morsiamen luettelot (2)
- postimyynti morsiamen myytävänä (2)
- postimyynti morsiamen myytävänä (0)
- postimyynti morsiamen oikeita tarinoita (4)
- postimyynti morsiamen palveluiden määritelmä (3)
- postimyynti morsiamen palveluiden määritelmä (0)
- postimyynti morsiamen palveluiden määritelmä (0)
- postimyynti morsiamen palvelut (4)
- postimyynti morsiamen sivusto (2)
- postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (3)
- postimyynti morsiamen sivustot lailliset (1)
- postimyynti morsiamen sivustot reddit (2)
- postimyynti morsiamen tarinoita (5)
- postimyynti morsiamen tiedot (7)
- postimyynti morsiamen todellinen (2)
- postimyynti morsiamen todellinen sivusto (2)
- postimyynti morsiamen todellinen? (1)
- postimyynti morsiamen tosiasiat (1)
- postimyynti morsiamen treffisivusto (2)
- postimyynti morsiamen treffisivustot (2)
- postimyynti morsiamen treffisivustot (0)
- postimyynti morsiamen treffit (2)
- postimyynti morsiamen työ? (3)
- postimyynti morsiamen työ? (0)
- postimyynti morsiamen työ? (0)
- postimyynti morsiamen verkkosivusto (2)
- postimyynti morsiamen verkkosivustojen arvostelut (3)
- postimyynti morsiamen verkkosivustot reddit (1)
- postimyynti morsiamen virastot (1)
- postimyynti morsiamen wiki (3)
- postimyynti morsiamen wikipedia (1)
- postimyynti morsiamenteollisuus (1)
- postimyynti morsiamenvirasto, jolla on paras maine (1)
- postimyynti morsian (11)
- postimyynti morsian (0)
- postimyynti morsian definitiom (1)
- postimyynti morsian määrittele (1)
- postimyynti morsian sen arvoinen (2)
- postimyynti morsian todellinen (1)
- postimyynti vaimo (4)
- postimyynti vaimoja (3)
- postimyynti-morsian (3)
- postitse järjestyksessä morsian (3)
- postitse järjestyksessä morsian (0)
- postitse järjestyksessä morsian (0)
- postitse tilata morsian (3)
- posto migliore per la sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- posto migliore per ricevere la sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- postorder brud (4)
- postorder brud agences (1)
- postorder brud artiklar (2)
- postorder brud bra idé? (1)
- postorder brud bra idГ©? (2)
- postorder brud bra idГ©? (0)
- postorder brud dating (3)
- postorder brud dating webbplats (1)
- postorder brud definition (3)
- postorder brud faq (3)
- postorder brud legit (2)
- postorder brud legit? (3)
- postorder brud legit? (0)
- postorder brud pГҐ riktigt (1)
- postorder brud pГҐ riktigt? (1)
- postorder brud recension (1)
- postorder brud recensioner (1)
- postorder brud reveiw (2)
- postorder brud riktiga historier (5)
- postorder brud till salu (1)
- postorder brud värt det (2)
- postorder brud värt det (0)
- postorder brud verklig (3)
- postorder brud verklig webbplats (1)
- postorder brud värt det (2)
- postorder brud värt det (0)
- postorder brud värt det? (2)
- postorder brud värt det? (0)
- postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- postorder brud webbplatser legitima (2)
- postorder brud webbplatser recensioner (1)
- postorder brud wiki (1)
- postorder brud wikipedia (2)
- postorder brudarbete? (3)
- postorder brudbyråer (1)
- postorder brudbyrГҐ (1)
- postorder brudbyrГҐer (3)
- postorder brudbyrГҐer (0)
- postorder brudbyrГҐer (0)
- postorder brudens datingsajter (1)
- postorder brudens fakta (4)
- postorder brudens webbplats (4)
- postorder brudens webbplats recensioner (1)
- postorder brudens webbplatser reddit (6)
- postorder brudesidor reddit (2)
- postorder brudesidor reddit (0)
- postorder brudhistoria (1)
- postorder brudhistorier (4)
- postorder brudhistorier reddit (1)
- postorder brudindustri (1)
- postorder brudinformation (1)
- postorder brudkataloger (2)
- postorder brudkupong (2)
- postorder brudkupong (0)
- postorder brudländer (2)
- postorder brudländer (0)
- postorder brudtjänst (1)
- postorder brudtjänstdefinition (1)
- postorder fruar (1)
- postordre brud (8)
- postordre brud agences (3)
- postordre brud agentur med det bedste omdГёmme (2)
- postordre brud agentur med det bedste omdГёmme (0)
- postordre brud arbejde? (1)
- postordre brud artikler (1)
- postordre brud dating sider (2)
- postordre brud dating site (5)
- postordre brud dating site (0)
- postordre brud datingside (5)
- postordre brud definere (4)
- postordre brud ekte (4)
- postordre brud ekte historier (2)
- postordre brud ekte nettsted (2)
- postordre brud faq (2)
- postordre brud for ekte (4)
- postordre brud for Г¦gte (3)
- postordre brud for Г¦gte (0)
- postordre brud for Г¦gte (0)
- postordre brud for Г¦gte? (1)
- postordre brud god idГ©? (3)
- postordre brud god idГ©? (0)
- postordre brud god idГ©? (0)
- postordre brud historie (1)
- postordre brud industri (1)
- postordre brud legit? (2)
- postordre brud legitime websteder (2)
- postordre brud nettsted (1)
- postordre brud nettsteder (4)
- postordre brud nettsteder gjennomgang (1)
- postordre brud nettsteder legitime (4)
- postordre brud nettsteder reddit (1)
- postordre brud pГҐ ordentlig? (1)
- postordre brud reveiw (2)
- postordre brud rigtige historier (1)
- postordre brud rigtigt sted (1)
- postordre brud til salgs (1)
- postordre brud tjenester (1)
- postordre brud verdt det (1)
- postordre brud verdt det? (2)
- postordre brud værd? (1)
- postordre brud wiki (2)
- postordre brud wikipedia (2)
- postordre brudarbeid? (1)
- postordre bruddatingsider (3)
- postordre brude anmeldelse (1)
- postordre brude artikler (2)
- postordre brude service (2)
- postordre brude websteder reddit (2)
- postordre brudeanmeldelse (1)
- postordre brudebureauer (1)
- postordre brudebyrГҐ med det beste omdГёmmet (1)
- postordre brudebyrГҐer (2)
- postordre brudebyrГҐer (0)
- postordre brudefakta (2)
- postordre brudefaq (4)
- postordre brudehistorier (1)
- postordre brudekatalog (6)
- postordre brudekatalog (0)
- postordre brudekupong (3)
- postordre brudeland (2)
- postordre brudesider (1)
- postordre brudesider legitime (1)
- postordre brudesider reddit (1)
- postordre brudhistorie (2)
- postordre brudhistorier (1)
- postordre brudindustri (1)
- postordre brudinfo (2)
- postordre brudinformasjon (1)
- postordre brudland (2)
- postordre brudtjeneste (1)
- postordre kone (3)
- postordre koner (2)
- postordre-brud (2)
- postordre-brude (1)
- postordrebrud (2)
- postordrebrud definere (3)
- postordrebruden (3)
- postordrebrudstedet (2)
- postordrev hustruer (2)
- Pouvez-vous commander un mail d'une mariГ©e (3)
- Pouvez-vous commander un mail d'une mariГ©e (0)
- Pouvez-vous commander un mail d'une mariГ©e (0)
- Povijest narudЕѕbe poЕЎte (1)
- PoЕЎta po narudЕѕbi mladenke (3)
- PoЕЎta po narudЕѕbi mladenke (0)
- PoЕЎta po narudЕѕbi mladenke (0)
- PoЕЎta po redoslijedu troЕЎkova mladenke (1)
- PoЕЎta po redu mladenka (1)
- poЕЎta za naruДЌivanje mladenke (1)
- Prava web mjesta za mladenke (2)
- Prave narudЕѕbe za mladenke (1)
- Pravi nalog za mail mladenke priДЌe (1)
- precio promedio de la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- precio promedio de una novia por correo (1)
- precio promedio para la novia del pedido por correo (2)
- precios promedio de las novias por correo (3)
- Pregled narudЕѕbe poЕЎte (2)
- Pregled narudЕѕbe poЕЎte (0)
- Pregled web stranica za mladenke (2)
- prezzi medi per la sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- prezzo medio della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- prezzo medio di una sposa per corrispondenza (4)
- prezzo medio per sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- Primary/Elementary Education (66186)
- prix moyen d'une mariГ©e par correspondance (2)
- prix moyen d'une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- prix moyen pour une mariГ©e par correspondance (4)
- prix moyen pour une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- prix moyen pour une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- prix moyen pour une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Prix ​​moyen de la mariée par correspondance (2)
- Prix ​​moyen de la mariée par correspondance (0)
- Prix ​​moyen pour la mariée par correspondance (4)
- Prix ​​moyen pour la mariée par correspondance (0)
- Prix ​​moyen pour la mariée par correspondance (0)
- Prix ​​moyen pour la mariée par correspondance (0)
- Prix ​​moyens des mariées par correspondance (4)
- Prix ​​moyens des mariées par correspondance (0)
- Prix ​​moyens des mariées par correspondance (0)
- Prix ​​moyens des mariées par correspondance (0)
- PronalaЕѕenje mladenke za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (1)
- PronaД‘ite Mail narudЕѕbe mladenke (1)
- ProsjeДЌna cijena narudЕѕbe poЕЎte (1)
- ProsjeДЌna dob narudЕѕbe poЕЎte (1)
- ProsjeДЌne cijene mladenke (1)
- ProsjeДЌni troЕЎak mladenke za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (1)
- pt-pt+2redbeans-recensao bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+alemanha-mulheres site de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (1)
- pt-pt+america-mulheres site de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (1)
- pt-pt+amolatina-revisao site de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (1)
- pt-pt+amourfeel-revisao bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- pt-pt+asiandate-revisao bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+asianfeels-revisao site de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (1)
- pt-pt+asiatico-mulheres-vs-american-mulheres bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+azerbaijao-mulheres site de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (1)
- pt-pt+belize-mulheres site de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (1)
- pt-pt+boliviana-mulheres site de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (1)
- pt-pt+bulgaro-mulheres site de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (1)
- pt-pt+checheno-mulheres site de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (1)
- pt-pt+cherry-blossoms-revisao site de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (1)
- pt-pt+chispa-revisao site de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (1)
- pt-pt+colombian-cupid-recensao bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+costa-rica-mulheres bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+cupid-com-recensao bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+escandinava-mulheres bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+escocesa-mulheres bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+mingle2-revisao bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+mulheres-arabes-quentes bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+mulheres-canadenses-vs-mulheres-americanas site de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- pt-pt+mulheres-chinesas-quentes bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+mulheres-eslovacas-quentes site de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (1)
- pt-pt+mulheres-finlandesas-quentes bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+mulheres-georgianas-quentes site de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (1)
- pt-pt+mulheres-indianas-quentes bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+mulheres-quentes-do-tajiquistao bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+mulheres-quentes-do-uzbequistao bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+mulheres-quentes-uruguai bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+mulheres-solteiras-com-criancas bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+noivas-checas bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+norueguesa-mulheres bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+positive-singles-recensao bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+quente-afro-mulheres bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+quente-azerbaijao-mulheres bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+quente-bogota-mulheres bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+quente-chechen-mulheres bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+quente-colombiana-mulheres bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+quente-jordanian-mulheres bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+romancetale-revisao bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+romena-noivas bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+sofiadate-recensao bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+tajiquistao-mulheres bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+turco-namoro-sites-e-apps bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- puedes enviar por correo a una novia (2)
- Puis-je obtenir une mariГ©e par correspondance si je suis dГ©jГ mariГ©e? (3)
- Puis-je obtenir une mariГ©e par correspondance si je suis dГ©jГ mariГ©e? (0)
- Puis-je obtenir une mariГ©e par correspondance si je suis dГ©jГ mariГ©e? (0)
- puoct (1)
- puoi spedire una sposa (4)
- PU_aug (4)
- pГҐ jakt etter ekteskap (4)
- pГҐ jakt etter ekteskap (0)
- pГҐ jakt etter ekteskap (0)
- pГҐ jakt etter ekteskap (0)
- pГҐ udkig efter en postordrebrud (1)
- pГҐ udkig efter Г¦gteskab (2)
- pГҐ udkig efter Г¦gteskab (0)
- Qu'est-ce qu'une mariГ©e par correspondance (8)
- Qu'est-ce qu'une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Qu'est-ce qu'une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Qu'est-ce qu'une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Qu'est-ce qu'une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Qu'est-ce qu'une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Qu'est-ce qu'une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Qu'est-ce qu'une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Qu'est-ce qu'une mariГ©e par correspondance? (7)
- Qu'est-ce qu'une mariГ©e par correspondance? (0)
- Qu'est-ce qu'une mariГ©e par correspondance? (0)
- Qu'est-ce qu'une mariГ©e par correspondance? (0)
- Qu'est-ce qu'une mariГ©e par correspondance? (0)
- Qu'est-ce qu'une mariГ©e par correspondance? (0)
- Qu'est-ce qu'une mariГ©e par correspondance? (0)
- Qu'est-ce qu'une mariГ©e. (2)
- Qu'est-ce qu'une mariГ©e. (0)
- Qu'est-ce que la mariГ©e par correspondance (10)
- Qu'est-ce que la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Qu'est-ce que la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Qu'est-ce que la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Qu'est-ce que la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Qu'est-ce que la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Qu'est-ce que la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Qu'est-ce que la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Qu'est-ce que la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Qu'est-ce que la mariГ©e par correspondance? (11)
- Qu'est-ce que la mariГ©e par correspondance? (0)
- Qu'est-ce que la mariГ©e par correspondance? (0)
- Qu'est-ce que la mariГ©e par correspondance? (0)
- Qu'est-ce que la mariГ©e par correspondance? (0)
- Qu'est-ce que la mariГ©e par correspondance? (0)
- Qu'est-ce que la mariГ©e par correspondance? (0)
- Qu'est-ce que la mariГ©e par correspondance? (0)
- Qu'est-ce que la mariГ©e par correspondance? (0)
- Qu'est-ce que la mariГ©e par correspondance? (0)
- Qu'est-ce que la mariГ©e par correspondance? (0)
- Qu'est-ce que les services de mariГ©e par correspondance (6)
- Qu'est-ce que les services de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Qu'est-ce que les services de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Qu'est-ce que les services de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Qu'est-ce que les services de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Qu'est-ce que les services de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- qual ГЁ il miglior paese della sposa per corrispondenza (7)
- qual ГЁ il miglior paese della sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- qual ГЁ il miglior paese della sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- qual ГЁ il miglior paese della sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- qual ГЁ il miglior paese della sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- qual ГЁ il miglior paese della sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- qual ГЁ il miglior paese della sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- qual ГЁ il miglior servizio di sposa per corrispondenza (3)
- qual ГЁ il miglior servizio di sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- qual ГЁ il miglior servizio di sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- qual ГЁ il miglior sito per sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- qual ГЁ il miglior sito per sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- qual ГЁ la sposa per corrispondenza? (2)
- qual ГЁ la sposa per corrispondenza? (0)
- quality singles site login (13)
- que es como la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- que es el servicio de novias por correo (3)
- que es el servicio de novias por correo (0)
- que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- que es novia de pedidos por correo (1)
- que es una novia de pedidos por correo (8)
- que noiva por correspondГЄncia (1)
- que novia de orden de correo (1)
- Quel est le meilleur pays de mariГ©e par correspondance (2)
- Quel est le meilleur pays de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Quel est le meilleur service de mariГ©e par correspondance (7)
- Quel est le meilleur service de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Quel est le meilleur service de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Quel est le meilleur service de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Quel est le meilleur service de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Quel est le meilleur service de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Quel est le meilleur service de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (2)
- Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- quelle est une mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- Quels sont les meilleurs sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- quicken loans cash advance (4)
- quicken loans payday loans (2)
- quicken payday loans (1)
- quickest cash advance (1)
- quickest cash advance com (1)
- quickest payday loan (1)
- quickest payday loan com (0)
- quickest payday loans (3)
- quickloan payday loan (1)
- quickpay payday loans (2)
- quiero una novia por correo (2)
- Real Mail bestellen Braut Site (5)
- Real Mail bestellen Brautwebsite (1)
- Real Mail narudЕѕbe mladenke web stranice (1)
- real mail order bride (3)
- real mail order bride sites (1)
- real mail order bride stories (2)
- real mail order bride website (2)
- real no credit check payday loans (1)
- real no credit check payday loans direct lender (2)
- real payday loan lenders no credit check (4)
- real payday loans no credit check (0)
- real singles site (8)
- real singles site review (9)
- recensione sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- recensioni del sito web della sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- recensioni di siti web per corrispondenza (4)
- recensioni per corrispondenza agenzia sposa (2)
- Recenzije web stranica za mladenke (3)
- reddit per corrispondenza legittima (2)
- reddit per corrispondenza legittima (0)
- review (12)
- reviews (9)
- revisiГіn de la novia por correo (2)
- revisiГіn de la novia por correo (0)
- revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (2)
- revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (0)
- Revue de la mariГ©e par correspondance (2)
- Revue de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Revue des sites des mariГ©es par correspondance (2)
- Revue des sites des mariГ©es par correspondance (0)
- Revues de l'agence par courrier Г©lectronique (2)
- Revues de l'agence par courrier Г©lectronique (0)
- Richmond installment loans near me (1)
- ricky casino australia (1)
- riktig postorder brud (3)
- riktiga postorder brud webbplatser (2)
- riktiga postorder brudens webbplatser (3)
- Rock Springs no credit check installment loans (1)
- Rokubetbetbet_aug (1)
- romanian-dating-sites-and-apps free online sites for singles (1)
- romanian-women+alexandria free online sites for singles (1)
- romanian-women+amara site free (1)
- romanian-women+bucharest site free (1)
- romanian-women+cluj-napoca free online sites for singles (1)
- romanian-women+constanta site free (1)
- romanian-women+deva free online sites for singles (1)
- romanian-women+iasi site free (1)
- romanian-women+siria free online sites for singles (1)
- rotujenvälinen postimyynti morsian (2)
- rotujenvälinen postimyynti morsian (0)
- russian mail order brides (1)
- russian-brides free online sites for singles (1)
- russian-women site free (1)
- russian-women+belgorod free online sites for singles (1)
- russian-women+chita free online sites for singles (1)
- russian-women+kazan free online sites for singles (1)
- russian-women+kemerovo free online sites for singles (1)
- russian-women+magnitogorsk free online sites for singles (1)
- russian-women+maykop free online sites for singles (0)
- russian-women+pskov free online sites for singles (1)
- russian-women+smolensk free online sites for singles (1)
- russian-women+sochi free online sites for singles (1)
- russian-women+tolyatti free online sites for singles (1)
- s+models+cz-south-bohemian+ceske-budejovice+squirting username (1)
- s+models+de-hh+hamburg tips (1)
- s+models+fr-brittany+rennes tips (1)
- s+models+fr-nouvelle-aquitaine+bordeaux tips (1)
- s+models+gb-england+liverpool visitors (1)
- s+models+it-emilia-romagna+parma tips (1)
- s+models+nl tips (1)
- s+models+nl visitors (1)
- safe payday loans no credit check (5)
- Salen installment loans near me (1)
- Sallisaw guaranteed installment loans for bad credit no credit check (1)
- salvadorian-women free online sites for singles (1)
- sann historia om postorderbruden (1)
- sann historie om postordrebruden (1)
- sann postorder brud (2)
- schweiz+aargau visitors (1)
- schweiz+aargau+brugg escort girl here (1)
- schweiz+aargau+brugg escort service (1)
- schweiz+aargau+zofingen escort girl (1)
- schweiz+appenzell-innerrhoden nutte buchen (1)
- schweiz+appenzell-innerrhoden sign in (1)
- schweiz+basel-landschaft+binningen escort girls (1)
- schweiz+basel-landschaft+binningen support (1)
- schweiz+basel-landschaft+liestal sign up (1)
- schweiz+basel-landschaft+munchenstein escorts (1)
- schweiz+basel-landschaft+mutenz escort service (1)
- schweiz+basel-landschaft+mutenz username (1)
- schweiz+basel-landschaft+oberwil escort girl (1)
- schweiz+basel-landschaft+oberwil username (1)
- schweiz+basel-landschaft+pratteln username (1)
- schweiz+basel-landschaft+reinach visitors (1)
- schweiz+freiburg escort girls (1)
- schweiz+freiburg support (1)
- schweiz+freiburg username (1)
- schweiz+freiburg+freiburg escort (1)
- schweiz+jura escort (1)
- schweiz+kanton-bern escort girl (1)
- schweiz+kanton-bern+bern support (1)
- schweiz+kanton-bern+bern tips (1)
- schweiz+kanton-bern+biel-bienne visitors (1)
- schweiz+kanton-bern+langenthal escort girl (1)
- schweiz+kanton-bern+langenthal tips (1)
- schweiz+kanton-bern+muri-bei-bern visitors (1)
- schweiz+kanton-bern+ostermundigen visitors (1)
- schweiz+kanton-genf+genf escort service (1)
- schweiz+kanton-glarus nutten buchen (1)
- schweiz+kanton-schwyz+einsiedeln sign in (1)
- schweiz+kanton-schwyz+ferienbach sign in (1)
- schweiz+kanton-solothurn escort girls (1)
- schweiz+kanton-solothurn+solothurn best escort platform (1)
- schweiz+kanton-solothurn+solothurn escort (1)
- schweiz+kanton-solothurn+solothurn support (1)
- schweiz+kanton-zug escort (1)
- schweiz+kanton-zug+baar escort girl link (1)
- schweiz+kanton-zug+baar nutten buchen (1)
- schweiz+luzern-stadt escort girl (1)
- schweiz+luzern-stadt username (1)
- schweiz+luzern-stadt+emmen escort (1)
- schweiz+luzern-stadt+emmen tips (1)
- schweiz+luzern-stadt+kriens sign up (1)
- schweiz+luzern-stadt+luzern escort buchen (1)
- schweiz+neuchatel escorts (1)
- schweiz+neuchatel+neuchatel visitors (1)
- schweiz+nidwalden escort girl (1)
- schweiz+schaffhausen-state+schaffhausen support (1)
- schweiz+st-gallen-zustand escort girl link (1)
- schweiz+st-gallen-zustand+buchs tips (1)
- schweiz+st-gallen-zustand+gossau sign in (1)
- schweiz+st-gallen-zustand+gossau username (1)
- schweiz+tessin escort girl (1)
- schweiz+tessin+lugano escort girl (1)
- schweiz+thurgau+arbon tips (1)
- schweiz+thurgau+kreuzlingen escort (1)
- schweiz+thurgau+kreuzlingen escort service (1)
- schweiz+thurgau+kreuzlingen support (1)
- schweiz+thurgau+romanshorn escorts (1)
- schweiz+thurgau+romanshorn sign up (1)
- schweiz+waadt escort near me (1)
- schweiz+waadt visitors (1)
- schweiz+waadt+lausanne escorts (1)
- schweiz+waadt+lausanne nutte buchen (1)
- schweiz+wallis tips (1)
- schweiz+wallis+monthey sign up (1)
- schweiz+zurich-kanton+adliswil sign up (1)
- schweiz+zurich-kanton+affoltern-am-albis nutten finden (1)
- schweiz+zurich-kanton+bassersdorf username (1)
- schweiz+zurich-kanton+dubendorf nutte buchen (1)
- schweiz+zurich-kanton+effretikon visitors (1)
- schweiz+zurich-kanton+hinwil escort near me (1)
- schweiz+zurich-kanton+hinwil username (2)
- schweiz+zurich-kanton+hinwil username (0)
- schweiz+zurich-kanton+kusnacht escort girl here (1)
- schweiz+zurich-kanton+meilen escorts (1)
- schweiz+zurich-kanton+pfaffikon visitors (1)
- schweiz+zurich-kanton+thalwil tips (1)
- schweiz+zurich-kanton+uster escort (1)
- schweiz+zurich-kanton+uster escort girl (1)
- schweiz+zurich-kanton+wallisellen escorts (1)
- schweiz+zurich-kanton+wetzikon visitors (1)
- schweiz+zurich-kanton+winterthur best escort platform (1)
- schweiz+zurich-kanton+winterthur username (1)
- secret-benefits-review free online sites for singles (1)
- secure payday loans no credit check (1)
- secured payday loans no credit check (1)
- selaa postimyynti morsiamen (2)
- Seneca bad credit installment loans (0)
- Seneca online installment loans instant approval (1)
- serbian-women+padina free online sites for singles (1)
- serbian-women+toba free online sites for singles (1)
- service (10)
- Service de mariГ©e de commande par correspondance lГ©gitime (1)
- Service de mariГ©e par correspondance (4)
- Service de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Service de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Service de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Service de mariГ©e par correspondance la mieux notГ©e (3)
- Service de mariГ©e par correspondance la mieux notГ©e (0)
- Service de mariГ©e par correspondance la mieux notГ©e (0)
- Service de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (1)
- Service de mariГ©e par correspondance rГ©el (6)
- Service de mariГ©e par correspondance rГ©el (0)
- Service de mariГ©e par correspondance rГ©el (0)
- Service de mariГ©e par correspondance rГ©el (0)
- Service de mariГ©e par correspondance rГ©el (0)
- services (15)
- Services de mariГ©e par correspondance (2)
- Services de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Services de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (2)
- Services de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- Services de mariГ©e par correspondance supГ©rieures (3)
- Services de mariГ©e par correspondance supГ©rieures (0)
- Services de mariГ©e par correspondance supГ©rieures (0)
- servicio de novia de pedidos por correo mejor calificado (3)
- servicio de novia de pedidos por correo real (3)
- servicio de novias de pedidos por correo legГtimo (1)
- servicio de novias por correo (2)
- servicio de novias por correo legГtimo (4)
- servicio de novias por correo legГtimo (0)
- servicio de novias por correo legГtimo (0)
- servicio de novias por correo legГtimo (0)
- servicios de novias de orden de correo superior (4)
- servicios de novias por correo (1)
- servicios de novias por correo legГtimo (1)
- servicios de novias por correo legГtimo (0)
- Servis mladenke s najviЕЎim ocijenjenim narudЕѕbama (1)
- servizio di sposa per corrispondenza legittimo (3)
- sex (6)
- sex site (10)
- sexy (9)
- shaadi-review free online sites for singles (1)
- Shiraz, Fars, Ir Climate Region, Monthly Averages, Historic Weather Data - 491 (4)
- short term cash advance no credit check (1)
- short term payday loans no credit check (1)
- should i buy a mail order bride (3)
- SIGNIFICES DE MAILLE (4)
- silverdaddies-review free online sites for singles (1)
- silversingles-review free online sites for singles (1)
- simplycashadvance.net+1000-dollar-payday-loan how to get a cash advance loan (1)
- simplycashadvance.net+borrow-money-online-instantly payday loans banks (1)
- simplycashadvance.net+borrow-money-online-instantly short payday loans no credit check (1)
- simplycashadvance.net+chime-loans what are good payday loan company (1)
- simplycashadvance.net+direct-deposit-loans what are good payday loan company (1)
- simplycashadvance.net+fast-payday-loans short payday loans no credit check (1)
- simplycashadvance.net+flex-loans short payday loans no credit check (1)
- simplycashadvance.net+get-a-personal-loan-with-no-credit-history what are good payday loan company (1)
- simplycashadvance.net+law-school-loans cash advance no credit check loan (1)
- simplycashadvance.net+legitimate-online-loans payday loan needed (1)
- simplycashadvance.net+loans-for-550-credit-score cash loan payday advance (0)
- simplycashadvance.net+loans-for-immigrants bad credit payday cash loan (1)
- simplycashadvance.net+loans-for-pensioners what are good payday loan company (1)
- simplycashadvance.net+no-teletrack-payday-loans payday loans banks (1)
- simplycashadvance.net+online-personal-loans-with-co-signer advance cash payday loans (1)
- simplycashadvance.net+payday-loans-for-self-employed payday cash advance loans near me (1)
- simplycashadvance.net+same-day-personal-loans payday cash advance loans near me (1)
- simplycashadvance.net+same-day-personal-loans payday loan needed (1)
- singapore-women free online sites for singles (1)
- single (10)
- single site (8)
- single-women-without-children free online sites for singles (1)
- singleasiangirls-review free online sites for singles (1)
- singles (9)
- singles site (6)
- singles sites (8)
- singles website (13)
- SipariЕџ Gelin NasД±l Posta YapД±lД±r (1)
- site (7)
- Site de la mariГ©e par correspondance des dix premiers (6)
- Site de la mariГ©e par correspondance des dix premiers (0)
- Site de la mariГ©e par correspondance des dix premiers (0)
- Site de la mariГ©e par correspondance des dix premiers (0)
- Site de la mariГ©e par correspondance des dix premiers (0)
- Site de la mariГ©e par correspondance des dix premiers (0)
- site de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (4)
- site de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- site de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- site de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- Site de mariГ©e par correspondance rГ©el (3)
- Site de mariГ©e par correspondance rГ©el (0)
- Site de mariГ©e par correspondance rГ©el (0)
- site de rencontres par courrier Г©lectronique (3)
- site de rencontres par courrier Г©lectronique (0)
- site de rencontres par courrier Г©lectronique (0)
- site for people (13)
- site free (6)
- site singles only (10)
- site Web de la mariГ©e par correspondance (5)
- site Web de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- site Web de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- site Web de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- site Web de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- site Web de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (2)
- site Web de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- sites (24)
- sites de mariГ©e par correspondance les mieux notГ©s (2)
- sites de mariГ©e par correspondance les mieux notГ©s (0)
- sites de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (4)
- sites de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- sites de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- sites de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- sites de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime reddit (6)
- sites de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime reddit (0)
- sites de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime reddit (0)
- sites de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime reddit (0)
- sites de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime reddit (0)
- sites de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime reddit (0)
- sites de mariГ©e par correspondance reddit (2)
- sites de mariГ©e par correspondance reddit (0)
- sites de mariГ©e par courrier lГ©gitime (6)
- sites de mariГ©e par courrier lГ©gitime (0)
- sites de mariГ©e par courrier lГ©gitime (0)
- sites de mariГ©e par courrier lГ©gitime (0)
- sites de mariГ©e par courrier lГ©gitime (0)
- sites de mariГ©e par courrier lГ©gitime (0)
- sites de mariГ©e par courrier par correspondance (2)
- sites de mariГ©e par courrier par correspondance (0)
- sites de mariГ©es par correspondance (5)
- sites de mariГ©es par correspondance (0)
- sites de mariГ©es par correspondance (0)
- sites de mariГ©es par correspondance (0)
- sites de mariГ©es par correspondance (0)
- sites de mariГ©s par correspondance rГ©els (1)
- sites de rencontres par courrier Г©lectronique (3)
- sites de rencontres par courrier Г©lectronique (0)
- sites de rencontres par courrier Г©lectronique (0)
- sites for adults (6)
- sites for free (13)
- sites for people (14)
- sites for professionals (5)
- sites for singles (28)
- sites free (5)
- sites in usa (12)
- sites lГ©gitimes de mariГ©e par correspondance (6)
- sites lГ©gitimes de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- sites lГ©gitimes de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- sites lГ©gitimes de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- sites lГ©gitimes de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- sites lГ©gitimes de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Sites Web de la mariГ©e par correspondance (5)
- sites Web de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- sites Web de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- sites Web de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- sites Web de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- sites Web de la meilleure vente par correspondance (1)
- Sites Web de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (3)
- Sites Web de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- Sites Web de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- Sites Web de mariГ©e par correspondance Reddit (4)
- Sites Web de mariГ©e par correspondance Reddit (0)
- Sites Web de mariГ©e par correspondance Reddit (0)
- Sites Web de mariГ©e par correspondance Reddit (0)
- Sites Web de mariГ©es par correspondance (2)
- Sites Web de mariГ©es par correspondance (0)
- siti di incontri per sposa per corrispondenza (3)
- siti di sposa legittimi per corrispondenza (2)
- siti di sposa per corrispondenza piГ№ votati (1)
- siti web di sposa legittimi per corrispondenza (2)
- siti web per corrispondenza (2)
- sitio de citas de novias por correo (1)
- sitio de la novia de orden de correo legГtimo (1)
- sitio de la novia de orden de correo superior (2)
- sitio de la novia de pedidos por correo real (1)
- sitio web de la novia de pedidos por correo (1)
- sitio web de la novia de pedidos por correo real (2)
- sitio web legГtimo de la novia por correo (2)
- sitio web legГtimo de la novia por correo (0)
- sitios de citas de novias por correo (4)
- sitios de novias de orden de correo superior (1)
- sitios de novias de pedidos por correo legГtimo (6)
- sitios de novias de pedidos por correo legГtimo (0)
- sitios de novias de pedidos por correo legГtimo (0)
- sitios de novias de pedidos por correo legГtimo (0)
- sitios de novias de pedidos por correo legГtimo (0)
- sitios de novias de pedidos por correo legГtimo (0)
- sitios de novias de pedidos por correo real (6)
- sitios de novias mejor calificados (2)
- sitios de novias por correo (1)
- sitios de novias por correo de leggit (2)
- sitios legГtimos de novias por correo (3)
- sitios legГtimos de novias por correo (0)
- sitios legГtimos de novias por correo (0)
- sitios web de novias de orden de correo superior (2)
- sitios web de novias de pedidos por correo legГtimo (6)
- sitios web de novias de pedidos por correo legГtimo (0)
- sitios web de novias de pedidos por correo legГtimo (0)
- sitios web de novias de pedidos por correo legГtimo (0)
- sitios web de novias de pedidos por correo legГtimo (0)
- sitios web de novias por correo (4)
- sito della sposa per corrispondenza reale (1)
- sito della sposa per corrispondenza superiore (2)
- sito reale sposa per corrispondenza (3)
- sito web della sposa per corrispondenza (5)
- sito web della sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- sito web della sposa per corrispondenza legittima (1)
- ska jag träffa en postorderbrud (2)
- ska jag träffa en postorderbrud (0)
- skal jeg gГҐ ut med en postordrebrud (2)
- skal jeg gГҐ ut med en postordrebrud (0)
- skulle jeg kjГёpe en postordrebrud (2)
- slot (1)
- slovakian-women+lucky free online sites for singles (1)
- slovenian-women free online sites for singles (1)
- slovenian-women+lucky free online sites for singles (1)
- So bestellen Sie eine Mail -Bestellung Braut (2)
- So bestellen Sie eine russische Mail -Bestellung Braut (4)
- So bestellen Sie Versandbestellbraut (1)
- So datieren Sie eine Versandbestellbraut (1)
- So erstellen Sie eine Versandbestellung Braut Reddit (1)
- So kaufen Sie eine Mail -Bestellung Braut (2)
- So machen Sie eine Mail -Bestellung Braut (2)
- So maile die Braut beenden Bestellung (2)
- Sober living (1)
- SociГ©tГ©s de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (5)
- SociГ©tГ©s de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- SociГ©tГ©s de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- SociГ©tГ©s de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- SociГ©tГ©s de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- sofiadate-review free online sites for singles (1)
- Software development (1)
- Soll ich eine Versandungsbraut kaufen (1)
- someone to write an essay for me (1)
- someone to write my essay for me (1)
- someone who can write my essay (4)
- someone write my essay (1)
- South West City bad credit installment loans (1)
- south-africa escort women (1)
- spanish-women+guadalajara free online sites for singles (1)
- spanish-women+mao free online sites for singles (1)
- spanish-women+rubi free online sites for singles (1)
- speedycashloan.net+300-dollar-payday-loan what are good payday loan company (1)
- speedycashloan.net+bad-credit-line-of-credit payday loan needed (1)
- speedycashloan.net+borrow-money-online-instantly advance cash payday loans (1)
- speedycashloan.net+checking-account-with-bad-credit payday cash advance loans near me (1)
- speedycashloan.net+disability-payday-loans payday loan needed (1)
- speedycashloan.net+edd-card-cash-advance payday loan needed (1)
- speedycashloan.net+high-risk-loans payday loan needed (1)
- speedycashloan.net+loan-for-vacation bad credit payday cash loan (1)
- speedycashloan.net+loans-for-bad-credit short payday loans no credit check (1)
- speedycashloan.net+loans-for-immigrants cash advance no credit check loan (1)
- speedycashloan.net+loans-with-instant-bank-verification payday loans banks (1)
- speedycashloan.net+parent-loans payday loan needed (1)
- speedycashloan.net+payday-advance-app cash advance no credit check loan (1)
- speedycashloan.net+payday-loans-with-no-checking-account what are good payday loan company (1)
- speedycashloan.net+payday-loans-with-savings-account payday cash advance loans near me (1)
- speedycashloan.net+same-day-personal-loans payday loan needed (1)
- speedycashloan.net+small-payday-loans what are good payday loan company (1)
- speedycashloan.net+student-loans short payday loans no credit check (1)
- speedycashloan.net+student-loans-without-co-signer payday cash advance loans near me (1)
- speedycashloan.net+variable-rate-loans payday loans banks (1)
- speedycashloan.net+web-cash-loans cash advance no credit check loan (1)
- sposa interrazziale per corrispondenza (1)
- sposa lesbica per corrispondenza (4)
- sposa mondo per corrispondenza spose (2)
- sposa per corrispondenza (9)
- sposa per corrispondenza calda (2)
- sposa per corrispondenza legittima (5)
- sposa per corrispondenza per davvero (1)
- sposa per corrispondenza piГ№ calda (2)
- sposa per corrispondenza piГ№ calda (0)
- Springhill installment loans near me (1)
- stable-index.com (1)
- Steamboat Springs guaranteed installment loans for bad credit (1)
- steroid (65)
- steroid-de (3)
- steroid-irl (1)
- steroid-us (1)
- storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- storia mail ordina sposa (1)
- storie di sposa per corrispondenza (6)
- storie di sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- storie di sposa per corrispondenza vera (2)
- strane mladenke (2)
- Suchen Sie eine Mail -Bestellung Braut (4)
- Suchen Sie eine Versandbestellbraut (6)
- sugar dating (1)
- sugar dating review (1)
- Sumter online installment loans (0)
- suosituimmat postimyynti morsiamen verkkosivustot (3)
- sv+albanska-brudar topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+amerikanska-kvinnor-mot-utlandska-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+asianbeautydating-recension topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+asianladyonline-recension topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (0)
- sv+benaughty-recension topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+dream-singles-recension topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (0)
- sv+eharmony-recension topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+ensamstaende-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+fdating-recension topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+findeuropeanbeauty-recension topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+fling-com-recension topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+franska-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+franska-kvinnor-mot-amerikanska-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+grekiska-dejting-webbplatser-och-appar topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+heta-chilenska-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+heta-egyptiska-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (0)
- sv+heta-iranska-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+heta-irlandska-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+heta-kanadensiska-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+heta-pakistanska-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+heta-paraguay-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+heta-polish-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+heta-ryska-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+heta-tjetjenska-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+hur-man-far-en-postorder-brud topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+islandska-brudar topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+japanska-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (0)
- sv+kambodjanska-brudar topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+kanadensiska-kvinnor-mot-amerikanska-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+kubanska-brudar topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+latin-woman-date-recension topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+malaysiska-brudar topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+mexikanska-brudar topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+mexikanska-dejting-webbplatser-och-appar topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+mogna-ensamstaende-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+norska-brudar topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+osteuropeiska-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+panamanska-brudar topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+phrendly-recension topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+positive-singles-recension topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+silverdaddies-recension topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+skotsk-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+spanska-brudar topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+svenska-dejting-webbplatser-och-appar topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+svenska-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+theluckydate-recension topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+tjeckiska-brudar topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+tunisiska-brudar topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+venezuelanska-brudar topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+vitryssland-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- swedish-women+trelleborg free online sites for singles (1)
- sweet bonanza (1)
- sweet bonanza TR (1)
- swiss-women free online sites for singles (1)
- swiss-women+zurich free online sites for singles (1)
- swoonbrides.net amourfeel Comment faire une mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- swoonbrides.net da+bedste-postordrebrude-sider bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- swoonbrides.net da+charmdate bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- swoonbrides.net da+vietnamesiske Г¦gte mail ordre brude websteder (1)
- swoonbrides.net de+heiseste-turkische-frauen Wie funktioniert die Mail -Bestellung Braut? (1)
- swoonbrides.net de+indische-braute Mail-Order-Braut (1)
- swoonbrides.net de+indonesische-braute Bester Mail -Bestellung Brautservice (1)
- swoonbrides.net de+lustige-romantik Wie funktioniert die Mail -Bestellung Braut? (1)
- swoonbrides.net de+mexikanische-braute Bester Mail -Bestellung Brautservice (1)
- swoonbrides.net de+romantik-touren Bester Mail -Bestellung Brautservice (1)
- swoonbrides.net de+thai-braute Wie funktioniert die Mail -Bestellung Braut? (1)
- swoonbrides.net de+turkische-braute Bester Mail -Bestellung Brautservice (0)
- swoonbrides.net es+como-obtener-un-novia-por-correo-si-quieres-una-esposa-perfecta mejor orden de correo novia (1)
- swoonbrides.net es+mejores-sitios-novia-por-correo mejor orden de correo novia (1)
- swoonbrides.net es+novia-por-correo-historias-de-exito agencia de novias por correo (1)
- swoonbrides.net es+novias-peruanas que es como la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- swoonbrides.net es+novias-suecas que es como la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- swoonbrides.net es+novias-turcas mejor orden de correo novia (1)
- swoonbrides.net es+novias-ucranianas que es como la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- swoonbrides.net es+romance-tours-latin-america que es como la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- swoonbrides.net fi+aasialainen legit postimyynti morsiamen sivustot reddit (1)
- swoonbrides.net fi+filippiinilaiset legit postimyynti morsiamen sivustot reddit (1)
- swoonbrides.net fi+indonesian-morsiamet etsi minulle postimyynti morsian (1)
- swoonbrides.net fi+kiinalaiset-morsiamet postimyynti morsian (1)
- swoonbrides.net fi+latvialaiset-morsiamet postimyynti morsian (1)
- swoonbrides.net fi+loytaa-ulkomainen-tyttoystava postimyynti morsian (1)
- swoonbrides.net fi+miten-aloittaa-online-treffikeskustelu postimyynti morsian (1)
- swoonbrides.net it+brasiliano trova una sposa (1)
- swoonbrides.net it+charmdate trova una sposa (1)
- swoonbrides.net it+donne-straniere-per-il-matrimonio trova una sposa (1)
- swoonbrides.net it+incontrare-ragazze-slave il posto migliore per ottenere una sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- swoonbrides.net it+le-ragazze-asiatiche-piu-calde trova una sposa (1)
- swoonbrides.net it+quanto-costa-sposare-una-filippina trova una sposa (1)
- swoonbrides.net it+spose-brasiliane trova una sposa (1)
- swoonbrides.net it+spose-peruviane trova una sposa (1)
- swoonbrides.net it+spose-ucraine il posto migliore per ottenere una sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- swoonbrides.net no+amerikanske-vs-asiatiske-kvinner hva er en postordrebrud (1)
- swoonbrides.net no+hotteste-asiatiske-jenter ekte postordre brud nettsted (1)
- swoonbrides.net no+hotteste-utenlandske-kvinner hva er en postordrebrud (1)
- swoonbrides.net pt+noivas-indianas correio em ordem noiva (1)
- swoonbrides.net pt+noivas-peruanas correio em ordem noiva (1)
- swoonbrides.net pt+noivas-venezuelanas correio em ordem noiva (1)
- swoonbrides.net pt+sites-de-namoro-brasileiros correio em ordem noiva (0)
- swoonbrides.net tours-damour-philippines Comment faire une mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- swoonbrides.net tr+kolombiya-tanisma-siteleri Posta siparişi gelini bulmak için en iyi yerler (1)
- swoonbrides.net tr+polonya-arkadaslik-sitesi Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Д°ncelemeleri (1)
- swoonbrides.net tr+posta-siparisi-gelinler-yasal Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Д°ncelemeleri (1)
- swoonbrides.net tr+sicak-yabanci-kadinlar Posta siparişi gelini bulmak için en iyi yerler (1)
- swoonbrides.net tr+slav-kizlarla-tanisin Posta siparişi gelini bulmak için en iyi yerler (1)
- swoonbrides.net tr+ukrayna Gelin Posta SipariЕџi (1)
- sähköpostitilaus morsian (1)
- SД±cak Posta SipariЕџi Gelin (1)
- SД±rada Posta Gelin (6)
- SД±rada Posta Gelin (0)
- SД±rada Posta Gelin (0)
- SД±rada Posta Gelin (0)
- SД±rada Posta Gelin (0)
- SД±rada Posta Gelin (0)
- SД±rada Posta Gelin TanД±mД± (2)
- SД±rada Posta Gelin TanД±mД± (0)
- SД±rayla gelin maliyeti (1)
- taiwanese-women free online sites for singles (1)
- Tarih Posta SipariЕџi Gelin (2)
- Tarih Posta SipariЕџi Gelin (0)
- tennesseetitleloans guaranteed installment loans for bad credit direct lenders only (1)
- thai women for marriage (1)
- thai-brides free online sites for singles (1)
- thai-women+pattaya free online sites for singles (1)
- thaiflirting-review free online sites for singles (1)
- the mail order bride (4)
- the mail order bride (0)
- theluckydate-review free online sites for singles (1)
- things to know when a (11)
- tips for a (3)
- todellinen postimyynti morsiamen palvelu (3)
- todellinen postimyynti morsiamen sivusto (3)
- Top -bewertete Versandauftragsbrautseiten (1)
- Top -bewertete Versandauftragsbrautservice (2)
- Top -Mail -Bestellung Braut (2)
- Top -Mail -Bestellung Braut Site (3)
- Top -Mail -Bestellung Braut sitzt (1)
- Top -Mail -Bestellung Brautlender (3)
- Top -Mail -Bestellung Brautseiten (2)
- Top -Mail -Bestellung Brautseiten. (3)
- Top -Mail -Bestellung Brautwebsites (2)
- Top -Mail -Brautnetz bestellen (4)
- Top 10 des sites de mariГ©es par correspondance (2)
- Top 10 des sites de mariГ©es par correspondance (0)
- Top 10 Mail -Bestellung Braut (4)
- Top 10 Mail bestellen Brautwebsites (3)
- Top 10 Mail narudЕѕbe mladenke (1)
- top 10 mail order bride (4)
- top 10 mail order bride sites (4)
- top 10 orden de correo novia (1)
- top 10 postordre brudesider (1)
- top 10 postordrebrud (1)
- Top 10 sites Web de mariГ©es par correspondance (2)
- Top 10 sites Web de mariГ©es par correspondance (0)
- top 10 sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- Top 10 Versandbestellbraut -Sites (1)
- Top 10 web mjesta za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (1)
- Top 10 web stranica za mladenke (1)
- top 5 postordre brudesider (1)
- Top 5 sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (3)
- Top 5 sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Top 5 sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Top 5 Versandbestellbraut -Sites (3)
- Top 5 web mjesta za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (1)
- Top Bride Mail. (2)
- top dating sites (1)
- top dating sites reviews (1)
- Top deset narudЕѕbe za mail mladenke Webites (1)
- Top dix marins de la vente par correspondance webite (3)
- Top Mail Bride Commande Web (6)
- top mail bride order web (1)
- top mail brudbeställningswebb (1)
- top mail brudbeställningswebb (1)
- Top Mail Command Bride Site (6)
- top mail order bride countries (0)
- Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- top mail order bride site (3)
- top mail order bride sits (1)
- top mail order bride websites (1)
- top rated mail order bride service (1)
- top rated mail order bride sites (2)
- Top Ten Mail bestellen Braut (1)
- Top Ten Mail bestellen Braut Site (5)
- top ten mail order bride site (2)
- top ten mail order bride webites (1)
- top ten per corrispondenza sito sposa (1)
- top ten per corrispondenza sposa webite (2)
- top ti postordre brudewebitter (1)
- topp 10 postorder brud (1)
- topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- topp 10 postorder brudens webbplatser (3)
- topp 10 postordre brud nettsteder (7)
- topp 5 postorder brudesidor (3)
- topp ordre brud (4)
- topp ordre brud nettsteder (5)
- topp ordre brudland (2)
- topp post brudebestillingsnett (2)
- topp postorder brud (1)
- topp postorder brud sitter (1)
- topp postorder brud webbplats (3)
- topp postorder brudens webbplatser (4)
- topp postorder brudländer (1)
- topp postorder brudtjänster (1)
- topp postorder brudtjänster (1)
- topp postordre brud nettsteder. (2)
- topp postordre brud sitter (1)
- topp ti postordre brud nettsteder (2)
- topp ti postordre brudeside (1)
- topp tio postorder brud webbplats (2)
- topppost beställning brudar webbplatser. (1)
- topprangerte postordrebrudesider (1)
- tosi postimyynti morsiamen tarinoita (2)
- tosi postimyynti morsian (3)
- tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (2)
- tr+2redbeans-inceleme Гњst Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmetleri (0)
- tr+ada-kadinlar Гњst Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmetleri (1)
- tr+amerikan-kadinlar-vs-yabanci-kadinlar Гњst Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmetleri (1)
- tr+arjantinli-gelinler Гњst Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmetleri (1)
- tr+jswipe-inceleme Gerçek Posta Siparişi Gelin (1)
- tr+kismia-inceleme Гњst Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmetleri (1)
- tr+kolombiyali-gelinler Гњst Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmetleri (1)
- tr+kolombiyali-kadin Gerçek Posta Siparişi Gelin (1)
- tr+koreli-gelinler Гњst Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmetleri (1)
- tr+latinfeels-inceleme Гњst Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmetleri (1)
- tr+letonyali-gelinler Гњst Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmetleri (1)
- tr+letonyali-kadinlar Гњst Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmetleri (1)
- tr+loveswans-inceleme Гњst Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmetleri (1)
- tr+meetnicerussian-inceleme Гњst Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmetleri (1)
- tr+moldova-kadinlar Гњst Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmetleri (1)
- tr+ourtime-inceleme Гњst Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmetleri (1)
- tr+rubrides-inceleme Гњst Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmetleri (1)
- tr+sicak-arap-kadinlar Гњst Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmetleri (1)
- tr+sicak-danimarkali-kadinlar Гњst Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmetleri (1)
- Travail des mariГ©es par correspondance? (4)
- Travail des mariГ©es par correspondance? (0)
- Travail des mariГ©es par correspondance? (0)
- Travail des mariГ©es par correspondance? (0)
- Trouver la mariГ©e par correspondance (6)
- Trouver la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Trouver la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Trouver la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Trouver la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Trouver la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- trouver une mariГ©e (6)
- trouver une mariГ©e (0)
- trouver une mariГ©e (0)
- trouver une mariГ©e (0)
- trouver une mariГ©e (0)
- trouver une mariГ©e (0)
- Trouver une mariГ©e par correspondance (3)
- Trouver une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Trouver une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Trouvez-moi une mariГ©e par correspondance (4)
- Trouvez-moi une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Trouvez-moi une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Trouvez-moi une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- trova la sposa per corrispondenza (4)
- trova una sposa per corrispondenza (4)
- trovami una sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- trovare una sposa per corrispondenza (3)
- true mail order bride (1)
- true mail order bride stories (1)
- true story of mail order bride (2)
- tryfansme.com onlyfans girl (1)
- tryfansme.com+category+asmr onlyfans (1)
- tryfansme.com+category+asmr onlyfans girl (1)
- tryfansme.com+category+bbc onlyfans girl (1)
- tryfansme.com+category+blowjob onlyfans girl (1)
- tryfansme.com+category+cosplay onlyfans girl (1)
- tryfansme.com+category+famous best onlyfans (1)
- tryfansme.com+category+fetish onlyfans women (1)
- tryfansme.com+category+fitness onlyfans women (1)
- tryfansme.com+category+hairy onlyfans girl here (1)
- tryfansme.com+category+milf onlyfans link (1)
- tryfansme.com+category+skinny onlyfans women (1)
- tryfansme.com+category+top onlyfans (1)
- tryfansme.com+category+voyeur onlyfans girls (1)
- tryfansme.com+category+xxx onlyfans link (1)
- udenlandske brude (1)
- uk (5)
- UluslararasД± Posta SipariЕџi Gelin (1)
- una novia legГtima por correo (1)
- una novia por correo (3)
- una sposa legittima per corrispondenza (1)
- una sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- Uncategorized (37)
- une mariГ©e par correspondance (3)
- une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Une mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (7)
- Une mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- Une mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- Une mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- Une mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- Une mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- Une mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- us cash advance loan company (3)
- us payday loan company (2)
- usa cash advance (1)
- usa cash advance loan (1)
- usa cash advance loans (1)
- usa cash payday loans (2)
- usa credit payday loans (1)
- usa payday loan (1)
- usa payday loan company (4)
- usa payday loan yor (1)
- usa payday loans (1)
- utenlandske bruder (1)
- Vacherie online installment loans (1)
- vad är den bästa postorderbrudwebbplatsen (1)
- vad är en postorderbrud (4)
- vad är en postorderbrud (0)
- vad är en postorderbrud (0)
- vad är en postorderbrud (0)
- vad är en postorderbrud? (1)
- vad är som postorder brud (1)
- vad en postorder brud (1)
- vad är den bästa postorderbrudtjänsten (1)
- vad är den bästa postorderbrudwebbplatsen (1)
- vad Г¤r en postorderbrud (7)
- vad Г¤r en postorderbrud (0)
- vad Г¤r en postorderbrud (0)
- vad Г¤r en postorderbrud (0)
- vad Г¤r en postorderbrud (0)
- vad Г¤r en postorderbrud (0)
- vad Г¤r en postorderbrud (0)
- vad Г¤r postorder brud (5)
- vad Г¤r postorder brud (0)
- vad Г¤r postorder brud (0)
- vad Г¤r postorder brud (0)
- vad Г¤r postorder brud (0)
- vad Г¤r postorderbruden? (2)
- vad Г¤r postorderbruden? (0)
- vad Г¤r som postorder brud (2)
- vad Г¤r som postorder brud (0)
- vale la pena la novia por correo (2)
- Valencia bad credit installment loans (1)
- Valencia online installment loans instant approval (1)
- Van Wert online installment loans instant approval (1)
- var hittar jag en postorderbrud (1)
- var kan jag fГҐ en postorderbrud (1)
- var kan jag hitta en postorderbrud (4)
- var man hittar en postorderbrud (1)
- var man kan köpa en postorderbrud (1)
- vendita per corrispondenza servizi per la sposa (6)
- vendita per corrispondenza siti sposa legittimi (1)
- vendita per corrispondenza sposa siti legittimi (2)
- vendita per corrispondenza sposa storie vere (3)
- vendita sposa incontri (1)
- vera sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- verdadera orden de correo novia (2)
- verde casino hungary (1)
- verde casino poland (1)
- veri e propri siti di sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- verklig postorder brudtjänst (2)
- verklig postorder brudtjänst (0)
- vero servizio di sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- Versandbestellbraut definitiom (1)
- Versandbestellbraut kaufen (1)
- Versandbestellbraut wert? (3)
- Versandbestellung Frau (3)
- Versandbraut durchsuchen (1)
- Versandbraut fГјr echte (1)
- vieraat morsiamet (1)
- viisi parasta postimyynti morsiamen sivustoa (3)
- voglio una sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- voinko saada postimyynti morsiamen, jos olen jo naimisissa? (1)
- voitko tilata morsiamen postitse (1)
- voltprofit.org (1)
- vrijedi li mladenka poЕЎte (1)
- vulkan vegas DE (5)
- vulkan vegas DE login (5)
- VulkanVegas Poland (3)
- VГ©ritable mariГ©e par correspondance (4)
- VГ©ritable mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- VГ©ritable mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- VГ©ritable mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Wagoner guaranteed installment loans for bad credit no credit check (1)
- Wahre Geschichte der Versandbestellung Braut (3)
- wahre Mail -Bestellung Brautgeschichten (2)
- want (9)
- want app (9)
- want app review (9)
- want reviews (9)
- want site (8)
- want site review (10)
- want site reviews (1)
- Warrensburg guaranteed installment loans for bad credit direct lenders only (1)
- Was fГјr eine Mail -Bestellung Braut (3)
- Was fГјr eine Mail -Bestellung Braut (0)
- Was fГјr eine Mail -Bestellung Braut (0)
- Was ist die beste Mail -Bestellung Braut. (1)
- Was ist die beste Versandungsbestellung Brautland (1)
- Was ist die Braut von Versandungsbestellungen? (2)
- Was ist die Versandbraut? (3)
- Was ist eine Mail -Bestellung Braut (7)
- Was ist eine Mail -Bestellung Braut? (4)
- Was ist eine Mail-Order-Braut (1)
- Was sind die besten Mail -Bestellbraut -Sites (2)
- Waukesha no credit check installment loans (0)
- Wauwatosa no credit check installment loans (1)
- web mjesto za mladenku za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (1)
- web stranica za dobru narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (3)
- web stranica za dobru narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (0)
- web stranica za dobru narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (0)
- Web stranice mladenke s najviЕЎe poЕЎte (2)
- Web stranice mladenke s najviЕЎe poЕЎte (0)
- Web stranice za mladenke (1)
- Web stranice za mladenke Reddit (5)
- Web za narudЕѕbu s najviЕЎe poЕЎte (1)
- website (4)
- websites (10)
- websites free (14)
- websites to pay for an essay (1)
- wha is cash advance (1)
- whar is a payday loan? (1)
- what a mail order bride (2)
- what a payday loan (0)
- what a payday loan is (1)
- what are a payday loan (1)
- what are cash advance (1)
- what are good payday loan company (2)
- what are payday advance loans (2)
- what are payday loan (1)
- what are payday loans (1)
- what are payday loans and how do they work (0)
- what are payday loans used for (1)
- what are payday loans? (2)
- what are payday loans\ (2)
- what are payday loans\ (0)
- what are the payday loans (1)
- what bank can i go to for cash advance (2)
- what banks do cash advance (1)
- what banks do payday loans? (3)
- what can you get payday loans for (2)
- what can you use payday loans for (1)
- what cash advance (1)
- what cash in advance (1)
- what do i need for a cash advance (3)
- what do i need for a payday loan (2)
- what do i need for cash advance (2)
- what do i need for payday loan (1)
- what do i need to get a cash advance (1)
- what do i need to get a payday loan (1)
- what do i need to get a payday loan? (3)
- what do i need to get payday loan (1)
- what do tou need for a payday loan (3)
- what do you need for a cash advance (1)
- what do you need for a payday advance loan (1)
- what do you need for a payday loan (4)
- what do you need for cash advance (1)
- what do you need for payday loan (1)
- what do you need for payday loans (1)
- what do you need to do a payday loan (3)
- what do you need to do a payday loan? (2)
- what do you need to get a cash advance (2)
- what do you need to get a cash advance loan (1)
- what do you need to get a payday loan (1)
- what do you need to get payday loan (2)
- what do you pay on a payday loan (3)
- what i need for a payday loan (1)
- what i need for payday loan (1)
- what i need to get a payday loan (3)
- what is a bank cash advance (2)
- what is a bank lobby cash advance (2)
- what is a cash advance (1)
- what is a cash advance apex (0)
- what is a cash advance at a bank (1)
- what is a cash advance loan (2)
- what is a cash advance loan? (1)
- what is a cash advance? (3)
- what is a good payday loan company (1)
- what is a mail order bride (2)
- what is a mail order bride? (1)
- what is a mail-order bride (1)
- what is a payday advance loan (2)
- what is a payday advance loans (1)
- what is a payday loan (1)
- what is a payday loan company (1)
- what is a payday loan? (3)
- what is advance america cash advance (1)
- what is advance cash (1)
- what is an cash advance (3)
- what is an cash advance loan (1)
- what is an payday loan (1)
- what is an payday loans (3)
- what is as mail order bride (2)
- what is bank cash advance (1)
- what is cash advance loan (1)
- what is interest cash advance (4)
- what is mail order bride services (1)
- what is mail order bride? (1)
- what is mail-order bride (1)
- what is my payday loan (2)
- what is needed for a payday loan (1)
- what is needed for payday loan (1)
- what is needed to get a cash advance (1)
- what is payday advance loans (1)
- what is payday loan company (2)
- what is payday loan usa (1)
- what is the best mail order bride country (1)
- what is the best mail order bride service (1)
- what is the best mail order bride site (3)
- what is the mail order bride? (1)
- what payday loans (1)
- what you need for a payday loan (2)
- what you need for cash advance (2)
- what you need for payday loan (3)
- what you need to get a payday loan (1)
- what's a cash advance (1)
- what's a cash advance loan (2)
- what's a mail order bride (1)
- what's cash advance? (4)
- what's meen cash advance (4)
- what's my cash advance limit? (1)
- what's needed for cash advance (2)
- what's needed for payday loan (1)
- what's needed to get a payday loan (1)
- what's payday loan (2)
- what's payday loan? (2)
- whats a cash advance (1)
- whats a cash advance loan (2)
- whats a cash advance? (1)
- whats a mail order bride (2)
- whats a mail order bride? (2)
- whats cash advance (2)
- whats interest cash advance (1)
- whats meen cash advance (3)
- whats needed for a payday loan (1)
- whats needed for cash advance (1)
- whats payday loans (1)
- when and where you get payday loan (1)
- where can i get a bad credit payday loan (3)
- where can i get a cash advance loan (2)
- where can i get a cash advance near me (2)
- where can i get a cash advance with bad credit (3)
- where can i get a mail order bride (1)
- where can i get a payday loan (2)
- where can i get a payday loan near me (2)
- where can i get a payday loan near me? (3)
- where can i get a payday loan with bad credit (1)
- where can i get a payday loan? (2)
- where can i get cash advance (3)
- where can i get cash advance? (2)
- where can i get my payday loan (2)
- where can i get payday loans near me (3)
- where can i go to get a cash advance (2)
- where can i go to get a payday loan (1)
- where can i have cash advance? (1)
- where can i use cash advance (2)
- where can you get a payday loan? (1)
- where can you get payday loans (2)
- where did payday loans come from (1)
- where do i buy a mail order bride (2)
- where do i get a payday loan (2)
- where do you get payday loans (1)
- where get cash advance (3)
- where get payday loans (3)
- Where Is Mostbet Lawful? All Available Mostbet States 2024 - 513 (1)
- Where Is Mostbet Legal? All Available Mostbet States 2024 - 697 (4)
- where is the nearest payday loan (2)
- where to buy a mail order bride (1)
- where to cash advance (2)
- where to do a cash advance (1)
- where to do cash advance (2)
- where to find a mail order bride (1)
- where to get a cash advance (2)
- where to get a payday loan (3)
- where to get a payday loan near me (1)
- where to get cash advance (1)
- where to get payday loan (1)
- where to get payday loan near me (3)
- where to get payday loans (1)
- where to go for cash advance (1)
- which payday loan (2)
- which payday loans (2)
- who do cash advance (1)
- who do payday loans (2)
- who does payday loans (1)
- who does payday loans near me (2)
- who is cash advance america (1)
- who is cash advance loans (2)
- who is cash advance? (3)
- who needs payday loans (1)
- who use payday loan (1)
- who uses payday loans (4)
- who uses payday loans and why (2)
- whst do i need for a payday loan (1)
- whta is a cash advance (1)
- why advance cash (1)
- why and where you get payday loan (1)
- why are payday loans popular (2)
- why are payday loans so popular (2)
- why get a cash advance (4)
- why get a payday loan (3)
- why get payday loans (4)
- why is a payday loan bad (1)
- Wie funktionieren Versandbestellbraut -Sites? (3)
- Wie funktioniert die Mail -Bestellung Braut? (3)
- Wie funktioniert die Versandbraut, Braut zu bestellen? (4)
- Wie funktioniert die Versandbraut, die Braut funktioniert? (1)
- Wie funktioniert eine Versandbestellung Braut (2)
- wie man beauftragte Braut (1)
- wie man eine Braut bestellt (2)
- Wie man eine Versandbestellbraut heiratet (4)
- wife finder (1)
- Wiki de la mariГ©e par correspondance (6)
- Wiki de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Wiki de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Wiki de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Wiki de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Wiki de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- wikipedia correo orden novia (2)
- Wikipedia Mail -Bestellung Braut (1)
- wikipedia mail order bride (10)
- wikipedia mail ordre brud (1)
- Wikipedia Posta SipariЕџi Gelin (2)
- Wikipedia Posta SipariЕџi Gelin (0)
- wikipedia postimyynti morsian (5)
- wikipedia postorder brud (4)
- wikipedia postorder brud (0)
- wikipedia postordrebrud (1)
- Willacoochee guaranteed installment loans for bad credit (1)
- Wo finde ich eine Mail -Bestellung Braut (4)
- Wo kann ich eine Versandungsbraut bekommen? (1)
- Wo kann man eine Versandbestellbraut finden (2)
- Wo kann man eine Versandbestellbraut kaufen (1)
- Woodland bad credit installment loans (1)
- Woodstock online installment loans (1)
- worldbrides.org amourfeel-anmeldelser bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- worldbrides.org asiatisk bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- worldbrides.org de+auf-die-schwarze-liste-gestellte-dating-sites Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- worldbrides.org de+bravodate-test Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- worldbrides.org de+chinesische-alleinstehende-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- worldbrides.org de+colombialady-test Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- worldbrides.org de+daterussiangirl-test Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- worldbrides.org de+easternhoneys-test Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- worldbrides.org de+estnische-alleinstehende-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- worldbrides.org de+europa Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- worldbrides.org de+heis-russian-brides Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- worldbrides.org de+heise-chinesische-braute Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- worldbrides.org de+heise-japanische-braute Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- worldbrides.org de+heise-mexico-braute Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- worldbrides.org de+heise-neuseelandische-braute Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- worldbrides.org de+heise-thai-braute Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- worldbrides.org de+katalogheirat-betrug Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- worldbrides.org de+kissrussianbeauty-test Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- worldbrides.org de+neuseelaender-alleinstehende-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- worldbrides.org de+norwegische-braute Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- worldbrides.org de+ozeanien Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- worldbrides.org de+russian-brides Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- worldbrides.org de+schwedische-braute Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- worldbrides.org de+schwedische-braute-kosten Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- worldbrides.org de+slawisches-land-mit-den-schonsten-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- worldbrides.org de+ukrainische-braute Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- worldbrides.org es+amourfactory-opinion que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- worldbrides.org es+amourfeel-opinion que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- worldbrides.org es+como-conocer-mujeres-asiaticas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- worldbrides.org es+como-conocer-mujeres-en-linea que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- worldbrides.org es+costo-promedio-de-novia-por-correo revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- worldbrides.org es+cuteasianwoman-opinion revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- worldbrides.org es+jollyromance-opinion que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- worldbrides.org es+latinwomendate-opinion revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- worldbrides.org es+mujeres-europeas-vs-mujeres-japonesas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- worldbrides.org es+mujeres-solteras-ucranianas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- worldbrides.org es+novias-brasil revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- worldbrides.org es+novias-brasil-calientes revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- worldbrides.org es+novias-calientes-de-nueva-zelanda que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- worldbrides.org es+novias-latvianas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- worldbrides.org es+novias-latvianas-calientes que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- worldbrides.org es+novias-lituanas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- worldbrides.org es+novias-mexico-calientes que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- worldbrides.org hvordan-man-undgar-postordrebrude-fidus bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- worldbrides.org it+come-incontrare-donne-online vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- worldbrides.org it+cuteasianwoman-recensione ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- worldbrides.org it+donne-single-australiane vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- worldbrides.org it+donne-single-italiane vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- worldbrides.org it+giapponese-donne-sole ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- worldbrides.org it+latinwomanlove-recensione ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- worldbrides.org it+latinwomendate-recensione ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- worldbrides.org it+meetslavicgirls-recensione ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- worldbrides.org it+paese-slavo-con-donne-piu-carine ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- worldbrides.org it+papua-nuova-guinea-donne-single ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- worldbrides.org it+spose-brasiliane vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- worldbrides.org it+spose-calde-svedesi ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- worldbrides.org it+spose-dominicane-calde vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- worldbrides.org it+spose-estoni ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- worldbrides.org it+spose-italiane ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- worldbrides.org it+ukrainebrides4you-recensione ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- worldbrides.org italienske-brude bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- worldbrides.org kinesiske-brude bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- worldbrides.org ladat-anmeldelser bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- worldbrides.org latin bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- worldbrides.org latinbeautydate-anmeldelser bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- worldbrides.org latinfeels-anmeldelser bedste postordre brudesider (0)
- worldbrides.org meetslavicgirls-anmeldelser bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- worldbrides.org polske-single-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- worldbrides.org pt+latim Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- worldbrides.org pt+mulheres-japonesas-como-homens-americanos Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- worldbrides.org pt+mulheres-solteiras Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- worldbrides.org pt+mulheres-solteiras-tailandesas Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- worldbrides.org pt+noivas-chinesas Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- worldbrides.org pt+ukrainebrides4you-recensao Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- worldbrides.org sv+asiabeautydate-recension postorder brudkataloger (1)
- worldbrides.org sv+colombialady-recension postorder brudkataloger (1)
- worldbrides.org sv+europeiska-kvinnor-kontra-japanska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- worldbrides.org sv+hur-man-undviker-postordrebrud-bedrageri postorder brudkataloger (1)
- worldbrides.org sv+ladat-recension postorder brudkataloger (1)
- worldbrides.org sv+latamdate-recension postorder brudkataloger (1)
- worldbrides.org sv+latin postorder brudkataloger (1)
- worldbrides.org sv+latinbeautydate-recension postorder brudkataloger (1)
- worldbrides.org sv+latinwomanlove-recension postorder brudkataloger (1)
- worldbrides.org sv+latinwomendate-recension postorder brudkataloger (1)
- worldbrides.org sv+lettiska-singel-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- worldbrides.org sv+meetslavicgirls-recension postorder brudkataloger (1)
- worldbrides.org sv+norska-brudar postorder brudkataloger (1)
- worldbrides.org sv+oceanien postorder brudkataloger (1)
- worldbrides.org sv+ukrainska-ensamstaende-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- worldbrides.org varme-italienske-brude bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- worldbrides.org varme-mexico-brude bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- worldbrides.org varme-thailandske-brude bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- write a essay for me (2)
- write an essay for me (1)
- write an essay for me cheap (1)
- write and essay for me (1)
- write essay cheap (1)
- write essay for me (1)
- write essay for me website (1)
- write for me an essay (2)
- write me essay for me (2)
- write my essay cheap online (2)
- write my essay fast (1)
- write my essay for me (1)
- write my essay for me best website (2)
- write my essay online (1)
- write my essay quick (1)
- writing an essay really fast (3)
- yabancД± gelinler (2)
- yabancД± gelinler (0)
- Yankton guaranteed installment loans for bad credit (1)
- yasal posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (2)
- yasal posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (0)
- yasal posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri reddit (3)
- yasal posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri reddit (0)
- yasal posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri reddit (0)
- yasal posta sipariЕџi gelini (7)
- yasal posta sipariЕџi gelini (0)
- yasal posta sipariЕџi gelini (0)
- yasal posta sipariЕџi gelini (0)
- yasal posta sipariЕџi gelini (0)
- yasal posta sipariЕџi gelini (0)
- yasal posta sipariЕџi gelini (0)
- yasal posta sipariЕџi gelini sitesi (2)
- yasal posta sipariЕџi gelini sitesi (0)
- yk (1)
- Yosemite installment loans online (1)
- yourinstallmentloans installment loans (1)
- Yuba City online installment loans instant approval (1)
- Zaten evliysem posta sipariЕџi gelini alabilir miyim? (2)
- Zaten evliysem posta sipariЕџi gelini alabilir miyim? (0)
- Архангельск (1)
- Барнаул (1)
- Брянск (1)
- ВїCuГЎl es el mejor paГs de novias por correo (1)
- ВїCuГЎl es el mejor servicio de novias por correo (1)
- ВїCuГЎl es el mejor sitio para novias por correo (3)
- ВїCuГЎl es el mejor sitio para novias por correo (0)
- ВїCuГЎl es el mejor sitio para novias por correo (0)
- ВїCuГЎl es la novia del pedido por correo? (3)
- ВїCuГЎl es la novia del pedido por correo? (0)
- ВїCuГЎl es la novia del pedido por correo? (0)
- ВїCuГЎles son los mejores sitios para novias por correo (4)
- ВїCuГЎles son los mejores sitios para novias por correo (0)
- ВїCuГЎles son los mejores sitios para novias por correo (0)
- ВїCuГЎles son los mejores sitios para novias por correo (0)
- ВїCГіmo funciona la novia por correo (5)
- ВїCГіmo funciona la novia por correo (0)
- ВїCГіmo funciona la novia por correo (0)
- ВїCГіmo funciona la novia por correo (0)
- ВїCГіmo funciona una novia por correo (3)
- ВїCГіmo funciona una novia por correo (0)
- ВїCГіmo funciona una novia por correo (0)
- ВїCГіmo funcionan los sitios de novias por correo (3)
- ВїCГіmo funcionan los sitios de novias por correo (0)
- ВїCГіmo funcionan los sitios de novias por correo (0)
- ВїDГіnde encuentro una novia de pedidos por correo (2)
- ВїDГіnde encuentro una novia de pedidos por correo (0)
- ВїDГіnde puedo encontrar una novia por correo (4)
- ВїDГіnde puedo encontrar una novia por correo (0)
- ВїDГіnde puedo encontrar una novia por correo (0)
- ВїDГіnde puedo encontrar una novia por correo (0)
- ВїPuedo obtener una novia por correo si ya estoy casado? (1)
- ВїQuГ© es la novia de pedidos por correo? (1)
- ВїQuГ© es una novia de pedidos por correo? (1)
- Вунд-2 (1)
- Г la recherche d'un mariage (1)
- Г¤r postorder brud verklig (6)
- Г¤r postorder brud verklig (0)
- Г¤r postorder brud verklig (0)
- Г¤r postorder brud verklig (0)
- Г¤r postorder brud verklig (0)
- Г¤r postorder brud verklig (0)
- är postorder brud värt det (1)
- Г¤r postorderbrud en riktig sak (3)
- Г¤r postorderbrud en riktig sak (0)
- Г¤r postorderbrud en riktig sak (0)
- Г¦gte mail ordre brudehistorier (2)
- Г¦gte mail ordre brudehistorier (0)
- Г¦gte postordre brudehistorier (2)
- Г¦gte postordre brudehistorier (0)
- Г¦gte postordre brudeside (1)
- Г¦gte postordre brudesider (1)
- Г¦gte postordrebrud (1)
- Г©pouses par correspondance (1)
- Г©pouses Г©trangГЁres (1)
- Гњst Nominal Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmeti (1)
- Гњst posta sipariЕџi gelin oturuyor (2)
- Гњst posta sipariЕџi gelin oturuyor (0)
- Гњst posta sipariЕџi gelin web siteleri (2)
- Гњst posta sipariЕџi gelin web siteleri (0)
- Гњst posta sipariЕџi gelin Гјlkeleri (3)
- Гњst posta sipariЕџi gelin Гјlkeleri (0)
- Гњst posta sipariЕџi gelin Гјlkeleri (0)
- Гњst posta sipariЕџi gelini sitesi (4)
- Гњst posta sipariЕџi gelini sitesi (0)
- Гњst posta sipariЕџi gelini sitesi (0)
- ГЁ la sposa per corrispondenza reale (2)
- ГЁ la sposa per corrispondenza reale (0)
- ГЁ la sposa per corrispondenza una cosa reale (4)
- ГЁ la sposa per corrispondenza una cosa reale (0)
- ГЁ la sposa per corrispondenza una cosa reale (0)
- ГЁ la sposa per corrispondenza una cosa reale (0)
- ГЁ sicuro per corrispondenza sposa (2)
- ГЁ sicuro per corrispondenza sposa (0)
- Гёverste postordre brudeland (1)
- Гёverste postordre brudeside (2)
- Гёverste postordre brudeside (0)
- Гёverste postordrebrud (1)
- Голицыно (1)
- Г‚ge moyen de la mariГ©e par correspondance (4)
- Г‚ge moyen de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Г‚ge moyen de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Г‚ge moyen de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Д°lk On Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Sitesi (1)
- Д°lk On Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Witebes (5)
- Д°lk On Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Witebes (0)
- Д°lk On Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Witebes (0)
- Д°lk On Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Witebes (0)
- Д°lk On Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Witebes (0)
- Д°yi posta sipariЕџi gelini web sitesi (1)
- Д±rklararasД± posta sipariЕџi gelini (1)
- ДЊlanci za mladenku (1)
- Е to je mladenka kao narudЕѕba poЕЎte (2)
- Е to je mladenka kao narudЕѕba poЕЎte (0)
- Е to je mladenka narudЕѕbenica (1)
- Е to je mladenka za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (2)
- Е to je mladenka za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (0)
- Е to je mladenka za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (0)
- Е to je mladenka za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte? (2)
- Е to je mladenka za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte? (0)
- Е to je narudЕѕba poЕЎte (1)
- Е to je narudЕѕba poЕЎte? (2)
- Е to je narudЕѕba poЕЎte? (0)
- Ећimdiye kadarki en iyi posta sipariЕџi gelini (1)
- ебар (1)
- Железнодорожный (1)
- казино (2)
- Казино (0)
- Комета Казино (1)
- Статьи-ч.1 (0)
- Форекс Брокеры (1)
- Форекс партнерская программа (1)
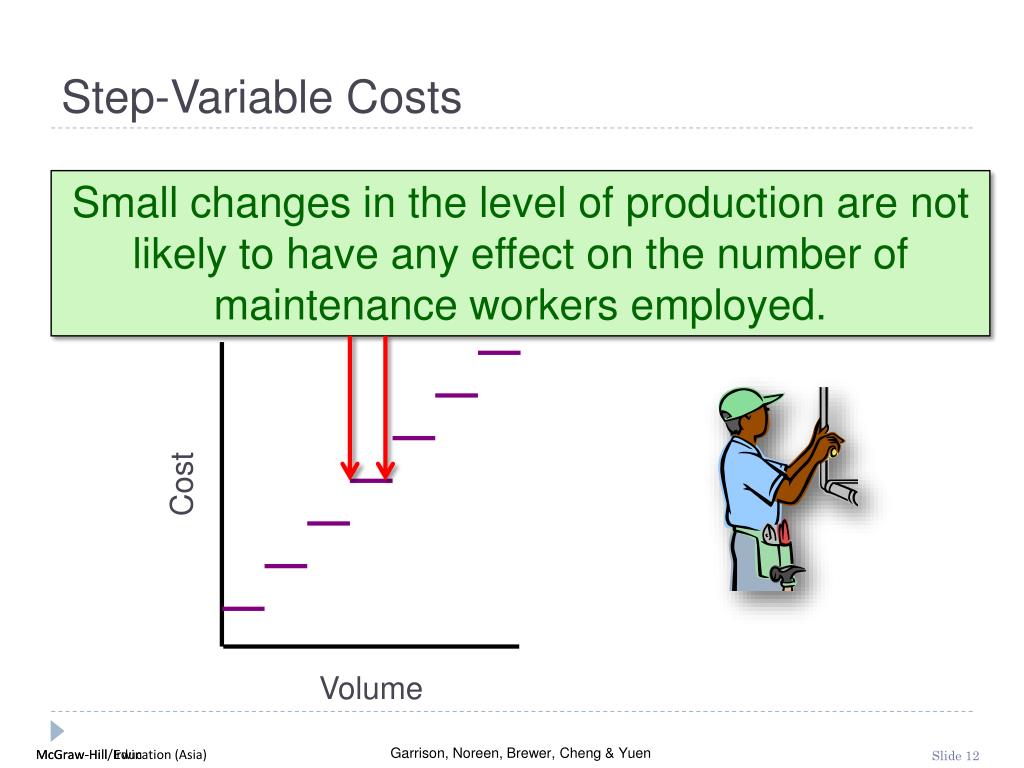
Commercial leases often have a fixed rent per month plus an additional rent based on the amount of production or sales. For example, rent is $5,000 plus five cents for each pencil that is made. The base rent of $5,000 is a fixed cost and the five cents per pencil is a variable cost. Fixed costs remain constant (in total) over somerelevant range of output. Depreciation, insurance, property taxes,and administrative salaries are examples of fixed costs.
Mixed Costs and Stepped Costs
Mixed costs are those that have both a fixed and variable component. It is important, however, to be able to separate mixed costs into their fixed and variable components because, typically, in the short run, we can only change variable costs but not most fixed costs. To examine how these mixed costs actually work, consider the Ocean Breeze hotel.
Avoidable Fixed Costs
Overtime shifts can help you produce more units without hiring additional full-time staff. You also avoid or delay additional costs related to recruiting, onboarding, times interest earned ratio calculator pricing strategy consultant and training. They help managers understand how costs change as production or activity levels vary, enabling more accurate budgeting and strategic decision-making.
Strategic Cost Management
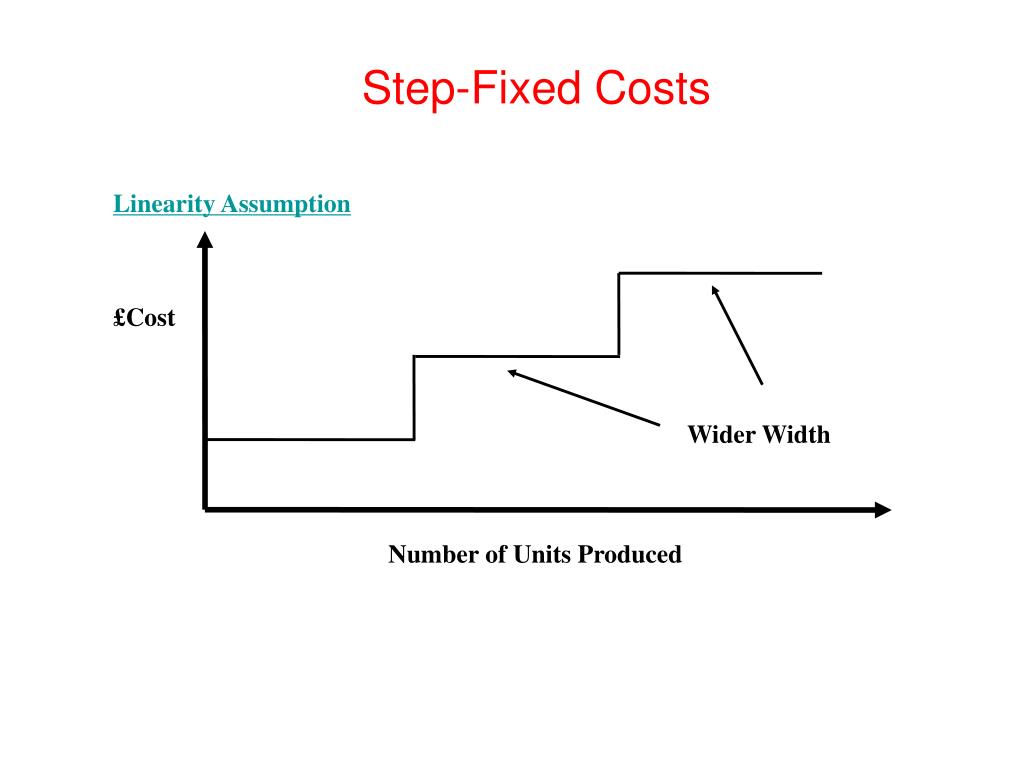
However, a manufacturing firm may carry product costs such as materials from one period to the other in order to have the costs “travel” with the units being produced. It is possible that both the selling and administrative costs and materials costs have both fixed and variable components. As a result, it may be necessary to analyze some fixed costs together with some variable costs. Ultimately, businesses strategically group costs in order to make them more useful for decision-making and planning. Two of the broadest and most common grouping of costs are product costs and period costs. If, at any point, the average variable cost per boat rises to the point that the price no longer covers the AVC, Carolina Yachts may consider halting production until the variable costs fall again.
They require managers to be mindful of the activity levels at which cost changes occur, as these thresholds can impact pricing, profitability analysis, and capacity planning. A fixed cost is an unavoidable operating expense that does not change in total over the short term, even if a business experiences variation in its level of activity. Table 2.2 illustrates the types of fixed costs for merchandising, service, and manufacturing organizations. Many costs do not vary in a strictly linearrelationship with volume. Managers usually separate mixed costs into theirfixed and variable components for decision-making purposes. Theyinclude the fixed portion of mixed costs with other fixed costs,while assuming the variable part changes with volume.
- When they produce 625 boats, Carolina Yachts has an AFC of $2,496 per boat.
- Because a step variable cost can remain approximately the same while activity levels change, this step effect can impact the allocated cost per manufactured unit.
- The moment you need a fourth account, your costs jump to $40 per month with the next level plan.
- Bert’s annual insurance premium is $10,800, which is $900 per month.
In short, total variable costs rise and fall as the level of activity (the cost driver) rises and falls. In analyzing the costs, Pat also needs to consider the total costs and average costs. The analysis will calculate the average fixed costs, the total fixed costs, the average variable costs, and the total variable costs.
If one employee can make 10,000 pencils, then the employee’s wage is constant over a production range of one to 10,000 pencils. If you make 25,000 pencils your cost triples because you need three employees. A mixed cost contains a fixed portion of costincurred even when the facility is idle, and a variable portionthat increases directly with volume. As the company increases its volume ofactivity, it runs more machines and runs them longer.
However, it is avoidable because the pencil maker can stop buying advertising and still stay in business (although sales volume may suffer). Variable costs are those costs that vary directly with the amount of production. For example, if you are a pencil maker, you need an eraser for each pencil you make. If erasers cost 20 cents each, the variable eraser cost of making 1,000 pencils is $200 (1,000 X $.20). If you make 2,000 pencils, the variable cost is $400 (2,000 X $.20). Total variable costs are the sum of all of the costs that vary in direct proportion to production.
- 1
- 0
Interesting articles
-
- 1
- 0
-
- 1
- 0
-
- 1
- 0
- All articles (77702)
- ! Без рубрики (62)
- 0.015869073920935062 (1)
- 0.038674021625345056 (1)
- 0.06454589940946609 (1)
- 0.07803953922161688 (1)
- 0.08447720963229288 (1)
- 0.08724027720202177 (1)
- 0.09638815068499595 (1)
- 0.09864464062235978 (1)
- 0.10403284341212138 (1)
- 0.12052478983094461 (1)
- 0.12839062591446115 (1)
- 0.12969665332177394 (1)
- 0.13558124162632557 (2)
- 0.1424390675038325 (1)
- 0.1481708440209787 (1)
- 0.1514062810253547 (1)
- 0.15216090002426153 (1)
- 0.19565264941740668 (1)
- 0.24264469978970604 (1)
- 0.2513073562640168 (1)
- 0.2748197173053596 (1)
- 0.30075697073364105 (1)
- 0.30636675912732214 (1)
- 0.3274347673029141 (1)
- 0.3544849106910273 (1)
- 0.363017420510207 (1)
- 0.3901353861396798 (1)
- 0.3914840337504165 (1)
- 0.3962447334682363 (1)
- 0.40348743805808984 (1)
- 0.44096099291640967 (1)
- 0.4493573902918411 (1)
- 0.4595404763683746 (2)
- 0.4689907730961512 (1)
- 0.49984518582056003 (1)
- 0.532814460619006 (1)
- 0.5366864896512812 (1)
- 0.5810755525161744 (1)
- 0.6150359674381758 (1)
- 0.6221958902382839 (1)
- 0.6933883185169163 (1)
- 0.6982825378806452 (1)
- 0.7007736873516788 (1)
- 0.7018830817991892 (1)
- 0.723094895999275 (1)
- 0.7364227578558207 (1)
- 0.7382361634424165 (1)
- 0.7414741488176279 (1)
- 0.7453430812965198 (1)
- 0.7655630714878285 (1)
- 0.7664188684331404 (1)
- 0.7675388179828142 (1)
- 0.7830403779384382 (1)
- 0.79853232509708 (1)
- 0.8626913304408897 (2)
- 0.8721060100275613 (1)
- 0.8967709789162543 (1)
- 0.9045499261478237 (1)
- 0.9259861774828386 (1)
- 0.9498377288041014 (1)
- 0.9690604938393559 (1)
- 0.978907854000516 (1)
- 0.9919333164848703 (1)
- 1 (13)
- 1 Win (1)
- 10 parasta postimyyntiä morsiamen (2)
- 10 parasta postimyyntiä morsiamen (0)
- 11275_ru (1)
- 1Win AZ Casino (4)
- 1win Azerbajany (3)
- 1Win br (1)
- 1win by (1)
- 1Win Casino (4)
- 1WIN Casino Brasil (3)
- 1Win cl (1)
- 1WIN Official In Russia (15)
- 1win Turkiye (2)
- 1win uzbekistan (3)
- 1winRussia (2)
- 1xbet apk (10)
- 1xbet AZ Casino (1)
- 1XBET AZ Giriş (3)
- 1xbet Azerbajan (3)
- 1xbet Azerbaydjan (5)
- 1xbet Brazil (3)
- 1xbet CASINO AZ (6)
- 1xbet egypt (1)
- 1xbet giriş (3)
- 1xbet Kazahstan (7)
- 1xbet Korea (1)
- 1xbet Morocco (4)
- 1xbet Online Casino (1)
- 1xbet qeydiyyat (1)
- 1xbet russia (1)
- 1xbet russian (1)
- 2 (5)
- 22bet IT (1)
- 711 (1)
- 9200_ru (1)
- 9460_ru (1)
- a cash advance (1)
- a cash advance is (1)
- a mail order bride (1)
- a payday advance loan (1)
- a payday loan (1)
- a payday loan company (2)
- a payday loan is (3)
- a payday loan? (1)
- about (2)
- Acheter la mariГ©e par correspondance (4)
- Acheter la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Acheter la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Acheter la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- acheter une mariГ©e par correspondance (5)
- acheter une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- acheter une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- acheter une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- acheter une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- adult (12)
- adult sites (7)
- advance advance cash loan payday (1)
- advance amer cash (2)
- advance amererica cash advance (4)
- advance america and cash advance (3)
- advance america cash (1)
- advance america cash advance (1)
- advance america cash advance payday loan (1)
- advance america cash advance price (2)
- advance america cash advances (1)
- advance america cash cash (3)
- advance america cash check? (2)
- advance america cash loan (1)
- advance america cash loans (1)
- advance america cash payday (1)
- advance america loan payday (2)
- advance america payday loan (1)
- advance america payday loan company (2)
- advance america payday loan near me (1)
- advance america payday loans (2)
- advance american cash (1)
- advance american cash advance (2)
- advance american payday loan (1)
- advance bad cash credit loan loan (1)
- advance bad credit loan payday (0)
- advance cash (0)
- advance cash advance (1)
- advance cash america loan (2)
- advance cash america near me (3)
- advance cash america payday loans (2)
- advance cash american (2)
- advance cash americia (1)
- advance cash cash loan payday (1)
- advance cash company (1)
- advance cash company loan (1)
- advance cash finance company (1)
- advance cash in (1)
- advance cash info (2)
- advance cash loan near me (2)
- advance cash loan payday (1)
- advance cash loans (2)
- advance cash log in (3)
- advance cash near me (4)
- advance cash now (2)
- advance cash payday (1)
- advance cash payday loan (2)
- advance cash payday loans (1)
- advance cash usa (1)
- advance cash usa payday loan (3)
- advance loan payday loan (1)
- advance loans payday (3)
- advance me cash advance (3)
- advance me payday loans (2)
- advance of america cash advance (1)
- advance of america payday loan (3)
- advance payday cash loan (1)
- advance payday loan (1)
- advance payday loan company (3)
- advance payday loan near me (4)
- advance payday loans (2)
- advance payday loans near me (2)
- advance the cash (2)
- advance to payday loans (1)
- advance usa payday loans (1)
- advanced america cash advance (2)
- advanced america cash advance near me (1)
- advanced american cash advance (1)
- advanced american cash advance near (1)
- advanced loan payday (3)
- advanced payday loan (2)
- advanced payday loans (1)
- advice (5)
- african-women free online sites for singles (1)
- Agence de messagerie de commande de mariГ©e (1)
- Agence de vente par correspondance (3)
- Agence de vente par correspondance avec la meilleure rГ©putation (2)
- Agence de vente par correspondance avec la meilleure rГ©putation (0)
- Agences de la mariГ©e par correspondance (6)
- Agences de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Agences de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Agences de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Agences de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Agences de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- agences de mariГ©e par correspondance (2)
- agences de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- agencia de correo de orden de novia (1)
- agencia de novias por correo (1)
- agencia de novias por correo con la mejor reputaciГіn (2)
- agencia de novias por correo con la mejor reputaciГіn (0)
- Agencija za mail za mladenku (1)
- agenzia sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- agenzie sposate per corrispondenza (4)
- AI News (1)
- albanian-brides free online sites for singles (1)
- all blog essay writing service cheap (1)
- america advance cash (2)
- america advance cash advance (1)
- america advance payday loan (2)
- america cash advance in (1)
- america cash advance loans (5)
- america cash advance near me (1)
- america cash payday loan (2)
- america cash payday loans (2)
- america payday loan (1)
- american advance cash (2)
- american advance payday loan (0)
- american advance payday loans (3)
- american bluebird and payday loans (2)
- american cash advance (2)
- american cash advance near me (1)
- american cash advance usa (2)
- american credit payday loans (1)
- american payday cash advance (2)
- american payday loan (1)
- american payday loans (1)
- american payday loans advance america (1)
- american-women+albuquerque-nm site free (1)
- american-women+anchorage-ky free online sites for singles (1)
- american-women+bakersfield-ca site free (1)
- american-women+brownsville-mn site free (1)
- american-women+chattanooga-tn site free (1)
- american-women+cincinnati-ia site free (1)
- american-women+cleveland-ga free online sites for singles (1)
- american-women+durham-ca free online sites for singles (1)
- american-women+el-paso-il site free (1)
- american-women+fort-lauderdale-fl free online sites for singles (1)
- american-women+fremont-oh free online sites for singles (1)
- american-women+gilbert-ia free online sites for singles (1)
- american-women+grand-prairie-tx free online sites for singles (1)
- american-women+henderson-wv free online sites for singles (1)
- american-women+henderson-wv site free (1)
- american-women+huntsville-tx site free (1)
- american-women+irvine-ca free online sites for singles (1)
- american-women+jersey-ga site free (1)
- american-women+lakewood-wa site free (1)
- american-women+las-vegas-nm site free (1)
- american-women+little-rock-sc free online sites for singles (1)
- american-women+los-angeles-ca site free (1)
- american-women+louisville-al site free (1)
- american-women+lubbock-tx free online sites for singles (1)
- american-women+madison-pa free online sites for singles (1)
- american-women+newport-news-va site free (1)
- american-women+ontario-oh free online sites for singles (1)
- american-women+orlando-fl free online sites for singles (0)
- american-women+philadelphia-tn free online sites for singles (1)
- american-women+reno-tx site free (1)
- american-women+rockford-mn site free (1)
- american-women+salem-ma site free (1)
- american-women+san-diego-ca free online sites for singles (1)
- american-women+san-francisco-ca site free (1)
- american-women+san-jose-az site free (1)
- american-women+santa-clarita-ca site free (1)
- american-women+surprise-ne site free (1)
- american-women+tallahassee-fl site free (0)
- american-women+tempe-az site free (1)
- american-women+visalia-ca site free (1)
- amourfeel-review free online sites for singles (1)
- and single site (11)
- Anderson online installment loans (1)
- anexsystem (1)
- anmeldelser av postordrebrudbyrГҐ (1)
- Annapolis Junction online installment loans (1)
- app (6)
- app for (10)
- app free (14)
- app reviews (8)
- apps (10)
- apps for adults (13)
- apps for iphone (11)
- apps free (14)
- apps reddit (11)
- Arcadia online installment loans instant approval (1)
- are cash advance loans (1)
- are payday loans (2)
- are payday loans bad (1)
- are payday loans bad for credit (1)
- are payday loans bad for your credit (2)
- are payday loans useful? (2)
- are-mail-order-brides-illegal free online sites for singles (1)
- argentinian-women+buenos-aires site free (1)
- armenian-women free online sites for singles (1)
- Articles de la mariГ©e par correspondance (3)
- Articles de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Articles de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Artificial intelligence (AI) (1)
- artГculos de novia por correo (4)
- artГculos de novia por correo (0)
- artГculos de novia por correo (0)
- ashley-madison-review free online sites for singles (1)
- asia-beauty-date-review free online sites for singles (1)
- asiame-review site free (1)
- asian brides (1)
- asian mail order bride (1)
- asianbeautydating-review site free (1)
- asianbeautyonline-review site free (1)
- asianladyonline-review site free (1)
- Athens guaranteed installment loans for bad credit direct lenders only (1)
- attractive-single-women free online sites for singles (1)
- au (1)
- Auf der Suche nach Ehe (1)
- Auf der Suche nach einer Mail -Bestellung Braut (5)
- Ault installment loans near me (1)
- Auslandische Brute (3)
- availableloan.net+500-dollar-payday-loan bad credit payday cash loan (0)
- availableloan.net+800-dollar-payday-loan advance cash payday loans (1)
- availableloan.net+balance-transfer-loans cash advance no credit check loan (1)
- availableloan.net+checking-account-with-bad-credit payday loan needed (1)
- availableloan.net+christmas-loans cash advance no credit check loan (1)
- availableloan.net+covid-19-personal-loans cash loan payday advance (1)
- availableloan.net+dental-loans-for-implants payday loan needed (1)
- availableloan.net+direct-express-emergency-cash advance cash payday loans (1)
- availableloan.net+i-need-money-now cash advance no credit check loan (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-ak+eagle get cash advance payday loans (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-ar+appleton how to do a payday loan (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-ar+victoria get cash advance payday loans (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-ca+ontario how to do a cash advance (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-ca+san-diego get cash advance payday loans (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-de+houston cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-ia+augusta nearby payday loans (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-ia+charlotte nearby payday loans (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-ia+portland nearby payday loans (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-il+golden-gate payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-il+hudson payday loans very bad credit (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-il+phoenix how to do a cash advance (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-il+riverside payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-in+hammond get cash advance payday loans (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-in+long-beach payday loans very bad credit (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-ky+edmonton bad credit loans no payday (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-ky+new-castle bad credit loans no payday (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-la+atlanta bad credit loans no payday (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-la+central payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-md+long-beach cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-mn+appleton how to do a payday loan (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-mn+kingston get cash advance payday loans (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-mo+philadelphia no credit check loan payday (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-mo+windsor nearby payday loans (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-ms+austin payday loans very bad credit (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-mt+columbus how to do a cash advance (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-nc+bolton how to do a cash advance (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-nc+nashville how to do a cash advance (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-ne+blue-springs how to do a cash advance (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-nv+kingston how much interest on a cash advance (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-nv+las-vegas nearby payday loans (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-ny+cleveland how to do a payday loan (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-oh+fresno how to do a cash advance (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-or+ontario how to do a payday loan (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-pa+eagle payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-sc+windsor get cash advance at bank (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-tn+charlotte payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-tn+kingston payday loans no credit check places (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-tx+los-angeles bad credit loans no payday (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-ut+central bad credit loans no payday (1)
- availableloan.net+installment-loans-wi+abbotsford my payday loan (1)
- availableloan.net+loans-for-400-credit-score payday loans banks (1)
- availableloan.net+loans-for-immigrants advance cash payday loans (1)
- availableloan.net+loans-for-pensioners what are good payday loan company (1)
- availableloan.net+loans-for-veterans bad credit payday cash loan (1)
- availableloan.net+medical-school-loans short payday loans no credit check (1)
- availableloan.net+no-origination-fee-personal-loan advance cash payday loans (1)
- availableloan.net+no-teletrack-installment-loans payday cash advance loans near me (1)
- availableloan.net+online-installment-loans-instant-approval cash advance no credit check loan (1)
- availableloan.net+payday-advance-app payday cash advance loans near me (1)
- availableloan.net+payday-loans-ar+austin payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- availableloan.net+payday-loans-ar+blue-mountain cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- availableloan.net+payday-loans-ar+nashville payday loans no credit check places (1)
- availableloan.net+payday-loans-az+miami how to do a payday loan (1)
- availableloan.net+payday-loans-ca+oasis how to do a cash advance (1)
- availableloan.net+payday-loans-ca+san-diego no credit check loan payday (1)
- availableloan.net+payday-loans-co+delta payday loans no credit check places (1)
- availableloan.net+payday-loans-de+magnolia payday loans very bad credit (1)
- availableloan.net+payday-loans-ga+jacksonville how to do a payday loan (1)
- availableloan.net+payday-loans-ia+riverside how much interest on a cash advance (1)
- availableloan.net+payday-loans-il+kingston how much interest on a cash advance (1)
- availableloan.net+payday-loans-in+atlanta get cash advance at bank (1)
- availableloan.net+payday-loans-in+columbus how much interest on a cash advance (0)
- availableloan.net+payday-loans-in+indianapolis how to do a payday loan (1)
- availableloan.net+payday-loans-with-prepaid-debit-card where to get payday loans near me (1)
- availableloan.net+personal-loans-mo+denver get cash advance payday loans (1)
- availableloan.net+personal-loans-mo+oakland bad credit loans no payday (1)
- availableloan.net+personal-loans-mo+philadelphia cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- availableloan.net+personal-loans-ms+columbus bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- availableloan.net+personal-loans-ne+emerald nearby payday loans (1)
- availableloan.net+personal-loans-ne+oakland no credit check loan payday (1)
- availableloan.net+personal-loans-nm+columbus bad credit loans no payday (1)
- availableloan.net+personal-loans-nm+san-jose bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- availableloan.net+personal-loans-ny+riverside cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- availableloan.net+personal-loans-oh+hamilton bad credit loans no payday (1)
- availableloan.net+personal-loans-ok+clearview how much interest on a cash advance (1)
- availableloan.net+personal-loans-tn+central payday loans very bad credit (1)
- availableloan.net+personal-loans-tx+lubbock payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- availableloan.net+personal-loans-tx+memphis how to do a payday loan (1)
- availableloan.net+personal-loans-tx+miami my payday loan (1)
- availableloan.net+personal-loans-tx+portland cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- availableloan.net+personal-loans-ut+central bad credit loans no payday (1)
- availableloan.net+personal-loans-va+new-castle no credit check loan payday (1)
- availableloan.net+personal-loans-wa+kingston bad credit loans no payday (1)
- availableloan.net+personal-loans-wi+columbus payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- availableloan.net+personal-loans-wi+dallas bad credit loans no payday (1)
- availableloan.net+personal-loans-wi+dallas bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- availableloan.net+personal-loans-wi+eagle how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- availableloan.net+personal-loans-wy+riverside how to do a cash advance (1)
- availableloan.net+quick-cash-loans short payday loans no credit check (1)
- availableloan.net+refinance-personal-loan payday loans banks (1)
- availableloan.net+same-day-payday-loans bad credit payday cash loan (1)
- availableloan.net+same-day-payday-loans short payday loans no credit check (1)
- availableloan.net+same-day-personal-loans advance cash payday loans (1)
- availableloan.net+signature-installment-loans advance cash payday loans (1)
- availableloan.net+signature-loans advance cash bank (1)
- availableloan.net+small-payday-loans cash loan payday advance (1)
- average cost of a mail order bride (1)
- average cost of mail order bride (1)
- average mail order bride prices (1)
- average price for mail order bride (2)
- average price of a mail order bride (1)
- average price of mail order bride (1)
- Avis des mariГ©es par correspondance (1)
- azerbaijan-women site free (1)
- azerbaijan-women+aran site free (1)
- Azerbajany Mostbet (3)
- är postorder brud värt det (1)
- b1bet apostas (3)
- bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (4)
- bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (0)
- bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (0)
- bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (0)
- bad bad credit payday loans (1)
- bad credi payday loans (2)
- bad crediit payday loans (2)
- bad credit and payday loans (2)
- bad credit cannot get payday loan (1)
- bad credit cash advance (4)
- bad credit cash advance loan (1)
- bad credit cash advance loans (3)
- bad credit credit loans not payday (1)
- bad credit guarenteed payday loan (1)
- bad credit loan payday (2)
- bad credit loans no payday (1)
- bad credit loans no payday loans (4)
- bad credit loans not payday (1)
- bad credit loans not payday advance (2)
- bad credit loans not payday loans (2)
- bad credit loans payday (1)
- bad credit loans payday advance (2)
- bad credit loans payday loans (2)
- bad credit loans that are not payday loans (2)
- bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- bad credit not payday loans (1)
- bad credit payday advance loan (2)
- bad credit payday advance loans (2)
- bad credit payday cash advance (1)
- bad credit payday loan (1)
- bad credit payday loan no bank check (4)
- bad credit payday loan no credit check (1)
- bad credit payday loan no credit check near me (2)
- bad credit payday loan no credit check us (1)
- bad credit payday loans (1)
- bad credit payday loans no credit check (4)
- badcreditloanapproving online installment loans (1)
- badoo-review site free (1)
- Ballwin guaranteed installment loans for bad credit direct lenders only (1)
- Bana bir posta sipariЕџi gelini bul (2)
- Bana bir posta sipariЕџi gelini bul (0)
- bank america payday loan (4)
- bank cash advance loans (2)
- bank payday loan (2)
- bank with cash advance (2)
- Bankobet (1)
- banks cash advance (2)
- banks for cash advance (1)
- banks payday loans (1)
- banks that do cash advance (2)
- banks that do payday loans (1)
- banks with payday loans (2)
- Basaribet (1)
- bästa land att hitta postorder brud (1)
- bästa landet att hitta en postorderbrud (1)
- bästa länder för en postorderbrud (2)
- bästa länder för en postorderbrud (0)
- bästa plats för postorderbrud (1)
- bästa postorder brud byrå reddit (1)
- bästa postorder brud platser (1)
- bästa postorder brudens webbplatser 2022 (1)
- bästa stället att få postorder brud (1)
- bästa webbplats postorder brud (3)
- bästa webbplats postorder brud (0)
- bästa webbplats postorder brud (0)
- beautiful women (1)
- beautiful-single-women site free (1)
- Bedford online installment loans instant approval (1)
- bedst bedГёmte postordre brudesider (2)
- bedst bedГёmte postordre brudesider (0)
- bedste land til postordre brud reddit (3)
- bedste land til postordrebrud (2)
- bedste lande til at fГҐ en postordrebrud (1)
- bedste legitime postordre brudewebsteder (1)
- bedste mail ordre brude sider anmeldelser (2)
- bedste mail ordre brude sider anmeldelser (0)
- bedste mail ordre brude websteder (2)
- bedste mail ordre brude websteder (0)
- bedste mail ordre brudewebsted (2)
- bedste omdГёmme mail ordre brud (1)
- bedste postordre brud agentur (3)
- bedste postordre brud agentur reddit (1)
- bedste postordre brud nogensinde (2)
- bedste postordre brud steder (1)
- bedste postordre brude service (1)
- bedste postordre brude websteder 2022 (3)
- bedste postordre brudefirma (2)
- bedste postordre brudeland (2)
- bedste postordre brudeside (2)
- bedste postordre brudesider (2)
- bedste postordrebrud (1)
- bedste rigtige postordre brudeside (2)
- bedste rigtige postordre brudeside (0)
- bedste rigtige postordre brudesider (1)
- bedste site mail ordre brud (1)
- bedste sted at fГҐ en postordrebrud (3)
- bedste sted at fГҐ en postordrebrud (0)
- bedste sted at fГҐ en postordrebrud (0)
- bedste steder for postordrebrud (1)
- belgian-women site free (1)
- benaughty-review site for people (1)
- Berthoud online installment loans (1)
- best apps (9)
- best asian dating sites (1)
- BEST bewertete Versandauftragsbrautseiten (1)
- best countries for a mail order bride (1)
- best countries to get a mail order bride (1)
- best country for mail order bride (1)
- best country for mail order bride reddit (1)
- best country to find a mail order bride (0)
- best country to find mail order bride (1)
- best dating reviews (1)
- best dating sites for over 40 (1)
- best dating websites (1)
- best essay cheap (1)
- best essay writing service reviews (1)
- best latin dating websites (1)
- best mail order bride agency (1)
- best mail order bride agency reddit (1)
- best mail order bride companies (2)
- best mail order bride company (3)
- best mail order bride countries (2)
- best mail order bride ever (0)
- best mail order bride places (2)
- best mail order bride site (1)
- best mail order bride site reddit (1)
- best mail order bride sites (1)
- best mail order bride sites reviews (2)
- best mail order bride websites (1)
- best mail order bride websites 2022 (2)
- best place to get a mail order bride (2)
- best place to get mail order bride (5)
- best places for mail order bride (2)
- best places to find mail order bride (1)
- best places to get mail order bride (2)
- best rangerte postordrebrudesider (5)
- best real mail order bride site (3)
- best real mail order bride sites (3)
- best site (8)
- best sites (21)
- best sites for singles (12)
- best website to find a mail order bride (3)
- best-pickup-lines free online sites for singles (1)
- Beste echte Mail -Bestellung Brautseite (5)
- Beste echte Mail -Bestellung Brautseiten (3)
- beste ekte postordre brudeside (1)
- beste land for en postordrebrud (2)
- beste land for postordre brud reddit (2)
- beste land for postordrebrud (3)
- beste land for ГҐ fГҐ en postordrebrud (1)
- beste landet ГҐ finne en postordrebrud (2)
- beste landet ГҐ finne en postordrebrud (0)
- beste landet ГҐ finne postordrebrud (3)
- beste landet ГҐ finne postordrebrud (0)
- beste landet ГҐ finne postordrebrud (0)
- beste legit postordre brud nettsteder (3)
- Beste legitime Mail -Bestellung Brautwebsites (1)
- Beste Lender fГјr eine Postanweisung Braut (2)
- Beste Lender fГјr eine Postanweisung Braut (0)
- Beste Lender, um eine Versandbestellbraut zu erhalten (1)
- Beste Mail -Bestellung Braut (2)
- Beste Mail -Bestellung Braut (0)
- Beste Mail -Bestellung Braut -Websites Bewertungen (3)
- Beste Mail -Bestellung Braut aller Zeiten (1)
- Beste Mail -Bestellung Braut Site Reddit (1)
- Beste Mail -Bestellung Braut Websites 2022 (1)
- Beste Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- Beste Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur Reddit (3)
- Beste Mail -Bestellung Brautpletze (2)
- Beste Mail -Bestellung Brautseite (2)
- Beste Mail -Bestellung Brautseiten (1)
- Beste Mail -Bestellung Brautunternehmen (1)
- Beste Mail -Bestellung Brautwebsite (1)
- Beste Mail -Bestellung Brautwebsites (6)
- beste nettsted for ГҐ finne en postordrebrud (2)
- beste nettsted for ГҐ finne en postordrebrud (0)
- beste nettsted post ordre brud (6)
- beste omdГёmme postordre brud (1)
- Beste Orte, um Versandbestellbraut zu erhalten (2)
- Beste Orte, um Versandbestellbraut zu finden (4)
- beste postordre brud nettsted (1)
- beste postordre brud nettsteder (4)
- beste postordre brud nettsteder 2022 (2)
- beste postordre brud nettstedet reddit (4)
- beste postordre brudbyrГҐ (2)
- beste postordre brudbyrГҐ (0)
- beste postordre brudebyrГҐ reddit (2)
- beste postordre brudebyrГҐ reddit (0)
- beste postordre brudeside (2)
- beste postordre brudfirma (2)
- beste postordre brudland (2)
- beste postordre brudplasser (3)
- beste postordre brudselskaper (1)
- beste postordre brudtjeneste (1)
- Beste Site -Mail -Bestellung Braut (2)
- beste steder for postordrebrud (2)
- beste steder ГҐ finne postordrebrud (2)
- beste steder ГҐ finne postordrebrud (0)
- beste steder ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- beste stedet for postordrebrud (1)
- beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (3)
- beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (0)
- beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (0)
- Beste Versandbestellung Braut Land (2)
- Beste Versandbestellung Braut Land (0)
- Beste Versandbestellung Brautlender (4)
- Bester Mail -Bestellung Brautservice (2)
- Bester Ort, um Versandbestellbraut zu erhalten (2)
- Bestes Land fГјr Versandbestellbraut Reddit (1)
- Bestes Land, um eine Versandbestellbraut zu finden (2)
- Bestes Land, um Versandbestellbraut zu finden (4)
- Bethesda installment loans near me (1)
- Betmotion brazil (1)
- bharat-matrimony-review free online sites for singles (1)
- bh_aug (2)
- bh_sep (1)
- BH_TOP (2)
- Bir Gelin Posta SipariЕџi (2)
- Bir Gelin Posta SipariЕџi (0)
- Bir gelin sipariЕџ edebilir misin (1)
- Bir Posta SipariЕџi Gelin (1)
- Bir posta siparişi gelini bulmak için en iyi web sitesi (1)
- Bir posta siparişi gelini bulmak için en iyi ülke (1)
- Bir posta sipariЕџi gelini bulun (1)
- Bir posta siparişi gelini için en iyi ülkeler (2)
- Bir posta siparişi gelini için en iyi ülkeler (0)
- Bir posta siparişi gelini için ortalama fiyat (3)
- Bir posta siparişi gelini için ortalama fiyat (0)
- Bir posta siparişi gelini için ortalama fiyat (0)
- bir posta sipariЕџi gelini nasД±l evlenir (2)
- bir posta sipariЕџi gelini nasД±l evlenir (0)
- Bir posta sipariЕџi gelini nasД±l Г§alД±ЕџД±r (3)
- Bir posta sipariЕџi gelini nasД±l Г§alД±ЕџД±r (0)
- Bir posta sipariЕџi gelini nasД±l Г§alД±ЕџД±r (0)
- Bir posta sipariЕџi gelini nerede bulabilirim (5)
- Bir posta sipariЕџi gelini nerede bulabilirim (0)
- Bir posta sipariЕџi gelini nerede bulabilirim (0)
- Bir posta sipariЕџi gelini nerede bulabilirim (0)
- Bir posta sipariЕџi gelini nerede bulabilirim (0)
- Bir posta sipariЕџi geliniyle Г§Д±kmalД± mД±yД±m (3)
- Bir posta sipariЕџi geliniyle Г§Д±kmalД± mД±yД±m (0)
- Bir posta sipariЕџi geliniyle Г§Д±kmalД± mД±yД±m (0)
- Bir posta sipariЕџinin ortalama fiyatД± (1)
- bizzo casino (1)
- bla gjennom postordrebruden (4)
- blog (145)
- bläddra i postorder bruden (1)
- bolivian-women+la-paz site free (1)
- bon site Web de mariГ©e par correspondance (7)
- bon site Web de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- bon site Web de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- bon site Web de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- bon site Web de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- bon site Web de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- bon site Web de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- book of ra (1)
- Bookkeeping (5)
- bosnian-women site free (1)
- bra postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- bra postorder brudens webbplats (2)
- Brandon guaranteed installment loans for bad credit (1)
- Braut Mail -Bestellung (1)
- Brautbestellversandagentur (1)
- bravodate-review free online sites for singles (1)
- brazilian-women+americana site free (1)
- brazilian-women+campina-grande site free (1)
- brazilian-women+formosa site free (1)
- brazilian-women+fortaleza site free (1)
- brazilian-women+natal free online sites for singles (1)
- brazilian-women+porto-alegre free online sites for singles (1)
- brazilian-women+porto-seguro free online sites for singles (1)
- brazilian-women+recife free online sites for singles (1)
- brazilian-women+santos site free (1)
- bride mail order (1)
- bride order mail (1)
- bride order mail agency (3)
- Bride World Order Mail Brides (2)
- brides (1)
- bridesconfidential.com costa-rican-bruder postordre brudinformasjon (1)
- bridesconfidential.com da+amerikanske-brude-til-aegteskab de bedste steder at finde postordrebrud (1)
- bridesconfidential.com da+indiske-brude de bedste steder at finde postordrebrud (1)
- bridesconfidential.com da+mexicanske-brude de bedste steder at finde postordrebrud (1)
- bridesconfidential.com da+mongolske-brude de bedste steder at finde postordrebrud (1)
- bridesconfidential.com da+norske-brude hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- bridesconfidential.com da+portugisiske-brude Г¦gte mail ordre brude websteder (1)
- bridesconfidential.com da+postordrebrude Г¦gte mail ordre brude websteder (1)
- bridesconfidential.com da+varme-mexicanske-kvinder de bedste steder at finde postordrebrud (1)
- bridesconfidential.com de+chinesische-hochzeitstraditionen Mail-Order-Braut (1)
- bridesconfidential.com de+heise-und-sexy-kolumbianische-frauen Wie funktioniert die Mail -Bestellung Braut? (1)
- bridesconfidential.com de+japanische-braute Top -bewertete Versandauftragsbrautseiten (1)
- bridesconfidential.com de+kambodschanische-braute Wie funktioniert die Mail -Bestellung Braut? (1)
- bridesconfidential.com de+okcupid-test Bester Mail -Bestellung Brautservice (1)
- bridesconfidential.com es+mujeres-rusas-calientes-y-sexys que es como la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- bridesconfidential.com es+novias-eslavas que es como la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- bridesconfidential.com es+novias-mexicanas agencias de novias por correo (1)
- bridesconfidential.com es+novias-rumanas que es como la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- bridesconfidential.com es+novias-tailandesas mejor orden de correo novia (1)
- bridesconfidential.com fi+albanialaiset-morsiamet oikeita postimyynti morsiamen tarinoita (1)
- bridesconfidential.com fi+kiinalaiset-morsiamet oikeita postimyynti morsiamen tarinoita (1)
- bridesconfidential.com fi+kuumat-ukrainalaiset-naiset legit postimyynti morsiamen sivustot reddit (1)
- bridesconfidential.com fi+kuumimmat-naiset-maailmassa postimyynti morsiamen tarinoita reddit (1)
- bridesconfidential.com fr+east-meet-east-avis sites de mariГ©e par correspondance les mieux notГ©s (0)
- bridesconfidential.com fr+les-femmes-les-plus-chaudes-du-monde sites de mariГ©e par correspondance les mieux notГ©s (1)
- bridesconfidential.com fr+mariees-irlandaises sites de mariГ©e par correspondance reddit (1)
- bridesconfidential.com hotteste-koreanske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ en postordrebrud (1)
- bridesconfidential.com it+donne-brasiliane-calde dove posso ottenere una sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- bridesconfidential.com it+donne-ucraine-calde il posto migliore per ottenere una sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- bridesconfidential.com it+le-donne-piu-calde-del-mondo dove posso ottenere una sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- bridesconfidential.com it+sposa-per-corrispondenza il posto migliore per ottenere una sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- bridesconfidential.com it+spose-colombiane dove posso ottenere una sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- bridesconfidential.com it+spose-costa-rican trova una sposa (1)
- bridesconfidential.com it+spose-honduregne trova una sposa (1)
- bridesconfidential.com main_es mejor orden de correo novia (1)
- bridesconfidential.com main_it sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- bridesconfidential.com main_no postordre brud pГҐ ordentlig? (1)
- bridesconfidential.com norske-bruder postordre brudinformasjon (1)
- bridesconfidential.com pt+noivas-argentinas correio em ordem noiva (1)
- bridesconfidential.com pt+noivas-indonesias melhor ordem de correio agГЄncia noiva reddit (1)
- bridesconfidential.com pt+noivas-turcas top dez site de noiva por ordem de correio (1)
- bridesconfidential.com sv+albaniska-brudar postorder brud definiera (1)
- bridesconfidential.com sv+heta-och-sexiga-ryska-kvinnor legitimte postorder brudtjänst (1)
- bridesconfidential.com sv+heta-och-sexiga-ryska-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brudens webbplatser (1)
- bridesconfidential.com sv+hetaste-koreanska-kvinnor postorder brud definition (1)
- bridesconfidential.com sv+indiska-brudar postorder brud definition (1)
- bridesconfidential.com sv+israeliska-brudar topp 10 postorder brudens webbplatser (0)
- bridesconfidential.com sv+rumanska-brudar topp 10 postorder brudens webbplatser (1)
- bridesconfidential.com svenske-bruder postordre brud pГҐ ordentlig? (1)
- bridesconfidential.com tr+avrupa-gelinleri Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Reddit NasД±l HazД±rlanД±r (1)
- bridesconfidential.com tr+brezilyali-gelinler En Д°yi Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmeti (1)
- bridesconfidential.com ungarske-bruder postordre brud pГҐ ordentlig? (1)
- brightwomen.net amolatina-recension postorder brudkataloger (1)
- brightwomen.net ar-postordrebrud-lagliga postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- brightwomen.net argentinska-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- brightwomen.net armensk-kvinna postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- brightwomen.net bangladesh-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- brightwomen.net belarus-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- brightwomen.net da+anastasia-date-anmeldelser hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net da+aserbajdsjanske-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- brightwomen.net da+belarus-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- brightwomen.net da+cambodian-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net da+dominikansk-kvinde hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net da+eharmony-anmeldelser bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- brightwomen.net da+hollandske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net da+italienske-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- brightwomen.net da+kazakhstan-kvinde hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net da+kinesiske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net da+kroatiske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net da+malaysiske-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- brightwomen.net da+maltesiske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net da+moldoviske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net da+pakistanske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net da+paraguayanske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net da+peruanske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net da+polsk-kvinde bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- brightwomen.net da+sri-lankan-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- brightwomen.net da+ukrainske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net da+varme-afrikanske-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- brightwomen.net da+varme-israelske-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- brightwomen.net da+varme-latinske-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- brightwomen.net da+varme-russiske-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- brightwomen.net da+varme-thailandske-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- brightwomen.net de+agyptische-frauen Mail-Order-Braut (1)
- brightwomen.net de+anastasia-date-test Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (0)
- brightwomen.net de+armenische-frau Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- brightwomen.net de+belgische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- brightwomen.net de+birmanische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- brightwomen.net de+britische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- brightwomen.net de+cupid-com-test Mail-Order-Braut (1)
- brightwomen.net de+deutsche-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- brightwomen.net de+die-kosten-von-katalogheirat Mail-Order-Braut (1)
- brightwomen.net de+eharmony-test Mail-Order-Braut (1)
- brightwomen.net de+filipino-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- brightwomen.net de+franzosische-frau Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- brightwomen.net de+georgische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- brightwomen.net de+haitianische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- brightwomen.net de+heise-asiatische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (0)
- brightwomen.net de+heise-filipino-frauen Mail-Order-Braut (1)
- brightwomen.net de+heise-indische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- brightwomen.net de+heise-thai-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- brightwomen.net de+israelische-frauen Mail-Order-Braut (1)
- brightwomen.net de+italienische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- brightwomen.net de+jamaikanische-frauen Mail-Order-Braut (1)
- brightwomen.net de+kubanische-frauen Mail-Order-Braut (1)
- brightwomen.net de+mongolische-frauen Mail-Order-Braut (1)
- brightwomen.net de+norwegische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- brightwomen.net de+osterreichische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- brightwomen.net de+polnische-frau Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- brightwomen.net de+russische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (0)
- brightwomen.net de+spanische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- brightwomen.net de+tschechische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- brightwomen.net de+uzbek-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- brightwomen.net de+will-katalogheirat-nur-mich-fur-mein-geld Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- brightwomen.net eharmony-recension postorder brudkataloger (1)
- brightwomen.net es+amolatina-opinion revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+mujer-japonesa que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+mujer-jordana que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+mujer-salvadorena que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+mujeres-afganas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+mujeres-argentinas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+mujeres-asiaticas-calientes que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+mujeres-azerbaiyanas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+mujeres-belgas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+mujeres-brasilenas-calientes revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+mujeres-colombianas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+mujeres-finlandesas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+mujeres-holandesas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+mujeres-iranies que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+mujeres-israelies-calientes revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+mujeres-lebanesas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+mujeres-lituanas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+mujeres-moldavas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+mujeres-panamenas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+mujeres-portuguesas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+mujeres-rumanas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+mujeres-rusas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+mujeres-vietnamitas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+mujeres-vietnamitas-calientes revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+novia-por-correo-solo-me-quieres-por-mi-dinero revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net es+son-legales-novia-por-correo que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- brightwomen.net fi+armenialainen-nainen tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- brightwomen.net fi+egyptilaiset-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- brightwomen.net fi+filippiininaiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- brightwomen.net fi+iranilaiset-naiset wikipedia postimyynti morsian (1)
- brightwomen.net fi+kreikkalaiset-naiset wikipedia postimyynti morsian (1)
- brightwomen.net fi+kuumat-meksikolaiset-naiset wikipedia postimyynti morsian (1)
- brightwomen.net fi+lyhyt-historia-postimyynnissa-morsian tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- brightwomen.net fi+macedonian-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- brightwomen.net fi+montenegro-naiset wikipedia postimyynti morsian (1)
- brightwomen.net fi+perulaiset-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- brightwomen.net fi+ruotsalainen-nainen wikipedia postimyynti morsian (1)
- brightwomen.net fi+serbialaiset-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- brightwomen.net fi+tanskalaiset-naiset wikipedia postimyynti morsian (1)
- brightwomen.net fi+tsekin-naiset wikipedia postimyynti morsian (1)
- brightwomen.net fi+turkkilaisen-naiset wikipedia postimyynti morsian (1)
- brightwomen.net fi+venalaiset-naiset wikipedia postimyynti morsian (1)
- brightwomen.net fi+venezuelalaiset-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- brightwomen.net filippinska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- brightwomen.net fr+arabian-saoudienne Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- brightwomen.net fr+femme-japonaise Mail dans l'ordre de la mariГ©e (1)
- brightwomen.net fr+femme-kazakhstan Mail dans l'ordre de la mariГ©e (1)
- brightwomen.net fr+femmes-afghanes Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- brightwomen.net fr+femmes-autrichiennes Mail dans l'ordre de la mariГ©e (1)
- brightwomen.net fr+femmes-bresiliennes-chaudes Mail dans l'ordre de la mariГ©e (1)
- brightwomen.net fr+femmes-bulgares Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- brightwomen.net fr+femmes-croates Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- brightwomen.net fr+femmes-cubaines Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- brightwomen.net fr+femmes-equatoriennes Mail dans l'ordre de la mariГ©e (1)
- brightwomen.net fr+femmes-irlandaises Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- brightwomen.net fr+femmes-irlandaises-chaudes Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- brightwomen.net fr+femmes-japonaises-chaudes Mail dans l'ordre de la mariГ©e (1)
- brightwomen.net fr+femmes-malaisiennes Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- brightwomen.net fr+femmes-norvegiennes Mail dans l'ordre de la mariГ©e (1)
- brightwomen.net fr+femmes-panamiennes Mail dans l'ordre de la mariГ©e (1)
- brightwomen.net fr+femmes-portoricaines Mail dans l'ordre de la mariГ©e (1)
- brightwomen.net fr+femmes-portugaises Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- brightwomen.net fr+femmes-tcheques Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- brightwomen.net fr+femmes-thai Mail dans l'ordre de la mariГ©e (1)
- brightwomen.net fr+femmes-thai-chaudes Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- brightwomen.net fr+le-cout-de-mariee-par-correspondance Mail dans l'ordre de la mariГ©e (1)
- brightwomen.net fransk-kvinna postorder brudens webbplats (0)
- brightwomen.net guatemalanska-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- brightwomen.net heta-filippinska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- brightwomen.net heta-irlandska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- brightwomen.net heta-japanska-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- brightwomen.net heta-ukrainska-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- brightwomen.net hur-fungerar-postordrebrud postorder brudkataloger (1)
- brightwomen.net indiska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- brightwomen.net it+anastasia-date-recensione ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- brightwomen.net it+belarus-donne etГ media della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- brightwomen.net it+come-funziona-sposa-per-corrispondenza ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- brightwomen.net it+donna-armena vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- brightwomen.net it+donna-giordana vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- brightwomen.net it+donna-polacca vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- brightwomen.net it+donna-svedese etГ media della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- brightwomen.net it+donne-afgane vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- brightwomen.net it+donne-africane-calde etГ media della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- brightwomen.net it+donne-belghe etГ media della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- brightwomen.net it+donne-boliviane vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- brightwomen.net it+donne-brasiliane ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- brightwomen.net it+donne-brasiliane-calde etГ media della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- brightwomen.net it+donne-del-bangladesh vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- brightwomen.net it+donne-ecuadoriane vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- brightwomen.net it+donne-filippine vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- brightwomen.net it+donne-giamaicane vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- brightwomen.net it+donne-indonesiane vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- brightwomen.net it+donne-messicane-calde vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- brightwomen.net it+donne-portoghesi ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- brightwomen.net it+donne-russe-calde ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- brightwomen.net it+donne-serbe vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- brightwomen.net it+donne-spagnole vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- brightwomen.net it+donne-ucraine ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- brightwomen.net it+donne-ucraine-calde ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- brightwomen.net it+donne-vietnamite-calde ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- brightwomen.net kazakhstan-kvinna postorder brudkataloger (1)
- brightwomen.net kinesiska-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- brightwomen.net latvianska-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- brightwomen.net luxemburgska-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- brightwomen.net main_it ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- brightwomen.net main_pt Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- brightwomen.net main_tr Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek (1)
- brightwomen.net malaysiska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- brightwomen.net no+bulgarske-kvinner online postordre brud (1)
- brightwomen.net no+dominikansk-kvinne online postordre brud (1)
- brightwomen.net no+greske-kvinner online postordre brud (1)
- brightwomen.net no+guyanese-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net no+indiske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net no+indonesiske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net no+italienske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net no+latviske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net no+meksikanske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net no+paraguayanske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net no+russiske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net no+saudiarabisk-kvinne beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net no+syriske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net no+varme-filippinske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net no+varme-latinske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- brightwomen.net osterrikiska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- brightwomen.net pt+cupid-com-recensao Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (0)
- brightwomen.net pt+mulher-do-cazaquistao Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- brightwomen.net pt+mulher-jordaniana Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- brightwomen.net pt+mulher-salvadorana Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- brightwomen.net pt+mulheres-africanas-gostosas Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- brightwomen.net pt+mulheres-checas Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- brightwomen.net pt+mulheres-chileanas Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- brightwomen.net pt+mulheres-croatas Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- brightwomen.net pt+mulheres-do-quirguistao Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- brightwomen.net pt+mulheres-guatemaltecas Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- brightwomen.net pt+mulheres-holandesas Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- brightwomen.net pt+mulheres-indianas Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- brightwomen.net pt+mulheres-iranianas Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- brightwomen.net pt+mulheres-israelenses Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- brightwomen.net pt+mulheres-israelenses-gostosas Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- brightwomen.net pt+mulheres-italianas-quentes Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- brightwomen.net pt+mulheres-mongois Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- brightwomen.net pt+mulheres-norueguesas Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- brightwomen.net pt+mulheres-peruanas Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- brightwomen.net pt+mulheres-russas-gostosas Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- brightwomen.net pt+mulheres-sirias Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- brightwomen.net pt+mulheres-uzbek Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- brightwomen.net pt+sri-lankan-women Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- brightwomen.net pt+tailandesas Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- brightwomen.net puerto-rico-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- brightwomen.net russian-cupid-recension postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- brightwomen.net schweiziska-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- brightwomen.net skotska-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- brightwomen.net tr+amolatina-inceleme Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek (1)
- brightwomen.net tr+anastasia-date-inceleme bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- brightwomen.net tr+belcikali-kadinlar Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek (1)
- brightwomen.net tr+danimarkali-kadinlar Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek (1)
- brightwomen.net tr+ermeni-kadin bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- brightwomen.net tr+estonyali-kadinlar bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- brightwomen.net tr+hintli-kadinlar bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- brightwomen.net tr+hirvat-kadinlar bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- brightwomen.net tr+malt-kadin bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- brightwomen.net tr+pakistanli-kadinlar bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- brightwomen.net tr+posta-siparisi-gelinler-maliyeti bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- brightwomen.net tr+sicak-israil-kadinlari bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- brightwomen.net tr+singapur-kadinlari bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- brightwomen.net tr+sri-lankan-kadinlar bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- brightwomen.net tr+suudi-arabistanli-kadin bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- brightwomen.net tr+turk-kadinlari bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- brightwomen.net tr+turkmen-kadinlar bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- brightwomen.net tr+ukraynali-kadinlar bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- brightwomen.net vietnamesiska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- browse mail order bride (1)
- brud mail ordre (1)
- brud ordre mail (3)
- brud ordre mail agentur (1)
- brud postorder (1)
- brudbeställning mail (1)
- brudbeställning mail (1)
- brudbeställning postbyrå (1)
- brude-tjenester til top mail-ordre (1)
- brudebestillings mail (1)
- brudebestillings postbyrГҐ (3)
- brudebestillings postbyrГҐ (0)
- brudebestillings postbyrГҐ (0)
- brudens världs postorder brudar (4)
- brudens världs postorder brudar (0)
- brudens världs postorder brudar (0)
- brudeparets ordre bruder (2)
- brudepostordre (1)
- brudesider med Гёverste postordre (2)
- brudesider med Гёverste postordre (0)
- Brush installment loans online (1)
- bt_aug (3)
- buen correo orden sitio web de la novia (2)
- buenos sitios de novias por correo (2)
- buon sito web per la sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- buona idea per la sposa per corrispondenza? (1)
- buona posta elettronica siti sposa (1)
- buscando matrimonio (4)
- buscando una novia por correo (2)
- buy a mail order bride (2)
- buy an essay online cheap (2)
- buy essay cheap (1)
- buy mail order bride (1)
- buy online essay cheap (1)
- buying a mail order bride (1)
- bästa land att hitta postorder brud (2)
- bästa land att hitta postorder brud (0)
- bästa landet att hitta en postorderbrud (2)
- bästa landet att hitta en postorderbrud (0)
- bästa länder för en postorderbrud (1)
- bästa plats för postorderbrud (1)
- bästa postorder brud byrå reddit (1)
- bästa postorder brud webbplats reddit (2)
- bästa postorder brud webbplats reddit (0)
- bästa postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- bästa postorder brud webbplatser recensioner (3)
- bästa postorder brud webbplatser recensioner (0)
- bästa postorder brud webbplatser recensioner (0)
- bästa postorder brudbyrå (1)
- bästa postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- bästa postorder brudens webbplatser 2022 (2)
- bästa postorder brudens webbplatser 2022 (0)
- bästa postorder brudens webbplatser reddit (4)
- bästa postorder brudens webbplatser reddit (0)
- bästa postorder brudens webbplatser reddit (0)
- bästa postorder brudens webbplatser reddit (0)
- bästa postorder brudföretag (2)
- bästa postorder brudföretag (0)
- bästa postorder brudland (2)
- bästa postorder brudland (0)
- bästa postorder brudländer (1)
- bästa postorderbrud någonsin (2)
- bästa postorderbrud någonsin (0)
- bästa rankade postorder brud webbplatser (3)
- bästa rankade postorder brud webbplatser (0)
- bästa rankade postorder brud webbplatser (0)
- bästa riktiga postorder brud webbplatser (3)
- bästa riktiga postorder brud webbplatser (0)
- bästa riktiga postorder brud webbplatser (0)
- bästa rykte postorder brud (1)
- bästa ställen att få postorder brud (2)
- bästa ställen att få postorder brud (0)
- bästa ställen att hitta postorderbrud (2)
- bästa ställen att hitta postorderbrud (0)
- bästa stället att få postorder brud (2)
- bästa stället att få postorder brud (0)
- bästa webbplats för att hitta en postorderbrud (2)
- bästa webbplats för att hitta en postorderbrud (0)
- bästa webbplats postorder brud (1)
- California guaranteed installment loans for bad credit (1)
- californiapaydayloanonline installment loans bad credit (1)
- cambodian-women free online sites for singles (1)
- cambodian-women+phnom-penh free online sites for singles (1)
- can anyone get a payday loan (1)
- can i get a cash advance (1)
- can i get a mail order bride if i am already married? (1)
- can i get a payday loan from a bank (5)
- can i get a payday loan with bad crdit (2)
- can i get a payday loan with very bad credit (2)
- can i get cash advance (2)
- can i get cash advance with no credit (0)
- can i have payday loans and get cash advance (3)
- can payday loan (2)
- can payday loans go on your credit (2)
- can payday loans improve your credit (1)
- can someone write my essay for me (1)
- can you get a cash advance (1)
- can you get a cash advance from bank (1)
- can you get a cash advance with no money? (1)
- can you get a payday loan from your bank (2)
- can you get a payday loan with no credit (3)
- can you get bad credit payday loan (1)
- can you get payday loan with no credit (1)
- can you get payday loans with bad credit (1)
- can you mail order a bride (1)
- Canfield bad credit installment loans (1)
- Canon City installment loans near me (1)
- cash advance (1)
- cash advance advance (3)
- cash advance advance america (1)
- cash advance america (1)
- cash advance america advance (2)
- cash advance america cash advance (2)
- cash advance america near me (2)
- cash advance america payday (2)
- cash advance america payday loan (2)
- cash advance america payday loans (2)
- cash advance america usa (3)
- cash advance america usa loan (1)
- cash advance american (1)
- cash advance and payday loans (2)
- cash advance at banks (1)
- cash advance bad credit (1)
- cash advance bad credit loans (3)
- cash advance bank (1)
- cash advance banking (1)
- cash advance banks (1)
- cash advance cash (3)
- cash advance cash advance (1)
- cash advance cash america (2)
- cash advance company (4)
- cash advance credit (1)
- cash advance d?finition (2)
- cash advance def (2)
- cash advance defintion (1)
- cash advance for bad credit (1)
- cash advance for bad credit no (1)
- cash advance for horrible credit (2)
- cash advance from your bank (1)
- cash advance how to (1)
- cash advance how to get it? (3)
- cash advance in america (2)
- cash advance in usa (1)
- cash advance is cash usa (1)
- cash advance is what (1)
- cash advance is? (2)
- cash advance items (5)
- cash advance lenders no check systems no credit check (2)
- cash advance lenders no credit check (1)
- cash advance loan (0)
- cash advance loan for bad credit (2)
- cash advance loan in usa (1)
- cash advance loan near me (3)
- cash advance loan no credit check (2)
- cash advance loan no interest (1)
- cash advance loan payday advance (1)
- cash advance loan usa (1)
- cash advance loand (2)
- cash advance loans bad credit (3)
- cash advance loans for bad credit (1)
- cash advance loans how do they work (3)
- cash advance loans no credit (1)
- cash advance loans no credit check direct lender (2)
- cash advance loans no credit check near me (1)
- cash advance loans now (1)
- cash advance loans usa (2)
- cash advance loans with no credit check (2)
- cash advance near (1)
- cash advance near me (1)
- cash advance near me bad credit (2)
- cash advance near me no credit check (1)
- cash advance near me now (1)
- cash advance nearby (3)
- cash advance nearme (1)
- cash advance neat me (1)
- cash advance new (2)
- cash advance newr me (4)
- cash advance no (1)
- cash advance no credit (3)
- cash advance no credit check (1)
- cash advance no credit check loan (3)
- cash advance no credit check near me (2)
- cash advance no credit check no bank account (1)
- cash advance no interest (1)
- cash advance now (2)
- cash advance now bad credit (3)
- cash advance now loan (1)
- cash advance now loans (3)
- cash advance now no credit check (1)
- cash advance of america (2)
- cash advance on a loan (2)
- cash advance payday advance (1)
- cash advance payday loan near me (2)
- cash advance payday loans near me (1)
- cash advance usa (2)
- cash advance usa loan (1)
- cash advance usa loan company (1)
- cash advance usa near me (2)
- cash advance usa price (1)
- cash advance what is (1)
- cash advance what is needed (1)
- cash advance with bad credit (1)
- cash advance with no (1)
- cash advance? (2)
- cash advances and payday loans (0)
- cash advances payday loans (1)
- cash america advance (4)
- cash america advance loans (1)
- cash america advance near me (1)
- cash america advance payday loans (1)
- cash america cash advance (1)
- cash america loans cash advance loans (1)
- cash america payday loan near me (1)
- cash america payday loans (3)
- cash an advance loan (1)
- cash and advance (2)
- cash and go payday loans (1)
- cash cash payday loan (2)
- cash company advance (3)
- cash credit payday loans (2)
- cash for you payday loans (0)
- cash go payday loan (3)
- cash in advance (0)
- cash in advance loans no credit check (5)
- cash in advance payday loan (2)
- cash in advance payday loans (1)
- cash loan advance (1)
- cash loan advance bad credit (2)
- cash loan now payday (3)
- cash loan payday (1)
- cash loan payday loan (1)
- cash loans advance (1)
- cash loans advance america (1)
- cash loans and payday advances (4)
- cash loans payday advance (1)
- cash loans payday loans (2)
- cash of advance (1)
- cash on advance (1)
- cash on go payday loans (3)
- cash payday advance loan (1)
- cash payday advance loans (2)
- cash payday loan (2)
- cash payday loan near me (1)
- cash payday loan now (1)
- cash payday loans (3)
- cash payday loans bad credit (2)
- cash to advance (2)
- cash to go payday loans (3)
- cash to payday loan (3)
- cash to payday loans near me (1)
- cash to you payday loans (1)
- cash usa payday loan (1)
- cashadvanceamerica.net+1-hour-direct-deposit-loans-in-minutes payday loan needed (1)
- cashadvanceamerica.net+250-dollar-payday-loan payday loans banks (1)
- cashadvanceamerica.net+300-dollar-payday-loan cash advance no credit check loan (1)
- cashadvanceamerica.net+5000-dollar-payday-loan advance cash payday loans (1)
- cashadvanceamerica.net+check-cashing-near-me payday loans banks (1)
- cashadvanceamerica.net+christmas-loans payday cash advance loans near me (1)
- cashadvanceamerica.net+fixed-rate-loans payday loans banks (1)
- cashadvanceamerica.net+payday-loans-for-self-employed payday loans banks (1)
- cashadvanceamerica.net+payday-loans-with-no-bank-account advance cash payday loans (1)
- cashadvanceamerica.net+personal-loans bad credit payday cash loan (1)
- cashadvanceamerica.net+school-loans-for-bad-credit how to get a cash advance loan (1)
- cashadvanceamerica.net+short-term payday loans banks (1)
- cashadvanceamerica.net+signature-installment-loans payday loans banks (1)
- cashadvanceamerica.net+students-loans-for-bad-credit cash loan payday advance (1)
- cashadvanceamerica.net+web-cash-loans bad credit payday cash loan (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+1500-dollar-payday-loan payday loan needed (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+3000-dollar-payday-loan bad credit payday cash loan (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+400-dollar-payday-loan payday loan needed (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+business-loans bad credit payday cash loan (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+emergency-loans-no-credit-check how to get a cash advance loan (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+flex-loans short payday loans no credit check (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+get-a-personal-loan-with-no-credit-history cash loan payday advance (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-al+carolina how much interest on a cash advance (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-ar+cincinnati how to do a cash advance (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-ar+portland get cash advance at bank (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-ca+richmond no credit check loan payday (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-ga+dallas how much interest on a cash advance (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-ia+portland nearby payday loans (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-il+augusta bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-in+richmond how to do a cash advance (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-ky+london payday loans no credit check places (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-la+spokane how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-mi+portland bad credit loans no payday (0)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-mn+long-beach how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-mo+birmingham payday loans very bad credit (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-ms+philadelphia payday loans very bad credit (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-nc+bolton payday loans very bad credit (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-nc+windsor bad credit loans no payday (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-nd+columbus how to do a cash advance (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-ne+columbus how to do a payday loan (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-nm+sacramento my payday loan (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-oh+cincinnati bad credit loans no payday (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-oh+hudson how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-oh+london no credit check loan payday (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-ok+clearview payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-or+ontario get cash advance at bank (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-pa+houston how to do a payday loan (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-pa+hudson bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-pa+oakwood how much interest on a cash advance (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-pa+riverside payday loans very bad credit (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-sc+central how to do a cash advance (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-tn+cleveland bad credit loans no payday (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-tx+cleveland how to do a cash advance (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-tx+oakwood payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-tx+san-antonio payday loans very bad credit (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-tx+tyler payday loans no credit check places (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-ut+cleveland payday loans very bad credit (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-va+victoria how to do a payday loan (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-wi+dallas bad credit loans no payday (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-wi+hammond how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-wi+ontario payday loans no credit check places (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-wv+carolina get cash advance payday loans (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-wv+prince payday loans no credit check places (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+installment-loans-wy+hudson how to do a payday loan (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+loans-by-phone cash loan payday advance (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+loans-for-bad-credit payday loan needed (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+no-origination-fee-personal-loan what are good payday loan company (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+payday-loans-al+blue-springs how to do a cash advance (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+payday-loans-ar+jacksonville how to do a payday loan (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+payday-loans-ca+bakersfield payday loans very bad credit (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+payday-loans-co+new-castle payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+payday-loans-de+magnolia payday loans no credit check places (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+payday-loans-fl+memphis get cash advance at bank (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+payday-loans-for-self-employed cash advance no credit check loan (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+payday-loans-for-self-employed short payday loans no credit check (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+payday-loans-ia+delta payday loans very bad credit (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+payday-loans-il+hammond how much interest on a cash advance (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+payday-loans-il+richmond payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-for-good-credit what are good payday loan company (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-mn+victoria how to do a payday loan (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-mo+bakersfield payday loans very bad credit (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-mo+birmingham cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-mo+memphis how to do a cash advance (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-ms+blue-mountain how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-ms+bolton payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-ms+columbus how to do a cash advance (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-ms+victoria bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-nc+hudson how to do a cash advance (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-nc+jacksonville how to do a payday loan (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-ne+emerald bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-nm+albuquerque payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-nv+las-vegas cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-oh+magnolia bad credit loans no payday (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-ok+tulsa nearby payday loans (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-or+phoenix how to do a cash advance (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-pa+delta payday loans very bad credit (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-pa+kingston nearby payday loans (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-ri+kingston my payday loan (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-tn+cleveland bad credit loans no payday (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-tn+nashville get cash advance payday loans (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-tx+combine bad credit loans no payday (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-tx+portland how much interest on a cash advance (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-tx+reno how much interest on a cash advance (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-ut+salt-lake-city get cash advance payday loans (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-wi+montreal get cash advance at bank (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+personal-loans-wv+carolina bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+signature-loans cash loan payday advance (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+small-loans cash advance no credit check loan (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+student-loan-rates advance cash payday loans (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com+sunday-payday-loans cash advance no credit check loan (1)
- cashadvancecompass.com_MAIN payday loan in usa (1)
- casino (27)
- casino en ligne fr (2)
- casino onlina ca (1)
- casino online ar (1)
- casinò online it (1)
- casinomhub_aug (1)
- Casinos (2)
- Casinozer gg Online (1)
- Castalia guaranteed installment loans for bad credit no credit check (1)
- Castle Rock guaranteed installment loans for bad credit (1)
- cataloghi di sposi per corrispondenza (2)
- catalogo sposa per corrispondenza (4)
- Catalogue de la mariГ©e par correspondance (8)
- Catalogue de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Catalogue de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Catalogue de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Catalogue de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Catalogue de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Catalogue de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Catalogue de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Catalogues de la commande par correspondance (4)
- Catalogues de la commande par correspondance (0)
- category+freiburg+freiburg+ladyboy escort near me (1)
- category+kanton-bern+biel-bienne+koreanisch escort near me (1)
- category+niederosterreich+stockerau+trans escort girls (1)
- category+nordrhein-westfalen+duren+frauen escort girl (1)
- category+oberosterreich+steyr+ladyboy escort girls (1)
- category+oberosterreich+steyr+trans escorts (1)
- category+rheinland-pfalz+koblenz+modell escort girls (1)
- category+vorarlberg+bregenz+trans escort buchen (1)
- category+wallis+video-mit-sex best escort girl here (1)
- catГЎlogo de novias por correo (4)
- catГЎlogo de novias por correo (0)
- catГЎlogo de novias por correo (0)
- catГЎlogo de novias por correo (0)
- cebuanas-review free online sites for singles (1)
- ch (1)
- chat-avenue-review free online sites for singles (1)
- Chatham installment loans near me (1)
- che cos'ГЁ il servizio di sposa per corrispondenza (3)
- che cos'ГЁ il servizio di sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- che cos'ГЁ il servizio di sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- che sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- cheap custom essay papers (1)
- cheap custom essay service (1)
- cheap essay (1)
- cheap essay buy (2)
- cheap essay for sale (1)
- cheap essay papers (1)
- cheap essay writing (1)
- cheap essay writing service fast (2)
- cheap essay writing service review (1)
- cheap essay writing service us (1)
- cheap write my essay (0)
- cheapest write my essay (2)
- cheapest write my essay service (2)
- chechen-women free online sites for singles (1)
- Chesapeake guaranteed installment loans for bad credit (1)
- Cheshire personal installment loans (1)
- Child development (6)
- chinese dating sites (1)
- chinese-women+altay free online sites for singles (1)
- chinese-women+chengdu free online sites for singles (1)
- chinese-women+guilin free online sites for singles (1)
- chinese-women+houma free online sites for singles (1)
- chinese-women+nanjing free online sites for singles (1)
- chinese-women+shangri-la free online sites for singles (1)
- chinese-women+taishan free online sites for singles (1)
- chinese-women+xuzhou free online sites for singles (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+1500-dollar-payday-loan how much of a payday loan can i get (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+2500-dollar-payday-loan short payday loans no credit check (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+500-dollar-payday-loan short payday loans no credit check (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+balance-transfer-loans payday loans banks (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+balance-transfer-loans short payday loans no credit check (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+emergency-loans payday cash advance loans near me (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+holiday-loans advance cash payday loans (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+im-in-desperate-need-of-a-loan-with-bad-credit payday cash advance loans near me (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-al+carolina payday loans very bad credit (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-al+riverside nearby payday loans (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-ar+cincinnati get cash advance payday loans (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-ar+kingston payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-az+tucson payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-ca+fresno payday loans very bad credit (0)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-ca+modesto my payday loan (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-ca+san-jose my payday loan (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-de+houston payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-de+new-castle nearby payday loans (0)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-ga+augusta payday loans very bad credit (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-ga+jacksonville nearby payday loans (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-id+eagle get cash advance at bank (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-il+atlanta my payday loan (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-il+columbus payday loans no credit check places (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-il+nashville how to do a payday loan (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-il+riverside how to do a cash advance (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-il+san-jose bad credit loans no payday (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-in+new-castle how to do a cash advance (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-ks+columbus payday loans very bad credit (0)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-ks+kansas-city bad credit loans no payday (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-ky+richmond bad credit loans no payday (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-la+atlanta how to do a payday loan (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-la+spokane how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-me+portland get cash advance payday loans (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-mi+portland nearby payday loans (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-mo+atlanta how to do a cash advance (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-mo+richmond get cash advance at bank (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-mo+richmond payday loans no credit check places (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-nc+bolton payday loans very bad credit (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-nc+hamilton how much interest on a cash advance (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-nc+hudson bad credit loans no payday (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-nc+windsor nearby payday loans (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-nj+windsor no credit check loan payday (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-oh+ontario get cash advance at bank (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-ok+castle bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-ok+clearview no credit check loan payday (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-or+phoenix nearby payday loans (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-pa+houston how to do a cash advance (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-sc+windsor bad credit loans no payday (0)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-tn+philadelphia my payday loan (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-tx+early bad credit loans no payday (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-tx+miami payday loans very bad credit (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-tx+richmond how to do a payday loan (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+installment-loans-wv+carolina cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+list-of-online-payday-lenders short payday loans no credit check (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+loans-for-surgery payday loans banks (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+loans-with-instant-bank-verification advance cash bank (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+medical-loans short payday loans no credit check (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+payday-loans-al+hamilton how to do a cash advance (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+payday-loans-ca+los-angeles payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+payday-loans-co+denver bad credit loans no payday (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+payday-loans-co+portland how to do a cash advance (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+payday-loans-ga+columbus no credit check loan payday (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+payday-loans-ia+jacksonville no credit check loan payday (0)
- clickcashadvance.com+payday-loans-il+augusta payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+payday-loans-il+cleveland nearby payday loans (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+payday-loans-il+hamilton nearby payday loans (0)
- clickcashadvance.com+payday-loans-il+ottawa nearby payday loans (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+payday-loans-il+richmond how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+payday-loans-that-accept-netspend-accounts short payday loans no credit check (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+payday-loans-with-prepaid-debit-card cash loan payday advance (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-mo+birmingham get cash advance at bank (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-mo+birmingham how to do a payday loan (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-mo+kingston how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-mo+montreal bad credit loans no payday (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-mo+oakwood how to do a payday loan (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-ms+austin payday loans very bad credit (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-ms+victoria how to do a payday loan (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-mt+hamilton how to do a cash advance (0)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-nc+hudson no credit check loan payday (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-nc+windsor bad credit loans no payday (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-nc+windsor no credit check loan payday (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-ne+eagle how to do a payday loan (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-nm+las-vegas payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-nv+oasis bad credit loans no payday (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-oh+bolton how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-oh+delta get cash advance at bank (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-oh+fresno how much interest on a cash advance (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-oh+hamilton payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-oh+ontario payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-ok+clearview payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-or+jacksonville payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-tn+central bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-tx+hamilton how much interest on a cash advance (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-tx+jacksonville my payday loan (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-tx+richmond get cash advance payday loans (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-ut+central payday loans very bad credit (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-va+alberta payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-vt+jacksonville bad credit loans no payday (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-wa+seattle my payday loan (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-wa+spokane nearby payday loans (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-wi+cleveland my payday loan (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+personal-loans-wi+eagle payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+pre-approved-installment-loans payday loans banks (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+pre-approved-personal-loan what are good payday loan company (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+same-day-personal-loans cash advance no credit check loan (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+single-payment-loans payday loan needed (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+sunday-payday-loans cash loan payday advance (1)
- clickcashadvance.com+tribal-loans-teletrack cash loan payday advance (1)
- Clinton guaranteed installment loans for bad credit direct lenders only (1)
- Codere Italy (4)
- Cognitive training/mental fitness (1)
- colombialady-review free online sites for singles (1)
- colombian women for marriage (1)
- colombian-women free online sites for singles (1)
- colombian-women+la-paz free online sites for singles (1)
- colombian-women+lourdes free online sites for singles (1)
- colombian-women+murillo free online sites for singles (1)
- Colorado online installment loans instant approval (1)
- come acquistare una sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- come fare una sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- come funziona la sposa per corrispondenza (8)
- come funziona la sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- come funziona una sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- come funzionano i siti di sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- come ordinare la sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- come ordinare una sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- come ordinare una sposa russa per corrispondenza (3)
- come ordinare una sposa russa per posta (1)
- come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (4)
- come spedire la sposa (1)
- come spedire una sposa (3)
- come sposare una sposa per corrispondenza (3)
- come uscire con una sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- Commandage mariГ©e Craigslist (1)
- Commande de courrier Г©lectronique (9)
- Commande de courrier Г©lectronique (0)
- Commande de courrier Г©lectronique (0)
- Commande de courrier Г©lectronique (0)
- Commande de courrier Г©lectronique (0)
- Commande de courrier Г©lectronique (0)
- Commande de courrier Г©lectronique (0)
- Commande de courrier Г©lectronique (0)
- Commande de courrier Г©lectronique (0)
- Commande par correspondance Definitiom (2)
- Commande par courrier lГ©gitime? (2)
- Commande par courrier lГ©gitime? (0)
- commander par courrier une mariГ©e (2)
- commander par courrier une mariГ©e (0)
- Commandez de la courrier mariГ©e rГ©elles histoires (2)
- Commandez de la courrier mariГ©e rГ©elles histoires (0)
- Commandez la mariГ©e rГ©el du site rГ©el (3)
- Commandez la mariГ©e rГ©el du site rГ©el (0)
- Commandez la mariГ©e rГ©el du site rГ©el (0)
- Commandez par la poste pour de vrai? (2)
- commanditГ© (6)
- commanditГ© (0)
- commanditГ© (0)
- commanditГ© (0)
- commanditГ© (0)
- commanditГ© (0)
- commanditГ© (0)
- Comment commander de la mariГ©e (2)
- Comment commander de la mariГ©e (0)
- Comment commander la commande par courrier mariГ©e (3)
- Comment commander la commande par courrier mariГ©e (0)
- Comment commander la commande par courrier mariГ©e (0)
- Comment commander par la poste une mariГ©e (4)
- Comment commander par la poste une mariГ©e (0)
- Comment commander par la poste une mariГ©e (0)
- Comment commander par la poste une mariГ©e (0)
- Comment commander une mariГ©e par correspondance (6)
- Comment commander une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Comment commander une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Comment commander une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Comment commander une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Comment commander une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Comment commander une mariГ©e par correspondance russe (6)
- Comment commander une mariГ©e par correspondance russe (0)
- Comment commander une mariГ©e par correspondance russe (0)
- Comment commander une mariГ©e par correspondance russe (0)
- Comment commander une mariГ©e par correspondance russe (0)
- Comment commander une mariГ©e par correspondance russe (0)
- Comment commander une mariГ©e russe mail (6)
- Comment commander une mariГ©e russe mail (0)
- Comment commander une mariГ©e russe mail (0)
- Comment commander une mariГ©e russe mail (0)
- Comment commander une mariГ©e russe mail (0)
- Comment commander une mariГ©e russe mail (0)
- Comment faire de la vente par la poste (3)
- Comment faire de la vente par la poste (0)
- Comment fonctionne la mariГ©e par courrier (3)
- Comment fonctionne la mariГ©e par courrier (0)
- Comment fonctionne la mariГ©e par courrier (0)
- Comment fonctionne une mariГ©e par correspondance (3)
- Comment fonctionne une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Comment fonctionne une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Comment fonctionnent la mariГ©e par courrier (4)
- Comment fonctionnent la mariГ©e par courrier (0)
- Comment fonctionnent la mariГ©e par courrier (0)
- Comment fonctionnent la mariГ©e par courrier (0)
- Comment fonctionnent les sites de mariГ©e par courrier (2)
- Comment fonctionnent les sites de mariГ©e par courrier (0)
- Comment prГ©parer une mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- Comment prГ©parer une mariГ©e par correspondance Reddit (2)
- Comment prГ©parer une mariГ©e par correspondance Reddit (0)
- Comment sortir avec une mariГ©e par correspondance (2)
- Comment sortir avec une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Comment Г©pouser une mariГ©e par correspondance (2)
- Comment Г©pouser une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Commout Mail Entre Russian Bride (1)
- compagnie di sposa legittime per corrispondenza (5)
- company cash advance (2)
- company loan new payday (1)
- company loan payday (1)
- company payday loans (1)
- compaГ±Гas de novias legГtimas de pedidos por correo (1)
- compra la sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- compra una sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- comprar correo orden novia (5)
- comprar una novia por correo (5)
- comprar una novia por correo (0)
- comprare una sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- correo de la novia orden (4)
- correo de pedidos de la novia (3)
- correo en orden cuestan novia (1)
- correo en orden novia (6)
- correo legГtimo ordenar sitios de novias reddit (4)
- correo legГtimo ordenar sitios de novias reddit (0)
- correo legГtimo ordenar sitios de novias reddit (0)
- correo lГ©sbico ordenar novia reddit (1)
- correo orden cupГіn de novia (5)
- correo orden cupГіn de novia (0)
- correo orden cupГіn de novia (0)
- correo orden cupГіn de novia (0)
- correo orden cupГіn de novia (0)
- correo orden de citas de novias (1)
- correo orden de cuentos de novias reddit (1)
- correo orden de los paГses de la novia (2)
- correo orden de los paГses de la novia (0)
- correo orden de preguntas frecuentes de la novia (1)
- correo orden de reseГ±as de sitios web de novias (5)
- correo orden de reseГ±as de sitios web de novias (0)
- correo orden de reseГ±as de sitios web de novias (0)
- correo orden de reseГ±as de sitios web de novias (0)
- correo orden de reseГ±as de sitios web de novias (0)
- correo orden de reseГ±as del sitio web de la novia (3)
- correo orden de reseГ±as del sitio web de la novia (0)
- correo orden de reseГ±as del sitio web de la novia (0)
- correo orden de trabajo de novia? (2)
- correo orden informaciГіn de la novia (4)
- correo orden informaciГіn de la novia (0)
- correo orden informaciГіn de la novia (0)
- correo orden informaciГіn de la novia (0)
- correo orden novia buena idea? (2)
- correo orden novia craigslist (3)
- correo orden novia definitiom (2)
- correo orden novia legГtima (3)
- correo orden novia legГtima (0)
- correo orden novia legГtima (0)
- correo orden novia legГtima? (1)
- correo orden novia real (1)
- correo orden novia reveiw (2)
- correo orden novia reveiw (0)
- correo orden novia sitio real (4)
- correo orden novia wiki (2)
- correo orden novia wikipedia (1)
- correo orden sitios de novias reddit (2)
- correo orden sitios web de novias reddit (1)
- correo para ordenar novia (3)
- correo superior bride order web (4)
- correo-pedido-novia (5)
- cos'ГЁ la sposa per corrispondenza (7)
- cos'ГЁ la sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- cos'ГЁ la sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- cos'ГЁ la sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- cos'ГЁ la sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- cos'ГЁ la sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- cos'ГЁ la sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- cos'ГЁ la sposa per corrispondenza? (1)
- cos'ГЁ una sposa per corrispondenza (7)
- cos'ГЁ una sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- cos'ГЁ una sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- cos'ГЁ una sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- cos'ГЁ una sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- cos'ГЁ una sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- cos'ГЁ una sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- cos'ГЁ una sposa per corrispondenza? (2)
- cos'ГЁ una sposa per corrispondenza? (0)
- costa-rican-brides free online sites for singles (1)
- costo medio della sposa per corrispondenza (3)
- costo medio di una sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- costo promedio de la novia del pedido por correo (3)
- costo promedio de una novia por correo (2)
- cougar-life-review site for people (1)
- Counter Strike 2 (1)
- countries-with-the-most-beautiful-women free online sites for singles (1)
- Coupon de mariГ©e par correspondance (2)
- Coupon de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- coupon sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- courrier des commandes de la mariГ©e (2)
- courrier des commandes de la mariГ©e (0)
- Courrier pour commander la mariГ©e (3)
- Courrier pour commander la mariГ©e (0)
- Courrier pour commander la mariГ©e (0)
- courrier Г©lectronique (2)
- courrier Г©lectronique (0)
- CoГ»t moyen d'une mariГ©e par correspondance (3)
- CoГ»t moyen d'une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- CoГ»t moyen d'une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- CoГ»t moyen de la mariГ©e par correspondance (5)
- CoГ»t moyen de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- CoГ»t moyen de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- CoГ»t moyen de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- CoГ»t moyen de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Creative teaching approaches (1)
- credit loan payday (3)
- credit payday loan (2)
- credit payday loans (1)
- Crofton guaranteed installment loans for bad credit (1)
- cummalot.com+category+anal only fans accounts (1)
- cummalot.com+category+bondage only fans (1)
- cummalot.com+category+cougar onlyfans accounts (1)
- cummalot.com+category+creampie only fans (1)
- cummalot.com+category+crossdresser only fans models (1)
- cummalot.com+category+cumshot onlyfans (1)
- cummalot.com+category+explicit only fans models (1)
- cummalot.com+category+german onlyfans (1)
- cummalot.com+category+hardcore best onlyfans (1)
- cummalot.com+category+hottest onlyfans (1)
- cummalot.com+category+midget only fans (1)
- cummalot.com+category+pornstar best onlyfans accounts (1)
- cummalot.com+category+small-tits onlyfans accounts (2)
- cummalot.com+category+streaming best only fans (1)
- cummalot.com+category+streaming onlyfans (1)
- cummalot.com+category+striptease onlyfans models (1)
- cummalot.com+category+taboo best only fans (1)
- cummalot.com+category+trans best only fans (1)
- cummalot.com+category+twitter onlyfans accounts (1)
- cummalot.com+category+xxx best only fans account (1)
- cupid-com-review site free (1)
- custom cheap essay (1)
- custom essay writing service cheap (1)
- czech-women site free (1)
- cГіmo casarse con una novia por correo (2)
- cГіmo casarse con una novia por correo (0)
- cГіmo comprar una novia por correo (1)
- cГіmo enviar por correo a la novia (4)
- cГіmo enviar por correo a la novia (0)
- cГіmo enviar por correo a la novia (0)
- cГіmo enviar por correo a la novia (0)
- cГіmo enviar por correo a una novia (4)
- cГіmo enviar por correo a una novia (0)
- cГіmo enviar por correo a una novia (0)
- cГіmo hacer pedidos por correo novia (4)
- cГіmo hacer pedidos por correo novia (0)
- cГіmo hacer pedidos por correo novia (0)
- cГіmo hacer un pedido por correo novia (1)
- cГіmo ordenar correo orden novia (1)
- cГіmo pedir una novia rusa por correo (3)
- cГіmo pedir una novia rusa por correo (0)
- cГіmo pedir una novia rusa por correo (0)
- cГіmo pedir una novia rusa por correo (0)
- cГіmo preparar un correo orden novia reddit (2)
- cГіmo preparar un correo orden novia reddit (0)
- cГіmo preparar una novia por correo (1)
- cГіmo salir con una novia por correo (2)
- cГіmo salir con una novia por correo (0)
- danish-women+aarhus free online sites for singles (1)
- danish-women+aarhus site free (1)
- Datation de la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- dateinasia-review site free (1)
- daterussiangirl-review site free (0)
- dateukrainiangirl-review site free (1)
- Dating Game Rules (1)
- dating sites guide (1)
- dating sites review (1)
- dating tips (1)
- dating women online (1)
- dating-in-your-30s free online sites for singles (1)
- de bedste steder at finde postordrebrud (1)
- de+adultfriendfinder-test Versandbestellbraut wert? (0)
- de+amerikanische-braeute Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+amourfactory-test Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+argentinisch-braeute Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+asiame-test Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+asianladyonline-test Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+asiatische-braeute Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+australische-braeute Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+bbwcupid-test Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+beste-laender-zu-finden-eine-treue-frau Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+blackpeoplemeet-test Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+britische-dating-sites-und-apps Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+catholicmatch-test Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+charmdate-test Versandbestellbraut wert? (0)
- de+charmromance-test Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+colombian-cupid-test Versandbestellung Frau (0)
- de+cupidates-test Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+dateniceukrainian-test Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+daterussiangirl-test Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+der-beste-ort-um-alleinstehende-frauen Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+deutsch-frauen Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+deutsche-dating-seiten-und-apps Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+die-schoensten-frauen-der-welt Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+dil-mil-test Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+dominikanische-dating-sites-und-apps Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+filipinocupid-test Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+findeuropeanbeauty-test Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+findmate-test Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+fitness-singles-test Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+guam-frauen Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+heated-affairs-test Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+heiss-griechische-frauen Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+heiss-polnisch-frauen Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+heisse-aethiopische-frauen Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+heisse-albanische-frauen Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+heisse-argentinische-frauen Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+heisse-frauen-aus-sri-lanka Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+heisse-indische-frauen Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+heisse-irakische-frauen Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+heisse-jordanische-frauen Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+heisse-kambodschanische-frauen Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+heisse-kanadische-frauen Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+heisse-kubanische-frauen Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+heisse-medellin-frauen Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+heisse-mongolische-frauen Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+heisse-niederlaendische-frauen Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+heisse-portugiesische-frauen Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+heisse-puerto-ricanische-frauen Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+heisse-slawische-frauen Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+heisse-slowenische-frauen Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+heisse-uruguay-frauen Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+heisse-usbekische-frauen Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+heisse-venezolanische-frauen Versandbestellung Frau (0)
- de+indiamatch-test Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+indianer-braeute Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+internationalcupid-test Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+israeli-frauen Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+italienische-braeute Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+jamaikanische-braeute Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+jdate-test Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+jeevansathi-test Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+jemanden-aus-einem-anderen-land-heiraten Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+junge-alleinstehende-frauen Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+kambodschanische-frauen Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+kismia-test Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+kolumbianische-braeute Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+koreanische-frauen Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+kroaten-frauen Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+liebe-mit-altersunterschied-moeglich Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+marokkanische-frauen Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+meetme-test Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+meetville-test Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+mexikanische-braeute Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+moldawien-frauen Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+mollige-alleinstehende-frauen Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+mongolen-frauen Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+norwegische-braeute Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+offene-beziehung Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+omegle-test Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+orchidromance-test Versandbestellung Frau (0)
- de+osteuropaeerinnen-frauen Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+peruanische-braeute Versandbestellbraut wert? (0)
- de+philippinische-braeute Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+portugiesisch-frauen Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+puerto-ricanische-frauen BEST bewertete Versandauftragsbrautseiten (1)
- de+pure-test Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+reife-alleinstehende-frauen Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+russische-dating-sites-und-apps Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+russische-vs-ukrainische-frauen-sind-es-irgendwelche-unterschiede Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+schwedische-braeute Versandbestellung Frau (0)
- de+schwedische-dating-sites-und-apps BEST bewertete Versandauftragsbrautseiten (1)
- de+schweizerinnen BEST bewertete Versandauftragsbrautseiten (1)
- de+secret-benefits-test BEST bewertete Versandauftragsbrautseiten (1)
- de+seeking-arrangement-test Versandbestellung Frau (0)
- de+serbisch-frauen BEST bewertete Versandauftragsbrautseiten (1)
- de+skandinavische-braeute Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+slawische-braeute BEST bewertete Versandauftragsbrautseiten (1)
- de+slowakische-braeute Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+somali-frauen BEST bewertete Versandauftragsbrautseiten (1)
- de+sri-lankan-braeute Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+suedafrikanische-frauen Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+tadschikistan-frauen Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+tinder-test BEST bewertete Versandauftragsbrautseiten (1)
- de+tuerkisch-braeute BEST bewertete Versandauftragsbrautseiten (1)
- de+turkmenistan-frauen BEST bewertete Versandauftragsbrautseiten (1)
- de+usbekistan-frauen Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+venezolanische-braeute Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+victoriabrides-test Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+was-ist-eine-mail-order-braut Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+whatsyourprice-test Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+wichtige-tipps-zum-dating-in-ihren-30ern Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- de+wie-finde-ich-eine-frau Versandbestellbraut wert? (0)
- de+wie-lange-bis-datiert-vor-ehe Versandbestellung Frau (1)
- de+wie-man-eine-versandhandelsbraut-wird Versandbestellbraut wert? (1)
- deberГa comprar una orden de correo novia (1)
- deberГa salir con una novia por correo (1)
- Definicija narudЕѕbe poЕЎte (1)
- definiciГіn de servicios de novias por correo (3)
- definiciГіn de servicios de novias por correo (0)
- definiciГіn de servicios de novias por correo (0)
- definisjon av postordre brud tjenester (5)
- definizione dei servizi per la sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- definizione sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- definição de serviços de noiva para pedidos por correio (1)
- Des Peres bad credit installment loans (1)
- deutschland username (1)
- deutschland+baden-wurttemberg+freiburg sign up (1)
- deutschland+baden-wurttemberg+freiburg support (1)
- deutschland+baden-wurttemberg+ludwigsburg username (1)
- deutschland+baden-wurttemberg+mannheim nutte buchen (1)
- deutschland+baden-wurttemberg+stuttgart tips (1)
- deutschland+baden-wurttemberg+villingen-schwenningen escort girl (1)
- deutschland+baden-wurttemberg+villingen-schwenningen tips (1)
- deutschland+bayern escort (1)
- deutschland+bayern+augsburg username (1)
- deutschland+bayern+erlangen visitors (1)
- deutschland+bayern+furth nutten finden (1)
- deutschland+bayern+furth sign up (1)
- deutschland+brandenburg+cottbus visitors (2)
- deutschland+hamburg-staat+hamburg sign in (1)
- deutschland+hessen+darmstadt sign up (1)
- deutschland+hessen+frankfurt escort girl (1)
- deutschland+niedersachsen+essen sign in (1)
- deutschland+niedersachsen+essen support (1)
- deutschland+niedersachsen+gottingen username (1)
- deutschland+niedersachsen+hannover sign up (1)
- deutschland+niedersachsen+hannover support (1)
- deutschland+niedersachsen+hannover tips (1)
- deutschland+niedersachsen+hildesheim escort girl link (1)
- deutschland+niedersachsen+munster tips (1)
- deutschland+niedersachsen+oldenburg nutten finden (1)
- deutschland+nordrhein-westfalen+aachen nutten finden (1)
- deutschland+nordrhein-westfalen+bonn visitors (1)
- deutschland+nordrhein-westfalen+dortmund escort near me (1)
- deutschland+nordrhein-westfalen+dortmund visitors (1)
- deutschland+nordrhein-westfalen+duisburg escort girl (1)
- deutschland+nordrhein-westfalen+duren username (1)
- deutschland+nordrhein-westfalen+hagen escort (1)
- deutschland+nordrhein-westfalen+hagen tips (1)
- deutschland+nordrhein-westfalen+halle escort girls (1)
- deutschland+nordrhein-westfalen+halle sign up (1)
- deutschland+nordrhein-westfalen+marl escort girl (1)
- deutschland+nordrhein-westfalen+marl nutten buchen (1)
- deutschland+nordrhein-westfalen+neuss sign in (1)
- deutschland+nordrhein-westfalen+neuss visitors (1)
- deutschland+nordrhein-westfalen+oberhausen escort (1)
- deutschland+nordrhein-westfalen+ratingen tips (1)
- deutschland+nordrhein-westfalen+remscheid escort (1)
- deutschland+rheinland-pfalz+ludwigshafen username (1)
- deutschland+rheinland-pfalz+trier username (1)
- deutschland+sachsen+chemnitz visitors (1)
- deutschland+sachsen+zwickau tips (1)
- deutschland+sachsen-anhalt escort girls (1)
- deutschland+sachsen-anhalt+dessau-rosslau sign up (1)
- deutschland+sachsen-anhalt+magdeburg escort girl link (1)
- deutschland+sachsen-anhalt+magdeburg nutten finden (1)
- deutschland+schleswig-holstein+kiel escorts (1)
- deutschland+thuringen support (1)
- devrais-je acheter une mariГ©e par correspondance (2)
- devrais-je acheter une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- devrais-je sortir avec une mariГ©e par correspondance (2)
- devrais-je sortir avec une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Die Mail -Bestellungsbrautstelle (1)
- Die Versandbestellbraut (1)
- diez mejores sitios para novias por correo (2)
- diez mejores sitios web de novias por correo (1)
- dj tools reviews (1)
- do payday loans go on credit (3)
- do payday loans go on your credit (1)
- dominican-dating-sites-and-apps free online sites for singles (1)
- donde compro una orden de correo novia (3)
- dove acquistare una sposa per corrispondenza (3)
- dove posso ottenere una sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- dove posso trovare una sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- dove trovare una sposa per corrispondenza (4)
- dove trovo una sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- Dream Honeymoon Destinations (1)
- Durchschnittliche Kosten einer Versandbestellbraut (1)
- Durchschnittliche Kosten fГјr Versandbestellbraut (3)
- Durchschnittliche Kosten fГјr Versandbestellbraut (0)
- Durchschnittliche Kosten fГјr Versandbestellbraut (0)
- Durchschnittliche Versandauftragspreise (1)
- Durchschnittsalter der Postanweisung Braut (2)
- Durchschnittspreis fГјr eine Versandbestellbraut (6)
- Durchschnittspreis fГјr eine Versandbestellbraut (0)
- Durchschnittspreis fГјr eine Versandbestellbraut (0)
- Durchschnittspreis fГјr eine Versandbestellbraut (0)
- Durchschnittspreis fГјr eine Versandbestellbraut (0)
- Durchschnittspreis fГјr eine Versandbestellbraut (0)
- Durchschnittspreis fГјr Versandbestellbraut (2)
- Durchschnittspreis fГјr Versandbestellbraut (0)
- dutch-women+arnhem site free (1)
- dutch-women+maastricht site free (1)
- DГ©couvrez la mariГ©e par correspondance (3)
- DГ©couvrez la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- DГ©couvrez la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- DГ©finition de la mariГ©e par correspondance (3)
- DГ©finition de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- DГ©finition de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- DГ©finition des services de vente par correspondance (1)
- dГіnde comprar una novia por correo (2)
- dГіnde comprar una novia por correo (0)
- dГіnde encontrar una novia por correo (5)
- dГіnde encontrar una novia por correo (0)
- dГіnde encontrar una novia por correo (0)
- dГіnde encontrar una novia por correo (0)
- dГіnde encontrar una novia por correo (0)
- e-mail ordine sposa (2)
- e-post ordre brud (3)
- e-post ordre brud nettsted anmeldelser (4)
- E-posta SipariЕџi Gelin (1)
- e-postorder brud (1)
- e-postordre brud nettsteder anmeldelser (3)
- easiest payday loans no credit check (1)
- easternhoneys-review free online sites for singles (1)
- Echte Versandauftragsbrautgeschichten (1)
- Echte Versandbestellbraut -Sites (3)
- Echte Versandungsbraut (2)
- Echter Mail -Bestellung Brautservice (1)
- ecuadorian-women+cuenca free online sites for singles (1)
- edad promedio de la novia del pedido por correo (3)
- Eine legitime Versandbrautbraut (3)
- Eine Versandauftragsbraut (3)
- Eine Versandauftragsbraut (0)
- ekte postordre brud nettsted (4)
- ekte postordre brud nettsteder (2)
- ekte postordre brudhistorier (4)
- ekte postordre brudtjeneste (6)
- ekte postordrebrud (6)
- el sitio de la novia por correo (4)
- el sitio de la novia por correo (0)
- elenco dei migliori siti di sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+500-dollar-payday-loan how to get a cash advance loan (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+business-loans what are good payday loan company (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+edd-card-cash-advance what are good payday loan company (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans bad credit payday cash loan (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-ak+houston how to do a payday loan (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-ar+victoria how much interest on a cash advance (0)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-fl+hudson how to do a payday loan (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-ga+kingston bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-ia+early how to do a cash advance (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-ia+early how to do a payday loan (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-ia+riverside cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-il+lawrence how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-il+oakland bad credit loans no payday (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-il+phoenix how to do a cash advance (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-in+columbus payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-in+hammond get cash advance payday loans (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-in+hammond how much interest on a cash advance (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-in+nashville nearby payday loans (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-ks+kansas-city payday loans no credit check places (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-ky+richmond how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-ky+sacramento payday loans very bad credit (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-la+baton-rouge bad credit loans no payday (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-la+hammond get cash advance payday loans (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-md+long-beach bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-mi+birmingham how much can you get on a payday loan (0)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-mi+memphis bad credit loans no payday (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-mn+alberta no credit check loan payday (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-mo+augusta payday loans very bad credit (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-mo+bakersfield get cash advance payday loans (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-mo+jacksonville how to do a cash advance (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-mo+oakwood bad credit loans no payday (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-ms+cleveland payday loans very bad credit (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-ms+hamilton how much interest on a cash advance (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-ms+hamilton how to do a cash advance (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-nc+charlotte payday loans very bad credit (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-nc+jacksonville how to do a cash advance (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-nc+nashville payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-nd+hamilton bad credit loans no payday (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-nj+kingston cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-oh+birmingham payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-oh+bolton nearby payday loans (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-oh+nashville nearby payday loans (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-ok+avant get cash advance payday loans (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-ok+miami payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-or+ontario how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-or+portland payday loans no credit check places (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-pa+austin how to do a payday loan (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-tx+hamilton payday loans very bad credit (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-tx+houston how to do a cash advance (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-tx+miami how to do a payday loan (0)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-ut+kingston bad credit loans no payday (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-va+new-castle payday loans very bad credit (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+installment-loans-wi+ontario nearby payday loans (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+legitimate-online-loans cash advance no credit check loan (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+loans-for-veterans what are good payday loan company (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+payday-loans-ak+central no credit check loan payday (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+payday-loans-al+jacksonville how to do a payday loan (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+payday-loans-ar+blue-mountain payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+payday-loans-ca+windsor no credit check loan payday (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+payday-loans-co+denver payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+payday-loans-ia+jacksonville bad credit loans no payday (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+payday-loans-id+eagle payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+payday-loans-il+cleveland payday loans very bad credit (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+payday-loans-il+magnolia get cash advance payday loans (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+payday-loans-il+ottawa payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+payday-loans-in+atlanta payday loans very bad credit (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+payday-loans-in+columbus bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+payday-loans-in+denver how to do a cash advance (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+payday-loans-that-accept-netspend-accounts cash advance no credit check loan (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+payday-loans-with-no-checking-account payday loans banks (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+payday-loans-with-savings-account payday loans banks (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+personal-loan-rates cash advance no credit check loan (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+personal-loans-ms+houston how to do a cash advance (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+personal-loans-nc+nashville how to do a payday loan (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+personal-loans-nj+kingston bad credit loans no payday (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+personal-loans-nj+magnolia get cash advance payday loans (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+personal-loans-nj+new-brunswick bad credit loans no payday (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+personal-loans-nm+kingston nearby payday loans (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+personal-loans-oh+cleveland payday loans very bad credit (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+personal-loans-oh+riverside bad credit loans no payday (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+personal-loans-oh+riverside my payday loan (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+personal-loans-or+ontario how to do a payday loan (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+personal-loans-pa+hudson bad credit loans no payday (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+personal-loans-pa+oakwood how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+personal-loans-tx+austin payday loan no credit check lender (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+personal-loans-tx+miami bad credit loans no payday (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+personal-loans-tx+portland payday loans very bad credit (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+personal-loans-ut+cleveland how much interest on a cash advance (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+personal-loans-ut+delta cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+personal-loans-va+new-castle get cash advance payday loans (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+personal-loans-wi+ontario how to do a payday loan (1)
- elitecashadvance.com+school-loans-for-bad-credit cash advance no credit check loan (1)
- elitesingles (1)
- En iyi 10 posta sipariЕџi gelin sitesi (1)
- En iyi 10 posta sipariЕџi gelini (3)
- En iyi 10 posta sipariЕџi gelini (0)
- En iyi 10 posta sipariЕџi gelini (0)
- En iyi 10 posta sipariЕџi gelini web siteleri (2)
- En iyi 10 posta sipariЕџi gelini web siteleri (0)
- En iyi 5 posta sipariЕџi gelin sitesi (2)
- En iyi 5 posta sipariЕџi gelin sitesi (0)
- En iyi posta sipariЕџi gelin hizmeti nedir (1)
- En iyi posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri nelerdir (4)
- En iyi posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri nelerdir (0)
- En iyi posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri nelerdir (0)
- En iyi posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri nelerdir (0)
- En iyi posta sipariЕџi gelin yerleri (2)
- En iyi posta sipariЕџi gelin yerleri (0)
- En iyi posta sipariЕџi gelin Гјlke (2)
- En iyi posta sipariЕџi gelin Гјlke (0)
- En iyi posta sipariЕџi gelin Гјlkesi nedir (3)
- En iyi posta sipariЕџi gelin Гјlkesi nedir (0)
- En iyi posta sipariЕџi gelin Гјlkesi nedir (0)
- En iyi posta sipariЕџi gelini sitesi (2)
- En iyi posta sipariЕџi gelini sitesi (0)
- En iyi posta sipariЕџi gelini sitesi nedir (1)
- En iyi posta sipariЕџi gelini web siteleri (2)
- En iyi posta sipariЕџi gelini web siteleri (0)
- En iyi posta sipariЕџi gelini web siteleri reddit (2)
- En iyi posta sipariЕџi gelini web siteleri reddit (0)
- En iyi posta sipariЕџi gelini web sitesi (3)
- En iyi posta sipariЕџi gelini web sitesi (0)
- En iyi posta sipariЕџi gelini web sitesi (0)
- En iyi site posta sipariЕџi gelin (1)
- en legitim postordrebrud (4)
- en legitim postordrebrud (0)
- en postorderbrud (4)
- en postordrebrud (3)
- En sД±cak posta sipariЕџi gelini (1)
- En İyi Gerçek Posta Siparişi Gelin Siteleri (4)
- En İyi Gerçek Posta Siparişi Gelin Siteleri (0)
- En İyi Gerçek Posta Siparişi Gelin Siteleri (0)
- En Д°yi Nominal Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Siteleri (3)
- En Д°yi Nominal Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Siteleri (0)
- En Д°yi Posta SipariЕџi Gelin (1)
- En Д°yi Posta SipariЕџi Gelin AjansД± (2)
- En Д°yi Posta SipariЕџi Gelin AjansД± (0)
- En Д°yi Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmeti (1)
- En Д°yi Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Siteleri Listesi (3)
- En Д°yi Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Siteleri Listesi (0)
- En Д°yi Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Siteleri Listesi (0)
- En Д°yi Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Siteleri Д°ncelemeleri (3)
- En Д°yi Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Siteleri Д°ncelemeleri (0)
- En Д°yi Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Siteleri Д°ncelemeleri (0)
- En Д°yi Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Sitesi Reddit (1)
- En Д°yi Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Гњlkeleri (1)
- En Д°yi Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Ећirketi (2)
- En Д°yi Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Ећirketi (0)
- En Д°yi Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Ећirketleri (1)
- En Д°yi Yasal Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Web Siteleri (1)
- en+austria+burgenland escort girls (1)
- en+austria+burgenland+eisenstadt escorts near me (1)
- en+austria+burgenland+eisenstadt tips (1)
- en+austria+carinthia+klagenfurt escorts near me (1)
- en+austria+carinthia+villach escort girl (1)
- en+austria+lower-austria+amstetten escort (1)
- en+austria+lower-austria+amstetten visitors (1)
- en+austria+lower-austria+bad-voslau escort near me (1)
- en+austria+lower-austria+korneuburg escort near me (1)
- en+austria+lower-austria+krems-an-der-donau tips (1)
- en+austria+lower-austria+traiskirchen best escort platform (1)
- en+austria+lower-austria+tulln escorts (1)
- en+austria+lower-austria+wiener-neustadt escort girl (1)
- en+austria+salzburg-state username (1)
- en+austria+salzburg-state+wals support (1)
- en+austria+tyrol+lienz username (1)
- en+austria+upper-austria+bad-ischl escort girl here (1)
- en+austria+upper-austria+braunau-am-inn escort girl link (1)
- en+austria+upper-austria+gmunden escort (1)
- en+austria+upper-austria+leonding escort (1)
- en+austria+upper-austria+linz visitors (1)
- en+austria+upper-austria+ried-im-innkreis username (1)
- en+austria+upper-austria+steyr escort service (1)
- en+austria+vienna-state escorts (1)
- en+austria+vienna-state+vienna username (1)
- en+austria+vorarlberg tips (1)
- en+austria+vorarlberg+bregenz find escort girls (1)
- en+austria+vorarlberg+dornbirn escort service (1)
- en+category+berlin-state+berlin+granny find escort (1)
- en+category+grisons+davos+trans find escort (1)
- en+category+styria+graz+japanese escort girls (1)
- en+category+vienna-state+vienna+muscular escort service (2)
- en+category+vienna-state+vienna+muscular escort service (0)
- en+germany+baden-wurttemberg+heidelberg escort girl link (1)
- en+germany+baden-wurttemberg+heilbronn visitors (1)
- en+germany+baden-wurttemberg+mannheim visitors (1)
- en+germany+baden-wurttemberg+reutlingen escort girl (1)
- en+germany+baden-wurttemberg+stuttgart escort (1)
- en+germany+baden-wurttemberg+tubingen username (1)
- en+germany+baden-wurttemberg+ulm escort (1)
- en+germany+bavaria escort girl (1)
- en+germany+bavaria+erlangen visitors (1)
- en+germany+bavaria+ingolstadt tips (1)
- en+germany+bavaria+wurzburg escort here link (1)
- en+germany+berlin-state tips (1)
- en+germany+brandenburg-state+potsdam support (1)
- en+germany+brandenburg-state+potsdam tips (1)
- en+germany+bremen-state tips (1)
- en+germany+bremen-state+bremen escort (1)
- en+germany+bremen-state+bremen escorts near me (1)
- en+germany+hesse escort girls (1)
- en+germany+hesse+hanau escort (1)
- en+germany+hesse+hanau escort girls (1)
- en+germany+lower-saxony+brunswick find escort (1)
- en+germany+lower-saxony+osnabruck escorts near me (1)
- en+germany+lower-saxony+wolfsburg support (1)
- en+germany+north-rhine-westphalia+bonn tips (1)
- en+germany+north-rhine-westphalia+hagen tips (1)
- en+germany+north-rhine-westphalia+minden visitors (1)
- en+germany+north-rhine-westphalia+witten username (1)
- en+germany+rhineland-palatinate+trier best escort platform (1)
- en+germany+saarland+saarbrucken escorts (1)
- en+germany+saxony+zwickau support (1)
- en+germany+saxony+zwickau username (1)
- en+germany+saxony-anhalt escort girl link (1)
- en+germany+saxony-anhalt+dessau-rosslau support (1)
- en+germany+thuringia+erfurt escort (1)
- en+s+models+ch visitors (1)
- en+s+models+de-bw+karlsruhe sign up (1)
- en+s+models+nl-nb+eindhoven username (1)
- en+switzerland best escort plattform (1)
- en+switzerland+aargau escort (1)
- en+switzerland+aargau+oftringen best escort platform (1)
- en+switzerland+aargau+oftringen find escort (1)
- en+switzerland+aargau+oftringen visitors (1)
- en+switzerland+aargau+spreitenbach tips (1)
- en+switzerland+aargau+wettingen escort (1)
- en+switzerland+aargau+zofingen username (1)
- en+switzerland+appenzell-ausserrhoden+herisau escorts near me (1)
- en+switzerland+basel-city username (1)
- en+switzerland+basel-landschaft best escort plattform (1)
- en+switzerland+basel-landschaft escort service (1)
- en+switzerland+basel-landschaft find escort (1)
- en+switzerland+basel-landschaft+binningen username (1)
- en+switzerland+basel-landschaft+liestal escort (1)
- en+switzerland+basel-landschaft+munchenstein escort (1)
- en+switzerland+basel-landschaft+oberwil find escort girls (1)
- en+switzerland+canton-of-bern+bern tips (1)
- en+switzerland+canton-of-bern+biel-bienne best escort platform (1)
- en+switzerland+canton-of-bern+langenthal support (1)
- en+switzerland+canton-of-bern+ostermundigen tips (1)
- en+switzerland+canton-of-bern+thun tips (1)
- en+switzerland+canton-of-schwyz support (1)
- en+switzerland+canton-of-schwyz+einsiedeln support (1)
- en+switzerland+canton-of-schwyz+einsiedeln visitors (1)
- en+switzerland+canton-of-schwyz+schwyz escorts near me (1)
- en+switzerland+canton-of-schwyz+schwyz tips (1)
- en+switzerland+canton-of-solothurn find escort (1)
- en+switzerland+canton-of-zug+zug escort near me (1)
- en+switzerland+geneva-state+geneva tips (1)
- en+switzerland+glarus-state+glarus find escort girls (1)
- en+switzerland+grisons escort near me (1)
- en+switzerland+grisons+davos tips (1)
- en+switzerland+jura escort girl (1)
- en+switzerland+lucerne-state+lucerne tips (1)
- en+switzerland+neuchatel visitors (1)
- en+switzerland+schaffhausen-state escort girls (1)
- en+switzerland+schaffhausen-state+schaffhausen visitors (1)
- en+switzerland+st-gallen-state+buchs escort girl (1)
- en+switzerland+st-gallen-state+st-gallen support (1)
- en+switzerland+thurgau escort near me (1)
- en+switzerland+thurgau+amriswil visitors (1)
- en+switzerland+thurgau+arbon visitors (1)
- en+switzerland+thurgau+kreuzlingen escort service (1)
- en+switzerland+thurgau+weinfelden find escort (1)
- en+switzerland+ticino escort girl here (1)
- en+switzerland+ticino+locarno escort girl here (1)
- en+switzerland+ticino+locarno visitors (1)
- en+switzerland+ticino+lugano support (1)
- en+switzerland+valais+martigny escort (1)
- en+switzerland+valais+sierre visitors (1)
- en+switzerland+valais+sion tips (1)
- en+switzerland+zurich-canton+adliswil escort (1)
- en+switzerland+zurich-canton+adliswil escort service (1)
- en+switzerland+zurich-canton+bulach escort sites (1)
- en+switzerland+zurich-canton+dietikon username (1)
- en+switzerland+zurich-canton+kloten escorts near me (1)
- en+switzerland+zurich-canton+pfaffikon escort (1)
- en+switzerland+zurich-canton+pfaffikon tips (1)
- en+switzerland+zurich-canton+regensdorf escort girl link (1)
- en+switzerland+zurich-canton+regensdorf find escort girls (1)
- en+switzerland+zurich-canton+thalwil escort girl (1)
- en+switzerland+zurich-canton+thalwil escort girl here (1)
- en+switzerland+zurich-canton+wadenswil escort girls (1)
- en+switzerland+zurich-canton+wallisellen escort girl link (1)
- en+switzerland+zurich-canton+winterthur find escort (1)
- encontrar correo orden novia (3)
- encontrar una novia (2)
- encontrar una novia por correo (4)
- encuГ©ntrame una novia por correo (3)
- encuГ©ntrame una novia por correo (0)
- encuГ©ntrame una novia por correo (0)
- er postordre brud ekte (3)
- er postordre brud sikker (2)
- er postordre brud trygt (1)
- er postordre brud verdt det (4)
- er postordre brud Г¦gte (3)
- er postordre brud Г¦gte (0)
- er postordre brud Г¦gte (0)
- er postordrebrud en rigtig ting (1)
- ES (4)
- es correo orden novia real (2)
- es correo orden novia segura (2)
- es la novia del pedido por correo algo real (2)
- es+amor-con-edad-diferencia-posible sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+asiafriendfinder-opinion mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+belga-mujeres sitios de novias por correo de leggit (0)
- es+belice-mujeres mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+bharat-matrimony-opinion mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+caliente-letonia-mujeres mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+caliente-moldovan-mujeres mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+caliente-nepal-mujeres mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+caliente-nigeriana-mujeres mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+caliente-sudafrica-mujeres sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+caliente-tayikistan-mujeres sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+cebuanas-opinion mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+charmdate-opinion mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+citas-en-tus-30 mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+conocer-mujeres-locales sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+corea-vs-china-vs-japonesa-mujeres sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+cougar-life-opinion sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+cuanto-tiempo-hasta-la-fecha-antes-del-matrimonio mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+dateinasia-opinion sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+dating-profile-tips-for-guys mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+dream-singles-opinion mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+eastmeeteast-opinion sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+espanol-citas-sitios-y-aplicaciones sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+espanol-mujeres sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+estonia-mujeres mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+europeandate-opinion mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+findukrainianbeauty-opinion sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+fitness-singles-opinion sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+historias-de-novias-por-correo mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+interracial-dating-central-opinion sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+japancupid-opinion mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+jollyromance-opinion mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+jpeoplemeet-opinion mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+kissrussianbeauty-opinion sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+las-mujeres-de-europa-del-este sitios de novias por correo de leggit (0)
- es+las-mujeres-rusas-contra-las-ucranianas-hay-alguna-diferencia mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+latin-woman-date-opinion mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+latinamericancupid-opinion mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (0)
- es+marroqui-mujeres sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+meetslavicgirls-opinion mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+mingle2-opinion sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+mujeres-austriacas-calientes sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+mujeres-britanicas-calientes mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+mujeres-calientes-caribenas mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+mujeres-calientes-de-bombay sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+mujeres-calientes-de-laos sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+mujeres-calientes-de-turkmenistan mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+mujeres-calientes-escandinavas mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+mujeres-calientes-israelies sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+mujeres-calientes-uzbekistan mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+mujeres-de-la-isla-caliente sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+mujeres-dominicanas-calientes sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+mujeres-ecuatorianas-calientes mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+mujeres-egipcias sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+mujeres-eslovacas-calientes sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+mujeres-espanolas-calientes sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+mujeres-finlandesas-calientes mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+mujeres-guatemaltecas-calientes mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+mujeres-hondurenas-calientes mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+mujeres-iraquies sitios de novias por correo de leggit (0)
- es+mujeres-jordanas mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+mujeres-latinas-calientes mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+mujeres-letonas mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+mujeres-libanesas-calientes sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+mujeres-nicaragueenses sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+mujeres-panamenas-calientes mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+mujeres-peruanas sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+mujeres-polacas-calientes mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+mujeres-portuguesas-calientes sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+mujeres-rusas sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+mujeres-salvadorenas-calientes mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+mujeres-siberianas sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+mujeres-solteras-altas sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+mujeres-solteras-con-ninos sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+mujeres-solteras-sin-hijos sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+mujeres-solteras-viejas mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+mujeres-sudanesas mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+mujeres-surcoreanas-calientes sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+mujeres-tailandesas-calientes sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+mujeres-turcas mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+novia-extranjera-a-visa-a-los-ee-uu sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+novias-albanesas mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+novias-brasilenas mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+novias-canadienses sitios de novias por correo de leggit (0)
- es+novias-checas mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+novias-costarricenses sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+novias-cubanas mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+novias-escandinavas sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+novias-haitianas mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+novias-hungaras sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+novias-jamaicanas mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+novias-japonesas mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+novias-mexicanas mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+novias-noruegas sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+novias-ucranianas mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+pequenas-mujeres-solteras sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+que-es-una-novia-por-correo sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+rubias-famosas-mujeres mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+singapur-mujeres sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+sitios-y-aplicaciones-de-citas-britanicos mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+sitios-y-aplicaciones-de-citas-colombianos sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+sitios-y-aplicaciones-de-citas-en-chino mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+sitios-y-aplicaciones-de-citas-indias sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+sitios-y-aplicaciones-de-citas-tailandeses sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+sitios-y-aplicaciones-de-citas-turcos mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+sueco-mujeres sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+theluckydate-opinion sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+turkmenistan-mujeres mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (0)
- es+uruguay-mujeres mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+uzbekistan-mujeres sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+valentime-opinion mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es+victoriabrides-opinion sitios de novias por correo de leggit (1)
- es+vietnamita-mujeres mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (1)
- es-steroid (7)
- esposa de pedidos por correo (2)
- esposas de pedidos por correo (1)
- esposas por ordem de correio (1)
- essay help cheap (1)
- essay papers cheap (1)
- essay write for me (2)
- essay writing for cheap (1)
- essay writing service cheap help (1)
- etsi minulle postimyynti morsian (2)
- etsi postimyynti morsian (3)
- etsitkö postimyynti morsiamaa (2)
- etsitkö postimyynti morsiamaa (0)
- etГ media della sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- etГ media della sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- europeandate-review site free (1)
- Evlilik ArД±yor (2)
- Evlilik ArД±yor (0)
- Faits de mariГ©e par correspondance (4)
- Faits de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Faits de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Faits de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Fall In Love With Someone You Don't Share A Common Language (1)
- fansfan.com+category+anal sign up (1)
- fansfan.com+category+asian search (1)
- fansfan.com+category+best search (1)
- fansfan.com+category+big-tits sign up (1)
- fansfan.com+category+blowjob username (1)
- fansfan.com+category+brunette search (1)
- fansfan.com+category+cougar support (1)
- fansfan.com+category+deepthroat search (1)
- fansfan.com+category+femdom tips (1)
- fansfan.com+category+fitness sign up (1)
- fansfan.com+category+foot-fetish sign in (1)
- fansfan.com+category+free sign up (1)
- fansfan.com+category+free support (1)
- fansfan.com+category+german sign in (1)
- fansfan.com+category+hairy sign up (1)
- fansfan.com+category+indian sign in (1)
- fansfan.com+category+interracial support (1)
- fansfan.com+category+male sign up (1)
- fansfan.com+category+masturbation tips (1)
- fansfan.com+category+mom-and-daughter sign in (1)
- fansfan.com+category+petite sign in (1)
- fansfan.com+category+pornstar visitors (1)
- fansfan.com+category+public support (1)
- fansfan.com+category+roleplay sign in (1)
- fansfan.com+category+small-tits sign up (1)
- fansfan.com+category+small-tits username (1)
- fansfan.com+category+snapchat visitors (1)
- fansfan.com+category+squirt search (1)
- fansfan.com+category+taboo support (1)
- fansfan.com+category+voyeur support (1)
- fansfan.com+category+youtube tips (1)
- FAQ de la commande par correspondance (1)
- fast payday loan company (3)
- fast payday loans company (1)
- femme de commande par correspondance (3)
- Festus online installment loans instant approval (1)
- fi+afrikkalaiset-naiset legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+amourfactory-arvostelu legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+armenialaiset-morsiamet parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+asianmelodies-arvostelu legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+australian-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+badoo-arvostelu legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+bangladesh-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+bolivialais-morsiamet parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+charmdate-arvostelu parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+chilelaiset-morsiamet parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+chinalovecupid-arvostelu parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+colombialady-arvostelu legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+dil-mil-arvostelu legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+eronneet-naimattomat-naiset legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+filipinocupid-arvostelu legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+filippiinilaiset-morsiamet legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+findasianbeauty-arvostelu legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+findmate-arvostelu legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+fitness-singles-arvostelu parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+godatenow-arvostelu parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+haitilaiset-morsiamet legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+hollantilaiset-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+honduran-morsiamet legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+hyesingles-arvostelu parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+indiamatch-arvostelu legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+intialaiset-treffisivustot-ja-sovellukset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+jemenin-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+jump4love-arvostelu legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+kanadalaiset-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+kanadan-morsiamet legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+karibian-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+kazakstan-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+kirgisia-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+kissrussianbeauty-arvostelu legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+kuinka-loytaa-vaimo-vuonna parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+kuuma-belize-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+kuuma-chilelais-naiset legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+kuuma-ecuador-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+kuuma-espanja-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+kuuma-hollantilaiset-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+kuuma-intialainen-naiset legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+kuuma-islanti-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+kuuma-jordanian-naiset legit postimyynti morsian (0)
- fi+kuuma-karibia-naiset legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+kuuma-kazakstan-naiset legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+kuuma-kuubalainen-naiset legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+kuuma-meksikolainen-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+kuuma-nicaraguan-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+kuuma-puerto-rican-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+kuuma-siperian-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+kuuma-slovakian-naiset legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+kuuma-sudanilaiset-naiset legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+kuuma-tadzikistan-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+kuuma-tanska-naiset legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+kuumat-balttilaiset-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+kuumat-eurooppalaiset-naiset legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+kuumat-laosin-naiset legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+kuumat-tsetseeni-naiset legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+la-date-arvostelu parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+latinfeels-arvostelu legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+libanonilaiset-morsiamet parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+liettualaiset-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+lovefort-arvostelu parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+maailman-kuumimmat-naiset legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+meetville-arvostelu legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+mongolian-naiset legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+nicaragualaiset-naiset legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+norja-morsiamet legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+nuoret-naimattomat-naiset legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+paras-tapa-tavata-naisia-verkossa parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+perun-morsiamet legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+pohjoismaiset-naiset legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+postimyyntimorsiamet-ovatko-he-laillisia legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+puertoricolais-treffisivustot-ja-sovellukset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+puolalaiset-treffisivustot-ja-sovellukset legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+ranska-treffisivustot-ja-sovellukset legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+romania-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+saksan-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+serbian-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (0)
- fi+shaadi-arvostelu legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+skandinaaviset-morsiamet parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+slovakian-morsiamet legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+slovakian-naiset legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+suomi-naiset legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+sveitsilaiset-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+syyrialaiset-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+tadzikistan-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+tawkify-arvostelu legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+treffit-30-luvulla legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+tsetseeni-naiset legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+turkkilaiset-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+turkkilaiset-treffisivustot-ja-sovellukset legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+ukrainalaiset-morsiamet parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+unkarilaiset-morsiamet parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+uruguay-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+venaejaen-naiset parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+venalaiset-vs-ukrainalaiset-naiset-ovat-siella-mitaan-eroja parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- fi+victoriyaclub-arvostelu legit postimyynti morsian (1)
- fi+yksinaiset-naiset-joilla-on-lapsia parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- filipino women for marriage (1)
- filipino-brides free online sites for singles (1)
- filipino-dating-sites-and-apps free online sites for singles (1)
- filipino-women free online sites for singles (1)
- filipino-women+banga site free (1)
- filipino-women+bulacan free online sites for singles (1)
- filipino-women+cadiz site free (1)
- filipino-women+cebu-city site free (1)
- filipino-women+dumaguete free online sites for singles (1)
- filipino-women+pagadian site free (1)
- filipino-women+san-juan free online sites for singles (1)
- filipino-women+san-juan site free (1)
- filipino-women+victorias site free (1)
- filipino-women+zamboanga site free (1)
- filipinocupid-review free online sites for singles (0)
- find a bride (3)
- find a bride (0)
- find a bride online (1)
- find a mail order bride (2)
- find en brud (1)
- find en postordrebrud (2)
- find en postordrebrud (0)
- find japanese wife online (1)
- find mig en postordrebrud (1)
- find nearest payday loan company (1)
- find payday loans no credit check (1)
- finde en postordrebrud (2)
- finde en postordrebrud (0)
- Finden Sie eine Braut (3)
- Finden Sie mir eine Versandbestellbraut (3)
- finding a mail order bride (1)
- finn en brud (3)
- finn en postordrebrud (3)
- finn meg en postordrebrud (1)
- finn postordrebrud (3)
- finne en postordrebrud (3)
- finnish-women site free (1)
- FinTech (5)
- first time payday loan no credit check (1)
- flirtwomen.net cupidates-review app free (1)
- flirtwomen.net da+varme-og-sexede-colombianske-kvinder de bedste steder at finde postordrebrud (1)
- flirtwomen.net de+datelatinbeauty-test Bester Mail -Bestellung Brautservice (1)
- flirtwomen.net de+heise-und-sexy-belarus-frauen Wie funktioniert die Mail -Bestellung Braut? (1)
- flirtwomen.net de+heise-und-sexy-irische-frauen Mail auf Bestellung Braut (1)
- flirtwomen.net de+heise-und-sexy-japanische-frauen Bester Mail -Bestellung Brautservice (1)
- flirtwomen.net de+heise-und-sexy-kolumbianische-frauen Top -bewertete Versandauftragsbrautseiten (1)
- flirtwomen.net de+heise-und-sexy-peruanische-frauen Top -bewertete Versandauftragsbrautseiten (1)
- flirtwomen.net de+heise-und-sexy-puertoricanische-frauen Wie funktioniert die Mail -Bestellung Braut? (1)
- flirtwomen.net es+latinwomanlove-opinion orden de correo novia vale la pena (1)
- flirtwomen.net es+mujeres-portuguesas-calientes-y-sexys orden de correo novia vale la pena (1)
- flirtwomen.net fi+kuumat-ja-seksikkaat-lansimaiset-aasialaiset-naiset postimyynti morsian (1)
- flirtwomen.net fi+kuumia-ja-seksikkaita-portugalilaisia-naisia postimyynti morsian (1)
- flirtwomen.net fr+femmes-suedoises-chaudes-et-sexy sites de mariГ©e par correspondance reddit (1)
- flirtwomen.net hot-and-sexy-argentinian-women app free (0)
- flirtwomen.net hot-and-sexy-icelandic-women websites (1)
- flirtwomen.net hot-and-sexy-romanian-women app free (1)
- flirtwomen.net hot-and-sexy-spanish-women sites for singles (1)
- flirtwomen.net it+datelatinbeauty-recensione trova una sposa (1)
- flirtwomen.net it+donne-norvegesi-calde-e-sexy trova una sposa (1)
- flirtwomen.net no+dateukrainiangirl-anmeldelse hva er en postordrebrud (1)
- flirtwomen.net no+varme-og-sexy-brasilianske-kvinner postordre brudinformasjon (1)
- flirtwomen.net no+varme-og-sexy-venezuela-kvinner postordre brudinformasjon (1)
- flirtwomen.net pt+meetnicerussian-recensao melhores paГses da noiva por correspondГЄncia (1)
- flirtwomen.net pt+mulheres-argentinas-quentes-e-sensuais melhores paГses da noiva por correspondГЄncia (1)
- flirtwomen.net pt+mulheres-cubanas-gostosas-e-sexy correio em ordem noiva (1)
- flirtwomen.net sv+charmcupid-recension topp 10 postorder brudens webbplatser (1)
- flirtwomen.net sv+heta-och-sexiga-latina-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brudens webbplatser (0)
- flirtwomen.net sv+heta-och-sexiga-turkiska-kvinnor postorder brud definition (1)
- flirtwomen.net sv+heta-och-sexiga-venezuela-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brudens webbplatser (1)
- flirtwomen.net tr+charmromance-inceleme Posta siparişi gelini bulmak için en iyi yerler (1)
- Florence installment loans near me (1)
- for adults (10)
- for free (16)
- foreign brides (2)
- fr+asiacharm-avis Commandez la mariГ©e rГ©el du site rГ©el (1)
- fr+belize-femmes Commandez la mariГ©e rГ©el du site rГ©el (1)
- fr+chat-avenue-avis Commandez la mariГ©e rГ©el du site rГ©el (1)
- fr+croates-femmes Commandez la mariГ©e rГ©el du site rГ©el (1)
- fr+daterussiangirl-avis Commandez la mariГ©e rГ©el du site rГ©el (1)
- fr+dateukrainiangirl-avis Commandez la mariГ©e rГ©el du site rГ©el (1)
- fr+dil-mil-avis Commandez la mariГ©e rГ©el du site rГ©el (1)
- fr+eharmony-avis Commandez la mariГ©e rГ©el du site rГ©el (1)
- fr+epouses-canadiennes Commandez la mariГ©e rГ©el du site rГ©el (1)
- fr+epouses-ethiopiennes Commandez la mariГ©e rГ©el du site rГ©el (1)
- fr+epouses-indonesiennes Commandez la mariГ©e rГ©el du site rГ©el (1)
- fr+fdating-avis Commandez la mariГ©e rГ©el du site rГ©el (1)
- free (29)
- free adult (7)
- free and single site (16)
- free apps (11)
- free online (10)
- free online sites for singles (13)
- free sex (12)
- free singles site (17)
- free site (9)
- free sites (9)
- free sites for (8)
- free websites (10)
- Gaithersburg installment loans near me (1)
- gdje kupiti mladenku za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (1)
- gdje mogu kupiti mladenku za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (1)
- gdje pronaći mladenku za narudžbu pošte (1)
- Gelin DГјnya Posta SipariЕџi Gelinleri (2)
- Gelin DГјnya Posta SipariЕџi Gelinleri (0)
- Gelin Posta SipariЕџi (1)
- Gelin SipariЕџ PostasД± (1)
- Gelin siparişi vermek için posta (3)
- Gelin siparişi vermek için posta (0)
- Gelin siparişi vermek için posta (0)
- gennemse postordrebrud (1)
- gennemsnitlige omkostninger ved postordrebrud (2)
- gennemsnitlige postordre brudepriser (1)
- gennemsnitspris for en postordrebrud (1)
- gennemsnitspris for postordrebrud (2)
- genomsnittlig kostnad för postorderbruden (1)
- genomsnittlig kostnad för en postorderbrud (1)
- genomsnittlig kostnad för postorderbruden (1)
- genomsnittliga postorder brudpriser (4)
- genomsnittspris för en postorderbrud (5)
- genomsnittspris för en postorderbrud (0)
- genomsnittspris för en postorderbrud (0)
- genomsnittspris för en postorderbrud (0)
- genomsnittspris för en postorderbrud (0)
- genomsnittspris för postorderbrud (2)
- genomsnittspris för postorderbrud (0)
- georgiapaydayloans installment loans bad credit (1)
- Gerçek için posta siparişi gelin? (3)
- Gerçek için posta siparişi gelin? (0)
- Gerçek için posta siparişi gelin? (0)
- Gerçek Posta Siparişi Gelin (5)
- Gerçek Posta Siparişi Gelin (0)
- Gerçek Posta Siparişi Gelin (0)
- Gerçek Posta Siparişi Gelin (0)
- Gerçek Posta Siparişi Gelin (0)
- Gerçek Posta Siparişi Gelin Hikayeleri (2)
- Gerçek Posta Siparişi Gelin Hikayeleri (0)
- Gerçek Posta Siparişi Gelin Hizmeti (1)
- Gerçek posta siparişi gelin siteleri (1)
- Gerçek Posta Siparişi Gelin Web Siteleri (3)
- Gerçek Posta Siparişi Gelin Web Siteleri (0)
- Gerçek Posta Siparişi Gelin Web Siteleri (0)
- Gerçek Posta Siparişi Gelin Web Sitesi (4)
- Gerçek Posta Siparişi Gelin Web Sitesi (0)
- Gerçek Posta Siparişi Gelin Web Sitesi (0)
- Gerçek Posta Siparişi Gelin Web Sitesi (0)
- Gerçek posta siparişi gelini sitesi (1)
- Gerçek İçin Posta Siparişi Gelin (4)
- Gerçek İçin Posta Siparişi Gelin (0)
- Gerçek İçin Posta Siparişi Gelin (0)
- get a cash advance (1)
- get a cash advance now (1)
- get a cash advance with bad credit (4)
- get a payday loan (3)
- get a payday loan near me (0)
- get a payday loan no credit check (0)
- get a payday loan no interest (2)
- get a payday loan now (1)
- get a payday loan now bad credit (1)
- get a payday loan with bad credit (1)
- get a payday loan with no credit (2)
- get a payday loans with other payday loans (3)
- get advance cash now (1)
- get cash advance (2)
- get cash advance at bank (1)
- get cash advance loans (1)
- get cash advance no credit check (1)
- get cash advance now (2)
- get cash advance payday loans (2)
- get cash in advance (2)
- get cash now on a payday loan (2)
- get cash now payday loan (3)
- get cash payday loan (1)
- get cash payday loan loan (2)
- get loan payday (1)
- get my payday loan (2)
- get oui of payday loans (2)
- get payday loan (1)
- get payday loan near me (1)
- get payday loan no credit check (1)
- get payday loan no interest (3)
- get payday loan now (2)
- getbride.org da+5-attraktive-og-beromte-blonde-kvinder-du-burde-kende bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- getbride.org da+amerikanske-kvinder-vs-europaeiske-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- getbride.org da+australske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org da+bedste-land-for-postordrebrude hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org da+britiske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (0)
- getbride.org da+canadiske-kvinder-vs-amerikanske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org da+cubanske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org da+hotteste-ukrainske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org da+indonesiske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org da+jamaicanske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org da+latin-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org da+portugisiske-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- getbride.org da+russian-cupid-anmeldelser bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- getbride.org da+russiske-kvinder-vs-amerikanske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org da+taiwanske-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- getbride.org da+tyrkiske-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- getbride.org da+tysk-datingside hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org da+varme-caribiske-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- getbride.org da+varme-chilenske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org da+varme-mexicanske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org de+amerikanische-frauen-gegen-europaische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- getbride.org de+arabische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- getbride.org de+australische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- getbride.org de+belgien-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- getbride.org de+chilaische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- getbride.org de+danische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- getbride.org de+daterussiangirl-test Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- getbride.org de+heise-britische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- getbride.org de+heise-dominikanische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- getbride.org de+heise-guatemalanische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- getbride.org de+heise-indonesische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- getbride.org de+heise-kambodschanische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- getbride.org de+heise-panamaische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- getbride.org de+heise-serbische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- getbride.org de+italienische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- getbride.org de+karibische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- getbride.org de+koreanische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- getbride.org de+latinfeels-test Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- getbride.org de+niederlandische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- getbride.org de+portugiesische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- getbride.org de+sexy-und-heise-russische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- getbride.org de+singapur-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- getbride.org de+slowakische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- getbride.org de+slowenische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- getbride.org de+spanische-dating-site Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- getbride.org de+taiwanesische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- getbride.org de+ukraine-dating-site Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- getbride.org es+el-salvador-mujeres que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+filipinas-sexy-y-caliente-mujeres que es la novia del pedido por correo (0)
- getbride.org es+mujer-francesa que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+mujeres-argentinas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+mujeres-asiaticas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+mujeres-camboyanas-calientes que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+mujeres-caribenas-calientes revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+mujeres-checas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+mujeres-chileanas-calientes que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+mujeres-de-pulido-caliente revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (0)
- getbride.org es+mujeres-egipcias que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+mujeres-eslovacas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+mujeres-finlandesas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+mujeres-francesas-calientes que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+mujeres-hungaras-calientes que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+mujeres-japonesas-vs-mujeres-americanas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+mujeres-kirguistan que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+mujeres-mexicanas-calientes revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+mujeres-peruanas-calientes que es la novia del pedido por correo (0)
- getbride.org es+mujeres-portuguesas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+mujeres-puertorriquenas-mas-calientes que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+mujeres-tajikistan revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+mujeres-turcas-calientes que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+mujeres-venezolanas-calientes revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+novias-rumanas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+paraguay-mujeres revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+russian-cupid-opinion revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (0)
- getbride.org es+sitio-de-citas-alemanas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+sitio-de-citas-espanol que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- getbride.org es+uruguay-mujeres que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- getbride.org filippiininaiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- getbride.org hollantilaiset-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- getbride.org islantilaiset-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- getbride.org it+asiandating-recensione vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- getbride.org it+donne-argentine vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- getbride.org it+donne-austriache ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- getbride.org it+donne-brasiliane ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- getbride.org it+donne-britanniche vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- getbride.org it+donne-bulgari ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- getbride.org it+donne-calde-di-taiwan ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- getbride.org it+donne-cambogiane-calde vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- getbride.org it+donne-caraibiche-calde vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- getbride.org it+donne-cilene ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- getbride.org it+donne-costa-rican vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- getbride.org it+donne-cubane vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- getbride.org it+donne-del-tajikistan ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- getbride.org it+donne-delleuropa-orientale ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- getbride.org it+donne-dominicane vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- getbride.org it+donne-etiopi vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- getbride.org it+donne-filippine ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- getbride.org it+donne-guatemalan-calde ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- getbride.org it+donne-messicane vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- getbride.org it+donne-olandesi ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- getbride.org it+donne-panamensi ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- getbride.org it+donne-russe vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- getbride.org it+donne-sloveni ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- getbride.org it+donne-svedesi ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- getbride.org it+donne-tailandesi vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- getbride.org it+donne-taiwanesi vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- getbride.org it+donne-uzbekistan vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- getbride.org it+donne-venezuelane ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- getbride.org it+donne-venezuelane-calde ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- getbride.org it+donne-vietnamite ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- getbride.org it+siti-di-incontri-dominicani vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- getbride.org it+sono-sposa-per-corrispondenza-illegali ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- getbride.org kazakstanin-naiset wikipedia postimyynti morsian (1)
- getbride.org kuubalaiset-naiset wikipedia postimyynti morsian (1)
- getbride.org kuumat-argentiinalaiset-naiset wikipedia postimyynti morsian (1)
- getbride.org kuumat-haitilaiset-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- getbride.org kuumat-indonesialaiset-naiset wikipedia postimyynti morsian (1)
- getbride.org kuumat-meksikolaiset-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- getbride.org kuumat-taiwan-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- getbride.org kuumia-ecuadorin-naisia wikipedia postimyynti morsian (1)
- getbride.org kuumimmat-brasilialaiset-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- getbride.org kuumimmat-korealaiset-naiset wikipedia postimyynti morsian (1)
- getbride.org latinalaiset-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- getbride.org latinfeels-arvostelu tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- getbride.org main_fi tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- getbride.org miten-saat-postimyynnissa-morsian tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- getbride.org moldovan-naiset wikipedia postimyynti morsian (1)
- getbride.org no+australske-kvinner online postordre brud (1)
- getbride.org no+dominikanske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org no+er-postordrebrud-ulovlig online postordre brud (1)
- getbride.org no+estonske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org no+etiopiske-kvinner online postordre brud (1)
- getbride.org no+europeiske-kvinner online postordre brud (1)
- getbride.org no+greske-kvinner online postordre brud (1)
- getbride.org no+italienske-kvinner online postordre brud (1)
- getbride.org no+kanadiske-bruder beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org no+kinesiske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (0)
- getbride.org no+kirgisiske-kvinner online postordre brud (0)
- getbride.org no+koreanske-kvinner online postordre brud (1)
- getbride.org no+makedonske-kvinner online postordre brud (1)
- getbride.org no+meksikanske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org no+mongolske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org no+nederlandske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org no+osteuropeiske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org no+pakistanske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org no+russiske-kvinner online postordre brud (1)
- getbride.org no+sexy-og-hete-russiske-kvinner online postordre brud (1)
- getbride.org no+singapore-kvinner online postordre brud (1)
- getbride.org no+slaviske-bruder online postordre brud (1)
- getbride.org no+sri-lanka-kvinner online postordre brud (1)
- getbride.org no+taiwanske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org no+tyrkiske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org no+ukrainske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (0)
- getbride.org no+varme-britiske-kvinner online postordre brud (1)
- getbride.org no+varme-guatemalanske-kvinner online postordre brud (1)
- getbride.org no+varme-japanske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org no+varme-nederlandske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org no+varme-serbiske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org no+varme-tsjekkiske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org no+varme-vietnamesiske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org no+venezuelanske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- getbride.org postimyynnissa-morsian-tilastot tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- getbride.org pt+estatisticas-noiva-por-correspondencia Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- getbride.org pt+mulheres-austriacas Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- getbride.org pt+mulheres-bosnianas Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- getbride.org pt+mulheres-britanicas-gostosas Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- getbride.org pt+mulheres-caribenhas-quentes Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- getbride.org pt+mulheres-chileanas-gostosas Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- getbride.org pt+mulheres-colombianas Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- getbride.org pt+mulheres-croatas Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- getbride.org pt+mulheres-de-belgica Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- getbride.org pt+mulheres-do-cazaquistao Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- getbride.org pt+mulheres-eslovenas Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- getbride.org pt+mulheres-estonianas Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- getbride.org pt+mulheres-etiopes Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- getbride.org pt+mulheres-haitianas-gostosas Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- getbride.org pt+mulheres-holandesas Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- getbride.org pt+mulheres-macedonias Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- getbride.org pt+mulheres-panamenhas-quentes Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- getbride.org pt+mulheres-peruanas-quentes Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- getbride.org pt+mulheres-porto-riquenhas Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- getbride.org pt+mulheres-romenas-gostosas Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- getbride.org pt+mulheres-russas Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- getbride.org pt+mulheres-russas-vs-americanas Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- getbride.org pt+russian-cupid-recensao Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- getbride.org pt+site-de-namoro-na-ucrania Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- getbride.org slaavilaiset-morsiamet tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- getbride.org suomalaiset-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- getbride.org sv+5-attraktiva-och-beromda-blonda-kvinnor-du-borde-kanna-till postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- getbride.org sv+amerikanska-kvinnor-mot-europeiska-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- getbride.org sv+ar-postordrebrud-olagliga postorder brudkataloger (1)
- getbride.org sv+cherryblossoms-recension postorder brudkataloger (1)
- getbride.org sv+egyptiska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- getbride.org sv+estniska-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- getbride.org sv+franska-kvinnor-mot-amerikanska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- getbride.org sv+heta-argentinska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (0)
- getbride.org sv+heta-asiatiska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- getbride.org sv+heta-guatemalanska-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- getbride.org sv+heta-haitianska-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- getbride.org sv+heta-hollandska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- getbride.org sv+heta-rumanska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- getbride.org sv+heta-tjeckiska-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- getbride.org sv+heta-ungerska-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- getbride.org sv+hetaste-indiska-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- getbride.org sv+hetaste-italienska-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- getbride.org sv+hetaste-kvinnor-i-puerto-rico postorder brudkataloger (1)
- getbride.org sv+islandska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- getbride.org sv+kambodjanska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- getbride.org sv+kanadiska-brudar postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- getbride.org sv+koreanska-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- getbride.org sv+makedonska-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (0)
- getbride.org sv+mexikanska-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- getbride.org sv+moldoviska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- getbride.org sv+pakistanska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (0)
- getbride.org sv+polska-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- getbride.org sv+portugisiska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- getbride.org sv+russian-cupid-recension postorder brudkataloger (0)
- getbride.org sv+schweiziska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- getbride.org sv+sexiga-och-heta-filippinska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- getbride.org sv+spanska-datingsida postorder brudkataloger (1)
- getbride.org sv+sri-lanka-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- getbride.org sv+thai-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- getbride.org sv+ukraina-datingsida postorder brudkataloger (1)
- getbride.org sv+ukrainedate-recension postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- getbride.org sv+vietnamesiska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- getbride.org taiwanilaiset-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- getbride.org tr+amerikali-kadinlar-vs-avrupa-kadinlari bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- getbride.org tr+arap-kadinlari Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek (1)
- getbride.org tr+avusturyali-kadinlar Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek (1)
- getbride.org tr+cek-kadinlari bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- getbride.org tr+dogu-avrupa-kadinlari-vs-amerikan-kadinlari Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek (0)
- getbride.org tr+el-salvador-kadinlari bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- getbride.org tr+guatemalan-kadinlar Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek (1)
- getbride.org tr+gurcu-kadinlar Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek (1)
- getbride.org tr+ingiliz-kadinlar bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- getbride.org tr+japon-kadin-vs-amerikan-kadin bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- getbride.org tr+japon-kadinlar bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- getbride.org tr+koreli-kadinlar Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek (1)
- getbride.org tr+kuba-kadinlari Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek (1)
- getbride.org tr+malezya-kadinlari bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- getbride.org tr+meksikali-kadinlar Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek (1)
- getbride.org tr+mogol-kadinlar bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- getbride.org tr+pakistanli-kadinlar bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- getbride.org tr+rus-kadinlari-vs-amerikali-kadinlar Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek (1)
- getbride.org tr+sicak-asyali-kadinlar Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek (1)
- getbride.org tr+sicak-bulgar-kadinlar bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- getbride.org tr+sicak-cek-kadinlar Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek (1)
- getbride.org tr+sicak-cila-kadinlar Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek (1)
- getbride.org tr+sicak-ingiliz-kadinlar bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- getbride.org tr+sicak-japon-kadinlar Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek (1)
- getbride.org tr+sicak-kolombiyali-kadinlar Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek (1)
- getbride.org tr+sicak-sili-kadinlari bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- getbride.org tr+sicak-turk-kadinlari bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- getbride.org tr+sirp-kadinlar bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- getbride.org tr+tajikistan-kadinlari bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- getbride.org tr+venezuela-kadinlari Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek (0)
- getbride.org vietnamilaiset-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- getting a cash advance (2)
- getting a cash advance at a bank (1)
- getting a loan from cash advance america (1)
- getting a payday loan with bad credit (1)
- getting cash advance (1)
- Getting Married In College (1)
- getting payday loan (1)
- girls for marriage (1)
- gjennomsnittlig kostnad for en postordrebrud (1)
- gjennomsnittlig kostnad for postordrebruden (1)
- gjennomsnittsalder for postordrebruden (1)
- gjennomsnittspris for en postordrebrud (1)
- gjennomsnittspris for postordrebrud (3)
- gjennomsnittspris pГҐ en postordrebrud (2)
- gjennomsnittspris pГҐ en postordrebrud (0)
- god postordre brudesider (1)
- gode postordre brud nettsteder (2)
- good mail order bride website (4)
- Goose Creek online installment loans (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net charm-date que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net chicas-chinas-calientes-y-sexys revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net chicas-coreanas-calientes-y-sexys que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net chicas-eslavas-calientes-y-sexys revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net chicas-filipinas-calientes-y-sexys que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net chicas-negras-calientes-y-sexys que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net chicas-ucranianas-calientes-y-sexys que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net chicas-vietnamitas-calientes-y-sexys que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net como-conocer-mujeres-en-linea que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net da+amerikanske-kvinder-vs-europaeiske-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net da+amour-factory bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net da+asia-me hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net da+asian-melodies bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net da+asiatiske-brude bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net da+date-ukrainsk-pige hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net da+find-asian-beauty hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net da+graeske-brude bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net da+hvordan-man-kober bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net da+jolly-romance bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net da+latin-kvinde-kaerlighed hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net da+sverige-brude bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net da+varme-og-sexede-kinesiske-piger bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net da+varme-og-sexede-russiske-piger bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net da+venezuelanske-brude bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net date-asian-woman que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net de+altere-braute Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (0)
- gorgeousbrides.net de+arabische-braute Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net de+asia-me Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net de+asiatische-braute Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net de+asiatische-frauen-treffen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net de+beste-lander-fur-dating Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (0)
- gorgeousbrides.net de+colombialady Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (0)
- gorgeousbrides.net de+costa-rica-braute Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net de+einfrau Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net de+franzosische-braute Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net de+frauen-die-altere-manner-suchen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net de+heise-und-sexy-ukrainische-madchen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net de+heise-und-sexy-venezolanische-madchen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net de+lateinamerikanische-frau-liebe Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net de+latin-beauty-date Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net de+russische-braute Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net de+slawische-braute Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net de+treffen-sie-ukrainische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net de+ukrainebride4you Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net de+was-ist-katalogheirat Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net de+werden-sie-ein-katalogheirat Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net de+wie-man-eine-frau-findet Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net fi+asian-melodies tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net fi+avioliiton-treffisivustot tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (0)
- gorgeousbrides.net fi+date-russian-girl tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (0)
- gorgeousbrides.net fi+irlantilaiset-morsiamet tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net fi+itakuusa tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net fi+italialaiset-morsiamet tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net fi+kuinka-ostaa tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net fi+kuumia-ja-seksikkaita-japanilaisia-tyttoja tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net fi+la-date tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net fi+mika-on-postimyynnissa-morsian tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net fi+oikeudelliset-kysymykset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net fi+puerto-rican-morsiamet tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net fi+romanialaiset-morsiamet tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net fi+tapaa-latinalaisia-naisia tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (0)
- gorgeousbrides.net fi+tavata-kiinalaisia-naisia tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net fi+yhden-naisen tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net it+amour-feel ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- gorgeousbrides.net it+asia-me vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net it+asian-beauty-online vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net it+asian-melodies ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- gorgeousbrides.net it+come-trovare vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net it+love-fort ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net it+ragazze-calde-e-sexy-del-mondo vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net it+ragazze-svedesi-calde-e-sexy ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net it+ragazze-ucraine-calde-e-sexy vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net it+ragazze-venezuelane-calde-e-sexy vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net it+spose-ceche vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net it+spose-cubane vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net it+spose-europee ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- gorgeousbrides.net it+spose-giapponesi vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net it+spose-honduregne ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (2)
- gorgeousbrides.net it+spose-venezuelane vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net it+ukrainebride4you vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net la-date que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net latin-beauty-date que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net latin-feels revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net lover-whirl revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net main_no beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net no+amour-factory beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net no+honduran-bruder beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net no+irske-bruder beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net novia-extranjera revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net novia-por-correo-meme revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net novias-albanesas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net novias-arabes que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net novias-australianas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net novias-brasilenas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net novias-chinas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net novias-filipinas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net novias-hondurenas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net novias-suecas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net novias-tailandesas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net paises-que-aman-a-los-hombres-estadounidenses revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net pt+conhecer-mulheres-asiaticas Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net pt+date-asian-woman Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net pt+date-russian-girl Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net pt+garotas-alemas-gostosas-e-sexy Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net pt+garotas-colombianas-gostosas-e-sexy Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net pt+garotas-espanholas-gostosas-e-sexy Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net pt+garotas-filipinas-gostosas-e-sexy Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net pt+garotas-italianas-gostosas-e-sexy Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net pt+garotas-romanas-gostosas-e-sexy Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net pt+garotas-suecas-gostosas-e-sexy Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net pt+la-date Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net pt+latam-date Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net pt+mulher-asiatica-fofa Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net pt+noivas-francesas Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- gorgeousbrides.net pt+noivas-hungaras Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net pt+noivas-japonesas Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net pt+noivas-vietnamitas Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net pt+questoes-legais Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net pt+sofiadate Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net sv+amerikanska-brudar postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net sv+amerikanska-kvinnor-mot-europeiska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net sv+asia-me postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net sv+asiatiska-brudar postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net sv+colombianska-brudar postorder brudkataloger (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net sv+costa-rican-brudar postorder brudkataloger (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net sv+date-asian-woman postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net sv+datum-ukrainsk-tjej postorder brudkataloger (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net sv+heta-och-sexiga-franska-flickor postorder brudkataloger (0)
- gorgeousbrides.net sv+heta-och-sexiga-koreanska-flickor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net sv+heta-och-sexiga-mexikanska-flickor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net sv+heta-och-sexiga-polska-flickor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net sv+heta-och-sexiga-thai-flickor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net sv+irlandska-brudar postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net sv+latin-brudar postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net sv+latvianska-brudar postorder brudkataloger (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net sv+mexikanska-brudar postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net sv+postordrebrud-bedragerier postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net sv+serbiska-brudar postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net sv+theluckydate postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net sv+traffa-asiatiska-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net sv+traffa-latinska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net sv+ukrainebride4you postorder brudkataloger (1)
- gorgeousbrides.net ukrainebride4you revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- Green City personal installment loans (1)
- guide to payday loans (2)
- Gute Mail -Bestellung Brautseiten (4)
- Gute Mail -Bestellung Brautwebsite (1)
- högst rankade postorder brudar webbplatser (1)
- högst rankade postorder brudtjänst (1)
- health (2)
- heartbrides.com alemanha-perfis-de-mulheres top dez site de noiva por ordem de correio (1)
- heartbrides.com da+filippinske-kvindelige-profiler Г¦gte mail ordre brude websteder (1)
- heartbrides.com da+honduranske-brude Г¦gte mail ordre brude websteder (1)
- heartbrides.com da+hvordan-fungerer-postordrebrude Г¦gte mail ordre brude websteder (1)
- heartbrides.com da+lande-der-elsker-amerikanske-maend hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- heartbrides.com de+lander-die-amerikanische-manner-lieben Bester Mail -Bestellung Brautservice (1)
- heartbrides.com de+tschechische-braute Wie funktioniert die Mail -Bestellung Braut? (1)
- heartbrides.com es+novias-africanas agencias de novias por correo (1)
- heartbrides.com es+novias-colombianas que es como la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- heartbrides.com es+novias-coreanas que es como la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- heartbrides.com es+perfiles-de-mujeres-ucranianas que es una novia de pedidos por correo (1)
- heartbrides.com fi+dominikaani-vs-puerto-rikaani todellinen postimyynti morsiamen sivusto (1)
- heartbrides.com fi+perun-morsiamet postimyynti morsian todellinen (1)
- heartbrides.com fr+cout-des-mariees-bresiliennes histoires de la mariГ©e par correspondance rГ©elle (1)
- heartbrides.com it+costo-delle-spose-filippine trova una sposa (1)
- heartbrides.com it+latin-feels-recensione puoi spedire una sposa (1)
- heartbrides.com it+profili-delle-donne-della-thailandia il posto migliore per ottenere una sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- heartbrides.com it+spose-portoricane dove posso ottenere una sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- heartbrides.com it+spose-turche dove posso ottenere una sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- heartbrides.com no+date-russian-girl-anmeldelse hva er en postordrebrud (1)
- heartbrides.com no+dominican-vs-puerto-rican postordre brudinformasjon (1)
- heartbrides.com no+slavisk hva er en postordrebrud (1)
- heartbrides.com no+ukrainebrides4you-anmeldelse hva er en postordrebrud (1)
- heartbrides.com noivas-bosnianas procurando casamento (1)
- heartbrides.com noivas-japonesas melhores paГses da noiva por correspondГЄncia (1)
- heartbrides.com noivas-japonesas uma noiva por correspondГЄncia (1)
- heartbrides.com noivas-paquistanesas melhores paГses da noiva por correspondГЄncia (1)
- heartbrides.com perfis-de-mulheres-bulgaras correio em ordem noiva (1)
- heartbrides.com perfis-de-mulheres-polonesas melhores paГses da noiva por correspondГЄncia (1)
- heartbrides.com site-de-namoro correio em ordem noiva (1)
- heartbrides.com sv+latin postorder brud definition (1)
- heartbrides.com sv+tyskland-kvinnor-profiler topp 10 postorder brudens webbplatser (1)
- heartbrides.com tr+alman-gelinleri Posta siparişi gelini bulmak için en iyi yerler (1)
- heartbrides.com tr+asyali-kadin-profilleri Posta SipariЕџi Gelin EndГјstrisi (1)
- heartbrides.com tr+cuteasianwoman-inceleme Posta siparişi gelini bulmak için en iyi yerler (1)
- heartbrides.com tr+filipina-gelinleri En Д°yi Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmeti (1)
- heartbrides.com tr+latin-women-date-inceleme En Д°yi Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmeti (1)
- heartbrides.com tr+tayland-gelinleri-maliyeti En Д°yi Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmeti (1)
- heartbrides.com tr+yabanci-bir-gelin-nasil-bulunur Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Web Siteleri Д°ncelemeleri (1)
- heated-affairs-review only reviews (1)
- heiГџeste Mail -Bestellung Braut (3)
- heiГџeste Mail -Bestellung Braut (0)
- heiГџeste Mail -Bestellung Braut (0)
- help me to write my essay (2)
- help me write my college essay (1)
- help me write my critical essay (1)
- help me write my essay online (2)
- help to write my essay (1)
- help write my essay today (1)
- hetaste postorderbruden (2)
- hi-ly.com (1)
- Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (2)
- Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- histoires de la mariГ©e par correspondance rГ©elle (5)
- histoires de la mariГ©e par correspondance rГ©elle (0)
- histoires de la mariГ©e par correspondance rГ©elle (0)
- histoires de la mariГ©e par correspondance rГ©elle (0)
- histoires de la mariГ©e par correspondance rГ©elle (0)
- histoires de la mariГ©e par la courrier Г©lectronique (5)
- histoires de la mariГ©e par la courrier Г©lectronique (0)
- histoires de la mariГ©e par la courrier Г©lectronique (0)
- histoires de la mariГ©e par la courrier Г©lectronique (0)
- histoires de la mariГ©e par la courrier Г©lectronique (0)
- Histoires de mariГ©e par correspondance reddit (2)
- Histoires de mariГ©e par correspondance reddit (0)
- Histoires de vente par correspondance (3)
- historia correo orden novia (3)
- historia om postorderbruden (1)
- historia real de la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- historiapostitilaus morsian (1)
- historias de novias de pedidos por correo (1)
- historias de novias de pedidos por correo real (1)
- historie postordre brud (2)
- historien til postordrebruden (1)
- Historique de la mariГ©e par correspondance (6)
- Historique de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Historique de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Historique de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Historique de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Historique de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- History -Mail -Bestellung Braut (1)
- history mail order bride (4)
- hitta en postorderbrud (4)
- hitta mig en postorderbrud (2)
- hitta postorder brud (2)
- honduran-women site free (1)
- hongkongcupid-review site free (1)
- horny (9)
- hot (2)
- hot mail order bride (2)
- hot mail ordre brud (3)
- hot-american-women free online sites for singles (1)
- hot-argentina-women free online sites for singles (1)
- hot-armenian-women free online sites for singles (1)
- hot-asian-women free online sites for singles (1)
- hot-bali-women free online sites for singles (0)
- hot-baltic-women site free (1)
- hot-bangladesh-women free online sites for singles (1)
- hot-brazilian-women site free (1)
- hot-costa-rican-women site free (1)
- hot-cuban-women free online sites for singles (1)
- hot-eastern-european-women site free (1)
- hot-egyptian-women site free (1)
- hot-ghanaian-women free online sites for singles (1)
- hot-guyana-women site free (1)
- hot-guyanese-women site free (1)
- hot-haitian-women site free (1)
- hot-indonesian-women site free (0)
- hot-iranian-women free online sites for singles (1)
- hot-jamaican-women free online sites for singles (1)
- hot-kazakhstan-women free online sites for singles (1)
- hot-kyrgyzstan-women site free (1)
- hot-latvia-women free online sites for singles (1)
- hot-nepal-women free online sites for singles (1)
- hot-peruvian-women site free (1)
- hot-scottish-women site free (1)
- hot-serbian-women site free (1)
- hot-siberian-women free online sites for singles (1)
- hot-somali-women free online sites for singles (1)
- hot-spanish-women free online sites for singles (1)
- hot-sudanese-women free online sites for singles (1)
- hot-venezuelan-women free online sites for singles (1)
- hot-vietnamese-women site free (1)
- hottest mail order bride (2)
- hottest mail order bride (0)
- hotteste postordrebrud (4)
- hotteste postordrebrud (0)
- hottestwomen.net da+danske-kvinder de bedste steder at finde postordrebrud (1)
- hottestwomen.net da+mongolske-kvinder Г¦gte mail ordre brude websteder (1)
- hottestwomen.net de+schwedische-frauen Top -bewertete Versandauftragsbrautseiten (1)
- hottestwomen.net de+wer-sollte-zuerst-nach-dem-ersten-datum-schreiben Beste Mail bestellen Braut Websites Reddit (1)
- hottestwomen.net es+mujer-britanica agencia de novias por correo (1)
- hottestwomen.net es+mujeres-chinas que es como la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- hottestwomen.net es+mujeres-filipinas agencias de novias por correo (1)
- hottestwomen.net es+mujeres-noruegas que es como la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- hottestwomen.net fi+dominikaaninen-nainen postimyynti morsian (1)
- hottestwomen.net fi+irlantilaiset-naiset postimyynti morsian (1)
- hottestwomen.net fi+slovenialaiset-naiset oikeita postimyynti morsiamen tarinoita (1)
- hottestwomen.net fr+les-femmes-laotiennes sites de mariГ©e par correspondance reddit (1)
- hottestwomen.net fr+les-femmes-tcheques sites de mariГ©e par correspondance reddit (1)
- hottestwomen.net it+donna-britannica trova una sposa (1)
- hottestwomen.net it+donna-portoricana migliori recensioni per i siti della sposa (1)
- hottestwomen.net no+argentinsk-kvinne postordre brudinformasjon (1)
- hottestwomen.net no+japanske-kvinner postordre brudinformasjon (1)
- hottestwomen.net no+malaysiske-kvinner postordre brudinformasjon (1)
- hottestwomen.net no+slovakiske-kvinner hva er en postordrebrud (1)
- hottestwomen.net pt+com-recensao noiva por correspondГЄncia (1)
- hottestwomen.net pt+mulher-cubana correio em ordem noiva (1)
- hottestwomen.net pt+mulheres-chinesas melhores paГses da noiva por correspondГЄncia (0)
- hottestwomen.net pt+mulheres-servias correio em ordem noiva (1)
- hottestwomen.net sirp-kadinlar En Д°yi Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmeti (1)
- hottestwomen.net sv+kroatiska-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brudens webbplatser (1)
- hottestwomen.net sv+latvianska-kvinnor postorder brudens webbplatser reddit (1)
- hottestwomen.net sv+litauiska-kvinnor postorder brud definition (1)
- hottestwomen.net sv+miss-travel-recension postorder brud definition (1)
- hottestwomen.net sv+salvadoranska-kvinnor postorder brud definition (1)
- How Can I Date A Girl From A Different Country (1)
- how can i get a payday loan (3)
- how can i get a payday loan? (2)
- how can you get a payday loan (1)
- how cash advance (1)
- how do a payday loan work (1)
- how do cash advance work (1)
- how do i do a cash advance (3)
- how do i do cash advance (2)
- how do i get a cash advance from a bank (1)
- how do i get a cash advance with (2)
- how do i get a cash advance? (1)
- how do i get a payday loan (1)
- how do i get a payday loan with bad credit (2)
- how do i get a payday loans (2)
- how do mail order bride sites work (0)
- how do payday loans (2)
- how do payday loans work (1)
- how do payday loans works (1)
- how do you do cash advance (2)
- how do you do cash advance? (1)
- how do you get a cash advance (3)
- how do you get a payday loan (1)
- how do you use a cash advance (3)
- how does a cash advance work (1)
- how does a cash advance works (1)
- how does a mail order bride work (1)
- how does a payday cash advance work (0)
- how does a payday loan interest work (4)
- how does advance cash work (2)
- how does cash advance america work (3)
- how does cash advance interest work (1)
- how does cash advance on (1)
- how does cash advance work (4)
- how does cash in advance work (3)
- how does cash in advance works (1)
- how does getting a cash advance work (1)
- how does mail order bride work (2)
- how does mail order bride works (2)
- how does payday cash advance work (1)
- how does payday loan work (2)
- how does payday loans work (3)
- how does the cash advance work (2)
- how is payday loans work (1)
- how much are payday loans (1)
- how much can i get for a payday loan (1)
- how much can i get from a payday loan (4)
- how much can i get from cash advance (1)
- how much can i get in a payday loan (1)
- how much can i get on a payday loan (1)
- how much can you get a payday loan for (1)
- how much can you get from a payday loan (2)
- how much can you get from payday loans (1)
- how much can you get on a cash advance (1)
- how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- how much can you get on a payday loan? (2)
- how much cash advance (1)
- how much cash advance can i get (0)
- how much cash can you get from a cash advance (1)
- how much could i get on a payday loan (1)
- how much do you get for payday loan (2)
- how much for a cash advance (2)
- how much for cash advance (1)
- how much interest cash advance (2)
- how much interest do payday loans charge? (2)
- how much interest do you pay on a cash advance (2)
- how much interest do you pay on a payday loan (1)
- how much interest for a payday loan (2)
- how much interest for cash advance (2)
- how much interest is on a payday loan (1)
- how much interest on a cash advance (1)
- how much interest on a payday loan (2)
- how much interest on cash advance (1)
- how much interest on payday loans (1)
- how much interest payday loan (1)
- how much is a cash advance (1)
- how much is a cash advance from advance america (2)
- how much is a payday loan for (2)
- how much is interest on a cash advance (2)
- how much is interest on cash advance (3)
- how much is my cash advance interest (1)
- how much is payday loan interest (1)
- how much is the interest on payday loans (2)
- how much of a cash advance can i get (2)
- how much of a payday loan can i get (1)
- how much to pay for payday loans (4)
- how mush interest on a payday loan (3)
- how payday loan work (4)
- how payday loans work in usa (3)
- how soon do i have to pay payday loans (1)
- how soon do you have to pay payday loan (2)
- how to cash advance (1)
- how to cash advance at other bank (2)
- how to cash advance from a bank (2)
- how to cash advance on credit (3)
- how to do a cash advance (4)
- how to do a mail order bride (1)
- how to do cash advance at bank (3)
- how to do mail order bride (1)
- how to do payday loan (3)
- how to do payday loans (1)
- how to get a cash advance from a bank (1)
- how to get a cash advance from a bank credit (2)
- how to get a cash advance from payday (2)
- how to get a cash advance loan (1)
- how to get a cash advance with bad credit (2)
- how to get a loan from cash advance (4)
- how to get a payday advance loan (2)
- how to get a payday loan (1)
- how to get a payday loan bad credit (2)
- how to get a payday loan with bad credit (2)
- how to get a payday loan with bad credit? (1)
- how to get a payday loan with no credit check (1)
- how to get cash advance from (1)
- how to get cash advance from bank (1)
- how to get cash advance loan (1)
- how to get cash advance out of your credit (3)
- how to get cash advance with bad credit (1)
- how to get cash from credit wtihout cash advance (3)
- how to get cash in advance (1)
- how to get payday loan with bad credit (2)
- how to get you payday loan (1)
- how to marry a mail order bride (3)
- how to order a mail order bride (1)
- how to order a russian mail order bride (3)
- how to order mail order bride (3)
- how to payday loan (1)
- how to payday loans (2)
- how to payday loans work (2)
- how to prepare a mail order bride (1)
- how to prepare a mail order bride reddit (3)
- how to use a cash advance (1)
- how to use cash advance (1)
- how to use credit cash advance (1)
- how to use payday loans (2)
- how-long-to-date-before-marriage free online sites for singles (1)
- hr+2redbeans-recenzija Prava narudЕѕba za mladenku (1)
- hr+afroromance-recenzija Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+asia-beauty-date-recenzija Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+azijske-nevjeste Prava narudЕѕba za mladenku (1)
- hr+belize-zene Prava narudЕѕba za mladenku (1)
- hr+brazilske-zene Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+cougar-life-recenzija Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+dateinasia-recenzija Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+daterussiangirl-recenzija Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+egipcanke-zene Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+europeandate-recenzija Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+findukrainianbeauty-recenzija Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+honduraske-zene Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+islandske-zene Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+jamajcanke-nevjeste Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+japancupid-recenzija Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+jpeoplemeet-recenzija Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+juznoafricke-zene Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+kineski-zene Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+koreancupid-recenzija Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+makedonija-zene Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+meetme-recenzija Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+meksicke-zene Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+najzgodnije-zene-na-svijetu Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+omegle-recenzija Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+pakistanske-zene Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+plavusa-poznate-zene Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+ruske-stranice-i-aplikacije-za-upoznavanje Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+ruski-zene Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+russianbeautydate-recenzija Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+vruce-armenske-zene Prava narudЕѕba za mladenku (1)
- hr+vruce-bangladeske-zene Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+vruce-bosanske-zene Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+vruce-britanske-zene Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+vruce-indonezijske-zene Prava narudЕѕba za mladenku (0)
- hr+vruce-irske-zene Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+vruce-istocnoeuropske-zene Prava narudЕѕba za mladenku (1)
- hr+vruce-izraelske-zene Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+vruce-makedonke-zene Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+vruce-portorikanske-zene Prava narudЕѕba za mladenku (1)
- hr+vruce-rumunjske-zene Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+vruce-slavenske-zene Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (1)
- hr+vruce-sudanske-zene Prava narudЕѕba za mladenku (1)
- huippuposti tilaus morsian (4)
- huippusähköpostitilaus morsiamen sivustot. (2)
- huippusähköpostitilaus morsiamen sivustot. (0)
- huipputarjous morsiamen maat (1)
- huipputarjous morsiamen palvelut (1)
- huipputarjous morsiamen sivustot (2)
- huipputarjous morsian istuu (3)
- hungarian-women free online sites for singles (1)
- Hungary escort girl here (1)
- hur beställer post brudarbete (1)
- hur beställer post brudarbete (6)
- hur beställer post brudarbete (0)
- hur beställer post brudarbete (0)
- hur beställer post brudarbete (0)
- hur beställer post brudarbete (0)
- hur beställer post brudarbete (0)
- hur fungerar en postorderbrud (2)
- hur fungerar postorderbrudplatser (1)
- hur man beställer en postorderbrud (2)
- hur man beställer en postorderbrud (0)
- hur man beställer en postorderbrud (4)
- hur man beställer en postorderbrud (0)
- hur man beställer en postorderbrud (0)
- hur man beställer en postorderbrud (0)
- hur man beställer en rysk brud (2)
- hur man beställer en rysk brud (0)
- hur man beställer en rysk postorderbrud (1)
- hur man beställer postorder brud (2)
- hur man beställer postorder brud (0)
- hur man förbereder en postorderbrud (1)
- hur man går med en postorderbrud (1)
- hur man gГҐr med en postorderbrud (1)
- hur man skickar beställning brud (4)
- hur man skickar beställning brud (0)
- hur man skickar beställning brud (0)
- hur man skickar beställning brud (0)
- hur man skickar en beställning av en brud (3)
- hur man skickar en beställning av en brud (0)
- hur man skickar en beställning av en brud (0)
- hva en postordrebrud (4)
- hva er de beste postordrebrudstedene (4)
- hva er den beste postordrebrudstedet (1)
- hva er den beste postordrebrudtjenesten (2)
- Hva er en postordre brud (1)
- hva er en postordrebrud (2)
- hva er en postordrebrud? (2)
- hva er postordre brud tjenester (2)
- hva er postordrebrud (7)
- hva er postordrebrud? (1)
- hva er postordrebruden? (2)
- hvad er de bedste postordre brudesider (3)
- hvad er den bedste postordre brude service (3)
- hvad er den bedste postordre brude service (0)
- hvad er en postordrebrud (5)
- hvad er en postordrebrud? (1)
- hvad er postordre brude tjenester (1)
- hvad er postordrebruden? (1)
- hvor du finner en postordrebrud (2)
- hvor du kan kjГёpe en postordrebrud (2)
- hvor du kan kjГёpe en postordrebrud (0)
- hvor finder jeg en postordrebrud (1)
- hvor finner jeg en postordrebrud (3)
- hvor kan jeg finde en postordrebrud (2)
- hvor kan jeg finne en postordrebrud (1)
- hvor kan jeg fГҐ en postordrebrud (2)
- hvor kan jeg fГҐ en postordrebrud (0)
- hvor kjГёper jeg en postordrebrud (1)
- hvor kГёber jeg en postordrebrud (2)
- hvor kГёber jeg en postordrebrud (0)
- hvordan bestille en russisk brud (1)
- hvordan bestille en russisk postordrebrud (4)
- hvordan date en postordrebrud (2)
- hvordan du bestiller en postordrebrud (2)
- hvordan du bestiller postordrebrud (3)
- hvordan du forbereder en postordre brud reddit (3)
- hvordan du forbereder en postordrebrud (3)
- hvordan du gifter deg med en postordrebrud (1)
- hvordan du gjГёr en postordrebrud (2)
- hvordan du gjГёr en postordrebrud (0)
- hvordan du gjГёr postordrebrud (5)
- hvordan du gjГёr postordrebrud (0)
- hvordan du gjГёr postordrebrud (0)
- hvordan du gjГёr postordrebrud (0)
- hvordan du gjГёr postordrebrud (0)
- hvordan du kan sende en brud pГҐ mail (1)
- hvordan du sender ordrebrud (2)
- hvordan fungerer en postordrebrud (2)
- hvordan fungerer postordre brud (2)
- hvordan fungerer postordrebruden (5)
- hvordan fungerer postordrebrudesider (1)
- hvordan fungerer postordrebrudswebsteder (3)
- hvordan fungerer postordrebrudswebsteder (0)
- hvordan kjГёpe en postordrebrud (1)
- hvordan man bestiller en russisk postbrud (1)
- hvordan man bestiller en russisk postordrebrud (3)
- hvordan man bestiller postordrebrud (1)
- hvordan man forbereder en postordre brud reddit (1)
- hvordan man forbereder en postordrebrud (2)
- hvordan man gГҐr ud med en postordrebrud (1)
- hvordan man kГёber en postordrebrud (1)
- hvordan man laver en postordrebrud (1)
- hvordan man sender en ordre (1)
- hyesingles-review free online sites for singles (1)
- hyviä postimyynti morsiamen sivustoja (1)
- i 10 migliori siti di sposa per corrispondenza (4)
- i 10 migliori siti di sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- i 10 migliori siti web di sposa per corrispondenza (3)
- i 5 migliori siti di sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- i migliori paesi della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- i migliori paesi per ottenere una sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- i migliori posti per la sposa per corrispondenza (3)
- i migliori siti web per la sposa per corrispondenza (3)
- i need a cash advance (2)
- i need a cash advance now (3)
- i need a loan not a payday loan (1)
- i need a payday loan (1)
- i need a payday loan bad credit (2)
- i need a payday loan but have bad credit (1)
- i need a payday loan but i have bad credit (1)
- i need a payday loan for bad credit (2)
- i need a payday loan no credit check (2)
- i need a payday loan now (1)
- i need a payday loan now with bad credit (2)
- i need a payday loan with no credit check (0)
- i need a payday loan? (1)
- i need a payday loans (1)
- i need cash advance now (5)
- i need payday loan (1)
- i need payday loans (1)
- i posti migliori per ricevere la sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- i posti migliori per trovare la sposa per corrispondenza (5)
- i siti della sposa con le migliori offerte (1)
- i want a mail order bride (1)
- Idaho guaranteed installment loans for bad credit (1)
- if a payday loan (2)
- if cash advance (4)
- il posto migliore per ottenere una sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- in cerca di matrimonio (3)
- in cerca di matrimonio (0)
- in cerca di una sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- India Mostbet (8)
- indian-dating-sites-and-apps free online sites for singles (1)
- indian-women+agartala free online sites for singles (1)
- indian-women+chandigarh free online sites for singles (1)
- indian-women+delhi free online sites for singles (1)
- indian-women+indore free online sites for singles (1)
- indian-women+jalandhar free online sites for singles (1)
- indian-women+kanpur free online sites for singles (1)
- indian-women+madurai free online sites for singles (0)
- indian-women+shimla free online sites for singles (1)
- indian-women+silchar free online sites for singles (1)
- indian-women+thiruvananthapuram free online sites for singles (0)
- indiancupid-review free online sites for singles (1)
- indonesian-women+surabaya free online sites for singles (1)
- indonesiancupid-review free online sites for singles (1)
- Industrie des mariГ©es par correspondance (4)
- Industrie des mariГ©es par correspondance (0)
- Industrie des mariГ©es par correspondance (0)
- Industrie des mariГ©es par correspondance (0)
- informaciГіn de la novia del pedido por correo (5)
- informaciГіn de la novia del pedido por correo (0)
- informaciГіn de la novia del pedido por correo (0)
- informaciГіn de la novia del pedido por correo (0)
- Informations sur les mariГ©es par correspondance (6)
- Informations sur les mariГ©es par correspondance (0)
- Informations sur les mariГ©es par correspondance (0)
- Informations sur les mariГ©es par correspondance (0)
- Informations sur les mariГ©es par correspondance (0)
- Informations sur les mariГ©es par correspondance (0)
- instabang-review site for people (1)
- installmentloansindian guaranteed installment loans for bad credit no credit check (1)
- installmentloansindian personal installment loans (1)
- installmentloansvirginia (2) guaranteed installment loans for bad credit no credit check (1)
- installmentloansvirginia (2) installment loans (1)
- installmentloansvirginia (2) installment loans no credit check (1)
- instant cash advance no credit check (1)
- instant payday loan direct lender no credit check (1)
- instant payday loan lenders no credit check (1)
- instant payday loan no credit check (2)
- instant payday loan no credit check direct lender (3)
- instant payday loans company (1)
- instant payday loans no brokers no credit check (1)
- instant payday loans no credit check (1)
- instant payday loans no credit check direct lenders (2)
- internasjonal postordrebrud (2)
- international mail order bride (1)
- international postordrebrud (2)
- international postordrebrud (0)
- Internationale Mail -Bestellung Braut (2)
- internationalwomen.net asiandate-recensione etГ media della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- internationalwomen.net charmdate-recensione etГ media della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+asiatiske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+belarus-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+bogota-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+bosniske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+brasilianske-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+cali-colombiske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+cambodian-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+ecuadorianske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+guyanesiske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+haitisk-kvinde hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+hot-latina-piger bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+indonesiske-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+internationale-datingsider bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+iranske-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+irske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+kazakhstan-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+kinesiske-piger hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+kroatiske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+lebanesiske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+mexicanske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+mode-lokale-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (0)
- internationalwomen.net da+nicaraguanske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+norske-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+osteuropaeiske-kvinder-der-daterer bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+russian-brides-anmeldelser bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+sloviske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+sverige-datingsider hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+sydafrikanske-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+tjekkiske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+varme-japanske-piger hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+varme-kinesiske-piger bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- internationalwomen.net da+varme-russiske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+agyptische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+asiatische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+asiatische-frauen-dating-sites Mail-Order-Braut (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+brasilianische-frauen Mail-Order-Braut (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+bulgarische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+cali-kolumbianische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+chatrooms-finden-ihren-besten-online-chatroom Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+heise-arabische-frauen Mail-Order-Braut (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+heise-indische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+heise-und-sexy-kolumbianische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+heiseste-frauen-der-welt Mail-Order-Braut (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+hong-kong-madchen Mail-Order-Braut (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+indische-dating-sites Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+internationale-dating-sites Mail-Order-Braut (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+italienische-madchen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+japanische-dating-sites Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+kubanische-madchen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+medellin-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+mexikanische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+moldawienfrauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+mongolische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+nigerianische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+nordische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+polnische-madchen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+russische-frauen-aus-websites Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+salvadorianische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+sao-paulo-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+schottische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+spanische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+tschechische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+turkische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- internationalwomen.net de+ukraine-date-test Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- internationalwomen.net donne-bionde-calde etГ media della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- internationalwomen.net donne-bogota vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- internationalwomen.net donne-bulgari etГ media della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- internationalwomen.net donne-cambogiane etГ media della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- internationalwomen.net donne-ceche etГ media della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- internationalwomen.net donne-coreane vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- internationalwomen.net donne-della-cartagena vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- internationalwomen.net donne-indiane vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- internationalwomen.net donne-nordiche vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- internationalwomen.net donne-portoghesi vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- internationalwomen.net donne-ucraine-calde vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+asiandate-opinion revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+chicas-cubanas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+chicas-de-filipina-caliente revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+chicas-hong-kong revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+chicas-suecas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+mujer-haitiana revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+mujeres-africanas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+mujeres-asiaticas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+mujeres-austriacas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+mujeres-colombianas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+mujeres-colombianas-calientes-y-sexys que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+mujeres-europeas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+mujeres-filipinas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+mujeres-ghana que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+mujeres-holandesas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+mujeres-indias revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+mujeres-irlandesas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+mujeres-lituanas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+mujeres-mongol que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+mujeres-negras-calientes revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+mujeres-nigerianas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+mujeres-noruegas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+mujeres-sudafricanas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+mujeres-suizas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+sitios-de-citas-colombianas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net es+sitios-de-citas-de-mujeres-rusas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- internationalwomen.net fi+aasialaisten-naisten-treffisivustot tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- internationalwomen.net fi+argentiinalaiset-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- internationalwomen.net fi+bolivian-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- internationalwomen.net fi+espanjalaiset-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- internationalwomen.net fi+etiopialaiset-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- internationalwomen.net fi+japanilaiset-treffisivustot tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- internationalwomen.net fi+kiinalaiset-treffisivustot tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- internationalwomen.net fi+kuumat-thaimaalaiset-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- internationalwomen.net fi+kuumia-japanilaisia-tyttoja tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- internationalwomen.net fi+latinalaiset-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (0)
- internationalwomen.net fi+latinalaisten-naisten-treffisivustot tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- internationalwomen.net fi+marokon-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- internationalwomen.net fi+paras-maa-loytaa-vaimo tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- internationalwomen.net fi+parhaat-rotujenvaliset-treffisivustot tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- internationalwomen.net fi+portugalilaiset-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- internationalwomen.net fi+ruotsin-treffisivustot tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- internationalwomen.net fi+suomalaiset-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- internationalwomen.net fr+femmes-asiatiques-chaudes Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- internationalwomen.net fr+femmes-autrichiennes Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- internationalwomen.net fr+femmes-ecossaises Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- internationalwomen.net fr+femmes-irlandaises-chaudes Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- internationalwomen.net fr+femmes-marocaines Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- internationalwomen.net fr+femmes-slovaques Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- internationalwomen.net fr+femmes-tcheques Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- internationalwomen.net fr+filles-chinoises Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- internationalwomen.net fr+filles-phillipina-chaudes Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- internationalwomen.net fr+filles-tijuana Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- internationalwomen.net fr+sites-de-rencontres-de-femmes-russes Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- internationalwomen.net latin-american-cupid-recensione vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- internationalwomen.net migliori-siti-di-incontri-interrazziali vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- internationalwomen.net no+albaniske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net no+bogota-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net no+irske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net no+kinesiske-jenter beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net no+mongolske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net no+pakistanske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net no+sexy-og-varme-brunette-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net no+sloveniske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net no+ukrainske-datingsider beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net no+uruguay-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net no+varme-meksikanske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- internationalwomen.net siti-di-incontri-giapponesi vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- internationalwomen.net sv+azerbaijan-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- internationalwomen.net sv+basta-landet-att-hitta-en-fru postorder brudkataloger (1)
- internationalwomen.net sv+belize-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- internationalwomen.net sv+bosniska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- internationalwomen.net sv+charmdate-recension postorder brudkataloger (1)
- internationalwomen.net sv+danska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- internationalwomen.net sv+heta-arabiska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (0)
- internationalwomen.net sv+heta-irlandska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- internationalwomen.net sv+heta-och-sexiga-colombianska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- internationalwomen.net sv+sexiga-och-heta-brunettkvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- internationalwomen.net sv+tyska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- internationalwomen.net sv+uruguay-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- internationalwomen.net tr+afrikali-kadinlar bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- internationalwomen.net tr+avustralya-kadinlari bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- internationalwomen.net tr+bogota-kadinlar bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- internationalwomen.net tr+danimarkali-kadinlar bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- internationalwomen.net tr+fince-kadinlar bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- internationalwomen.net tr+hint-tanisma-siteleri bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- internationell postorderbrud (1)
- internet payday loans no credit check (2)
- interracial dating (1)
- Interracial Mail -Bestellung Braut (1)
- interracial postorder brud (1)
- interracial postordre brud (1)
- Iraan installment loans near me (1)
- is a cash advance a loan (1)
- is a cash advance bad (3)
- is a cash advance bad for your credit (2)
- is a payday loan secured? (1)
- is cash advance (2)
- is cash advance a loan (1)
- is cash advance bad (2)
- is cash advance bad for your credit (2)
- is mail order bride a real thing (2)
- is mail order bride safe (1)
- is mail order bride worth it (2)
- is payday loan (2)
- Ist die Versandbraut real (1)
- Ist Versandbestellbraut eine echte Sache (1)
- Ist Versandbestellbraut es wert? (1)
- Ist Versandbestellbraut sicher (1)
- Istinita priДЌa o mladenki (2)
- Istinita priДЌa o mladenki (0)
- IT Education (1)
- IT Vacancies (1)
- IT Вакансії (1)
- IT Образование (3)
- it+2redbeans-recensione come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+adultfriendfinder-recensione come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+asiacharm-recensione come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+bali-donne come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+belga-donne come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+blackpeoplemeet-recensione come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+calde-donne-norvegesi come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+calde-donne-svedesi come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+canadese-donne come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+coreano-donne come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+costa-rican-donne come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+dateasianwoman-recensione come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+dateeuropeangirl-recensione come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+donne-africane-calde come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+donne-alte-singole come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+donne-armene-calde come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+donne-calde-mumbai come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+donne-calde-tagikistan come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+donne-coreane-contro-cinesi-contro-giapponesi come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+donne-indiane come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+donne-iraniane come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (0)
- it+donne-malesi-calde come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+donne-marocchine-calde come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+donne-mongole-calde come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+donne-pachistane-calde come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+donne-single-mature come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+donne-single-senza-figli come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+donne-venezuelane-calde come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+feeld-recensione come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+filippino-donne come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+filippino-spose come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+german-spose come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (0)
- it+interracial-dating-central-recensione come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+islandese-spose ordine postale legittimo sposa russa (1)
- it+italo-donne come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+jeevansathi-recensione ordine postale legittimo sposa russa (1)
- it+jswipe-recensione top 10 sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- it+jump4love-recensione come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+kazakistan-donne ordine postale legittimo sposa russa (1)
- it+laos-donne ordine postale legittimo sposa russa (0)
- it+leta-media-del-matrimonio top 10 sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- it+malaysian-spose top 10 sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- it+malese-donne come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+match-recensione top 10 sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- it+matchtruly-recensione come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+meetme-recensione ordine postale legittimo sposa russa (1)
- it+meetnicerussian-recensione ordine postale legittimo sposa russa (0)
- it+messicano-spose come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+mingle2-recensione top 10 sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- it+mongolo-donne top 10 sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- it+mumbai-donne top 10 sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- it+muslima-recensione top 10 sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- it+paesi-che-amano-gli-uomini-americani come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+paesi-con-le-donne-piu-belle top 10 sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- it+polacco-siti-e-app-di-incontri come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+positive-singles-recensione ordine postale legittimo sposa russa (1)
- it+pure-recensione top 10 sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- it+relazione-aperta top 10 sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- it+rosebrides-recensione top 10 sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- it+rumeno-siti-di-incontri-e-app come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+secret-benefits-recensione come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+shaadi-recensione come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+silversingles-recensione top 10 sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- it+singapore-donne come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+siti-di-incontri-indiani-e-app ordine postale legittimo sposa russa (1)
- it+siti-e-app-di-incontri-messicani come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+siti-e-app-di-incontri-portoricani come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+siti-e-app-di-incontri-tailandesi come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+spagnolo-siti-e-app-di-incontri come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+sposare-qualcuno-da-un-altro-paese ordine postale legittimo sposa russa (1)
- it+spose-cinesi come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+tagikistan-donne come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+ucraino-donne ordine postale legittimo sposa russa (1)
- it+ungherese-spose come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+uzbekistan-donne come preparare un ordine postale sposa reddit (1)
- it+vietnamita-donne ordine postale legittimo sposa russa (1)
- it-steroid (8)
- Jag vill ha en postorderbrud (2)
- japanese women for marriage (1)
- Je li mladenka narudЕѕba prava prava stvar (1)
- Je veux une mariГ©e par correspondance (3)
- Je veux une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Je veux une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- jeg vil ha en postordrebrud (2)
- Jeg vil have en postordrebrud (1)
- JetX Casino (1)
- Kahoka guaranteed installment loans for bad credit direct lenders only (1)
- kaikkien aikojen paras postimyynti (3)
- Kako napraviti mladenku za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (2)
- Kako napraviti mladenku za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (0)
- Kako radi mladenka za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (1)
- Kako radi mladenke za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (1)
- Kako radi na narudЕѕbi Mail (1)
- Kakva narudЕѕba poЕЎte (1)
- kan du skicka en brud (2)
- Kann ich eine Versandungsbraut bekommen, wenn ich bereits verheiratet bin? (1)
- Kasyno Online PL (1)
- Kauf einer Mail -Bestellung Braut (3)
- Kaufen Sie eine Mail -Bestellung Braut (2)
- köp en postorderbrud (1)
- Kenbridge online installment loans (1)
- kenosha+erotic-massage username (1)
- keskimääräiset postimyynti morsiamen hinnat (2)
- keskimääräiset postimyynti morsiamen hinnat (0)
- king johnnie (2)
- kjГёp en postordrebrud (1)
- kjГёp postordrebrud (2)
- kjГёp postordrebrud (0)
- Koja je najbolja sluЕѕba za mladenku za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (1)
- Koja je najbolja web stranica za mladenku (2)
- koja je narudЕѕba poЕЎte (1)
- kuinka mennä naimisiin postimyynti morsiamen kanssa (1)
- kuinka postimyynti morsiamen (2)
- kuinka tehdä postimyynti morsiamen (4)
- kuinka tehdä postimyynti morsiamen (0)
- kuinka tehdä postimyynti morsiamen (0)
- kuinka tehdä postimyynti morsiamen (0)
- kuinka tilata morsiamen postitse (3)
- kuinka tilata postia venäläinen morsian (5)
- kuinka tilata postia venäläinen morsian (0)
- kuinka tilata postia venäläinen morsian (0)
- kuinka tilata postia venäläinen morsian (0)
- kuinka tilata postia venäläinen morsian (0)
- kuinka tilata postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- kuinka valmistaa postimyynti morsiamen (3)
- kuinka valmistaa postimyynti morsian reddit (4)
- Kupnja mladenke za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (2)
- Kupnja mladenke za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (0)
- kymmenen eniten postimyynti morsiamen sivusto (5)
- kymmenen eniten postimyynti morsiamen verkkosivustot (1)
- kymmenen parasta postimyynti morsiamen sivustoa (2)
- Können Sie eine Braut bestellen? (4)
- Können Sie eine Braut bestellen? (0)
- Können Sie eine Braut bestellen? (0)
- Können Sie eine Braut bestellen? (0)
- köp postorder brud (3)
- köp postorder brud (0)
- köp postorder brud (0)
- köper en postorderbrud (1)
- kГёb postordrebrud (1)
- La commande par correspondance en vaut-elle la peine (3)
- La commande par correspondance en vaut-elle la peine (0)
- La courrier Г©lectronique en vaut la peine? (3)
- La courrier Г©lectronique en vaut la peine? (0)
- La courrier Г©lectronique en vaut la peine? (0)
- La Jara installment loans near me (1)
- la mariГ©e par correspondance (2)
- la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- La mariГ©e par correspondance en vaut la peine (3)
- La mariГ©e par correspondance en vaut la peine (0)
- La mariГ©e par correspondance en vaut la peine (0)
- La mariГ©e par correspondance est-elle une chose rГ©elle (2)
- La mariГ©e par correspondance est-elle une chose rГ©elle (0)
- la migliore sposa per corrispondenza di sempre (1)
- la novia de la orden de correo superior se sienta (1)
- la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- la sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- la sposa per corrispondenza ne vale la pena? (2)
- laillinen postimyynti morsiamen verkkosivusto (3)
- laillinen postimyynti morsian (4)
- lailliset postimyynti morsiamen palvelut (3)
- lailliset postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (2)
- lailliset postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (0)
- lailliset postimyynti morsiamen verkkosivustot (4)
- lailliset postimyyntiyritykset (1)
- latin brides (1)
- latin mail order bride (1)
- latin mail order brides (1)
- Laurel installment loans near me (1)
- Le site de la mariГ©e par correspondance (4)
- Le site de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Le site de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Le site de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- legale Versandhandel Seiten für Bräute (7)
- Legale Versandhandel Seiten für Bräute (0)
- legale Versandhandel Seiten für Bräute (0)
- Legale Versandhandel Seiten für Bräute (0)
- legale Versandhandel Seiten für Bräute (0)
- Legale Versandhandel Seiten für Bräute (0)
- Legale Versandhandel Seiten für Bräute (0)
- leggi led per corrispondenza i siti della sposa (2)
- Leggit Mail bestellen Brautseiten (1)
- leggit mail order bride sites (3)
- leggit post beställning brud webbplatser (1)
- leggit postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (2)
- leggit postordre brud nettsteder (3)
- Legit Mail narudЕѕba mladenka (1)
- Legit Mail narudЕѕbe mladenke (1)
- legit mail order bride (1)
- legit mail order bride service (1)
- legit mail order bride sites (1)
- legit mail order bride sites reddit (5)
- legit mail ordre brud (1)
- legit mail ordre brude service (1)
- legit mail ordre brude site (2)
- legit mail ordre brude site (0)
- legit mail ordre russisk brud (1)
- legit no credit check payday loans (2)
- legit payday loan no credit check (3)
- legit postimyynti morsian (5)
- legit postorder brud (5)
- legit postorder brud webbplatser (3)
- legit postorder brud webbplatser (0)
- legit postorder brud webbplatser reddit (5)
- legit postorder brud webbplatser reddit (0)
- legit postorder ryska bruden (6)
- legit postordre brud (2)
- legit postordre brud nettsted (2)
- legit postordre brud nettsteder (5)
- legit postordre brudtjeneste (3)
- legitim mail ordre brude service (1)
- legitim postorder brud (1)
- legitim postorder brud webbplats (1)
- legitim postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- legitim postorder brudens webbplats (1)
- legitim postorder brudföretag (1)
- legitim postorder brudtjänst (1)
- legitim postordre brudeside (3)
- legitim postordre brudewebsted (3)
- legitim postordre brudsted (2)
- legitimale Mail -Bestellung Braut (5)
- legitimate mail order bride companies (1)
- legitimate mail order bride services (1)
- legitimate mail order bride site (2)
- legitimate mail order bride sites (1)
- legitimate mail order bride websites (1)
- legitimate payday loans no credit check (1)
- legitime Mail -Bestellung Braut Site (3)
- legitime Mail -Bestellung Brautdienste (1)
- legitime Mail bestellen Brautunternehmen (1)
- Legitime Mail bestellen Brautwebsite (1)
- legitime Mail bestellen Brautwebsites (1)
- legitime postordre brude tjenester (3)
- legitime postordre brudesider (1)
- legitime postordre brudevirksomheder (1)
- legitime postordre brudtjenester (1)
- legitime postordrebrud nettsteder (1)
- legitime postordrebrudesider (3)
- legitime postordrebrudselskaper (3)
- legitime Versandbestellbraut (2)
- legitime Versandbestellbrautstandorte (3)
- legitimer Versandauftragsbrautservice (3)
- legitimert postordre brudtjeneste (2)
- legitimna web stranica za mladenku (2)
- legitimt postordrebrud nettsted (1)
- Legitimte -Mail -Bestellung Brautservice (1)
- legitimte mail narudЕѕbe mladenke (1)
- legitimte mail order bride service (2)
- legitimte postimyynti morsiamen palvelu (6)
- legititna poЕЎta naredba ruska mladenka (1)
- legittimare il servizio di sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- LeoVegas Finland (6)
- LeoVegas Sweden (4)
- Les meilleurs pays pour obtenir une mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- Les meilleurs sites de mariГ©es par correspondance. (6)
- Les meilleurs sites de mariГ©es par correspondance. (0)
- Les meilleurs sites de mariГ©es par correspondance. (0)
- Les meilleurs sites de mariГ©es par correspondance. (0)
- Les meilleurs sites de mariГ©es par correspondance. (0)
- Les meilleurs sites de mariГ©es par correspondance. (0)
- Les sites de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitimes (10)
- Les sites de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitimes (0)
- Les sites de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitimes (0)
- Les sites de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitimes (0)
- Les sites de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitimes (0)
- Les sites de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitimes (0)
- Les sites de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitimes (0)
- Les sites de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitimes (0)
- Les sites de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitimes (0)
- Les sites de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitimes (0)
- lesbian mail order bride (1)
- Lesbienne Mail Commande Bride Reddit (2)
- lesbische Versandbestellung Braut (3)
- lesbisk postorder brud (4)
- lesbisk postorder brud reddit (2)
- lesbisk postordre bruden reddit (3)
- lesbisk postordrebrud (3)
- lesbo postimyynti morsian reddit (1)
- letar efter en postorderbrud (1)
- letar efter Г¤ktenskap (1)
- Lewistown online installment loans instant approval (1)
- Lezbijska narudЕѕba za mladenku Reddit (3)
- Lezbijska narudЕѕba za mladenku Reddit (0)
- Lezbijska narudЕѕba za mladenku Reddit (0)
- Lezbiyen Posta SipariЕџi Gelin (5)
- Lezbiyen Posta SipariЕџi Gelin (0)
- Lezbiyen Posta SipariЕџi Gelin (0)
- Lezbiyen Posta SipariЕџi Gelin (0)
- Lezbiyen Posta SipariЕџi Gelin (0)
- liechtenstein escort girl (1)
- list of best mail order bride sites (1)
- lista över bästa postorderbrudsajter (1)
- lista de los mejores sitios para novias por correo (3)
- lista över bästa postorderbrudsajter (1)
- Liste der besten Mail -Bestell -Braut -Sites (3)
- Liste der besten Mail -Bestell -Braut -Sites (0)
- Liste des meilleurs sites de mariГ©es par correspondance (1)
- Live Credit Score For Montana Sixth Is V Pirin Blagoevgrad - 827 (4)
- loan cash advance (2)
- loan cash advance near me (1)
- loan for bad credit not a payday loan (1)
- loan for cash advance (4)
- loan for payday (2)
- loan instead of payday loan (1)
- loan me payday loan (1)
- loan payday advance (2)
- loan payday bad credit (3)
- loan payday loan (1)
- loan payday loans near me (1)
- loan payday no credit check (2)
- loan to pay payday loan (5)
- loans and cash advance (2)
- loans bad credit payday (2)
- loans but not payday loans (1)
- loans cash advance (2)
- loans for bad credit no payday loans (3)
- loans for bad credit not payday (3)
- loans for bad credit not payday loans (1)
- loans for bad credit payday (2)
- loans for bad credit payday loans (2)
- loans for payday (3)
- loans instead of payday (1)
- loans near me payday (2)
- loans no payday loans (0)
- loans not payday (2)
- loans not payday for bad credit (1)
- loans not payday loans (1)
- loans now but not payday (3)
- loans payday (2)
- loans payday bad credit (1)
- loans payday cash advance (3)
- loans payday loan (2)
- loans payday loans (1)
- loans to payday (1)
- loans with bad credit not payday loans (2)
- loans with no credit check no payday loeans (3)
- local (10)
- local payday loans no credit check (1)
- login (11)
- long term payday loans no credit check (3)
- looking for a cash advance (1)
- looking for a mail order bride (2)
- looking for a payday loan (1)
- looking for a payday loan with bad credit (1)
- looking for marriage (1)
- looking for payday loan (1)
- los 10 mejores sitios para novias por correo (3)
- los 10 principales sitios web de novias por correo (2)
- los 5 mejores sitios para novias por correo (2)
- los mejores paГses para obtener un pedido por correo novia (5)
- los mejores paГses para obtener un pedido por correo novia (0)
- los mejores paГses para obtener un pedido por correo novia (0)
- los mejores paГses para obtener un pedido por correo novia (0)
- Lotoclub (1)
- lovingwomen.org asiatische-chatrooms Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- lovingwomen.org athiopische-dating-sites Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (0)
- lovingwomen.org beste-lander-um-zu-heiraten Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- lovingwomen.org bestes-afrikanisches-land-um-eine-frau-zu-finden Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- lovingwomen.org brasilianische-braut Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- lovingwomen.org chinesische-dating-sites Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+aeldre-kvinder-der-soger-yngre-maend hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+bedste-europaeiske-land-til-at-finde-en-kone bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+bedste-land-til-dating hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+brasilianske-datingsider hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+cambodian-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+chatrum-med-singler bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+chilenske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+cubanske-datingsider bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+dating-com-anmeldelser hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+dating-kultur-i-japan bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+europaeiske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (0)
- lovingwomen.org da+europaeiske-postordrebrude-websteder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+filipina-brud bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+franske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+gifte-sig-med-en-japansk-kvinde hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+graeske-datingsider hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+graeske-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+hotteste-og-mest-sexede-kvinder-i-verden bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+hvordan-man-finder-en-kone bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+italienske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+japanske-chatrum hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+koreansk-brud bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+latin-dating-sider bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+latin-postordrebrude-sider hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+mexicanske-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+rumaenske-datingsider bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+thai-datingsider hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+thailandske-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+tjekkiske-datingsider bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+udenlandske-kvinder-pa-udkig-efter-amerikanske-maend bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- lovingwomen.org da+uruguay-kvinder hvor man kan kГёbe en postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org dating-com-test Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- lovingwomen.org dating-sites-fur-die-ehe Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- lovingwomen.org dating-sites-fur-ernsthafte-beziehungen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- lovingwomen.org die-heisesten-und-sexiesten-frauen-der-welt Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- lovingwomen.org e-mail-bestellung-heiratsstatistik Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- lovingwomen.org ecuadorianische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (0)
- lovingwomen.org el-salvador-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- lovingwomen.org es+casarse-con-una-mujer-dominicana revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- lovingwomen.org es+cultura-de-citas-en-mexico revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- lovingwomen.org es+donde-conocer-mujeres-solteras revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- lovingwomen.org es+mejor-pais-para-salir revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- lovingwomen.org es+mejores-paises-para-casarse revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (0)
- lovingwomen.org es+mujeres-buscando-matrimonio revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- lovingwomen.org es+mujeres-checas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- lovingwomen.org es+mujeres-cubanas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- lovingwomen.org es+mujeres-eslavas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- lovingwomen.org es+mujeres-latinas-calientes-y-sexys revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- lovingwomen.org es+mujeres-rumanas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- lovingwomen.org es+mujeres-turcas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- lovingwomen.org es+mujeres-vietnamitas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- lovingwomen.org es+salas-de-chat-mexicanas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- lovingwomen.org es+salas-de-chat-ucranianas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- lovingwomen.org es+sitios-de-citas-armenias revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- lovingwomen.org es+sitios-de-citas-caribenas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- lovingwomen.org es+sitios-de-citas-checas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- lovingwomen.org es+sitios-de-citas-coreanas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- lovingwomen.org es+sitios-de-citas-de-larga-distancia revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- lovingwomen.org es+sitios-de-citas-de-pakistan que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- lovingwomen.org es+sitios-de-citas-espanolas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- lovingwomen.org es+sitios-de-citas-griegas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- lovingwomen.org es+sitios-de-citas-portuguesas que es la novia del pedido por correo (0)
- lovingwomen.org es+sitios-de-citas-venezolanas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- lovingwomen.org es+sitios-de-citas-vietnamitas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- lovingwomen.org europaische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- lovingwomen.org fi+turkkilaiset-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- lovingwomen.org fi+ukrainalainen-morsian wikipedia postimyynti morsian (1)
- lovingwomen.org fi+uruguay-naiset tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- lovingwomen.org fi+vietnamilainen-morsian wikipedia postimyynti morsian (1)
- lovingwomen.org filipino-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (0)
- lovingwomen.org fr+bumble-avis Histoire de la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- lovingwomen.org franzosische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- lovingwomen.org frauen-polieren Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- lovingwomen.org guatemalanische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- lovingwomen.org heise-und-sexy-deutsche-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- lovingwomen.org heise-und-sexy-kolumbianische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- lovingwomen.org heise-und-sexy-koreanische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- lovingwomen.org heise-und-sexy-latina-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- lovingwomen.org heise-und-sexy-spanische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- lovingwomen.org heise-und-sexy-ukrainische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- lovingwomen.org internationale-chatrooms Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+come-trovare-una-moglie ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+cultura-degli-appuntamenti-in-cina ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+cultura-degli-appuntamenti-in-dominicano vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+cultura-degli-appuntamenti-nella-corea-del-sud ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+donne-asiatiche ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+donne-brasiliane ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+donne-cilene ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+donne-colombiane-calde-e-sexy ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+donne-costa-rican vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+donne-europee vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+donne-rumene ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+donne-slave vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- lovingwomen.org it+donne-spagnole-calde-e-sexy ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+donne-vietnamite vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+il-miglior-paese-per-un-uomo-americano-per-trovare-una-moglie ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+siti-asiatici-sposa-per-corrispondenza ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+siti-di-incontri-argentini vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+siti-di-incontri-brasiliani vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+siti-di-incontri-caraibici ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+siti-di-incontri-coreani ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+siti-di-incontri-dominicani vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+sposa-messicana vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+sposa-per-corrispondenza-prezzo vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+sposa-rumena vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+sposa-russa vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- lovingwomen.org it+sposare-qualcuno-di-un-altro-paese vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- lovingwomen.org it+sposare-una-donna-messicana vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- lovingwomen.org italienische-dating-sites Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- lovingwomen.org italienische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- lovingwomen.org jamaikanische-dating-sites Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- lovingwomen.org japanische-braut Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (0)
- lovingwomen.org katalogheirat-standorte Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- lovingwomen.org kolumbianische-braut Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- lovingwomen.org kolumbianische-dating-sites Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- lovingwomen.org koreanische-braut Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (0)
- lovingwomen.org koreanische-dating-sites Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- lovingwomen.org main_it vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- lovingwomen.org main_pt Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- lovingwomen.org main_sv postorder brudkataloger (1)
- lovingwomen.org mexikanische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+armeniske-datingsider online postordre brud (0)
- lovingwomen.org no+asiatiske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+beste-land-a-gifte-seg-i online postordre brud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+brasilianske-datingsider online postordre brud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+colombian-brud online postordre brud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+colombian-datingsider beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+dating-com-anmeldelse online postordre brud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+datingkultur-i-brasil online postordre brud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+datingkultur-i-sor-korea online postordre brud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+datingsider-for-ekteskap online postordre brud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+europeiske-kvinner online postordre brud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+franske-datingsider online postordre brud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+franske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+gifte-deg-med-en-brasiliansk-kvinne beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+jamaicanske-datingsider beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+japansk-brud online postordre brud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+karibiske-datingsider online postordre brud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+kinesisk-brud online postordre brud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+koreanske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+kosta-rican-datingsider beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+kubanske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+portugisiske-datingsider beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+postordrebrud-priser beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+puertorikanske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+russisk-brud beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+slovakiske-kvinner online postordre brud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+thai-brud beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+tsjekkiske-datingsider online postordre brud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+ukrainske-datingsider online postordre brud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+varme-og-sexy-filippinske-kvinner beste stedet ГҐ fГҐ postordrebrud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+varme-og-sexy-koreanske-kvinner online postordre brud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+venezuelansk-brud online postordre brud (1)
- lovingwomen.org no+venezuelanske-kvinner online postordre brud (1)
- lovingwomen.org panamaische-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- lovingwomen.org pt+casar-com-uma-mulher-colombiana Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- lovingwomen.org pt+cultura-de-namoro-em-dominicano Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- lovingwomen.org pt+cultura-de-namoro-no-mexico Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- lovingwomen.org pt+melhor-pais-com-as-mulheres-mais-bonitas Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- lovingwomen.org pt+mulheres-alemas-gostosas-e-sexy Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- lovingwomen.org pt+mulheres-colombianas Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- lovingwomen.org pt+mulheres-equatorianas Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- lovingwomen.org pt+mulheres-eslavas Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- lovingwomen.org pt+mulheres-eslovacas Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- lovingwomen.org pt+mulheres-gregas Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- lovingwomen.org pt+mulheres-italianas-gostosas-e-sexy Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- lovingwomen.org pt+mulheres-mexicanas-gostosas-e-sexy Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- lovingwomen.org pt+mulheres-ucranianas-quentes-e-sensuais Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- lovingwomen.org pt+mulheres-vietnamitas Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- lovingwomen.org pt+noiva-vietnamita Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- lovingwomen.org pt+onde-conhecer-mulheres-solteiras Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- lovingwomen.org pt+sites-asiaticos-noiva-por-correspondencia Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- lovingwomen.org pt+sites-de-namoro-armenios Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- lovingwomen.org pt+sites-de-namoro-brasileiros Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- lovingwomen.org pt+sites-de-namoro-de-longa-distancia Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- lovingwomen.org pt+sites-de-namoro-eslavo Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- lovingwomen.org pt+sites-de-namoro-indianos Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- lovingwomen.org pt+sites-de-namoro-italianos Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- lovingwomen.org pt+sites-de-namoro-latino Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- lovingwomen.org pt+sites-de-namoro-no-caribe Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- lovingwomen.org rumanische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (0)
- lovingwomen.org russische-dating-sites Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- lovingwomen.org slowenische-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- lovingwomen.org sv+asiandate-recension postorder brudkataloger (1)
- lovingwomen.org sv+basta-afrikanska-land-att-hitta-en-fru postorder brudkataloger (1)
- lovingwomen.org sv+basta-europeiska-land-att-hitta-en-fru postorder brudkataloger (1)
- lovingwomen.org sv+basta-land-for-dejting postorder brudkataloger (1)
- lovingwomen.org sv+basta-lander-med-de-mest-lojala-fruarna postorder brudkataloger (1)
- lovingwomen.org sv+basta-landet-att-hitta-en-fru postorder brudkataloger (1)
- lovingwomen.org sv+belarus-dating-webbplatser postorder brudkataloger (1)
- lovingwomen.org sv+datingkultur-i-mexiko postorder brudkataloger (1)
- lovingwomen.org sv+datingsajter-for-allvarliga-relationer postorder brudkataloger (1)
- lovingwomen.org sv+el-salvador-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- lovingwomen.org sv+europeiska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- lovingwomen.org sv+indiska-datingsajter postorder brudkataloger (1)
- lovingwomen.org sv+japanska-chattrum postorder brudkataloger (1)
- lovingwomen.org sv+japanska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (0)
- lovingwomen.org sv+kubanska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- lovingwomen.org sv+latin-postordrebrud-webbplatser postorder brudkataloger (1)
- lovingwomen.org sv+postorder-aktenskapstatistik postorder brudkataloger (1)
- lovingwomen.org sv+puerto-rico-datingsidor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- lovingwomen.org sv+ryska-datingsajter postorder brudkataloger (1)
- lovingwomen.org sv+slaviska-postordrebrud-webbplatser postorder brudkataloger (1)
- lovingwomen.org sv+spanska-datingsajter postorder brudkataloger (1)
- lovingwomen.org sv+yngre-kvinnor-som-soker-aldre-man postorder brudkataloger (1)
- lovingwomen.org tr+amerikali-bir-adam-icin-bir-es-bulmak-icin-en-iyi-ulke Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek (1)
- lovingwomen.org tr+asya-sohbet-odalari bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- lovingwomen.org tr+avrupa-posta-siparisi-gelinler-siteleri bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- lovingwomen.org tr+bekarlarla-sohbet-odalari bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- lovingwomen.org tr+bumble-inceleme bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- lovingwomen.org tr+cinde-flort-kulturu Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek (1)
- lovingwomen.org tr+hong-kong-tanisma-siteleri bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- lovingwomen.org tr+isvec-arkadaslik-siteleri bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- lovingwomen.org tr+italyan-tanisma-siteleri Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek (1)
- lovingwomen.org tr+japon-tanisma-siteleri bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- lovingwomen.org tr+japonyada-flort-kulturu bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- lovingwomen.org tr+kolombiyali-kadinlar bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- lovingwomen.org tr+kosta-rika-kadinlar Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek (1)
- lovingwomen.org tr+posta-siparisi-gelinler-nasil-calisir bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- lovingwomen.org tr+romen-kadinlar bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- lovingwomen.org tr+romen-tanisma-siteleri bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- lovingwomen.org tr+sicak-ve-seksi-japon-kadinlar bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- lovingwomen.org tr+taylandli-kadinlar bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- lovingwomen.org tr+vietnamli-gelin bacaklД± posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (1)
- lovingwomen.org ukrainische-chatrooms Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- lovingwomen.org vietnamesische-braut Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- low interest payday loans no credit check (3)
- luettelo parhaista postimyynti morsiamen sivustoista (3)
- lunaprofitmax.org (1)
- löytää morsian (2)
- löytää morsian (0)
- löytää postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- macedonia-women+cair free online sites for singles (1)
- macedonia-women+skopje free online sites for singles (1)
- Macon bad credit installment loans (1)
- Macon online installment loans (1)
- Mail -Bestellung Braut (5)
- Mail -Bestellung Braut -Websites ?ГјberprГјfen (2)
- Mail -Bestellung Braut -Websites ?ГјberprГјfen (0)
- Mail -Bestellung Braut Datierung (1)
- Mail -Bestellung Braut definieren (1)
- Mail -Bestellung Braut echt (2)
- Mail -Bestellung Braut es wert ist (2)
- Mail -Bestellung Braut legitim (3)
- Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur mit dem besten Ruf (2)
- Mail -Bestellung Brautagenturen (2)
- Mail -Bestellung Brautbewertung (1)
- Mail -Bestellung Brautdating Site (3)
- Mail -Bestellung Brautdefinition (1)
- Mail -Bestellung Brautdienste (2)
- Mail -Bestellung Brautdienste Definition (1)
- Mail -Bestellung Brautindustrie (3)
- Mail -Bestellung Brautkatalog (4)
- Mail -Bestellung Brautkataloge (1)
- Mail -Bestellung Brautservice (6)
- Mail -Bestellung Bride Agency Reviews (2)
- Mail an die Braut bestellen (3)
- Mail an die Braut bestellen (0)
- Mail auf Bestellung Braut (1)
- Mail bestellen Braut Arbeit? (1)
- Mail bestellen Braut Craigslist (3)
- Mail bestellen Braut echte Geschichten (1)
- Mail bestellen Braut FAQ (2)
- Mail bestellen Braut gute Idee? (1)
- Mail bestellen Braut legitim (1)
- Mail bestellen Braut Reales Standort (2)
- Mail bestellen Braut Reveiw (3)
- Mail bestellen Braut Websites Reddit (1)
- Mail bestellen Braut Wiki (6)
- Mail bestellen Braut Wikipedia (1)
- Mail bestellen Brautartikel (1)
- Mail bestellen Brautbewertungen (3)
- Mail bestellen Brautdating -Sites (3)
- Mail bestellen Brautgeschichten (1)
- Mail bestellen Brautgesetze (2)
- Mail bestellen Brautinformationen (1)
- Mail bestellen Brautstandorte legitim (2)
- Mail bestellen Brautwebes Reddit (2)
- Mail bestellen Brautwebsite (5)
- Mail bestellen Brautwebsites (1)
- Mail bestellen eine Braut (1)
- Mail bestellen Frauen (1)
- mail bestil en brud (3)
- Mail Bride Order (2)
- mail brud ordre (1)
- mail brudbeställning (1)
- Mail dans l'ordre de la mariГ©e (7)
- Mail dans l'ordre de la mariГ©e (0)
- Mail dans l'ordre de la mariГ©e (0)
- Mail dans l'ordre de la mariГ©e (0)
- Mail dans l'ordre de la mariГ©e (0)
- Mail dans l'ordre de la mariГ©e (0)
- Mail dans l'ordre de la mariГ©e (0)
- Mail dans l'ordre du coГ»t de la mariГ©e (4)
- Mail dans l'ordre du coГ»t de la mariГ©e (0)
- Mail dans l'ordre du coГ»t de la mariГ©e (0)
- Mail dans l'ordre du coГ»t de la mariГ©e (0)
- Mail dans la dГ©finition de la mariГ©e (3)
- Mail dans la dГ©finition de la mariГ©e (0)
- Mail dans la dГ©finition de la mariГ©e (0)
- mail for ГҐ bestille brud (4)
- mail for ГҐ bestille brud (0)
- mail for ГҐ bestille brud (0)
- mail for ГҐ bestille brud (0)
- mail för att beställa brud (2)
- mail för att beställa brud (0)
- mail i ordning brud kostar (2)
- mail i ordning bruddefinition (2)
- mail i ordre brud (3)
- mail i ordre brudefinition (1)
- mail i rekkefГёlge brud (5)
- mail i rekkefГёlge brud (0)
- mail i rekkefГёlge brud (0)
- mail i rekkefГёlge brud (0)
- mail i rekkefГёlge brud (0)
- Mail in der Bestellung Brautdefinition (2)
- mail in order bride (1)
- mail in ordine definizione sposa (5)
- Mail Mail (2)
- Mail narudЕѕba Katalog mladenke (2)
- Mail narudЕѕba Katalog mladenke (0)
- Mail narudЕѕba mladenka definira (1)
- Mail narudЕѕba mladenka vrijedi (1)
- Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (2)
- Mail narudЕѕba mladenka zakonita (0)
- Mail narudЕѕbe mladenke agencije (1)
- Mail narudЕѕbe mladenke web stranice Reddit (4)
- Mail narudЕѕbe mladenke web stranice Reddit (0)
- Mail narudЕѕbe mladenke web stranice Reddit (0)
- Mail narudЕѕbe mladenke web stranice Reddit (0)
- Mail narudЕѕbe za mladenke (1)
- Mail narudЕѕbe za mladenke legitimne (4)
- Mail narudЕѕbe za mladenke legitimne (0)
- Mail narudЕѕbe za mladenke legitimne (0)
- Mail narudЕѕbe za mladenke legitimne (0)
- Mail narudЕѕbena agencija s najboljom reputacijom (1)
- Mail on Order Bride (4)
- mail order bride (3)
- mail order bride agency (1)
- mail order bride agency with the best reputation (2)
- mail order bride articles (1)
- mail order bride catalog (2)
- mail order bride catalogs (1)
- mail order bride catalogue (2)
- mail order bride catalogue (0)
- mail order bride countries (1)
- mail order bride coupon (2)
- mail order bride craigslist (1)
- mail order bride dating (2)
- mail order bride dating site (1)
- mail order bride dating sites (1)
- mail order bride define (2)
- mail order bride definitiom (0)
- mail order bride facts (1)
- mail order bride faq (0)
- mail order bride for real (3)
- mail order bride good idea? (1)
- mail order bride industry (3)
- mail order bride info (0)
- mail order bride legit sites (2)
- mail order bride legit? (1)
- mail order bride pricing (1)
- mail order bride real (1)
- mail order bride real stories (2)
- mail order bride review (2)
- mail order bride review (0)
- mail order bride reviews (2)
- mail order bride service (2)
- mail order bride services definition (1)
- mail order bride sites legitimate (2)
- mail order bride sites reddit (3)
- mail order bride sites review (2)
- mail order bride stories (3)
- mail order bride story (2)
- mail order bride website reviews (1)
- mail order bride websites (2)
- mail order bride websites reddit (1)
- mail order bride websites reviews (1)
- mail order bride wiki (4)
- mail order bride work? (2)
- mail order bride worth it? (2)
- mail order brides (1)
- mail order girlfriend (1)
- mail order sposa informazioni (1)
- mail order wife (3)
- mail order wives (3)
- mail order wives (0)
- mail ordina le informazioni sulla sposa (2)
- mail ordina una sposa (3)
- mail ordre brude anmeldelser (1)
- mail ordre brude definition (2)
- mail ordre brude info (1)
- mail ordre brude websted anmeldelser (1)
- mail ordre brude websteder anmeldelser (1)
- mail ordre brudesider gennemgang (2)
- mail pГҐ bestilling brud (1)
- mail på beställning brud (2)
- mail på beställning brud (0)
- mail til ordre brud (1)
- mail to order bride (1)
- mail-order bride (1)
- Mail-Order-Braut (7)
- Mail-order-bride (3)
- mail-order-brides-statistics free online sites for singles (1)
- Mail. Bride Legit (3)
- maila i ordning brud (2)
- Mailbrautbestellung (6)
- main de username (1)
- main_pt-pt bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- malaysian-women+johor-bahru free online sites for singles (1)
- Mandeville installment loans near me (1)
- mariГ©e par correspondance (16)
- mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance chaude (5)
- mariГ©e par correspondance chaude (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance chaude (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance chaude (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance chaude (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance dГ©finir (3)
- mariГ©e par correspondance dГ©finir (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance dГ©finir (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance en ligne (3)
- mariГ©e par correspondance en ligne (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance en ligne (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance internationale (4)
- mariГ©e par correspondance internationale (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance internationale (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance internationale (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance interraciale (2)
- mariГ©e par correspondance interraciale (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance la plus chaude (2)
- mariГ©e par correspondance la plus chaude (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance lesbienne (2)
- mariГ©e par correspondance lesbienne (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (11)
- mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance pour de vrai (2)
- mariГ©e par correspondance pour de vrai (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance reveiw (3)
- mariГ©e par correspondance reveiw (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance reveiw (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance rГ©elle (8)
- mariГ©e par correspondance rГ©elle (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance rГ©elle (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance rГ©elle (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance rГ©elle (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance rГ©elle (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance rГ©elle (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance rГ©elle (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance wikipedia (4)
- mariГ©e par correspondance wikipedia (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance wikipedia (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance wikipedia (0)
- mariГ©e par correspondance Г vendre (2)
- mariГ©e par correspondance Г vendre (0)
- mariГ©e par courrier wikipedia (2)
- mariГ©e par courrier wikipedia (0)
- mariГ©e par la poste d'historique (1)
- Marriage Certificate Requirements (1)
- Marshall online installment loans (1)
- Masalbet (1)
- Mechanicsville online installment loans instant approval (1)
- medelålder för postorderbruden (1)
- meet asian women (1)
- meet women online (1)
- meetme-review free online sites for singles (1)
- meetslavicgirls-review free online sites for singles (1)
- Meilleur endroit pour la mariГ©e par correspondance (2)
- Meilleur endroit pour la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleur endroit pour obtenir la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- Meilleur endroit pour obtenir une mariГ©e par correspondance (2)
- Meilleur endroit pour obtenir une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleur pays de mariГ©e par correspondance (3)
- Meilleur pays de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleur pays de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleur pays pour la mariГ©e par correspondance (2)
- Meilleur pays pour la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleur pays pour la mariГ©e par correspondance Reddit (3)
- Meilleur pays pour la mariГ©e par correspondance Reddit (0)
- Meilleur pays pour la mariГ©e par correspondance Reddit (0)
- Meilleur pays pour trouver la mariГ©e par correspondance (3)
- Meilleur pays pour trouver la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleur pays pour trouver la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleur pays pour trouver une mariГ©e par correspondance (6)
- Meilleur pays pour trouver une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleur pays pour trouver une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleur pays pour trouver une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleur pays pour trouver une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleur pays pour trouver une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleur service de mariГ©e par correspondance (3)
- Meilleur service de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleur service de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (2)
- Meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance reddit (1)
- Meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance rГ©el (1)
- Meilleur site Web de mariГ©e par correspondance (2)
- Meilleur site Web de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleur site Web pour trouver une mariГ©e par correspondance (3)
- Meilleur site Web pour trouver une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleur site Web pour trouver une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleure agence de mariГ©e par correspondance (4)
- Meilleure agence de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleure agence de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleure agence de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleure agence de mariГ©e par correspondance reddit (1)
- Meilleure entreprise de mariГ©e par correspondance (3)
- Meilleure entreprise de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleure entreprise de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleure mariГ©e de la vente par correspondance du site (1)
- Meilleure mariГ©e par correspondance (4)
- Meilleure mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleure mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleure mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleure mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleure mariГ©e par correspondance de tous les temps (4)
- Meilleure mariГ©e par correspondance de tous les temps (0)
- Meilleure mariГ©e par correspondance de tous les temps (0)
- Meilleure mariГ©e par correspondance de tous les temps (0)
- Meilleure mariГ©e par correspondance de tous les temps (0)
- Meilleure Г©pouse de vente par correspondance de rГ©putation (2)
- Meilleure Г©pouse de vente par correspondance de rГ©putation (0)
- Meilleures sociГ©tГ©s de mariГ©es par correspondance (1)
- Meilleurs avis sur les sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- Meilleurs endroits pour la mariГ©e par correspondance (4)
- Meilleurs endroits pour la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleurs endroits pour la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleurs endroits pour la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleurs endroits pour obtenir la mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- Meilleurs endroits pour trouver la mariГ©e par correspondance (2)
- Meilleurs endroits pour trouver la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleurs lieux de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- Meilleurs pays de la mariГ©e par correspondance (2)
- Meilleurs pays de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- meilleurs pays pour une mariГ©e par correspondance (6)
- meilleurs pays pour une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- meilleurs pays pour une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- meilleurs pays pour une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- meilleurs pays pour une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- meilleurs pays pour une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleurs sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (2)
- Meilleurs sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Meilleurs sites de mariГ©s par correspondance rГ©el (3)
- Meilleurs sites de mariГ©s par correspondance rГ©el (0)
- Meilleurs sites de mariГ©s par correspondance rГ©el (0)
- Meilleurs sites Web de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (1)
- Meilleurs sites Web de mariГ©es par correspondance reddit (1)
- mejor agencia de pedidos por correo (1)
- mejor correo orden novia agencia reddit (2)
- mejor correo orden sitios web de novias reddit (2)
- mejor correo pedido novia paГs (3)
- mejor correo pedido novia paГs (0)
- mejor correo pedido novia paГs (0)
- mejor lugar para la novia por correo (1)
- mejor lugar para recibir pedidos por correo novia (2)
- mejor lugar para recibir un pedido por correo novia (1)
- mejor novia de pedidos por correo (1)
- mejor orden de correo de la novia (1)
- mejor orden de correo novia (1)
- mejor paГs para encontrar la novia del pedido por correo (5)
- mejor paГs para encontrar la novia del pedido por correo (0)
- mejor paГs para encontrar la novia del pedido por correo (0)
- mejor paГs para encontrar la novia del pedido por correo (0)
- mejor paГs para encontrar una novia por correo (2)
- mejor paГs para encontrar una novia por correo (0)
- mejor paГs para la novia del pedido por correo (3)
- mejor paГs para la novia del pedido por correo (0)
- mejor paГs para la novia del pedido por correo (0)
- mejor paГs para pedidos por correo novia reddit (4)
- mejor paГs para pedidos por correo novia reddit (0)
- mejor paГs para pedidos por correo novia reddit (0)
- mejor paГs para pedidos por correo novia reddit (0)
- mejor reputaciГіn correo orden novia (2)
- mejor reputaciГіn correo orden novia (0)
- mejor sitio de novias de pedidos por correo real (1)
- mejor sitio de novias por correo (3)
- mejor sitio web de la novia por correo (2)
- mejor sitio web para encontrar una novia por correo (0)
- mejores empresas de novias por correo (2)
- mejores lugares para encontrar la novia por correo (2)
- mejores lugares para la novia por correo (2)
- mejores lugares para novias por correo (4)
- mejores lugares para recibir pedidos por correo novia (2)
- mejores paГses de novias por correo (1)
- mejores paГses para una novia por correo (3)
- mejores paГses para una novia por correo (0)
- mejores pedidos por correo de reseГ±as de sitios de novias (3)
- mejores pedidos por correo de reseГ±as de sitios de novias (0)
- mejores pedidos por correo de reseГ±as de sitios de novias (0)
- mejores sitios de novias de pedidos por correo real (4)
- mejores sitios de novias de pedidos por correo real (0)
- mejores sitios para novias por correo (2)
- mejores sitios para novias por correo (0)
- mejores sitios web de novias por correo (2)
- mejores sitios web de novias por correo 2022 (2)
- mejores sitios web de novias por correo legГtimo (3)
- mejores sitios web de novias por correo legГtimo (0)
- mejores sitios web de novias por correo legГtimo (0)
- melhor ordem de correio do site noiva (1)
- Melville online installment loans (1)
- Mental Math benefits (2)
- Mercedes installment loans near me (1)
- Mercedes installment loans online (1)
- MeД‘unarodna narudЕѕba poЕЎte (1)
- MeЕџru bir posta sipariЕџi gelini (2)
- MeЕџru bir posta sipariЕџi gelini (0)
- MeЕџru posta sipariЕџi gelin hizmeti (1)
- MeЕџru posta sipariЕџi gelin hizmetleri (1)
- MeЕџru posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (2)
- MeЕџru posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (0)
- MeЕџru posta sipariЕџi gelin web siteleri (3)
- MeЕџru posta sipariЕџi gelin web siteleri (0)
- MeЕџru posta sipariЕџi gelin web siteleri (0)
- MeЕџru posta sipariЕџi gelini (1)
- MeЕџru posta sipariЕџi gelini sitesi (3)
- MeЕџru posta sipariЕџi gelini sitesi (0)
- MeЕџru posta sipariЕџi gelini sitesi (0)
- Miami guaranteed installment loans for bad credit no credit check (1)
- miglior ordine di posta sposa sito reddit (1)
- miglior ordine postale agenzia sposa reddit (1)
- miglior ordine postale sposa paese (1)
- miglior paese per la sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- miglior paese per trovare la sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- miglior paese per trovare una sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- miglior servizio di sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- miglior sito per corrispondenza sposa (3)
- miglior sito per sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- miglior sito per sposa per corrispondenza reale (3)
- miglior sito web per la sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- miglior sito web per trovare una sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- migliore agenzia sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- migliore compagnia di sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- migliore reputazione per corrispondenza sposa (4)
- migliore sposa per corrispondenza (3)
- migliori compagnie di sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- migliori paesi sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- migliori recensioni per i siti della sposa (2)
- migliori siti di sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- migliori siti web di sposa ordinazione per corrispondenza (1)
- migliori siti web per la sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- migliori vendita per corrispondenza siti web sposa 2022 (1)
- mikä on paras postimyynti morsiamen maa (3)
- mikä on paras postimyynti morsiamen maa (0)
- mikä on paras postimyynti morsiamen maa (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsiamen palvelut (5)
- mikä on postimyynti morsiamen palvelut (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsiamen palvelut (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsiamen palvelut (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsiamen palvelut (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsiamena (1)
- mikä on postimyynti morsian (13)
- mikä on postimyynti morsian (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsian (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsian (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsian (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsian (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsian (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsian (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsian (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsian (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsian (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsian (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsian (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsian? (10)
- mikä on postimyynti morsian? (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsian? (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsian? (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsian? (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsian? (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsian? (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsian? (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsian? (0)
- mikä on postimyynti morsian? (0)
- mikä postimyynti morsian (3)
- mikä postimyynti morsian (0)
- mikä postimyynti morsian (0)
- MINDES MINDES Web lokacije. (1)
- Missouri guaranteed installment loans for bad credit direct lenders only (1)
- mistä löydän postimyynti morsiamen (2)
- mistä löydän postimyynti morsiamen (0)
- mistä löytää postimyynti morsiamen (2)
- mistä löytää postimyynti morsiamen (0)
- mistä ostaa postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- mistä ostan postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- mistä saan postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- miten postimyynti morsiamen sivustot toimivat (2)
- miten postimyynti morsian toimii (3)
- Mjesto za mladenku s gornjom poЕЎtom (2)
- Mjesto za mladenku s gornjom poЕЎtom (0)
- mladenka (1)
- mladenka lezbijske poЕЎte (1)
- mladenka s najviЕЎe poЕЎte (1)
- mladenke za mladenke mladenke (2)
- mogli per corrispondenza (1)
- moldova-women+chisinau free online sites for singles (1)
- mongolian-women free online sites for singles (1)
- Monte Vista online installment loans (1)
- Montross guaranteed installment loans for bad credit (1)
- morsiamen maailman postimyynti morsiamet (2)
- morsiamen postimyynti (3)
- morsiamen tilausposti (5)
- mostbet apk (17)
- mostbet az 90 (18)
- Mostbet AZ Casino (4)
- Mostbet Azerbaijan (5)
- Mostbet Bonus Program Code Amnyxlm For National Football League Week 7: $200 Broncos-saints Bonus Amnewyork - 195 (4)
- Mostbet Casino (3)
- Mostbet Casino AZ (1)
- Mostbet Casino Azerbaycan (5)
- Mostbet Casino Review Marketing Promotions, Slots & More" - 812 (4)
- mostbet giriş (12)
- mostbet hungary (1)
- Mostbet in Russia (3)
- Mostbet India (6)
- mostbet italy (1)
- Mostbet kazinosu (3)
- mostbet kirish (1)
- Mostbet kumarhanesi (3)
- Mostbet Online Casino (1)
- mostbet ozbekistonda (2)
- Mostbet Referral Bonus, Get Some Sort Of Free Bonus 2024" - 399 (0)
- mostbet royxatga olish (1)
- mostbet tr (2)
- mostbet uz (7)
- Mostbet UZ Casino (2)
- Mostbet UZ Kirish (5)
- mostbet-ru-serg (13)
- Mount Gilead guaranteed installment loans for bad credit no credit check (1)
- MoЕѕete li naruДЌiti mladenku (1)
- my cash advance payday loans (1)
- my cash now payday loan (2)
- my cash now payday loans (1)
- my cash payday loan (1)
- my payday loan (1)
- my payday loan com (1)
- my payday loans (1)
- Najbolja mjesta za dobivanje mladenke za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (2)
- Najbolja mjesta za dobivanje mladenke za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (0)
- Najbolja mjesta za pronalaЕѕenje mladenke za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (2)
- Najbolja mjesta za pronalaЕѕenje mladenke za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (0)
- Najbolja narudЕѕba poЕЎte (1)
- Najbolja narudЕѕba za mladenke (3)
- Najbolja narudЕѕba za mladenke (0)
- Najbolja narudЕѕba za mladenke (0)
- Najbolja narudЕѕba za mladenku (5)
- Najbolja narudЕѕba za mladenku (0)
- Najbolja narudЕѕba za mladenku (0)
- Najbolja narudЕѕba za mladenku (0)
- Najbolja narudЕѕba za mladenku (0)
- Najbolja narudЕѕba za mladenku Reddit (3)
- Najbolja narudЕѕba za mladenku Reddit (0)
- Najbolja narudЕѕba za mladenku Reddit (0)
- Najbolja web stranica za pronalaЕѕenje mladenke za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (1)
- Najbolja zemlja za mladenku za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (2)
- Najbolja zemlja za mladenku za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (0)
- Najbolja zemlja za pronalaЕѕenje mladenke za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (1)
- Najbolje mjesto za mladenku za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (2)
- Najbolje mjesto za mladenku za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (0)
- Najbolje narudЕѕbe mladenke (2)
- Najbolje narudЕѕbe mladenke (0)
- Najbolje narudЕѕbe za mladenke (3)
- Najbolje narudЕѕbe za mladenke (0)
- Najbolje narudЕѕbe za mladenke (0)
- Najbolje narudЕѕbe za mladenke 2022 (1)
- Najbolje narudЕѕbe za mladenke recenzije (1)
- Najbolje ocijenjene web stranice za mladenke (1)
- Najbolje ocijenjene web stranice za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (3)
- Najbolje ocijenjene web stranice za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (0)
- Najbolje ocijenjene web stranice za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (0)
- Najbolje web stranice za mladenke prave poЕЎte (1)
- Najbolje zemlje za mladenku za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (4)
- Najbolje zemlje za mladenku za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (0)
- najbolje zemlje za mladenku za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (0)
- Najbolje zemlje za mladenku za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (0)
- Najtoplija narudЕѕba poЕЎte (1)
- NajviЕЎe narudЕѕbe zaruДЌnice sjedi (1)
- NarudЕѕba poЕЎte (1)
- NarudЕѕba poЕЎte Dobra ideja? (1)
- NarudЕѕba poЕЎte Legit? (1)
- narudЕѕba poЕЎte mladenka craigslist (3)
- narudЕѕba poЕЎte mladenka craigslist (0)
- narudЕѕba poЕЎte mladenka wiki (2)
- narudЕѕba poЕЎte mladenka wiki (0)
- narudЕѕba poЕЎte mladenka wikipedia (1)
- narudЕѕbe maila za mladenke reddit (1)
- NarudЕѕbe za mladenke (2)
- NarudЕѕbe za mladenke (0)
- NaruДЌite mail mladenku (3)
- NaruДЌite mail mladenku (0)
- NaruДЌite mail mladenku (0)
- NaruДЌivanje poЕЎte FAQ FAQ (2)
- NaruДЌivanje poЕЎte FAQ FAQ (0)
- NaruДЌivanje poЕЎte Legalne stranice mladenke (2)
- NaruДЌivanje poЕЎte Legalne stranice mladenke (0)
- NaruДЌivanje poЕЎte mladenka Real web mjesto (3)
- NaruДЌivanje poЕЎte mladenka Real web mjesto (0)
- NaruДЌivanje poЕЎte mladenka Real web mjesto (0)
- NaruДЌivanje poЕЎte stvarne priДЌe (2)
- NaruДЌivanje poЕЎte stvarne priДЌe (0)
- NaruДЌivanje za mladenku kupon (2)
- NaruДЌivanje za mladenku kupon (0)
- nationaltitleloan guaranteed installment loans for bad credit no credit check (1)
- nationaltitleloan online installment loans (1)
- navegar por correo orden novia (1)
- Ne posta sipariЕџi gelin (3)
- Ne posta sipariЕџi gelin (0)
- near me cash advance (3)
- nearby cash advance (3)
- nearby payday loan (2)
- nearby payday loans (1)
- nearest payday loan near me (1)
- nearest payday loan to me (2)
- nearest payday loans (2)
- nearest payday loans from here (1)
- need a cash advance (1)
- need a cash advance now (3)
- need a loan but not a payday loan (3)
- need a loan not a payday loan (1)
- need a payday loan (1)
- need a payday loan bad credit (2)
- need a payday loan no credit check (1)
- need a payday loan now (2)
- need a payday loan now bad credit (0)
- need a payday loan with no credit check (2)
- need a payday loans (1)
- need cash advance (3)
- need cash no payday loans (2)
- need cash now payday loan (1)
- need payday loan (1)
- need payday loan now (1)
- need payday loan now bad credit (2)
- need payday loans (2)
- need someone to write my essay (0)
- need to be a member cash advance (2)
- need to get a payday loan (2)
- Nevjesta narudЕѕba poЕЎte (1)
- Nevjesta za internetsku poЕЎta (1)
- Nevjesta za narudžbu vruće pošte (1)
- new cash advance (1)
- new payday loan (2)
- new payday loans bad credit (2)
- new payday loans no credit check (1)
- new year payday loan (1)
- News (3)
- next payday loan for bad credit no credit check (1)
- nl+argentinie escort girl here (1)
- nl+australie escort dating platform (1)
- nl+italie escort women (1)
- nl+polen escort girl link (1)
- no credit check advance payday loans (1)
- no credit check bad credit payday loans (3)
- no credit check cash advance lenders (3)
- no credit check cash advance loans (2)
- no credit check cash advance near me (2)
- no credit check cash advance places near me (1)
- no credit check direct deposit payday loans (1)
- no credit check direct lender payday loan (1)
- no credit check direct lender payday loans (1)
- no credit check instant cash advance (1)
- no credit check instant payday loans (2)
- no credit check loan payday (2)
- no credit check no payday loans (2)
- no credit check non payday loan (1)
- no credit check non payday loans (2)
- no credit check payday loan (1)
- no credit check payday loan direct lenders (1)
- no credit check payday loan direct lenders only (1)
- no credit check payday loan lender (1)
- no credit check payday loan lenders (3)
- no credit check payday loan near me (1)
- no credit check payday loans direct lender (2)
- no credit check payday loans lenders only (2)
- no credit check payday loans near me (1)
- no credit check payday loans on line (1)
- no credit check payday low intrest loan (3)
- no+afroromance-anmeldelse topp postordre brud sitter (1)
- no+apent-forhold topp postordre brud sitter (1)
- no+asianfeels-anmeldelse topp postordre brud sitter (1)
- no+australske-bruder topp postordre brud sitter (1)
- no+beste-land-a-finne-en-lojal-kone topp postordre brud sitter (1)
- no+bosniske-kvinner topp postordre brud sitter (1)
- North Dakota guaranteed installment loans for bad credit (1)
- novia de pedidos por correo (4)
- novias extranjeras (1)
- Oak Ridge guaranteed installment loans for bad credit (1)
- Oakland online installment loans (0)
- Ohio online installment loans instant approval (1)
- oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- oikeat postimyynti morsiamen verkkosivustot (1)
- oikeita postimyynti morsiamen tarinoita (2)
- Oklahoma guaranteed installment loans for bad credit direct lenders only (1)
- on postimyynti morsian todellinen (2)
- on postimyynti morsian todellinen asia (1)
- onde eu compro uma noiva por correspondГЄncia (1)
- onedayloan no credit check installment loans (1)
- online (28)
- Online -Mail -Bestellung Braut (3)
- Online Casino (1)
- online casino au (1)
- online dating (1)
- Online Dating First Date Kiss (1)
- online mail order bride (1)
- online mail ordre brud (1)
- online postorder brud (1)
- online postordre brud (1)
- online-postitilaus morsian (1)
- only (15)
- only consumer reports (15)
- only reviews (8)
- or payday loan (1)
- orden de correo de la industria de la novia (2)
- orden de correo de la novia (6)
- orden de correo de las agencias de la novia (3)
- orden de correo de las agencias de la novia (0)
- orden de correo definiciГіn de novia (1)
- orden de correo electrГіnico novia (2)
- orden de correo electrГіnico novia (0)
- orden de correo en lГnea novia (2)
- orden de correo en lГnea novia (0)
- orden de correo historia de la novia (2)
- orden de correo interracial novia (2)
- orden de correo legГtimo novia (4)
- orden de correo legГtimo novia (0)
- orden de correo legГtimo novia (0)
- orden de correo legГtimo novia (0)
- orden de correo lГ©sbico novia (5)
- orden de correo lГ©sbico novia (0)
- orden de correo lГ©sbico novia (0)
- orden de correo lГ©sbico novia (0)
- orden de correo lГ©sbico novia (0)
- orden de correo novia (3)
- orden de correo novia de verdad (2)
- orden de correo novia de verdad? (2)
- orden de correo novia definir (2)
- orden de correo novia vale la pena (3)
- orden de correo novia vale la pena? (3)
- orden de correo real novia (2)
- orden de correo una novia (1)
- ordenar por correo hechos de novia (3)
- ordenar por correo historias de novias (1)
- order an essay cheap (1)
- order essay online cheap (1)
- ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- ordine postale legittimo sposa russa (3)
- ordine postale sposa definire (1)
- ordine postale sposa definizione (3)
- ordine postale sposa legittima (2)
- ordine postale sposa legittima? (1)
- ordini postali recensioni sposa (2)
- ordini postali recensioni sposa (0)
- Ortalama posta sipariЕџi gelin fiyatlarД± (1)
- ostaa postimyynti morsiamen (4)
- ostamalla postimyynti morsiamen (6)
- osterreich+niederosterreich+amstetten escort girls (1)
- osterreich+niederosterreich+amstetten visitors (1)
- osterreich+niederosterreich+baden-bei-wien escort girl link (1)
- osterreich+niederosterreich+brunn-am-gebirge escort buchen (1)
- osterreich+niederosterreich+stockerau escort (1)
- osterreich+niederosterreich+traiskirchen username (2)
- osterreich+niederosterreich+traiskirchen username (0)
- osterreich+niederosterreich+tulln best escort platform (1)
- osterreich+niederosterreich+tulln escort girl (1)
- osterreich+niederosterreich+tulln sign up (1)
- osterreich+niederosterreich+wiener-neustadt nutte buchen (1)
- osterreich+oberosterreich escort girl (1)
- osterreich+oberosterreich+ansfelden escort buchen (1)
- osterreich+oberosterreich+ansfelden sign in (1)
- osterreich+oberosterreich+gmunden best escort platform (1)
- osterreich+oberosterreich+gmunden sign in (1)
- osterreich+oberosterreich+traun escorts (1)
- osterreich+oberosterreich+traun sign in (1)
- osterreich+oberosterreich+vocklabruck escort girl (1)
- osterreich+oberosterreich+wels escort service (1)
- osterreich+salzburg-staat+salzburg support (1)
- osterreich+steiermark+bruck-an-der-mur tips (1)
- osterreich+tirol+hall-in-tirol escort girl (1)
- osterreich+tirol+hall-in-tirol visitors (1)
- osterreich+tirol+kufstein escort near me (1)
- osterreich+vorarlberg nutten finden (1)
- osterreich+vorarlberg+bregenz escort girl here (1)
- osterreich+vorarlberg+bregenz escort girls (1)
- osterreich+vorarlberg+bregenz support (1)
- osterreich+vorarlberg+bregenz tips (1)
- osterreich+wiener-staat best escort platform (1)
- ourtime-review free online sites for singles (1)
- oГ№ acheter une mariГ©e par correspondance (4)
- oГ№ acheter une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- oГ№ acheter une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- oГ№ acheter une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- OГ№ puis-je acheter une mariГ©e par correspondance (6)
- OГ№ puis-je acheter une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- OГ№ puis-je acheter une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- OГ№ puis-je acheter une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- OГ№ puis-je acheter une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- OГ№ puis-je acheter une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- oГ№ puis-je obtenir une mariГ©e par correspondance (6)
- oГ№ puis-je obtenir une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- oГ№ puis-je obtenir une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- oГ№ puis-je obtenir une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- oГ№ puis-je obtenir une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- oГ№ puis-je obtenir une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- oГ№ puis-je trouver une mariГ©e par correspondance (3)
- oГ№ puis-je trouver une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- oГ№ puis-je trouver une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- oГ№ trouver une mariГ©e par correspondance (4)
- oГ№ trouver une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- oГ№ trouver une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- oГ№ trouver une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- pagbet brazil (1)
- panamanian-women free online sites for singles (1)
- paraguay-women+santa-maria site free (1)
- paraguay-women+trinidad free online sites for singles (1)
- paras maa löytää postimyynti morsiamen (9)
- paras maa löytää postimyynti morsiamen (0)
- paras maa löytää postimyynti morsiamen (0)
- paras maa löytää postimyynti morsiamen (0)
- paras maa löytää postimyynti morsiamen (0)
- paras maa löytää postimyynti morsiamen (0)
- paras maa löytää postimyynti morsiamen (0)
- paras maa löytää postimyynti morsiamen (0)
- paras maa löytää postimyynti morsiamen (0)
- paras maa postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- paras maa postimyynti morsiamen reddit (2)
- paras maa postimyynti morsiamen reddit (0)
- paras paikka postimyynti morsiamenelle (2)
- paras paikka saada postimyynti morsiamen (3)
- paras postimyynti morsiamen maa (3)
- paras postimyynti morsiamen palvelu (2)
- paras postimyynti morsiamen sivusto (1)
- paras postimyynti morsiamen verkkosivusto (4)
- paras postimyynti morsiamenvirasto (2)
- paras postimyynti morsiamenvirasto reddit (1)
- paras postimyynti morsiamenyritys (1)
- paras postimyynti morsian (2)
- paras sivustopostitilaus morsian (3)
- paras sivustopostitilaus morsian (0)
- paras todellinen postimyynti morsiamen sivusto (2)
- parhaat legit postimyynti morsiamen verkkosivustot (3)
- parhaat maat postimyynti morsiamen kanssa (2)
- parhaat maat saada postimyynti morsiamen (1)
- parhaat oikeat postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (1)
- parhaat paikat löytää postimyynti morsiamen (3)
- parhaat paikat löytää postimyynti morsiamen (0)
- parhaat paikat löytää postimyynti morsiamen (0)
- parhaat paikat postimyynti morsiamen (2)
- parhaat paikat saada postimyynti morsiamen (5)
- parhaat postimyynti morsiamen paikat (1)
- parhaat postimyynti morsiamen sivustojen arvostelut (2)
- parhaat postimyynti morsiamen verkkosivustot 2022 (3)
- parhaat postimyynti morsiamen verkkosivustot reddit (6)
- parhaat postimyynti morsiamenyritykset (4)
- parhaiten arvioidut postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (6)
- parhaiten arvioitu postimyynti morsiamen palvelu (2)
- Parnu Jk Vaprus Vs Tartu Jk Tammeka Result 2-2 Meistriliiga On 18 September 2024" - 106 (2)
- pay advance and cash advance (3)
- pay cash advance (3)
- pay cash advance loans (2)
- pay cash in advance (2)
- pay for a essay (1)
- pay for an essay (1)
- pay for an essay online (1)
- pay for essay writers (1)
- pay for someone to do my essay (1)
- pay for someone to write an essay (2)
- pay for someone to write essay (1)
- pay for someone to write my essay (1)
- pay payday loan (1)
- pay payday loans (2)
- pay someone to write essay for you (1)
- pay someone to write my essay for me (1)
- pay you to write my essay (1)
- payday advance cash (1)
- payday advance cash america (3)
- payday advance cash loans (3)
- payday advance loan (2)
- payday advance loan near me (1)
- payday advance loans bad (1)
- payday advance loans bad credit (1)
- payday advance loans for bad credit (1)
- payday advance loans near me (2)
- payday advance loans no credit check (2)
- payday advance loans with no credit check (2)
- payday advances loan (0)
- payday advances or payday loans (1)
- payday and cash advance loans (1)
- payday bad credit loan (2)
- payday bad credit loans (3)
- payday bank loans (1)
- payday cash advance bad credit (2)
- payday cash advance for bad credit (1)
- payday cash advance loan (2)
- payday cash advance loan bad credit (2)
- payday cash advance loans com (1)
- payday cash advance loans near me (3)
- payday cash advance near me (3)
- payday cash advance no credit check (1)
- payday cash loan (3)
- payday cash loan advance (1)
- payday cash loans (1)
- payday cash loans bad credit (1)
- payday cash loans with bad credit (1)
- payday in advance loans (1)
- payday instant loans no credit check (1)
- payday istallment loans (2)
- payday loan (1)
- payday loan advance (1)
- payday loan advance near me (3)
- payday loan advances (1)
- payday loan agency no credit check (2)
- payday loan america (1)
- payday loan american (4)
- payday loan at a bank (1)
- payday loan bad credit (1)
- payday loan bad credit loan (2)
- payday loan bad credit no credit check (2)
- payday loan bad credit no credit check direct lender (1)
- payday loan bad credit no credit check near me (2)
- payday loan bad for credit (1)
- payday loan bank (2)
- payday loan banks (3)
- payday loan cash (2)
- payday loan cash advance (4)
- payday loan cash advance near me (3)
- payday loan cash america (1)
- payday loan cash in minutess (1)
- payday loan companies no credit check (1)
- payday loan companies with no credit check (2)
- payday loan company (2)
- payday loan company near me (2)
- payday loan compay in usa (2)
- payday loan creator (2)
- payday loan def (1)
- payday loan direct lender no credit check (1)
- payday loan direct lender only no credit check (0)
- payday loan direct lenders no credit check (2)
- payday loan for (1)
- payday loan for bad credit (2)
- payday loan for bad credit and no credit check (1)
- payday loan for bad credit near me (2)
- payday loan for no credit (2)
- payday loan for terrible credit (3)
- payday loan for very bad credit (1)
- payday loan in (2)
- payday loan in usa (2)
- payday loan interest (1)
- payday loan interest rates? (2)
- payday loan leanders (2)
- payday loan lender no credit check (1)
- payday loan lender only no credit check (2)
- payday loan lenders no credit check (3)
- payday loan lenders no credit check list (2)
- payday loan lenders with no credit check (1)
- payday loan loans (1)
- payday loan near (1)
- payday loan near me bad credit (2)
- payday loan near me no interest (1)
- payday loan nearby (2)
- payday loan nearest me (2)
- payday loan needed (1)
- payday loan new (2)
- payday loan no (3)
- payday loan no broker no credit check (1)
- payday loan no credit (2)
- payday loan no credit check (1)
- payday loan no credit check bad credit (2)
- payday loan no credit check direct lender (1)
- payday loan no credit check direct lenders (3)
- payday loan no credit check instant (1)
- payday loan no credit check instant payout (1)
- payday loan no credit check lender (2)
- payday loan no credit check no bank account (1)
- payday loan no credit check no bank statement (2)
- payday loan no credit check no checking account (0)
- payday loan no credit check or bank account (1)
- payday loan no direct deposit no credit check (3)
- payday loan no hard credit check (2)
- payday loan no interest (1)
- payday loan now (1)
- payday loan now no credit check (1)
- payday loan now with bad credit (2)
- payday loan of america (1)
- payday loan or cash advance (1)
- payday loan organization no credit check (3)
- payday loan payday loans (1)
- payday loan places near me no credit check (2)
- payday loan places no credit check (1)
- payday loan usa (1)
- payday loan what do i need (3)
- payday loan what is payday loan (1)
- payday loan with (1)
- payday loan with bad credit (3)
- payday loan with bad credit and no credit check (2)
- payday loan with bad credit near me (2)
- payday loan with no credit (2)
- payday loan with no credit check (3)
- payday loan with no interest (2)
- payday loan with very bad credit (1)
- payday loan work (2)
- payday loan works (2)
- payday loan? (1)
- payday loans (1)
- payday loans advance (3)
- payday loans advances (5)
- payday loans america (5)
- payday loans and cash (2)
- payday loans and cash advances (2)
- payday loans and credit (1)
- payday loans and how they work (2)
- payday loans are bad (3)
- payday loans as (1)
- payday loans bad cradit? (1)
- payday loans bad credit (1)
- payday loans bad credit advance america (1)
- payday loans bad credit loans and cash advance loans (1)
- payday loans bad credit no credit check (2)
- payday loans bad credit payday loans (1)
- payday loans bad creditt (4)
- payday loans bad for credit (1)
- payday loans bank (3)
- payday loans banks (1)
- payday loans cash (3)
- payday loans cash advance (4)
- payday loans cash advance america (2)
- payday loans cash advance for bad credit (1)
- payday loans cash advance no credit check (2)
- payday loans cash loans (1)
- payday loans cash now (2)
- payday loans com (1)
- payday loans company (1)
- payday loans credit (2)
- payday loans def (1)
- payday loans direct lender bad credit no credit check (1)
- payday loans direct lenders no credit check (5)
- payday loans direct lenders only no credit check (2)
- payday loans direct lenders with no credit check (5)
- payday loans facts (2)
- payday loans finder (2)
- payday loans for (1)
- payday loans for anyone (5)
- payday loans for awful credit (2)
- payday loans for bad credit direct lender no credit check (2)
- payday loans for bad credit loans (1)
- payday loans for bad credit near me (1)
- payday loans for bad credit no credit check (2)
- payday loans for extremely bad credit (1)
- payday loans for fair credit (3)
- payday loans for horrible credit (2)
- payday loans for no credit check (1)
- payday loans for nocredit (1)
- payday loans for usa (1)
- payday loans for very bad credit (2)
- payday loans forbad credit (2)
- payday loans how much interest (0)
- payday loans how they work (1)
- payday loans how to (2)
- payday loans in usa (2)
- payday loans lenders near me no credit check (1)
- payday loans lenders no credit check (0)
- payday loans lenders not brokers no credit check (1)
- payday loans low interest no credit check (1)
- payday loans near me (1)
- payday loans near me bad credit (5)
- payday loans near me for bad credit (3)
- payday loans near me no credit (1)
- payday loans near me no credit check (2)
- payday loans near me no credit check direct payday loans (1)
- payday loans near me no credit check near me (1)
- payday loans near me no credit check no bank account (1)
- payday loans near me with bad credit (2)
- payday loans near me with no credit check (2)
- payday loans nearby (1)
- payday loans neat me (2)
- payday loans need credit (1)
- payday loans new (1)
- payday loans no (3)
- payday loans no bad credit (1)
- payday loans no bank account no credit check (2)
- payday loans no bank account no credit check near me (2)
- payday loans no credit (1)
- payday loans no credit check (1)
- payday loans no credit check direct deposit (4)
- payday loans no credit check direct lender (2)
- payday loans no credit check direct lenders (2)
- payday loans no credit check direct lenders only (3)
- payday loans no credit check instant decision (2)
- payday loans no credit check instant payout (2)
- payday loans no credit check lender (1)
- payday loans no credit check lenders (2)
- payday loans no credit check lenders only (1)
- payday loans no credit check low interest (3)
- payday loans no credit check near me (1)
- payday loans no credit check no checking account (3)
- payday loans no credit check no direct deposit (2)
- payday loans no credit check no lenders (1)
- payday loans no credit check or bank account (5)
- payday loans no credit check places (1)
- payday loans no credit check usa (3)
- payday loans no debit card credit check (2)
- payday loans now (1)
- payday loans now bad credit (1)
- payday loans of america (2)
- payday loans on (1)
- payday loans on bad credit (3)
- payday loans on benefits no credit check (3)
- payday loans only (1)
- payday loans only in cash (2)
- payday loans or bad credit loans (1)
- payday loans or cash advance (1)
- payday loans or cash advances (4)
- payday loans places near me no credit check (2)
- payday loans that work (3)
- payday loans tomorrow (1)
- payday loans usa (2)
- payday loans use passport (1)
- payday loans very bad credit (2)
- payday loans what are (3)
- payday loans what are they (2)
- payday loans what do i need (2)
- payday loans what do you need (3)
- payday loans what is (1)
- payday loans with (3)
- payday loans with bad credit (1)
- payday loans with bad credit near me (2)
- payday loans with bad credit no credit check (1)
- payday loans with no credit (5)
- payday loans with no credit check (3)
- payday loans with no credit check or bank account (1)
- payday loans with no credit check or checking account (3)
- payday loans with no job verification or credit check (3)
- payday loans: (2)
- payday loans? (2)
- payday loans\ (1)
- payday no credit check loan (1)
- payday now cash advance (3)
- payday now loans (2)
- payday usa loan (1)
- payday usa loans (1)
- paydayloanadvance online installment loans no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+abbeville cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+akron nearby payday loans (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+alexander-city cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+allgood nearby payday loans (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+arab cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+argo bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+ariton my payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+ashland how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+babbie how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+baileyton get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+ballplay bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+banks get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+belle-fontaine cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+berlin bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+billingsley my payday loan (0)
- paydayloanalabama.com+birmingham cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+blountsville my payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+blue-ridge how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+bon-secour cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+brantleyville payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+brent how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+brewton payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+bristow-cove no credit check loan payday (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+brook-highland cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+brookside my payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+camp-hill cash advance loans with no credit check (0)
- paydayloanalabama.com+cardiff cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+carolina cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+center-point bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+centre get a cash advance (0)
- paydayloanalabama.com+chunchula cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+citronelle nearby payday loans (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+cleveland payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+clio nearby payday loans (0)
- paydayloanalabama.com+coats-bend cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+coffee-springs cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+coffeeville bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+colony cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+columbiana payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+concord get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+cordova cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+cottondale get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+cottonwood my payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+cowarts my payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+crossville cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+cusseta bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+dadeville cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+daleville payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+delta payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+elkmont payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+elmore cash advance loans with no credit check (0)
- paydayloanalabama.com+eunola how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+evergreen get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+excel payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+fairfield get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+fayette bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+five-points my payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+florala get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+fort-payne get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+frisco-city no credit check loan payday (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+fultondale cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+gainesville payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+geraldine cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+gilbertown get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+goldville my payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+goshen cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+grove-hill cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+gu-win cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+guin payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+gulfcrest get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+guntersville get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+hamilton get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+hatton how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+hazel-green cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+helena bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+highland-lakes my payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+hokes-bluff bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+hollins get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+homewood cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+hytop how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+ivalee no credit check loan payday (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+kellyton get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+kimberly my payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+lincoln bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+littleville bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+lowndesboro nearby payday loans (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+luverne get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+madrid get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+malcolm payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+maplesville payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+marbury payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+maytown how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+mccalla payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+mcintosh my payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+memphis bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+midland-city cash to go and advance america (2)
- paydayloanalabama.com+mignon cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+millbrook cash to go and advance america (2)
- paydayloanalabama.com+millport get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+mobile cash to go and advance america (2)
- paydayloanalabama.com+monroeville no credit check loan payday (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+mooresville get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+morrison-crossroads get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+mountain-brook get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+mulga nearby payday loans (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+munford cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+nances-creek my payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+natural-bridge my payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+new-union payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+newton my payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+newville bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+nixburg payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+north-courtland get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+oak-grove get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+ohatchee cash to go and advance america (2)
- paydayloanalabama.com+oneonta get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+orrville cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+paint-rock get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+pea-ridge get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+pelham cash to go and advance america (2)
- paydayloanalabama.com+pell-city get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+pinckard cash to go and advance america (2)
- paydayloanalabama.com+pine-apple cash to go and advance america (2)
- paydayloanalabama.com+pine-level cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+pine-ridge payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+pinson my payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+point-clear bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+pollard my payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+prichard bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+rainsville payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+ray cash to go and advance america (2)
- paydayloanalabama.com+rosa cash to go and advance america (2)
- paydayloanalabama.com+sand-rock payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+sanford cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+saraland bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+selma payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+shoal-creek get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+shorter payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+sipsey get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+slocomb how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+smoke-rise how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+somerville no credit check loan payday (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+south-vinemont get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+spanish-fort my payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+springville cash to go and advance america (2)
- paydayloanalabama.com+st-florian get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+st-stephens my payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+stapleton payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+sterrett how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+sumiton nearby payday loans (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+sylvania get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+talladega get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+thomaston get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+thomasville cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+tillmans-corner payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+union-springs payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+valley bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+vandiver my payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+vestavia-hills cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+vina my payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+vincent get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+west-point cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+woodstock my payday loan (1)
- paydayloanalabama.com+yellow-bluff how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+air-force-academy no credit check loan payday (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+alamosa-east get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+amherst bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+arvada bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+avon get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+battlement-mesa get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+berkley get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+black-forest cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+blende get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+bonanza-mountain-estates nearby payday loans (0)
- paydayloancolorado.net+boone my payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+branson bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+brick-center cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+brush cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+burlington payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+calhan get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+capulin cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+carbondale bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+castle-pines-village get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+cattle-creek how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+cedaredge how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+center how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+cherry-creek get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+collbran payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+colona cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+colorado-city get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+cope payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+copper-mountain get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+de-beque get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+deer-trail cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+divide bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+dove-creek get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+eads payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+eaton cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+echo-hills get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+el-jebel cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+eldora payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+empire get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+estes-park nearby payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+evans my payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+evergreen no credit check loan payday (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+fairmount payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+flagler cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+fleming cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+floyd-hill get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+fort-carson payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+fort-garland my payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+fort-lupton no credit check loan payday (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+four-square-mile how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+fowler bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+gardner cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+genesee get cash advance at bank (0)
- paydayloancolorado.net+genoa my payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+georgetown cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+gleneagle cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+granby cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+grand-junction nearby payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+greeley my payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+gunbarrel cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+hartman cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+haswell how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+heeney get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+hidden-lake payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+highlands-ranch nearby payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+hillrose no credit check loan payday (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+hoehne cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+holly-hills no credit check loan payday (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+hooper cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+indian-hills bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+jackson-lake payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+johnstown get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+ken-caryl no credit check loan payday (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+kittredge bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+la-junta-gardens get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+laird nearby payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+lake-city how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+lamar cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+las-animas payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+limon get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+lincoln-park nearby payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+littleton cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+lochbuie get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+loghill-village payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+loma nearby payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+lone-tree get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+longmont cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+mancos bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+manzanola no credit check loan payday (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+matheson my payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+mead my payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+meeker my payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+moffat get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+montrose get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+mount-crested-butte no credit check loan payday (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+mountain-view cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+mountain-village cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+new-castle get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+niwot get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+norwood no credit check loan payday (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+nucla cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+nunn get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+oak-creek get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+olathe get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+ophir cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+orchard-city cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+orchard-mesa cash advance loans with no credit check (0)
- paydayloancolorado.net+padroni get cash advance at bank (0)
- paydayloancolorado.net+pagosa-springs how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+palisade bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+paonia cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+parachute cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+peoria bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+pitkin my payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+placerville get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+poncha-springs bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+ramah nearby payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+rangely payday loan instant funding no credit check (0)
- paydayloancolorado.net+redlands cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+rock-creek-park get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+roxborough-park my payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+saguache cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+san-luis my payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+security-widefield get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+sedalia cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+seven-hills nearby payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+severance no credit check loan payday (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+sheridan get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+sheridan-lake nearby payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+silt bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+silver-plume how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+silverton no credit check loan payday (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+simla payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+snyder payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+st-ann-highlands get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+stepping-stone bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+sterling-ranch cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+strasburg bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+stratton bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+superior payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+tabernash my payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+tall-timber cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+towaoc get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+trail-side cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+upper-bear-creek how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+vilas my payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+walden get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+walsh cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+westminster my payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+windsor payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+woodland-park my payday loan (1)
- paydayloancolorado.net+woodmoor get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloanmaryland guaranteed installment loans for bad credit no credit check (1)
- paydayloanmaryland.com guaranteed installment loans for bad credit (1)
- paydayloanmaryland.com guaranteed installment loans for bad credit no credit check (1)
- paydayloanmaryland.com installment loans no credit check (1)
- paydayloanmissouri.com installment loans bad credit (1)
- paydayloanmissouri.com personal installment loans (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+baltic no credit check loan payday (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+bantam cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+bigelow-corners my payday loan (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+botsford cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+branchville get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+branford-center cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+bridgeport payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+bridgewater cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+bristol get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+broad-brook payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+candlewood-isle get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+candlewood-knolls cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+candlewood-lake-club payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+cannondale payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+chester-center cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+collinsville nearby payday loans (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+cos-cob bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+coventry-lake no credit check loan payday (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+crystal-lake bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+danbury nearby payday loans (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+darien-downtown cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+dodgingtown cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+falls-village payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+gaylordsville get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+glastonbury-center my payday loan (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+heritage-village get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+indian-field get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+inglenook bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+kensington get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+lakeside-woods my payday loan (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+mansfield-center cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+new-britain get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+new-canaan payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+new-haven my payday loan (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+noank get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+noroton payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+northwest-harwinton how much can you get on a payday loan (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+norwalk payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+norwich cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+old-saybrook-center get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+oxoboxo-river get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+pemberwick payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+plantsville my payday loan (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+plattsville payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+quasset-lake cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+quinnipiac-university cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+riverton cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+sacred-heart-university payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+saugatuck cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+south-coventry cash advance loans with no credit check (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+southport get cash advance at bank (0)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+storrs cash to go and advance america (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+suffield-depot bad credit no credit check payday loans (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+tashua get cash advance at bank (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+torrington get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+trumbull-center no credit check loan payday (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+wallingford-center payday loan instant funding no credit check (1)
- paydayloansconnecticut.com+wauregan get a cash advance (1)
- paydayloansindiana online installment loans (1)
- paydayloansnc personal installment loans (1)
- paydayloansnc.com installment loans bad credit (1)
- paydayloansohio bad credit installment loans (1)
- paydayloansohio tribal installment loans direct lenders no credit check (1)
- paydayloanssouthcarolina installment loans near me (1)
- paydayloanssouthdakota no credit check installment loans (1)
- paydayloanssouthdakota online installment loans no credit check (1)
- paydayloanstennessee no credit check installment loans (1)
- paydayloantexas bad credit installment loans (1)
- paydayloantexas installment loans no credit check (1)
- paydayloantexas installment loans online (1)
- paydayloantexas personal installment loans (1)
- paydayloanwisconsin online installment loans no credit check (0)
- Pays des mariГ©es par correspondance (8)
- Pays des mariГ©es par correspondance (0)
- Pays des mariГ©es par correspondance (0)
- Pays des mariГ©es par correspondance (0)
- Pays des mariГ©es par correspondance (0)
- Pays des mariГ©es par correspondance (0)
- Pays des mariГ©es par correspondance (0)
- Pays des mariГ©es par correspondance (0)
- pb_aug (3)
- PB_TOP (1)
- Pdc World Darts Championship Odds, Picks: Betting Breakdown Intended For Day 1 - 473 (2)
- pedidos por correo de catГЎlogos de novias (1)
- pedidos por correo de reseГ±as de agencias de novias (1)
- pedidos por correo de reseГ±as de novias (2)
- pedidos por correo de reseГ±as de novias (0)
- pedidos por correo sitios de novias legГtimos (3)
- pedidos por correo sitios de novias legГtimos (0)
- per corrispondenza (4)
- per corrispondenza i siti della sposa reddit (1)
- per corrispondenza la sposa ne vale la pena (2)
- per corrispondenza paesi sposa (1)
- per corrispondenza sposa reale (1)
- per corrispondenza sposa siti web reddit (2)
- per corrispondenza sposa siti web reddit (0)
- per corrispondenza sposa storia (1)
- per corrispondenza sposa storie reddit (2)
- per corrispondenza sposa wikipedia (2)
- per corrispondenza storie di sposi (3)
- personalloancolorado no credit check installment loans (1)
- peruvian-women+laredo site free (1)
- peruvian-women+miramar free online sites for singles (1)
- peruvian-women+vice free online sites for singles (1)
- peruvian-women+vice site free (1)
- Petersburg online installment loans (1)
- petite-single-women free online sites for singles (1)
- Pin UP AZ Casino (1)
- Pin UP AZ Online (1)
- Pin Up Brazil (1)
- pin up casino (5)
- Pin UP Casino AZ (4)
- Pin UP Online AZ (1)
- pinco (1)
- PinUp apk (30)
- pitäisikö minun ostaa postimyynti morsiamen (3)
- pitäisikö minun ostaa postimyynti morsiamen (0)
- pitäisikö minun ostaa postimyynti morsiamen (0)
- pitäisikö minun päivätä postimyynti morsiamen (2)
- pitäisikö minun päivätä postimyynti morsiamen (0)
- Pixbet Cassino (1)
- Pl-steroid (2)
- plinko (1)
- Podaci o narudЕѕbi poЕЎte (3)
- Podaci o narudЕѕbi poЕЎte (0)
- Podaci o narudЕѕbi poЕЎte (0)
- poland escort girl link (1)
- polish dating sites (1)
- polish-brides free online sites for singles (1)
- polish-women+lodz site free (1)
- polish-women+poznan site free (1)
- portuguese-women+anta free online sites for singles (1)
- portuguese-women+beja free online sites for singles (1)
- portuguese-women+beja site free (0)
- portuguese-women+fatima free online sites for singles (1)
- portuguese-women+monsanto free online sites for singles (1)
- posso ottenere una sposa per corrispondenza se sono giГ sposato? (1)
- post brud ordre (3)
- Post in der Bestellung Braut (3)
- Post in der Bestellung Brautkosten (3)
- post-order-brud (4)
- posta dell'ordine della sposa (2)
- Posta Gelin SipariЕџi (1)
- posta in ordine costo sposa (1)
- posta in ordine sposa (2)
- posta per ordinare la sposa (4)
- Posta sipariЕџ gelini nedir? (3)
- Posta sipariЕџ gelini nedir? (0)
- Posta sipariЕџ gelini nedir? (0)
- posta sipariЕџi (5)
- posta sipariЕџi (0)
- posta sipariЕџi (0)
- posta sipariЕџi (0)
- posta sipariЕџi (0)
- posta sipariЕџi eЕџleri (1)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin (2)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin AjanslarД± (3)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin AjanslarД± (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin AjanslarД± (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin AjansД± (1)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin AjansД± Д°ncelemeleri (1)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin ArkadaЕџ Siteleri (2)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin ArkadaЕџ Siteleri (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Bilgileri (3)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Bilgileri (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Bilgileri (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Bilgisi (1)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Bulma (1)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelin buna deДџer (3)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelin buna deДџer (0)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelin buna deДџer (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Craigslist (2)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Craigslist (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin EndГјstrisi (3)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin EndГјstrisi (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin EndГјstrisi (0)
- Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek (1)
- Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek Hikayeler (2)
- Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek Hikayeler (0)
- Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek Site (2)
- Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçek Site (0)
- Posta Siparişi Gelin Gerçekleri (1)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hikayeleri (4)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hikayeleri (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hikayeleri (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hikayeleri (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hikayesi (3)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hikayesi (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hikayesi (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmeti (2)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmeti (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmetleri Nedir (2)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmetleri Nedir (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmetleri TanД±mД± (3)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmetleri TanД±mД± (0)
- posta sipariЕџi gelin iyi fikir? (1)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin KataloglarД± (2)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin KataloglarД± (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin KataloДџu (4)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin KataloДџu (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin KataloДџu (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin KataloДџu (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Kuponu (1)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Makaleleri (3)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Makaleleri (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Makaleleri (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin NasД±l HazД±rlanД±r (3)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin NasД±l HazД±rlanД±r (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin NasД±l HazД±rlanД±r (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin NasД±l SatД±n AlД±nД±r (3)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin NasД±l SatД±n AlД±nД±r (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin NasД±l SatД±n AlД±nД±r (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin NasД±l YapД±lД±r (4)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin NasД±l YapД±lД±r (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin NasД±l YapД±lД±r (0)
- posta sipariЕџi gelin nasД±l Г§alД±ЕџД±r (2)
- posta sipariЕџi gelin nasД±l Г§alД±ЕџД±r (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin NasД±l Г‡alД±ЕџД±r (1)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Nedir (6)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Nedir (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Nedir (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Nedir (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Nedir (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Nedir (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Reddit NasД±l HazД±rlanД±r (1)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Siteleri (3)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Siteleri (0)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri meЕџru (2)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri meЕџru (0)
- posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri nasД±l Г§alД±ЕџД±r (2)
- posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri nasД±l Г§alД±ЕџД±r (0)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri reddit (1)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Siteleri Д°ncelemesi (1)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin SSS (2)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin SSS (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin TanД±mД± (3)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin TanД±mД± (0)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelin tanД±Еџma sitesi (1)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Tarihi (1)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Web Siteleri (2)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Web Siteleri (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Web Siteleri Д°ncelemeleri (2)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Web Siteleri Д°ncelemeleri (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Web Sitesi (3)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Web Sitesi (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Web Sitesi (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Web Sitesi YorumlarД± (2)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Web Sitesi YorumlarД± (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Wiki (1)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Wikipedia (2)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Wikipedia (0)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelin yasal mД±? (1)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Yasal Siteleri (2)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Yasal Siteleri (0)
- posta sipariЕџi gelin Гјlkeleri (2)
- posta sipariЕџi gelin Гјlkeleri (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Д°ncelemesi (1)
- posta sipariЕџi geline deДџer mi (1)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini (2)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini (0)
- Posta siparişi gelini almak için en iyi yer (1)
- Posta siparişi gelini almak için en iyi ülkeler (2)
- Posta siparişi gelini almak için en iyi ülkeler (0)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini almalД± mД±yД±m (3)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini almalД± mД±yД±m (0)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini almalД± mД±yД±m (0)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini arД±yor (3)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini arД±yor (0)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini arД±yor (0)
- Posta siparişi gelini bulmak için en iyi yerler (2)
- Posta siparişi gelini bulmak için en iyi yerler (0)
- posta siparişi gelini bulmak için en iyi ülke (1)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini bulun (2)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini bulun (0)
- Posta siparişi gelini flört (2)
- Posta siparişi gelini flört (0)
- posta siparişi gelini gerçek bir şey mi (1)
- posta siparişi gelini gerçek mi (2)
- posta siparişi gelini gerçek mi (0)
- posta sipariЕџi gelini gГјvenli mi (1)
- posta siparişi gelini için en iyi yer (1)
- posta siparişi gelini için en iyi yerler (1)
- posta siparişi gelini için en iyi ülke (1)
- posta siparişi gelini için ortalama fiyat (3)
- posta siparişi gelini için ortalama fiyat (0)
- posta siparişi gelini için ortalama fiyat (0)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini nasД±l sipariЕџ edilir (6)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini nasД±l sipariЕџ edilir (0)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini nasД±l sipariЕџ edilir (0)
- posta sipariЕџi gelini nasД±l sipariЕџ edilir (0)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini nasД±l sipariЕџ edilir (0)
- posta sipariЕџi gelini nasД±l yapД±lД±r (2)
- posta sipariЕџi gelini nasД±l yapД±lД±r (0)
- posta sipariЕџi gelini nasД±l Г§alД±ЕџД±r (1)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini nedir (5)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini nedir (0)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini nedir (0)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini nedir (0)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini nedir (0)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini nedir? (3)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini nedir? (0)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini nedir? (0)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini nereden alabilirim (3)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini nereden alabilirim (0)
- Posta siparişi gelini reddit için en iyi ülke (2)
- Posta siparişi gelini reddit için en iyi ülke (0)
- posta sipariЕџi gelini reveiw (2)
- posta sipariЕџi gelini reveiw (0)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini satД±n almak (2)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini satД±n almak (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelini SatД±n AlД±n (3)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelini SatД±n AlД±n (0)
- Posta SipariЕџi Gelini SatД±n AlД±n (0)
- Posta sipariЕџi gelini tanД±mlayД±n (1)
- posta sipariЕџi gelini web siteleri reddit (3)
- posta sipariЕџi gelini web siteleri reddit (0)
- posta sipariЕџi gelinin ortalama fiyatД± (1)
- posta sipariЕџi gelinin ortalama maliyeti (1)
- Posta Siparişi Gelinine Göz atın (3)
- Posta Siparişi Gelinine Göz atın (0)
- Posta sipariЕџi karД±sД± (3)
- Posta sipariЕџi karД±sД± (0)
- posta sipariЕџi nereden alД±nД±r (1)
- posta su ordinazione sposa (5)
- posti migliori per la sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- posti morsiamen määritelmän mukaan (2)
- posti morsiamen määritelmän mukaan (0)
- postimyynti (6)
- postimyynti morsiamen (2)
- postimyynti morsiamen agences (2)
- postimyynti morsiamen artikkeleita (1)
- postimyynti morsiamen arvoinen? (4)
- postimyynti morsiamen arvostelu (5)
- postimyynti morsiamen arvostelut (3)
- postimyynti morsiamen craigslist (1)
- postimyynti morsiamen faq (4)
- postimyynti morsiamen historia (1)
- postimyynti morsiamen hyvä idea? (1)
- postimyynti morsiamen keski-ikä (1)
- postimyynti morsiamen keskimääräinen hinta (8)
- postimyynti morsiamen keskimääräinen hinta (0)
- postimyynti morsiamen keskimääräinen hinta (0)
- postimyynti morsiamen keskimääräinen hinta (0)
- postimyynti morsiamen keskimääräinen hinta (0)
- postimyynti morsiamen keskimääräinen hinta (0)
- postimyynti morsiamen keskimääräinen hinta (0)
- postimyynti morsiamen keskimääräinen hinta (0)
- postimyynti morsiamen keskimääräiset kustannukset (2)
- postimyynti morsiamen keskimääräiset kustannukset (0)
- postimyynti morsiamen legit (3)
- postimyynti morsiamen legit? (1)
- postimyynti morsiamen luettelot (2)
- postimyynti morsiamen myytävänä (2)
- postimyynti morsiamen myytävänä (0)
- postimyynti morsiamen oikeita tarinoita (4)
- postimyynti morsiamen palveluiden määritelmä (3)
- postimyynti morsiamen palveluiden määritelmä (0)
- postimyynti morsiamen palveluiden määritelmä (0)
- postimyynti morsiamen palvelut (4)
- postimyynti morsiamen sivusto (2)
- postimyynti morsiamen sivustot (3)
- postimyynti morsiamen sivustot lailliset (1)
- postimyynti morsiamen sivustot reddit (2)
- postimyynti morsiamen tarinoita (5)
- postimyynti morsiamen tiedot (7)
- postimyynti morsiamen todellinen (2)
- postimyynti morsiamen todellinen sivusto (2)
- postimyynti morsiamen todellinen? (1)
- postimyynti morsiamen tosiasiat (1)
- postimyynti morsiamen treffisivusto (2)
- postimyynti morsiamen treffisivustot (2)
- postimyynti morsiamen treffisivustot (0)
- postimyynti morsiamen treffit (2)
- postimyynti morsiamen työ? (3)
- postimyynti morsiamen työ? (0)
- postimyynti morsiamen työ? (0)
- postimyynti morsiamen verkkosivusto (2)
- postimyynti morsiamen verkkosivustojen arvostelut (3)
- postimyynti morsiamen verkkosivustot reddit (1)
- postimyynti morsiamen virastot (1)
- postimyynti morsiamen wiki (3)
- postimyynti morsiamen wikipedia (1)
- postimyynti morsiamenteollisuus (1)
- postimyynti morsiamenvirasto, jolla on paras maine (1)
- postimyynti morsian (11)
- postimyynti morsian (0)
- postimyynti morsian definitiom (1)
- postimyynti morsian määrittele (1)
- postimyynti morsian sen arvoinen (2)
- postimyynti morsian todellinen (1)
- postimyynti vaimo (4)
- postimyynti vaimoja (3)
- postimyynti-morsian (3)
- postitse järjestyksessä morsian (3)
- postitse järjestyksessä morsian (0)
- postitse järjestyksessä morsian (0)
- postitse tilata morsian (3)
- posto migliore per la sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- posto migliore per ricevere la sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- postorder brud (4)
- postorder brud agences (1)
- postorder brud artiklar (2)
- postorder brud bra idé? (1)
- postorder brud bra idГ©? (2)
- postorder brud bra idГ©? (0)
- postorder brud dating (3)
- postorder brud dating webbplats (1)
- postorder brud definition (3)
- postorder brud faq (3)
- postorder brud legit (2)
- postorder brud legit? (3)
- postorder brud legit? (0)
- postorder brud pГҐ riktigt (1)
- postorder brud pГҐ riktigt? (1)
- postorder brud recension (1)
- postorder brud recensioner (1)
- postorder brud reveiw (2)
- postorder brud riktiga historier (5)
- postorder brud till salu (1)
- postorder brud värt det (2)
- postorder brud värt det (0)
- postorder brud verklig (3)
- postorder brud verklig webbplats (1)
- postorder brud värt det (2)
- postorder brud värt det (0)
- postorder brud värt det? (2)
- postorder brud värt det? (0)
- postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- postorder brud webbplatser legitima (2)
- postorder brud webbplatser recensioner (1)
- postorder brud wiki (1)
- postorder brud wikipedia (2)
- postorder brudarbete? (3)
- postorder brudbyråer (1)
- postorder brudbyrГҐ (1)
- postorder brudbyrГҐer (3)
- postorder brudbyrГҐer (0)
- postorder brudbyrГҐer (0)
- postorder brudens datingsajter (1)
- postorder brudens fakta (4)
- postorder brudens webbplats (4)
- postorder brudens webbplats recensioner (1)
- postorder brudens webbplatser reddit (6)
- postorder brudesidor reddit (2)
- postorder brudesidor reddit (0)
- postorder brudhistoria (1)
- postorder brudhistorier (4)
- postorder brudhistorier reddit (1)
- postorder brudindustri (1)
- postorder brudinformation (1)
- postorder brudkataloger (2)
- postorder brudkupong (2)
- postorder brudkupong (0)
- postorder brudländer (2)
- postorder brudländer (0)
- postorder brudtjänst (1)
- postorder brudtjänstdefinition (1)
- postorder fruar (1)
- postordre brud (8)
- postordre brud agences (3)
- postordre brud agentur med det bedste omdГёmme (2)
- postordre brud agentur med det bedste omdГёmme (0)
- postordre brud arbejde? (1)
- postordre brud artikler (1)
- postordre brud dating sider (2)
- postordre brud dating site (5)
- postordre brud dating site (0)
- postordre brud datingside (5)
- postordre brud definere (4)
- postordre brud ekte (4)
- postordre brud ekte historier (2)
- postordre brud ekte nettsted (2)
- postordre brud faq (2)
- postordre brud for ekte (4)
- postordre brud for Г¦gte (3)
- postordre brud for Г¦gte (0)
- postordre brud for Г¦gte (0)
- postordre brud for Г¦gte? (1)
- postordre brud god idГ©? (3)
- postordre brud god idГ©? (0)
- postordre brud god idГ©? (0)
- postordre brud historie (1)
- postordre brud industri (1)
- postordre brud legit? (2)
- postordre brud legitime websteder (2)
- postordre brud nettsted (1)
- postordre brud nettsteder (4)
- postordre brud nettsteder gjennomgang (1)
- postordre brud nettsteder legitime (4)
- postordre brud nettsteder reddit (1)
- postordre brud pГҐ ordentlig? (1)
- postordre brud reveiw (2)
- postordre brud rigtige historier (1)
- postordre brud rigtigt sted (1)
- postordre brud til salgs (1)
- postordre brud tjenester (1)
- postordre brud verdt det (1)
- postordre brud verdt det? (2)
- postordre brud værd? (1)
- postordre brud wiki (2)
- postordre brud wikipedia (2)
- postordre brudarbeid? (1)
- postordre bruddatingsider (3)
- postordre brude anmeldelse (1)
- postordre brude artikler (2)
- postordre brude service (2)
- postordre brude websteder reddit (2)
- postordre brudeanmeldelse (1)
- postordre brudebureauer (1)
- postordre brudebyrГҐ med det beste omdГёmmet (1)
- postordre brudebyrГҐer (2)
- postordre brudebyrГҐer (0)
- postordre brudefakta (2)
- postordre brudefaq (4)
- postordre brudehistorier (1)
- postordre brudekatalog (6)
- postordre brudekatalog (0)
- postordre brudekupong (3)
- postordre brudeland (2)
- postordre brudesider (1)
- postordre brudesider legitime (1)
- postordre brudesider reddit (1)
- postordre brudhistorie (2)
- postordre brudhistorier (1)
- postordre brudindustri (1)
- postordre brudinfo (2)
- postordre brudinformasjon (1)
- postordre brudland (2)
- postordre brudtjeneste (1)
- postordre kone (3)
- postordre koner (2)
- postordre-brud (2)
- postordre-brude (1)
- postordrebrud (2)
- postordrebrud definere (3)
- postordrebruden (3)
- postordrebrudstedet (2)
- postordrev hustruer (2)
- Pouvez-vous commander un mail d'une mariГ©e (3)
- Pouvez-vous commander un mail d'une mariГ©e (0)
- Pouvez-vous commander un mail d'une mariГ©e (0)
- Povijest narudЕѕbe poЕЎte (1)
- PoЕЎta po narudЕѕbi mladenke (3)
- PoЕЎta po narudЕѕbi mladenke (0)
- PoЕЎta po narudЕѕbi mladenke (0)
- PoЕЎta po redoslijedu troЕЎkova mladenke (1)
- PoЕЎta po redu mladenka (1)
- poЕЎta za naruДЌivanje mladenke (1)
- Prava web mjesta za mladenke (2)
- Prave narudЕѕbe za mladenke (1)
- Pravi nalog za mail mladenke priДЌe (1)
- precio promedio de la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- precio promedio de una novia por correo (1)
- precio promedio para la novia del pedido por correo (2)
- precios promedio de las novias por correo (3)
- Pregled narudЕѕbe poЕЎte (2)
- Pregled narudЕѕbe poЕЎte (0)
- Pregled web stranica za mladenke (2)
- prezzi medi per la sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- prezzo medio della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- prezzo medio di una sposa per corrispondenza (4)
- prezzo medio per sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- Primary/Elementary Education (66186)
- prix moyen d'une mariГ©e par correspondance (2)
- prix moyen d'une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- prix moyen pour une mariГ©e par correspondance (4)
- prix moyen pour une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- prix moyen pour une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- prix moyen pour une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Prix ​​moyen de la mariée par correspondance (2)
- Prix ​​moyen de la mariée par correspondance (0)
- Prix ​​moyen pour la mariée par correspondance (4)
- Prix ​​moyen pour la mariée par correspondance (0)
- Prix ​​moyen pour la mariée par correspondance (0)
- Prix ​​moyen pour la mariée par correspondance (0)
- Prix ​​moyens des mariées par correspondance (4)
- Prix ​​moyens des mariées par correspondance (0)
- Prix ​​moyens des mariées par correspondance (0)
- Prix ​​moyens des mariées par correspondance (0)
- PronalaЕѕenje mladenke za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (1)
- PronaД‘ite Mail narudЕѕbe mladenke (1)
- ProsjeДЌna cijena narudЕѕbe poЕЎte (1)
- ProsjeДЌna dob narudЕѕbe poЕЎte (1)
- ProsjeДЌne cijene mladenke (1)
- ProsjeДЌni troЕЎak mladenke za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (1)
- pt-pt+2redbeans-recensao bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+alemanha-mulheres site de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (1)
- pt-pt+america-mulheres site de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (1)
- pt-pt+amolatina-revisao site de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (1)
- pt-pt+amourfeel-revisao bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- pt-pt+asiandate-revisao bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+asianfeels-revisao site de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (1)
- pt-pt+asiatico-mulheres-vs-american-mulheres bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+azerbaijao-mulheres site de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (1)
- pt-pt+belize-mulheres site de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (1)
- pt-pt+boliviana-mulheres site de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (1)
- pt-pt+bulgaro-mulheres site de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (1)
- pt-pt+checheno-mulheres site de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (1)
- pt-pt+cherry-blossoms-revisao site de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (1)
- pt-pt+chispa-revisao site de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (1)
- pt-pt+colombian-cupid-recensao bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+costa-rica-mulheres bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+cupid-com-recensao bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+escandinava-mulheres bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+escocesa-mulheres bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+mingle2-revisao bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+mulheres-arabes-quentes bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+mulheres-canadenses-vs-mulheres-americanas site de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- pt-pt+mulheres-chinesas-quentes bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+mulheres-eslovacas-quentes site de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (1)
- pt-pt+mulheres-finlandesas-quentes bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+mulheres-georgianas-quentes site de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (1)
- pt-pt+mulheres-indianas-quentes bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+mulheres-quentes-do-tajiquistao bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+mulheres-quentes-do-uzbequistao bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+mulheres-quentes-uruguai bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+mulheres-solteiras-com-criancas bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+noivas-checas bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+norueguesa-mulheres bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+positive-singles-recensao bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+quente-afro-mulheres bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+quente-azerbaijao-mulheres bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+quente-bogota-mulheres bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+quente-chechen-mulheres bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+quente-colombiana-mulheres bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+quente-jordanian-mulheres bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+romancetale-revisao bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+romena-noivas bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+sofiadate-recensao bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+tajiquistao-mulheres bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- pt-pt+turco-namoro-sites-e-apps bons sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- puedes enviar por correo a una novia (2)
- Puis-je obtenir une mariГ©e par correspondance si je suis dГ©jГ mariГ©e? (3)
- Puis-je obtenir une mariГ©e par correspondance si je suis dГ©jГ mariГ©e? (0)
- Puis-je obtenir une mariГ©e par correspondance si je suis dГ©jГ mariГ©e? (0)
- puoct (1)
- puoi spedire una sposa (4)
- PU_aug (4)
- pГҐ jakt etter ekteskap (4)
- pГҐ jakt etter ekteskap (0)
- pГҐ jakt etter ekteskap (0)
- pГҐ jakt etter ekteskap (0)
- pГҐ udkig efter en postordrebrud (1)
- pГҐ udkig efter Г¦gteskab (2)
- pГҐ udkig efter Г¦gteskab (0)
- Qu'est-ce qu'une mariГ©e par correspondance (8)
- Qu'est-ce qu'une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Qu'est-ce qu'une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Qu'est-ce qu'une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Qu'est-ce qu'une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Qu'est-ce qu'une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Qu'est-ce qu'une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Qu'est-ce qu'une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Qu'est-ce qu'une mariГ©e par correspondance? (7)
- Qu'est-ce qu'une mariГ©e par correspondance? (0)
- Qu'est-ce qu'une mariГ©e par correspondance? (0)
- Qu'est-ce qu'une mariГ©e par correspondance? (0)
- Qu'est-ce qu'une mariГ©e par correspondance? (0)
- Qu'est-ce qu'une mariГ©e par correspondance? (0)
- Qu'est-ce qu'une mariГ©e par correspondance? (0)
- Qu'est-ce qu'une mariГ©e. (2)
- Qu'est-ce qu'une mariГ©e. (0)
- Qu'est-ce que la mariГ©e par correspondance (10)
- Qu'est-ce que la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Qu'est-ce que la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Qu'est-ce que la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Qu'est-ce que la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Qu'est-ce que la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Qu'est-ce que la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Qu'est-ce que la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Qu'est-ce que la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Qu'est-ce que la mariГ©e par correspondance? (11)
- Qu'est-ce que la mariГ©e par correspondance? (0)
- Qu'est-ce que la mariГ©e par correspondance? (0)
- Qu'est-ce que la mariГ©e par correspondance? (0)
- Qu'est-ce que la mariГ©e par correspondance? (0)
- Qu'est-ce que la mariГ©e par correspondance? (0)
- Qu'est-ce que la mariГ©e par correspondance? (0)
- Qu'est-ce que la mariГ©e par correspondance? (0)
- Qu'est-ce que la mariГ©e par correspondance? (0)
- Qu'est-ce que la mariГ©e par correspondance? (0)
- Qu'est-ce que la mariГ©e par correspondance? (0)
- Qu'est-ce que les services de mariГ©e par correspondance (6)
- Qu'est-ce que les services de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Qu'est-ce que les services de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Qu'est-ce que les services de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Qu'est-ce que les services de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Qu'est-ce que les services de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- qual ГЁ il miglior paese della sposa per corrispondenza (7)
- qual ГЁ il miglior paese della sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- qual ГЁ il miglior paese della sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- qual ГЁ il miglior paese della sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- qual ГЁ il miglior paese della sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- qual ГЁ il miglior paese della sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- qual ГЁ il miglior paese della sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- qual ГЁ il miglior servizio di sposa per corrispondenza (3)
- qual ГЁ il miglior servizio di sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- qual ГЁ il miglior servizio di sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- qual ГЁ il miglior sito per sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- qual ГЁ il miglior sito per sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- qual ГЁ la sposa per corrispondenza? (2)
- qual ГЁ la sposa per corrispondenza? (0)
- quality singles site login (13)
- que es como la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- que es el servicio de novias por correo (3)
- que es el servicio de novias por correo (0)
- que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- que es novia de pedidos por correo (1)
- que es una novia de pedidos por correo (8)
- que noiva por correspondГЄncia (1)
- que novia de orden de correo (1)
- Quel est le meilleur pays de mariГ©e par correspondance (2)
- Quel est le meilleur pays de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Quel est le meilleur service de mariГ©e par correspondance (7)
- Quel est le meilleur service de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Quel est le meilleur service de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Quel est le meilleur service de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Quel est le meilleur service de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Quel est le meilleur service de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Quel est le meilleur service de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (2)
- Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- quelle est une mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- Quels sont les meilleurs sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- quicken loans cash advance (4)
- quicken loans payday loans (2)
- quicken payday loans (1)
- quickest cash advance (1)
- quickest cash advance com (1)
- quickest payday loan (1)
- quickest payday loan com (0)
- quickest payday loans (3)
- quickloan payday loan (1)
- quickpay payday loans (2)
- quiero una novia por correo (2)
- Real Mail bestellen Braut Site (5)
- Real Mail bestellen Brautwebsite (1)
- Real Mail narudЕѕbe mladenke web stranice (1)
- real mail order bride (3)
- real mail order bride sites (1)
- real mail order bride stories (2)
- real mail order bride website (2)
- real no credit check payday loans (1)
- real no credit check payday loans direct lender (2)
- real payday loan lenders no credit check (4)
- real payday loans no credit check (0)
- real singles site (8)
- real singles site review (9)
- recensione sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- recensioni del sito web della sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- recensioni di siti web per corrispondenza (4)
- recensioni per corrispondenza agenzia sposa (2)
- Recenzije web stranica za mladenke (3)
- reddit per corrispondenza legittima (2)
- reddit per corrispondenza legittima (0)
- review (12)
- reviews (9)
- revisiГіn de la novia por correo (2)
- revisiГіn de la novia por correo (0)
- revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (2)
- revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (0)
- Revue de la mariГ©e par correspondance (2)
- Revue de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Revue des sites des mariГ©es par correspondance (2)
- Revue des sites des mariГ©es par correspondance (0)
- Revues de l'agence par courrier Г©lectronique (2)
- Revues de l'agence par courrier Г©lectronique (0)
- Richmond installment loans near me (1)
- ricky casino australia (1)
- riktig postorder brud (3)
- riktiga postorder brud webbplatser (2)
- riktiga postorder brudens webbplatser (3)
- Rock Springs no credit check installment loans (1)
- Rokubetbetbet_aug (1)
- romanian-dating-sites-and-apps free online sites for singles (1)
- romanian-women+alexandria free online sites for singles (1)
- romanian-women+amara site free (1)
- romanian-women+bucharest site free (1)
- romanian-women+cluj-napoca free online sites for singles (1)
- romanian-women+constanta site free (1)
- romanian-women+deva free online sites for singles (1)
- romanian-women+iasi site free (1)
- romanian-women+siria free online sites for singles (1)
- rotujenvälinen postimyynti morsian (2)
- rotujenvälinen postimyynti morsian (0)
- russian mail order brides (1)
- russian-brides free online sites for singles (1)
- russian-women site free (1)
- russian-women+belgorod free online sites for singles (1)
- russian-women+chita free online sites for singles (1)
- russian-women+kazan free online sites for singles (1)
- russian-women+kemerovo free online sites for singles (1)
- russian-women+magnitogorsk free online sites for singles (1)
- russian-women+maykop free online sites for singles (0)
- russian-women+pskov free online sites for singles (1)
- russian-women+smolensk free online sites for singles (1)
- russian-women+sochi free online sites for singles (1)
- russian-women+tolyatti free online sites for singles (1)
- s+models+cz-south-bohemian+ceske-budejovice+squirting username (1)
- s+models+de-hh+hamburg tips (1)
- s+models+fr-brittany+rennes tips (1)
- s+models+fr-nouvelle-aquitaine+bordeaux tips (1)
- s+models+gb-england+liverpool visitors (1)
- s+models+it-emilia-romagna+parma tips (1)
- s+models+nl tips (1)
- s+models+nl visitors (1)
- safe payday loans no credit check (5)
- Salen installment loans near me (1)
- Sallisaw guaranteed installment loans for bad credit no credit check (1)
- salvadorian-women free online sites for singles (1)
- sann historia om postorderbruden (1)
- sann historie om postordrebruden (1)
- sann postorder brud (2)
- schweiz+aargau visitors (1)
- schweiz+aargau+brugg escort girl here (1)
- schweiz+aargau+brugg escort service (1)
- schweiz+aargau+zofingen escort girl (1)
- schweiz+appenzell-innerrhoden nutte buchen (1)
- schweiz+appenzell-innerrhoden sign in (1)
- schweiz+basel-landschaft+binningen escort girls (1)
- schweiz+basel-landschaft+binningen support (1)
- schweiz+basel-landschaft+liestal sign up (1)
- schweiz+basel-landschaft+munchenstein escorts (1)
- schweiz+basel-landschaft+mutenz escort service (1)
- schweiz+basel-landschaft+mutenz username (1)
- schweiz+basel-landschaft+oberwil escort girl (1)
- schweiz+basel-landschaft+oberwil username (1)
- schweiz+basel-landschaft+pratteln username (1)
- schweiz+basel-landschaft+reinach visitors (1)
- schweiz+freiburg escort girls (1)
- schweiz+freiburg support (1)
- schweiz+freiburg username (1)
- schweiz+freiburg+freiburg escort (1)
- schweiz+jura escort (1)
- schweiz+kanton-bern escort girl (1)
- schweiz+kanton-bern+bern support (1)
- schweiz+kanton-bern+bern tips (1)
- schweiz+kanton-bern+biel-bienne visitors (1)
- schweiz+kanton-bern+langenthal escort girl (1)
- schweiz+kanton-bern+langenthal tips (1)
- schweiz+kanton-bern+muri-bei-bern visitors (1)
- schweiz+kanton-bern+ostermundigen visitors (1)
- schweiz+kanton-genf+genf escort service (1)
- schweiz+kanton-glarus nutten buchen (1)
- schweiz+kanton-schwyz+einsiedeln sign in (1)
- schweiz+kanton-schwyz+ferienbach sign in (1)
- schweiz+kanton-solothurn escort girls (1)
- schweiz+kanton-solothurn+solothurn best escort platform (1)
- schweiz+kanton-solothurn+solothurn escort (1)
- schweiz+kanton-solothurn+solothurn support (1)
- schweiz+kanton-zug escort (1)
- schweiz+kanton-zug+baar escort girl link (1)
- schweiz+kanton-zug+baar nutten buchen (1)
- schweiz+luzern-stadt escort girl (1)
- schweiz+luzern-stadt username (1)
- schweiz+luzern-stadt+emmen escort (1)
- schweiz+luzern-stadt+emmen tips (1)
- schweiz+luzern-stadt+kriens sign up (1)
- schweiz+luzern-stadt+luzern escort buchen (1)
- schweiz+neuchatel escorts (1)
- schweiz+neuchatel+neuchatel visitors (1)
- schweiz+nidwalden escort girl (1)
- schweiz+schaffhausen-state+schaffhausen support (1)
- schweiz+st-gallen-zustand escort girl link (1)
- schweiz+st-gallen-zustand+buchs tips (1)
- schweiz+st-gallen-zustand+gossau sign in (1)
- schweiz+st-gallen-zustand+gossau username (1)
- schweiz+tessin escort girl (1)
- schweiz+tessin+lugano escort girl (1)
- schweiz+thurgau+arbon tips (1)
- schweiz+thurgau+kreuzlingen escort (1)
- schweiz+thurgau+kreuzlingen escort service (1)
- schweiz+thurgau+kreuzlingen support (1)
- schweiz+thurgau+romanshorn escorts (1)
- schweiz+thurgau+romanshorn sign up (1)
- schweiz+waadt escort near me (1)
- schweiz+waadt visitors (1)
- schweiz+waadt+lausanne escorts (1)
- schweiz+waadt+lausanne nutte buchen (1)
- schweiz+wallis tips (1)
- schweiz+wallis+monthey sign up (1)
- schweiz+zurich-kanton+adliswil sign up (1)
- schweiz+zurich-kanton+affoltern-am-albis nutten finden (1)
- schweiz+zurich-kanton+bassersdorf username (1)
- schweiz+zurich-kanton+dubendorf nutte buchen (1)
- schweiz+zurich-kanton+effretikon visitors (1)
- schweiz+zurich-kanton+hinwil escort near me (1)
- schweiz+zurich-kanton+hinwil username (2)
- schweiz+zurich-kanton+hinwil username (0)
- schweiz+zurich-kanton+kusnacht escort girl here (1)
- schweiz+zurich-kanton+meilen escorts (1)
- schweiz+zurich-kanton+pfaffikon visitors (1)
- schweiz+zurich-kanton+thalwil tips (1)
- schweiz+zurich-kanton+uster escort (1)
- schweiz+zurich-kanton+uster escort girl (1)
- schweiz+zurich-kanton+wallisellen escorts (1)
- schweiz+zurich-kanton+wetzikon visitors (1)
- schweiz+zurich-kanton+winterthur best escort platform (1)
- schweiz+zurich-kanton+winterthur username (1)
- secret-benefits-review free online sites for singles (1)
- secure payday loans no credit check (1)
- secured payday loans no credit check (1)
- selaa postimyynti morsiamen (2)
- Seneca bad credit installment loans (0)
- Seneca online installment loans instant approval (1)
- serbian-women+padina free online sites for singles (1)
- serbian-women+toba free online sites for singles (1)
- service (10)
- Service de mariГ©e de commande par correspondance lГ©gitime (1)
- Service de mariГ©e par correspondance (4)
- Service de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Service de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Service de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Service de mariГ©e par correspondance la mieux notГ©e (3)
- Service de mariГ©e par correspondance la mieux notГ©e (0)
- Service de mariГ©e par correspondance la mieux notГ©e (0)
- Service de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (1)
- Service de mariГ©e par correspondance rГ©el (6)
- Service de mariГ©e par correspondance rГ©el (0)
- Service de mariГ©e par correspondance rГ©el (0)
- Service de mariГ©e par correspondance rГ©el (0)
- Service de mariГ©e par correspondance rГ©el (0)
- services (15)
- Services de mariГ©e par correspondance (2)
- Services de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Services de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (2)
- Services de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- Services de mariГ©e par correspondance supГ©rieures (3)
- Services de mariГ©e par correspondance supГ©rieures (0)
- Services de mariГ©e par correspondance supГ©rieures (0)
- servicio de novia de pedidos por correo mejor calificado (3)
- servicio de novia de pedidos por correo real (3)
- servicio de novias de pedidos por correo legГtimo (1)
- servicio de novias por correo (2)
- servicio de novias por correo legГtimo (4)
- servicio de novias por correo legГtimo (0)
- servicio de novias por correo legГtimo (0)
- servicio de novias por correo legГtimo (0)
- servicios de novias de orden de correo superior (4)
- servicios de novias por correo (1)
- servicios de novias por correo legГtimo (1)
- servicios de novias por correo legГtimo (0)
- Servis mladenke s najviЕЎim ocijenjenim narudЕѕbama (1)
- servizio di sposa per corrispondenza legittimo (3)
- sex (6)
- sex site (10)
- sexy (9)
- shaadi-review free online sites for singles (1)
- Shiraz, Fars, Ir Climate Region, Monthly Averages, Historic Weather Data - 491 (4)
- short term cash advance no credit check (1)
- short term payday loans no credit check (1)
- should i buy a mail order bride (3)
- SIGNIFICES DE MAILLE (4)
- silverdaddies-review free online sites for singles (1)
- silversingles-review free online sites for singles (1)
- simplycashadvance.net+1000-dollar-payday-loan how to get a cash advance loan (1)
- simplycashadvance.net+borrow-money-online-instantly payday loans banks (1)
- simplycashadvance.net+borrow-money-online-instantly short payday loans no credit check (1)
- simplycashadvance.net+chime-loans what are good payday loan company (1)
- simplycashadvance.net+direct-deposit-loans what are good payday loan company (1)
- simplycashadvance.net+fast-payday-loans short payday loans no credit check (1)
- simplycashadvance.net+flex-loans short payday loans no credit check (1)
- simplycashadvance.net+get-a-personal-loan-with-no-credit-history what are good payday loan company (1)
- simplycashadvance.net+law-school-loans cash advance no credit check loan (1)
- simplycashadvance.net+legitimate-online-loans payday loan needed (1)
- simplycashadvance.net+loans-for-550-credit-score cash loan payday advance (0)
- simplycashadvance.net+loans-for-immigrants bad credit payday cash loan (1)
- simplycashadvance.net+loans-for-pensioners what are good payday loan company (1)
- simplycashadvance.net+no-teletrack-payday-loans payday loans banks (1)
- simplycashadvance.net+online-personal-loans-with-co-signer advance cash payday loans (1)
- simplycashadvance.net+payday-loans-for-self-employed payday cash advance loans near me (1)
- simplycashadvance.net+same-day-personal-loans payday cash advance loans near me (1)
- simplycashadvance.net+same-day-personal-loans payday loan needed (1)
- singapore-women free online sites for singles (1)
- single (10)
- single site (8)
- single-women-without-children free online sites for singles (1)
- singleasiangirls-review free online sites for singles (1)
- singles (9)
- singles site (6)
- singles sites (8)
- singles website (13)
- SipariЕџ Gelin NasД±l Posta YapД±lД±r (1)
- site (7)
- Site de la mariГ©e par correspondance des dix premiers (6)
- Site de la mariГ©e par correspondance des dix premiers (0)
- Site de la mariГ©e par correspondance des dix premiers (0)
- Site de la mariГ©e par correspondance des dix premiers (0)
- Site de la mariГ©e par correspondance des dix premiers (0)
- Site de la mariГ©e par correspondance des dix premiers (0)
- site de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (4)
- site de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- site de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- site de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- Site de mariГ©e par correspondance rГ©el (3)
- Site de mariГ©e par correspondance rГ©el (0)
- Site de mariГ©e par correspondance rГ©el (0)
- site de rencontres par courrier Г©lectronique (3)
- site de rencontres par courrier Г©lectronique (0)
- site de rencontres par courrier Г©lectronique (0)
- site for people (13)
- site free (6)
- site singles only (10)
- site Web de la mariГ©e par correspondance (5)
- site Web de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- site Web de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- site Web de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- site Web de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- site Web de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (2)
- site Web de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- sites (24)
- sites de mariГ©e par correspondance les mieux notГ©s (2)
- sites de mariГ©e par correspondance les mieux notГ©s (0)
- sites de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (4)
- sites de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- sites de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- sites de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- sites de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime reddit (6)
- sites de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime reddit (0)
- sites de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime reddit (0)
- sites de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime reddit (0)
- sites de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime reddit (0)
- sites de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime reddit (0)
- sites de mariГ©e par correspondance reddit (2)
- sites de mariГ©e par correspondance reddit (0)
- sites de mariГ©e par courrier lГ©gitime (6)
- sites de mariГ©e par courrier lГ©gitime (0)
- sites de mariГ©e par courrier lГ©gitime (0)
- sites de mariГ©e par courrier lГ©gitime (0)
- sites de mariГ©e par courrier lГ©gitime (0)
- sites de mariГ©e par courrier lГ©gitime (0)
- sites de mariГ©e par courrier par correspondance (2)
- sites de mariГ©e par courrier par correspondance (0)
- sites de mariГ©es par correspondance (5)
- sites de mariГ©es par correspondance (0)
- sites de mariГ©es par correspondance (0)
- sites de mariГ©es par correspondance (0)
- sites de mariГ©es par correspondance (0)
- sites de mariГ©s par correspondance rГ©els (1)
- sites de rencontres par courrier Г©lectronique (3)
- sites de rencontres par courrier Г©lectronique (0)
- sites de rencontres par courrier Г©lectronique (0)
- sites for adults (6)
- sites for free (13)
- sites for people (14)
- sites for professionals (5)
- sites for singles (28)
- sites free (5)
- sites in usa (12)
- sites lГ©gitimes de mariГ©e par correspondance (6)
- sites lГ©gitimes de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- sites lГ©gitimes de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- sites lГ©gitimes de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- sites lГ©gitimes de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- sites lГ©gitimes de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Sites Web de la mariГ©e par correspondance (5)
- sites Web de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- sites Web de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- sites Web de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- sites Web de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- sites Web de la meilleure vente par correspondance (1)
- Sites Web de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (3)
- Sites Web de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- Sites Web de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- Sites Web de mariГ©e par correspondance Reddit (4)
- Sites Web de mariГ©e par correspondance Reddit (0)
- Sites Web de mariГ©e par correspondance Reddit (0)
- Sites Web de mariГ©e par correspondance Reddit (0)
- Sites Web de mariГ©es par correspondance (2)
- Sites Web de mariГ©es par correspondance (0)
- siti di incontri per sposa per corrispondenza (3)
- siti di sposa legittimi per corrispondenza (2)
- siti di sposa per corrispondenza piГ№ votati (1)
- siti web di sposa legittimi per corrispondenza (2)
- siti web per corrispondenza (2)
- sitio de citas de novias por correo (1)
- sitio de la novia de orden de correo legГtimo (1)
- sitio de la novia de orden de correo superior (2)
- sitio de la novia de pedidos por correo real (1)
- sitio web de la novia de pedidos por correo (1)
- sitio web de la novia de pedidos por correo real (2)
- sitio web legГtimo de la novia por correo (2)
- sitio web legГtimo de la novia por correo (0)
- sitios de citas de novias por correo (4)
- sitios de novias de orden de correo superior (1)
- sitios de novias de pedidos por correo legГtimo (6)
- sitios de novias de pedidos por correo legГtimo (0)
- sitios de novias de pedidos por correo legГtimo (0)
- sitios de novias de pedidos por correo legГtimo (0)
- sitios de novias de pedidos por correo legГtimo (0)
- sitios de novias de pedidos por correo legГtimo (0)
- sitios de novias de pedidos por correo real (6)
- sitios de novias mejor calificados (2)
- sitios de novias por correo (1)
- sitios de novias por correo de leggit (2)
- sitios legГtimos de novias por correo (3)
- sitios legГtimos de novias por correo (0)
- sitios legГtimos de novias por correo (0)
- sitios web de novias de orden de correo superior (2)
- sitios web de novias de pedidos por correo legГtimo (6)
- sitios web de novias de pedidos por correo legГtimo (0)
- sitios web de novias de pedidos por correo legГtimo (0)
- sitios web de novias de pedidos por correo legГtimo (0)
- sitios web de novias de pedidos por correo legГtimo (0)
- sitios web de novias por correo (4)
- sito della sposa per corrispondenza reale (1)
- sito della sposa per corrispondenza superiore (2)
- sito reale sposa per corrispondenza (3)
- sito web della sposa per corrispondenza (5)
- sito web della sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- sito web della sposa per corrispondenza legittima (1)
- ska jag träffa en postorderbrud (2)
- ska jag träffa en postorderbrud (0)
- skal jeg gГҐ ut med en postordrebrud (2)
- skal jeg gГҐ ut med en postordrebrud (0)
- skulle jeg kjГёpe en postordrebrud (2)
- slot (1)
- slovakian-women+lucky free online sites for singles (1)
- slovenian-women free online sites for singles (1)
- slovenian-women+lucky free online sites for singles (1)
- So bestellen Sie eine Mail -Bestellung Braut (2)
- So bestellen Sie eine russische Mail -Bestellung Braut (4)
- So bestellen Sie Versandbestellbraut (1)
- So datieren Sie eine Versandbestellbraut (1)
- So erstellen Sie eine Versandbestellung Braut Reddit (1)
- So kaufen Sie eine Mail -Bestellung Braut (2)
- So machen Sie eine Mail -Bestellung Braut (2)
- So maile die Braut beenden Bestellung (2)
- Sober living (1)
- SociГ©tГ©s de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (5)
- SociГ©tГ©s de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- SociГ©tГ©s de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- SociГ©tГ©s de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- SociГ©tГ©s de mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- sofiadate-review free online sites for singles (1)
- Software development (1)
- Soll ich eine Versandungsbraut kaufen (1)
- someone to write an essay for me (1)
- someone to write my essay for me (1)
- someone who can write my essay (4)
- someone write my essay (1)
- South West City bad credit installment loans (1)
- south-africa escort women (1)
- spanish-women+guadalajara free online sites for singles (1)
- spanish-women+mao free online sites for singles (1)
- spanish-women+rubi free online sites for singles (1)
- speedycashloan.net+300-dollar-payday-loan what are good payday loan company (1)
- speedycashloan.net+bad-credit-line-of-credit payday loan needed (1)
- speedycashloan.net+borrow-money-online-instantly advance cash payday loans (1)
- speedycashloan.net+checking-account-with-bad-credit payday cash advance loans near me (1)
- speedycashloan.net+disability-payday-loans payday loan needed (1)
- speedycashloan.net+edd-card-cash-advance payday loan needed (1)
- speedycashloan.net+high-risk-loans payday loan needed (1)
- speedycashloan.net+loan-for-vacation bad credit payday cash loan (1)
- speedycashloan.net+loans-for-bad-credit short payday loans no credit check (1)
- speedycashloan.net+loans-for-immigrants cash advance no credit check loan (1)
- speedycashloan.net+loans-with-instant-bank-verification payday loans banks (1)
- speedycashloan.net+parent-loans payday loan needed (1)
- speedycashloan.net+payday-advance-app cash advance no credit check loan (1)
- speedycashloan.net+payday-loans-with-no-checking-account what are good payday loan company (1)
- speedycashloan.net+payday-loans-with-savings-account payday cash advance loans near me (1)
- speedycashloan.net+same-day-personal-loans payday loan needed (1)
- speedycashloan.net+small-payday-loans what are good payday loan company (1)
- speedycashloan.net+student-loans short payday loans no credit check (1)
- speedycashloan.net+student-loans-without-co-signer payday cash advance loans near me (1)
- speedycashloan.net+variable-rate-loans payday loans banks (1)
- speedycashloan.net+web-cash-loans cash advance no credit check loan (1)
- sposa interrazziale per corrispondenza (1)
- sposa lesbica per corrispondenza (4)
- sposa mondo per corrispondenza spose (2)
- sposa per corrispondenza (9)
- sposa per corrispondenza calda (2)
- sposa per corrispondenza legittima (5)
- sposa per corrispondenza per davvero (1)
- sposa per corrispondenza piГ№ calda (2)
- sposa per corrispondenza piГ№ calda (0)
- Springhill installment loans near me (1)
- stable-index.com (1)
- Steamboat Springs guaranteed installment loans for bad credit (1)
- steroid (65)
- steroid-de (3)
- steroid-irl (1)
- steroid-us (1)
- storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- storia mail ordina sposa (1)
- storie di sposa per corrispondenza (6)
- storie di sposa per corrispondenza (0)
- storie di sposa per corrispondenza vera (2)
- strane mladenke (2)
- Suchen Sie eine Mail -Bestellung Braut (4)
- Suchen Sie eine Versandbestellbraut (6)
- sugar dating (1)
- sugar dating review (1)
- Sumter online installment loans (0)
- suosituimmat postimyynti morsiamen verkkosivustot (3)
- sv+albanska-brudar topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+amerikanska-kvinnor-mot-utlandska-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+asianbeautydating-recension topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+asianladyonline-recension topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (0)
- sv+benaughty-recension topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+dream-singles-recension topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (0)
- sv+eharmony-recension topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+ensamstaende-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+fdating-recension topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+findeuropeanbeauty-recension topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+fling-com-recension topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+franska-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+franska-kvinnor-mot-amerikanska-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+grekiska-dejting-webbplatser-och-appar topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+heta-chilenska-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+heta-egyptiska-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (0)
- sv+heta-iranska-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+heta-irlandska-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+heta-kanadensiska-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+heta-pakistanska-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+heta-paraguay-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+heta-polish-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+heta-ryska-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+heta-tjetjenska-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+hur-man-far-en-postorder-brud topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+islandska-brudar topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+japanska-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (0)
- sv+kambodjanska-brudar topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+kanadensiska-kvinnor-mot-amerikanska-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+kubanska-brudar topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+latin-woman-date-recension topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+malaysiska-brudar topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+mexikanska-brudar topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+mexikanska-dejting-webbplatser-och-appar topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+mogna-ensamstaende-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+norska-brudar topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+osteuropeiska-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+panamanska-brudar topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+phrendly-recension topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+positive-singles-recension topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+silverdaddies-recension topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+skotsk-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+spanska-brudar topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+svenska-dejting-webbplatser-och-appar topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+svenska-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+theluckydate-recension topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+tjeckiska-brudar topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+tunisiska-brudar topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+venezuelanska-brudar topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- sv+vitryssland-kvinnor topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- swedish-women+trelleborg free online sites for singles (1)
- sweet bonanza (1)
- sweet bonanza TR (1)
- swiss-women free online sites for singles (1)
- swiss-women+zurich free online sites for singles (1)
- swoonbrides.net amourfeel Comment faire une mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- swoonbrides.net da+bedste-postordrebrude-sider bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- swoonbrides.net da+charmdate bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- swoonbrides.net da+vietnamesiske Г¦gte mail ordre brude websteder (1)
- swoonbrides.net de+heiseste-turkische-frauen Wie funktioniert die Mail -Bestellung Braut? (1)
- swoonbrides.net de+indische-braute Mail-Order-Braut (1)
- swoonbrides.net de+indonesische-braute Bester Mail -Bestellung Brautservice (1)
- swoonbrides.net de+lustige-romantik Wie funktioniert die Mail -Bestellung Braut? (1)
- swoonbrides.net de+mexikanische-braute Bester Mail -Bestellung Brautservice (1)
- swoonbrides.net de+romantik-touren Bester Mail -Bestellung Brautservice (1)
- swoonbrides.net de+thai-braute Wie funktioniert die Mail -Bestellung Braut? (1)
- swoonbrides.net de+turkische-braute Bester Mail -Bestellung Brautservice (0)
- swoonbrides.net es+como-obtener-un-novia-por-correo-si-quieres-una-esposa-perfecta mejor orden de correo novia (1)
- swoonbrides.net es+mejores-sitios-novia-por-correo mejor orden de correo novia (1)
- swoonbrides.net es+novia-por-correo-historias-de-exito agencia de novias por correo (1)
- swoonbrides.net es+novias-peruanas que es como la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- swoonbrides.net es+novias-suecas que es como la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- swoonbrides.net es+novias-turcas mejor orden de correo novia (1)
- swoonbrides.net es+novias-ucranianas que es como la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- swoonbrides.net es+romance-tours-latin-america que es como la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- swoonbrides.net fi+aasialainen legit postimyynti morsiamen sivustot reddit (1)
- swoonbrides.net fi+filippiinilaiset legit postimyynti morsiamen sivustot reddit (1)
- swoonbrides.net fi+indonesian-morsiamet etsi minulle postimyynti morsian (1)
- swoonbrides.net fi+kiinalaiset-morsiamet postimyynti morsian (1)
- swoonbrides.net fi+latvialaiset-morsiamet postimyynti morsian (1)
- swoonbrides.net fi+loytaa-ulkomainen-tyttoystava postimyynti morsian (1)
- swoonbrides.net fi+miten-aloittaa-online-treffikeskustelu postimyynti morsian (1)
- swoonbrides.net it+brasiliano trova una sposa (1)
- swoonbrides.net it+charmdate trova una sposa (1)
- swoonbrides.net it+donne-straniere-per-il-matrimonio trova una sposa (1)
- swoonbrides.net it+incontrare-ragazze-slave il posto migliore per ottenere una sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- swoonbrides.net it+le-ragazze-asiatiche-piu-calde trova una sposa (1)
- swoonbrides.net it+quanto-costa-sposare-una-filippina trova una sposa (1)
- swoonbrides.net it+spose-brasiliane trova una sposa (1)
- swoonbrides.net it+spose-peruviane trova una sposa (1)
- swoonbrides.net it+spose-ucraine il posto migliore per ottenere una sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- swoonbrides.net no+amerikanske-vs-asiatiske-kvinner hva er en postordrebrud (1)
- swoonbrides.net no+hotteste-asiatiske-jenter ekte postordre brud nettsted (1)
- swoonbrides.net no+hotteste-utenlandske-kvinner hva er en postordrebrud (1)
- swoonbrides.net pt+noivas-indianas correio em ordem noiva (1)
- swoonbrides.net pt+noivas-peruanas correio em ordem noiva (1)
- swoonbrides.net pt+noivas-venezuelanas correio em ordem noiva (1)
- swoonbrides.net pt+sites-de-namoro-brasileiros correio em ordem noiva (0)
- swoonbrides.net tours-damour-philippines Comment faire une mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- swoonbrides.net tr+kolombiya-tanisma-siteleri Posta siparişi gelini bulmak için en iyi yerler (1)
- swoonbrides.net tr+polonya-arkadaslik-sitesi Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Д°ncelemeleri (1)
- swoonbrides.net tr+posta-siparisi-gelinler-yasal Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Д°ncelemeleri (1)
- swoonbrides.net tr+sicak-yabanci-kadinlar Posta siparişi gelini bulmak için en iyi yerler (1)
- swoonbrides.net tr+slav-kizlarla-tanisin Posta siparişi gelini bulmak için en iyi yerler (1)
- swoonbrides.net tr+ukrayna Gelin Posta SipariЕџi (1)
- sähköpostitilaus morsian (1)
- SД±cak Posta SipariЕџi Gelin (1)
- SД±rada Posta Gelin (6)
- SД±rada Posta Gelin (0)
- SД±rada Posta Gelin (0)
- SД±rada Posta Gelin (0)
- SД±rada Posta Gelin (0)
- SД±rada Posta Gelin (0)
- SД±rada Posta Gelin TanД±mД± (2)
- SД±rada Posta Gelin TanД±mД± (0)
- SД±rayla gelin maliyeti (1)
- taiwanese-women free online sites for singles (1)
- Tarih Posta SipariЕџi Gelin (2)
- Tarih Posta SipariЕџi Gelin (0)
- tennesseetitleloans guaranteed installment loans for bad credit direct lenders only (1)
- thai women for marriage (1)
- thai-brides free online sites for singles (1)
- thai-women+pattaya free online sites for singles (1)
- thaiflirting-review free online sites for singles (1)
- the mail order bride (4)
- the mail order bride (0)
- theluckydate-review free online sites for singles (1)
- things to know when a (11)
- tips for a (3)
- todellinen postimyynti morsiamen palvelu (3)
- todellinen postimyynti morsiamen sivusto (3)
- Top -bewertete Versandauftragsbrautseiten (1)
- Top -bewertete Versandauftragsbrautservice (2)
- Top -Mail -Bestellung Braut (2)
- Top -Mail -Bestellung Braut Site (3)
- Top -Mail -Bestellung Braut sitzt (1)
- Top -Mail -Bestellung Brautlender (3)
- Top -Mail -Bestellung Brautseiten (2)
- Top -Mail -Bestellung Brautseiten. (3)
- Top -Mail -Bestellung Brautwebsites (2)
- Top -Mail -Brautnetz bestellen (4)
- Top 10 des sites de mariГ©es par correspondance (2)
- Top 10 des sites de mariГ©es par correspondance (0)
- Top 10 Mail -Bestellung Braut (4)
- Top 10 Mail bestellen Brautwebsites (3)
- Top 10 Mail narudЕѕbe mladenke (1)
- top 10 mail order bride (4)
- top 10 mail order bride sites (4)
- top 10 orden de correo novia (1)
- top 10 postordre brudesider (1)
- top 10 postordrebrud (1)
- Top 10 sites Web de mariГ©es par correspondance (2)
- Top 10 sites Web de mariГ©es par correspondance (0)
- top 10 sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- Top 10 Versandbestellbraut -Sites (1)
- Top 10 web mjesta za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (1)
- Top 10 web stranica za mladenke (1)
- top 5 postordre brudesider (1)
- Top 5 sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (3)
- Top 5 sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Top 5 sites de mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Top 5 Versandbestellbraut -Sites (3)
- Top 5 web mjesta za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (1)
- Top Bride Mail. (2)
- top dating sites (1)
- top dating sites reviews (1)
- Top deset narudЕѕbe za mail mladenke Webites (1)
- Top dix marins de la vente par correspondance webite (3)
- Top Mail Bride Commande Web (6)
- top mail bride order web (1)
- top mail brudbeställningswebb (1)
- top mail brudbeställningswebb (1)
- Top Mail Command Bride Site (6)
- top mail order bride countries (0)
- Top Mail Order Bride se trouve (1)
- top mail order bride site (3)
- top mail order bride sits (1)
- top mail order bride websites (1)
- top rated mail order bride service (1)
- top rated mail order bride sites (2)
- Top Ten Mail bestellen Braut (1)
- Top Ten Mail bestellen Braut Site (5)
- top ten mail order bride site (2)
- top ten mail order bride webites (1)
- top ten per corrispondenza sito sposa (1)
- top ten per corrispondenza sposa webite (2)
- top ti postordre brudewebitter (1)
- topp 10 postorder brud (1)
- topp 10 postorder brud webbplatser (1)
- topp 10 postorder brudens webbplatser (3)
- topp 10 postordre brud nettsteder (7)
- topp 5 postorder brudesidor (3)
- topp ordre brud (4)
- topp ordre brud nettsteder (5)
- topp ordre brudland (2)
- topp post brudebestillingsnett (2)
- topp postorder brud (1)
- topp postorder brud sitter (1)
- topp postorder brud webbplats (3)
- topp postorder brudens webbplatser (4)
- topp postorder brudländer (1)
- topp postorder brudtjänster (1)
- topp postorder brudtjänster (1)
- topp postordre brud nettsteder. (2)
- topp postordre brud sitter (1)
- topp ti postordre brud nettsteder (2)
- topp ti postordre brudeside (1)
- topp tio postorder brud webbplats (2)
- topppost beställning brudar webbplatser. (1)
- topprangerte postordrebrudesider (1)
- tosi postimyynti morsiamen tarinoita (2)
- tosi postimyynti morsian (3)
- tosi tarina postimyynti morsiamen (2)
- tr+2redbeans-inceleme Гњst Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmetleri (0)
- tr+ada-kadinlar Гњst Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmetleri (1)
- tr+amerikan-kadinlar-vs-yabanci-kadinlar Гњst Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmetleri (1)
- tr+arjantinli-gelinler Гњst Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmetleri (1)
- tr+jswipe-inceleme Gerçek Posta Siparişi Gelin (1)
- tr+kismia-inceleme Гњst Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmetleri (1)
- tr+kolombiyali-gelinler Гњst Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmetleri (1)
- tr+kolombiyali-kadin Gerçek Posta Siparişi Gelin (1)
- tr+koreli-gelinler Гњst Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmetleri (1)
- tr+latinfeels-inceleme Гњst Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmetleri (1)
- tr+letonyali-gelinler Гњst Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmetleri (1)
- tr+letonyali-kadinlar Гњst Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmetleri (1)
- tr+loveswans-inceleme Гњst Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmetleri (1)
- tr+meetnicerussian-inceleme Гњst Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmetleri (1)
- tr+moldova-kadinlar Гњst Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmetleri (1)
- tr+ourtime-inceleme Гњst Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmetleri (1)
- tr+rubrides-inceleme Гњst Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmetleri (1)
- tr+sicak-arap-kadinlar Гњst Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmetleri (1)
- tr+sicak-danimarkali-kadinlar Гњst Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmetleri (1)
- Travail des mariГ©es par correspondance? (4)
- Travail des mariГ©es par correspondance? (0)
- Travail des mariГ©es par correspondance? (0)
- Travail des mariГ©es par correspondance? (0)
- Trouver la mariГ©e par correspondance (6)
- Trouver la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Trouver la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Trouver la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Trouver la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Trouver la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- trouver une mariГ©e (6)
- trouver une mariГ©e (0)
- trouver une mariГ©e (0)
- trouver une mariГ©e (0)
- trouver une mariГ©e (0)
- trouver une mariГ©e (0)
- Trouver une mariГ©e par correspondance (3)
- Trouver une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Trouver une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Trouvez-moi une mariГ©e par correspondance (4)
- Trouvez-moi une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Trouvez-moi une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Trouvez-moi une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- trova la sposa per corrispondenza (4)
- trova una sposa per corrispondenza (4)
- trovami una sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- trovare una sposa per corrispondenza (3)
- true mail order bride (1)
- true mail order bride stories (1)
- true story of mail order bride (2)
- tryfansme.com onlyfans girl (1)
- tryfansme.com+category+asmr onlyfans (1)
- tryfansme.com+category+asmr onlyfans girl (1)
- tryfansme.com+category+bbc onlyfans girl (1)
- tryfansme.com+category+blowjob onlyfans girl (1)
- tryfansme.com+category+cosplay onlyfans girl (1)
- tryfansme.com+category+famous best onlyfans (1)
- tryfansme.com+category+fetish onlyfans women (1)
- tryfansme.com+category+fitness onlyfans women (1)
- tryfansme.com+category+hairy onlyfans girl here (1)
- tryfansme.com+category+milf onlyfans link (1)
- tryfansme.com+category+skinny onlyfans women (1)
- tryfansme.com+category+top onlyfans (1)
- tryfansme.com+category+voyeur onlyfans girls (1)
- tryfansme.com+category+xxx onlyfans link (1)
- udenlandske brude (1)
- uk (5)
- UluslararasД± Posta SipariЕџi Gelin (1)
- una novia legГtima por correo (1)
- una novia por correo (3)
- una sposa legittima per corrispondenza (1)
- una sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- Uncategorized (37)
- une mariГ©e par correspondance (3)
- une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- une mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Une mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (7)
- Une mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- Une mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- Une mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- Une mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- Une mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- Une mariГ©e par correspondance lГ©gitime (0)
- us cash advance loan company (3)
- us payday loan company (2)
- usa cash advance (1)
- usa cash advance loan (1)
- usa cash advance loans (1)
- usa cash payday loans (2)
- usa credit payday loans (1)
- usa payday loan (1)
- usa payday loan company (4)
- usa payday loan yor (1)
- usa payday loans (1)
- utenlandske bruder (1)
- Vacherie online installment loans (1)
- vad är den bästa postorderbrudwebbplatsen (1)
- vad är en postorderbrud (4)
- vad är en postorderbrud (0)
- vad är en postorderbrud (0)
- vad är en postorderbrud (0)
- vad är en postorderbrud? (1)
- vad är som postorder brud (1)
- vad en postorder brud (1)
- vad är den bästa postorderbrudtjänsten (1)
- vad är den bästa postorderbrudwebbplatsen (1)
- vad Г¤r en postorderbrud (7)
- vad Г¤r en postorderbrud (0)
- vad Г¤r en postorderbrud (0)
- vad Г¤r en postorderbrud (0)
- vad Г¤r en postorderbrud (0)
- vad Г¤r en postorderbrud (0)
- vad Г¤r en postorderbrud (0)
- vad Г¤r postorder brud (5)
- vad Г¤r postorder brud (0)
- vad Г¤r postorder brud (0)
- vad Г¤r postorder brud (0)
- vad Г¤r postorder brud (0)
- vad Г¤r postorderbruden? (2)
- vad Г¤r postorderbruden? (0)
- vad Г¤r som postorder brud (2)
- vad Г¤r som postorder brud (0)
- vale la pena la novia por correo (2)
- Valencia bad credit installment loans (1)
- Valencia online installment loans instant approval (1)
- Van Wert online installment loans instant approval (1)
- var hittar jag en postorderbrud (1)
- var kan jag fГҐ en postorderbrud (1)
- var kan jag hitta en postorderbrud (4)
- var man hittar en postorderbrud (1)
- var man kan köpa en postorderbrud (1)
- vendita per corrispondenza servizi per la sposa (6)
- vendita per corrispondenza siti sposa legittimi (1)
- vendita per corrispondenza sposa siti legittimi (2)
- vendita per corrispondenza sposa storie vere (3)
- vendita sposa incontri (1)
- vera sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- verdadera orden de correo novia (2)
- verde casino hungary (1)
- verde casino poland (1)
- veri e propri siti di sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- verklig postorder brudtjänst (2)
- verklig postorder brudtjänst (0)
- vero servizio di sposa per corrispondenza (2)
- Versandbestellbraut definitiom (1)
- Versandbestellbraut kaufen (1)
- Versandbestellbraut wert? (3)
- Versandbestellung Frau (3)
- Versandbraut durchsuchen (1)
- Versandbraut fГјr echte (1)
- vieraat morsiamet (1)
- viisi parasta postimyynti morsiamen sivustoa (3)
- voglio una sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- voinko saada postimyynti morsiamen, jos olen jo naimisissa? (1)
- voitko tilata morsiamen postitse (1)
- voltprofit.org (1)
- vrijedi li mladenka poЕЎte (1)
- vulkan vegas DE (5)
- vulkan vegas DE login (5)
- VulkanVegas Poland (3)
- VГ©ritable mariГ©e par correspondance (4)
- VГ©ritable mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- VГ©ritable mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- VГ©ritable mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Wagoner guaranteed installment loans for bad credit no credit check (1)
- Wahre Geschichte der Versandbestellung Braut (3)
- wahre Mail -Bestellung Brautgeschichten (2)
- want (9)
- want app (9)
- want app review (9)
- want reviews (9)
- want site (8)
- want site review (10)
- want site reviews (1)
- Warrensburg guaranteed installment loans for bad credit direct lenders only (1)
- Was fГјr eine Mail -Bestellung Braut (3)
- Was fГјr eine Mail -Bestellung Braut (0)
- Was fГјr eine Mail -Bestellung Braut (0)
- Was ist die beste Mail -Bestellung Braut. (1)
- Was ist die beste Versandungsbestellung Brautland (1)
- Was ist die Braut von Versandungsbestellungen? (2)
- Was ist die Versandbraut? (3)
- Was ist eine Mail -Bestellung Braut (7)
- Was ist eine Mail -Bestellung Braut? (4)
- Was ist eine Mail-Order-Braut (1)
- Was sind die besten Mail -Bestellbraut -Sites (2)
- Waukesha no credit check installment loans (0)
- Wauwatosa no credit check installment loans (1)
- web mjesto za mladenku za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (1)
- web stranica za dobru narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (3)
- web stranica za dobru narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (0)
- web stranica za dobru narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (0)
- Web stranice mladenke s najviЕЎe poЕЎte (2)
- Web stranice mladenke s najviЕЎe poЕЎte (0)
- Web stranice za mladenke (1)
- Web stranice za mladenke Reddit (5)
- Web za narudЕѕbu s najviЕЎe poЕЎte (1)
- website (4)
- websites (10)
- websites free (14)
- websites to pay for an essay (1)
- wha is cash advance (1)
- whar is a payday loan? (1)
- what a mail order bride (2)
- what a payday loan (0)
- what a payday loan is (1)
- what are a payday loan (1)
- what are cash advance (1)
- what are good payday loan company (2)
- what are payday advance loans (2)
- what are payday loan (1)
- what are payday loans (1)
- what are payday loans and how do they work (0)
- what are payday loans used for (1)
- what are payday loans? (2)
- what are payday loans\ (2)
- what are payday loans\ (0)
- what are the payday loans (1)
- what bank can i go to for cash advance (2)
- what banks do cash advance (1)
- what banks do payday loans? (3)
- what can you get payday loans for (2)
- what can you use payday loans for (1)
- what cash advance (1)
- what cash in advance (1)
- what do i need for a cash advance (3)
- what do i need for a payday loan (2)
- what do i need for cash advance (2)
- what do i need for payday loan (1)
- what do i need to get a cash advance (1)
- what do i need to get a payday loan (1)
- what do i need to get a payday loan? (3)
- what do i need to get payday loan (1)
- what do tou need for a payday loan (3)
- what do you need for a cash advance (1)
- what do you need for a payday advance loan (1)
- what do you need for a payday loan (4)
- what do you need for cash advance (1)
- what do you need for payday loan (1)
- what do you need for payday loans (1)
- what do you need to do a payday loan (3)
- what do you need to do a payday loan? (2)
- what do you need to get a cash advance (2)
- what do you need to get a cash advance loan (1)
- what do you need to get a payday loan (1)
- what do you need to get payday loan (2)
- what do you pay on a payday loan (3)
- what i need for a payday loan (1)
- what i need for payday loan (1)
- what i need to get a payday loan (3)
- what is a bank cash advance (2)
- what is a bank lobby cash advance (2)
- what is a cash advance (1)
- what is a cash advance apex (0)
- what is a cash advance at a bank (1)
- what is a cash advance loan (2)
- what is a cash advance loan? (1)
- what is a cash advance? (3)
- what is a good payday loan company (1)
- what is a mail order bride (2)
- what is a mail order bride? (1)
- what is a mail-order bride (1)
- what is a payday advance loan (2)
- what is a payday advance loans (1)
- what is a payday loan (1)
- what is a payday loan company (1)
- what is a payday loan? (3)
- what is advance america cash advance (1)
- what is advance cash (1)
- what is an cash advance (3)
- what is an cash advance loan (1)
- what is an payday loan (1)
- what is an payday loans (3)
- what is as mail order bride (2)
- what is bank cash advance (1)
- what is cash advance loan (1)
- what is interest cash advance (4)
- what is mail order bride services (1)
- what is mail order bride? (1)
- what is mail-order bride (1)
- what is my payday loan (2)
- what is needed for a payday loan (1)
- what is needed for payday loan (1)
- what is needed to get a cash advance (1)
- what is payday advance loans (1)
- what is payday loan company (2)
- what is payday loan usa (1)
- what is the best mail order bride country (1)
- what is the best mail order bride service (1)
- what is the best mail order bride site (3)
- what is the mail order bride? (1)
- what payday loans (1)
- what you need for a payday loan (2)
- what you need for cash advance (2)
- what you need for payday loan (3)
- what you need to get a payday loan (1)
- what's a cash advance (1)
- what's a cash advance loan (2)
- what's a mail order bride (1)
- what's cash advance? (4)
- what's meen cash advance (4)
- what's my cash advance limit? (1)
- what's needed for cash advance (2)
- what's needed for payday loan (1)
- what's needed to get a payday loan (1)
- what's payday loan (2)
- what's payday loan? (2)
- whats a cash advance (1)
- whats a cash advance loan (2)
- whats a cash advance? (1)
- whats a mail order bride (2)
- whats a mail order bride? (2)
- whats cash advance (2)
- whats interest cash advance (1)
- whats meen cash advance (3)
- whats needed for a payday loan (1)
- whats needed for cash advance (1)
- whats payday loans (1)
- when and where you get payday loan (1)
- where can i get a bad credit payday loan (3)
- where can i get a cash advance loan (2)
- where can i get a cash advance near me (2)
- where can i get a cash advance with bad credit (3)
- where can i get a mail order bride (1)
- where can i get a payday loan (2)
- where can i get a payday loan near me (2)
- where can i get a payday loan near me? (3)
- where can i get a payday loan with bad credit (1)
- where can i get a payday loan? (2)
- where can i get cash advance (3)
- where can i get cash advance? (2)
- where can i get my payday loan (2)
- where can i get payday loans near me (3)
- where can i go to get a cash advance (2)
- where can i go to get a payday loan (1)
- where can i have cash advance? (1)
- where can i use cash advance (2)
- where can you get a payday loan? (1)
- where can you get payday loans (2)
- where did payday loans come from (1)
- where do i buy a mail order bride (2)
- where do i get a payday loan (2)
- where do you get payday loans (1)
- where get cash advance (3)
- where get payday loans (3)
- Where Is Mostbet Lawful? All Available Mostbet States 2024 - 513 (1)
- Where Is Mostbet Legal? All Available Mostbet States 2024 - 697 (4)
- where is the nearest payday loan (2)
- where to buy a mail order bride (1)
- where to cash advance (2)
- where to do a cash advance (1)
- where to do cash advance (2)
- where to find a mail order bride (1)
- where to get a cash advance (2)
- where to get a payday loan (3)
- where to get a payday loan near me (1)
- where to get cash advance (1)
- where to get payday loan (1)
- where to get payday loan near me (3)
- where to get payday loans (1)
- where to go for cash advance (1)
- which payday loan (2)
- which payday loans (2)
- who do cash advance (1)
- who do payday loans (2)
- who does payday loans (1)
- who does payday loans near me (2)
- who is cash advance america (1)
- who is cash advance loans (2)
- who is cash advance? (3)
- who needs payday loans (1)
- who use payday loan (1)
- who uses payday loans (4)
- who uses payday loans and why (2)
- whst do i need for a payday loan (1)
- whta is a cash advance (1)
- why advance cash (1)
- why and where you get payday loan (1)
- why are payday loans popular (2)
- why are payday loans so popular (2)
- why get a cash advance (4)
- why get a payday loan (3)
- why get payday loans (4)
- why is a payday loan bad (1)
- Wie funktionieren Versandbestellbraut -Sites? (3)
- Wie funktioniert die Mail -Bestellung Braut? (3)
- Wie funktioniert die Versandbraut, Braut zu bestellen? (4)
- Wie funktioniert die Versandbraut, die Braut funktioniert? (1)
- Wie funktioniert eine Versandbestellung Braut (2)
- wie man beauftragte Braut (1)
- wie man eine Braut bestellt (2)
- Wie man eine Versandbestellbraut heiratet (4)
- wife finder (1)
- Wiki de la mariГ©e par correspondance (6)
- Wiki de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Wiki de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Wiki de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Wiki de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Wiki de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- wikipedia correo orden novia (2)
- Wikipedia Mail -Bestellung Braut (1)
- wikipedia mail order bride (10)
- wikipedia mail ordre brud (1)
- Wikipedia Posta SipariЕџi Gelin (2)
- Wikipedia Posta SipariЕџi Gelin (0)
- wikipedia postimyynti morsian (5)
- wikipedia postorder brud (4)
- wikipedia postorder brud (0)
- wikipedia postordrebrud (1)
- Willacoochee guaranteed installment loans for bad credit (1)
- Wo finde ich eine Mail -Bestellung Braut (4)
- Wo kann ich eine Versandungsbraut bekommen? (1)
- Wo kann man eine Versandbestellbraut finden (2)
- Wo kann man eine Versandbestellbraut kaufen (1)
- Woodland bad credit installment loans (1)
- Woodstock online installment loans (1)
- worldbrides.org amourfeel-anmeldelser bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- worldbrides.org asiatisk bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- worldbrides.org de+auf-die-schwarze-liste-gestellte-dating-sites Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- worldbrides.org de+bravodate-test Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- worldbrides.org de+chinesische-alleinstehende-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- worldbrides.org de+colombialady-test Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- worldbrides.org de+daterussiangirl-test Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- worldbrides.org de+easternhoneys-test Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- worldbrides.org de+estnische-alleinstehende-frauen Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- worldbrides.org de+europa Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- worldbrides.org de+heis-russian-brides Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- worldbrides.org de+heise-chinesische-braute Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- worldbrides.org de+heise-japanische-braute Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- worldbrides.org de+heise-mexico-braute Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- worldbrides.org de+heise-neuseelandische-braute Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- worldbrides.org de+heise-thai-braute Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- worldbrides.org de+katalogheirat-betrug Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- worldbrides.org de+kissrussianbeauty-test Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- worldbrides.org de+neuseelaender-alleinstehende-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- worldbrides.org de+norwegische-braute Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- worldbrides.org de+ozeanien Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- worldbrides.org de+russian-brides Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- worldbrides.org de+schwedische-braute Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- worldbrides.org de+schwedische-braute-kosten Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- worldbrides.org de+slawisches-land-mit-den-schonsten-frauen Mail -Bestellung Brautagentur (1)
- worldbrides.org de+ukrainische-braute Echte Versandbestellbrautwebsites (1)
- worldbrides.org es+amourfactory-opinion que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- worldbrides.org es+amourfeel-opinion que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- worldbrides.org es+como-conocer-mujeres-asiaticas que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- worldbrides.org es+como-conocer-mujeres-en-linea que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- worldbrides.org es+costo-promedio-de-novia-por-correo revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- worldbrides.org es+cuteasianwoman-opinion revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- worldbrides.org es+jollyromance-opinion que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- worldbrides.org es+latinwomendate-opinion revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- worldbrides.org es+mujeres-europeas-vs-mujeres-japonesas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- worldbrides.org es+mujeres-solteras-ucranianas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- worldbrides.org es+novias-brasil revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- worldbrides.org es+novias-brasil-calientes revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- worldbrides.org es+novias-calientes-de-nueva-zelanda que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- worldbrides.org es+novias-latvianas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- worldbrides.org es+novias-latvianas-calientes que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- worldbrides.org es+novias-lituanas revisiГіn de sitios de novias por correo (1)
- worldbrides.org es+novias-mexico-calientes que es la novia del pedido por correo (1)
- worldbrides.org hvordan-man-undgar-postordrebrude-fidus bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- worldbrides.org it+come-incontrare-donne-online vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- worldbrides.org it+cuteasianwoman-recensione ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- worldbrides.org it+donne-single-australiane vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- worldbrides.org it+donne-single-italiane vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- worldbrides.org it+giapponese-donne-sole ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- worldbrides.org it+latinwomanlove-recensione ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- worldbrides.org it+latinwomendate-recensione ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- worldbrides.org it+meetslavicgirls-recensione ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- worldbrides.org it+paese-slavo-con-donne-piu-carine ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- worldbrides.org it+papua-nuova-guinea-donne-single ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- worldbrides.org it+spose-brasiliane vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- worldbrides.org it+spose-calde-svedesi ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- worldbrides.org it+spose-dominicane-calde vera storia della sposa per corrispondenza (1)
- worldbrides.org it+spose-estoni ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- worldbrides.org it+spose-italiane ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- worldbrides.org it+ukrainebrides4you-recensione ordine di posta lesbica sposa reddit (1)
- worldbrides.org italienske-brude bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- worldbrides.org kinesiske-brude bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- worldbrides.org ladat-anmeldelser bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- worldbrides.org latin bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- worldbrides.org latinbeautydate-anmeldelser bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- worldbrides.org latinfeels-anmeldelser bedste postordre brudesider (0)
- worldbrides.org meetslavicgirls-anmeldelser bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- worldbrides.org polske-single-kvinder bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- worldbrides.org pt+latim Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- worldbrides.org pt+mulheres-japonesas-como-homens-americanos Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- worldbrides.org pt+mulheres-solteiras Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- worldbrides.org pt+mulheres-solteiras-tailandesas Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- worldbrides.org pt+noivas-chinesas Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- worldbrides.org pt+ukrainebrides4you-recensao Quel est le meilleur site de mariГ©e par correspondance (1)
- worldbrides.org sv+asiabeautydate-recension postorder brudkataloger (1)
- worldbrides.org sv+colombialady-recension postorder brudkataloger (1)
- worldbrides.org sv+europeiska-kvinnor-kontra-japanska-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- worldbrides.org sv+hur-man-undviker-postordrebrud-bedrageri postorder brudkataloger (1)
- worldbrides.org sv+ladat-recension postorder brudkataloger (1)
- worldbrides.org sv+latamdate-recension postorder brudkataloger (1)
- worldbrides.org sv+latin postorder brudkataloger (1)
- worldbrides.org sv+latinbeautydate-recension postorder brudkataloger (1)
- worldbrides.org sv+latinwomanlove-recension postorder brudkataloger (1)
- worldbrides.org sv+latinwomendate-recension postorder brudkataloger (1)
- worldbrides.org sv+lettiska-singel-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- worldbrides.org sv+meetslavicgirls-recension postorder brudkataloger (1)
- worldbrides.org sv+norska-brudar postorder brudkataloger (1)
- worldbrides.org sv+oceanien postorder brudkataloger (1)
- worldbrides.org sv+ukrainska-ensamstaende-kvinnor postorder brudkataloger (1)
- worldbrides.org varme-italienske-brude bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- worldbrides.org varme-mexico-brude bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- worldbrides.org varme-thailandske-brude bedste postordre brudesider (1)
- write a essay for me (2)
- write an essay for me (1)
- write an essay for me cheap (1)
- write and essay for me (1)
- write essay cheap (1)
- write essay for me (1)
- write essay for me website (1)
- write for me an essay (2)
- write me essay for me (2)
- write my essay cheap online (2)
- write my essay fast (1)
- write my essay for me (1)
- write my essay for me best website (2)
- write my essay online (1)
- write my essay quick (1)
- writing an essay really fast (3)
- yabancД± gelinler (2)
- yabancД± gelinler (0)
- Yankton guaranteed installment loans for bad credit (1)
- yasal posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (2)
- yasal posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri (0)
- yasal posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri reddit (3)
- yasal posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri reddit (0)
- yasal posta sipariЕџi gelin siteleri reddit (0)
- yasal posta sipariЕџi gelini (7)
- yasal posta sipariЕџi gelini (0)
- yasal posta sipariЕџi gelini (0)
- yasal posta sipariЕџi gelini (0)
- yasal posta sipariЕџi gelini (0)
- yasal posta sipariЕџi gelini (0)
- yasal posta sipariЕџi gelini (0)
- yasal posta sipariЕџi gelini sitesi (2)
- yasal posta sipariЕџi gelini sitesi (0)
- yk (1)
- Yosemite installment loans online (1)
- yourinstallmentloans installment loans (1)
- Yuba City online installment loans instant approval (1)
- Zaten evliysem posta sipariЕџi gelini alabilir miyim? (2)
- Zaten evliysem posta sipariЕџi gelini alabilir miyim? (0)
- Архангельск (1)
- Барнаул (1)
- Брянск (1)
- ВїCuГЎl es el mejor paГs de novias por correo (1)
- ВїCuГЎl es el mejor servicio de novias por correo (1)
- ВїCuГЎl es el mejor sitio para novias por correo (3)
- ВїCuГЎl es el mejor sitio para novias por correo (0)
- ВїCuГЎl es el mejor sitio para novias por correo (0)
- ВїCuГЎl es la novia del pedido por correo? (3)
- ВїCuГЎl es la novia del pedido por correo? (0)
- ВїCuГЎl es la novia del pedido por correo? (0)
- ВїCuГЎles son los mejores sitios para novias por correo (4)
- ВїCuГЎles son los mejores sitios para novias por correo (0)
- ВїCuГЎles son los mejores sitios para novias por correo (0)
- ВїCuГЎles son los mejores sitios para novias por correo (0)
- ВїCГіmo funciona la novia por correo (5)
- ВїCГіmo funciona la novia por correo (0)
- ВїCГіmo funciona la novia por correo (0)
- ВїCГіmo funciona la novia por correo (0)
- ВїCГіmo funciona una novia por correo (3)
- ВїCГіmo funciona una novia por correo (0)
- ВїCГіmo funciona una novia por correo (0)
- ВїCГіmo funcionan los sitios de novias por correo (3)
- ВїCГіmo funcionan los sitios de novias por correo (0)
- ВїCГіmo funcionan los sitios de novias por correo (0)
- ВїDГіnde encuentro una novia de pedidos por correo (2)
- ВїDГіnde encuentro una novia de pedidos por correo (0)
- ВїDГіnde puedo encontrar una novia por correo (4)
- ВїDГіnde puedo encontrar una novia por correo (0)
- ВїDГіnde puedo encontrar una novia por correo (0)
- ВїDГіnde puedo encontrar una novia por correo (0)
- ВїPuedo obtener una novia por correo si ya estoy casado? (1)
- ВїQuГ© es la novia de pedidos por correo? (1)
- ВїQuГ© es una novia de pedidos por correo? (1)
- Вунд-2 (1)
- Г la recherche d'un mariage (1)
- Г¤r postorder brud verklig (6)
- Г¤r postorder brud verklig (0)
- Г¤r postorder brud verklig (0)
- Г¤r postorder brud verklig (0)
- Г¤r postorder brud verklig (0)
- Г¤r postorder brud verklig (0)
- är postorder brud värt det (1)
- Г¤r postorderbrud en riktig sak (3)
- Г¤r postorderbrud en riktig sak (0)
- Г¤r postorderbrud en riktig sak (0)
- Г¦gte mail ordre brudehistorier (2)
- Г¦gte mail ordre brudehistorier (0)
- Г¦gte postordre brudehistorier (2)
- Г¦gte postordre brudehistorier (0)
- Г¦gte postordre brudeside (1)
- Г¦gte postordre brudesider (1)
- Г¦gte postordrebrud (1)
- Г©pouses par correspondance (1)
- Г©pouses Г©trangГЁres (1)
- Гњst Nominal Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Hizmeti (1)
- Гњst posta sipariЕџi gelin oturuyor (2)
- Гњst posta sipariЕџi gelin oturuyor (0)
- Гњst posta sipariЕџi gelin web siteleri (2)
- Гњst posta sipariЕџi gelin web siteleri (0)
- Гњst posta sipariЕџi gelin Гјlkeleri (3)
- Гњst posta sipariЕџi gelin Гјlkeleri (0)
- Гњst posta sipariЕџi gelin Гјlkeleri (0)
- Гњst posta sipariЕџi gelini sitesi (4)
- Гњst posta sipariЕџi gelini sitesi (0)
- Гњst posta sipariЕџi gelini sitesi (0)
- ГЁ la sposa per corrispondenza reale (2)
- ГЁ la sposa per corrispondenza reale (0)
- ГЁ la sposa per corrispondenza una cosa reale (4)
- ГЁ la sposa per corrispondenza una cosa reale (0)
- ГЁ la sposa per corrispondenza una cosa reale (0)
- ГЁ la sposa per corrispondenza una cosa reale (0)
- ГЁ sicuro per corrispondenza sposa (2)
- ГЁ sicuro per corrispondenza sposa (0)
- Гёverste postordre brudeland (1)
- Гёverste postordre brudeside (2)
- Гёverste postordre brudeside (0)
- Гёverste postordrebrud (1)
- Голицыно (1)
- Г‚ge moyen de la mariГ©e par correspondance (4)
- Г‚ge moyen de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Г‚ge moyen de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Г‚ge moyen de la mariГ©e par correspondance (0)
- Д°lk On Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Sitesi (1)
- Д°lk On Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Witebes (5)
- Д°lk On Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Witebes (0)
- Д°lk On Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Witebes (0)
- Д°lk On Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Witebes (0)
- Д°lk On Posta SipariЕџi Gelin Witebes (0)
- Д°yi posta sipariЕџi gelini web sitesi (1)
- Д±rklararasД± posta sipariЕџi gelini (1)
- ДЊlanci za mladenku (1)
- Е to je mladenka kao narudЕѕba poЕЎte (2)
- Е to je mladenka kao narudЕѕba poЕЎte (0)
- Е to je mladenka narudЕѕbenica (1)
- Е to je mladenka za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (2)
- Е to je mladenka za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (0)
- Е to je mladenka za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte (0)
- Е to je mladenka za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte? (2)
- Е to je mladenka za narudЕѕbu poЕЎte? (0)
- Е to je narudЕѕba poЕЎte (1)
- Е to je narudЕѕba poЕЎte? (2)
- Е to je narudЕѕba poЕЎte? (0)
- Ећimdiye kadarki en iyi posta sipariЕџi gelini (1)
- ебар (1)
- Железнодорожный (1)
- казино (2)
- Казино (0)
- Комета Казино (1)
- Статьи-ч.1 (0)
- Форекс Брокеры (1)
- Форекс партнерская программа (1)
